Cervical and Uterine Disorders: Endometrial Polyps to Endometriosis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
hyperplastic, glands, Tamoxifen, Lynch, contraception
Endometrial Polyps: Background
-Localized ___________ (usually benign) overgrowths of endometrial _______ and stroma around a vascular core
Forms a projection from the surface of the endometrium, can be pedunculated
-Risk Factors → _________ use, obesity, postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy, _____ and Cowden Syndrome
-Preventative Factors → oral ____________ or levonorgestrel IUD
bleeding, incidentally, ultrasound, postmenopausal, biopsy
Endometrial Polyps: Presentation and Diagnosis
-Most common symptom is abnormal uterine _________, typically intermenstrual bleeding
-Often also found __________ when imaging performed for other reasons
-Transvaginal ________ is the first-line imaging study
-Sonohysterography or diagnostic hysteroscopy for the following patients → uncertain findings on TVUS, ____________ patients with a thickened endometrium on TVUS
Those patients need a ______ to rule out cancer
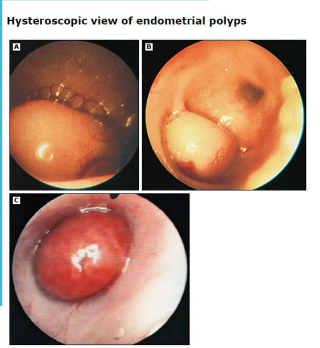
polypectomy, polypectomy, asymptomatic
Endometrial Polyp Management
-Postmenopausal → ____________
-Premenopausal
A ___________ is indicated if the patient is symptomatic, at risk for endometrial hyperplasia, the polyp is > 1.5cm in diameter, there are multiple polyps, the polyps are prolapsed into the endocervix, and if there is infertility
If ____________ and none of the above → manage expectantly
benign, black, tumors, fibroblasts, early, alcohol
Uterine Fibroids: Background
-Also known as uterine leiomyomas or myomas
-MC ______ pelvic neoplasm in females
More common in _____ females
-Noncancerous monoclonal _______ arising from the smooth muscle cells and ____________ of the myometrium
-Risk Factors → nulliparity, ______ menarche (<10 years old), prenatal exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES), and ________ use (especially beer)
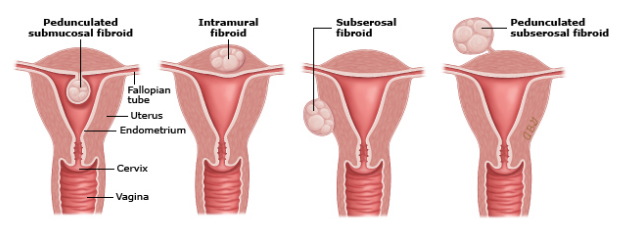
prolonged, pressure, compression, infertility, palpated, mobile, irregular
Uterine Fibroids: Clinical Presentation
-Can be found incidentally on imaging or symptomatic
-Possible symptoms:
Heavy or ________ bleeding
Pelvic _________ or pain
Urinary tract or bowel issues due to ____________ by fibroids
Dysmenorrhea
Dyspareunia
__________
-Physical exam:
Abdominal exam → large fibroids can be _________ abdominally
Pelvic exam → enlarged, ______ uterus with an __________ contour
hCG, anemia, ultrasound, fertility, MRI, calcification
Uterine Fibroids: Labs and Imaging
-Labs → ___ to rule out pregnancy, may have iron deficiency _______
-Imaging → pelvic ___________ is the first imaging study of choice
Step 2 → saline infusion sonography or hysteroscopy for patients with suspected submucous fibroids or those desiring _________
Step 3 → ___ may be needed when complex intervention is planned
-If ____________ is seen in a fibroid on an ultrasound, that implies that it has degenerated
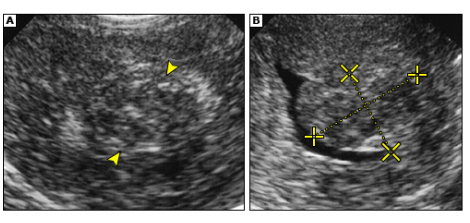
myomectomy, laparoscopic, medications, hysterectomy, myomectomy
Uterine Fibroids: Management
-Submucosal fibroids (type 0, 1, 2) → hysteroscopic ____________
-Fully within muscle wall fibroids type 3-7 → medications or ____________ myomectomy
-Patients who do not desire future fertility → ____________, uterine artery embolization, endometrial ablation, ______________
-Patients who desire fertility → ____________
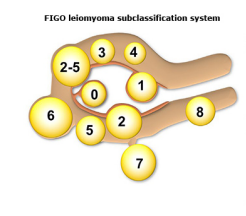
IUD, antifibrinolytic, menopause, estrogen, shrinking, adhesions, Cesarean, surgical
Uterine Fibroids: Pharmacotherapy and Prognosis
-Combined estrogen-progestin contraceptives
-Progestin-releasing ___
-Tranexamic acid → ____________ and antihemophilic agent that can be taken during menses
-GnRH analogs → temporarily induce __________-like state to lower ________ levels, leading to __________ of fibroids
-Approximately 12% of patients undergo repeat surgery within 8 years
-Postop pelvic ___________ may impact fertility, so _________ delivery may be necessary for future pregnancy secondary to disruption of the myometrium
-Definitive __________ therapy is curative
hypertrophy, bleeding, pain
Uterine Adenomyosis: Background
-Disorder in which endometrial glands and stroma are present within the myometrium, resulting in ___________ of the surrounding myometrium
-Pathogenesis is unknown
-Usually occurs in the 4th and 5th decades of life
-Typical symptoms are heavy menstrual ___________, dysmenorrhea, and chronic pelvic ____
mobile, enlarged, boggy, ultrasound, MRI, diffuse
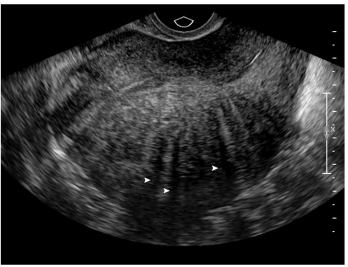
Uterine Adenomyosis: Evaluation
-Pelvic exam → uterus is _______, diffusely __________, and soft
“_______ globular enlargement”
-Transvaginal ____________ is first-line imaging choice
-___ is used to distinguish between ______ and focal adenomyosis, focal adenomyosis and leiomyomas, and/or to help with treatment
NSAIDs, IUD, aromatase, completed, hysterectomy, resection
Uterine Adenomyosis: Management
-First line → _______ and levonorgestrel ___
-Alternatives → oral contraceptive pills, GnRH analogs, _________ inhibitors
-Definitive treatment for patients who have ___________ childbearing and in whom first-line therapies were ineffective or contraindicated → ____________
-Alternatives to hysterectomy → uterine artery embolization, uterus sparing __________
herniation, vaginal, anterior, bladder, posterior, rectum, intestines, apex
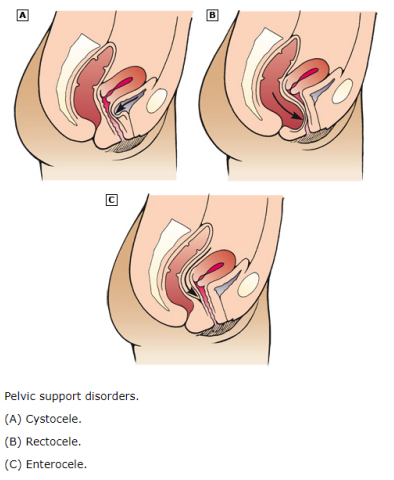
Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Background
-The __________ of the pelvic organs to or beyond the ________ walls
-Anterior compartment prolapse (cystocele) → hernia of _________ vaginal wall often associated with descent of the bladder
Letter A on diagram
-Posterior compartment prolapse (rectocele) → hernia of __________ vaginal segment often associated with descent of the ______
Letter B on diagram
-Enterocele → hernia of the _________ to or through the vaginal wall
Letter C on diagram
-Apical compartment prolapse → descent of the ____ of the vagina into the lower vagina, to the hymen, or beyond the vaginal introitus
-Uterine procidentia → herniation of all three compartments through vaginal introitus
increases, age, surgery, obesity
Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Risk Factors
-Parity → the risk of pelvic organ prolapse ___________ with increasing parity
-Vaginal birth
-Advancing ___
-Menopause
-Genetic predisposition
-Prior pelvic ________ → especially hysterectomy
-Connective tissue disorders
-Increased intra-abdominal pressure → _______ or straining associated with chronic constipation or coughing
bulge, vagina, upright, incomplete
Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Clinical Findings
-Sensation of a _____ or protrusion in the ________
Described as feeling like something is falling out of the vagina
May be worse when _______ and less noticeable when supine
-Pelvic pressure
-Constipation
-Sense of __________ bladder or bowel emptying
Due to a “kink” in the urethra
-Dyspareunia
POP-Q, hymen, degree
Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Classification Systems
-Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification (___-_) System
Commonly used method for classifying pelvic organ prolapse
The ________ acts as the fixed point of reference, with six defined points for measurement and three other landmarks
Provide a quantitative representation of anterior, apical, and posterior vaginal prolapse relative to the hymen
-Baden-Walker System
An alternative staging system
Includes a _______ of prolapse relative to the hymen for each prolapsed structure
fiber, loss, pessaries
Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Treatment
-Supportive measures → high-_____ diet and laxatives to improve constipation, weight ____, pelvic muscle training, vaginal _________
-Surgery
outside, pelvis, estrogen, inflammation, pain
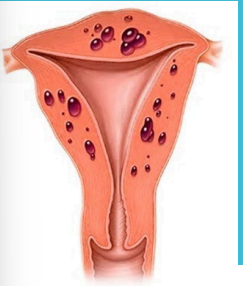
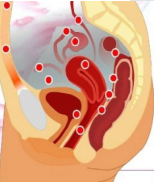
Endometriosis: Background
-Endometrial glands and stroma that occur _______ the uterine cavity
-Lesions are typically located in the _____ but can occur at multiple sites like bowel, diaphragm, and pleural cavity
-This ___________-dependent, benign, ectopic endometrial tissue results in ____________ that can cause debilitating symptoms
Dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, chronic ____, and infertility
retrograde, fallopian, metaplasia, uterus, spread, family, estrogen, DES, lower, late
Endometriosis: Background and Risk Factors
-Pathogenesis is multifactorial but there are several theories of development
_________ menstruation → blood travels out through the ________ tubes and into the abdominal cavity
__________ of coelomic epithelium → some cells in the body can change to become the same as endometrial cells
Lymphatics → cells from the lining of the ________ travel through the blood vessels/lymphatic
Endometriosis can _______ at the time of the surgery
Altered immunity
-Factors Increasing Risk
_______ history, nulliparity, prolonged exposure to endogenous ________, shorter menstrual cycles, exposure to ___ in utero, taller height, and ______ BMI
-Factors Reducing Risk
Multiple births, extended intervals of lactation, ____ menarche (after age 14)
ovarian, broad, bladder, pain, sharp, bleeding, constipation, pain
Endometriosis: Presentation
-Common sites
Most common → ovary and _________ fossa
Cul-de-sac
______ ligaments
Uterosacral ligaments
________
-Common symptoms
Chronic abdominal/pelvic _____ and/or pressure, typically described as dull, throbbing, _____, and/or burning
Severe dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, heavy menstrual _________, infertility
-Other possible symptoms
Low back _____, chronic fatigue, dysuria, dyschezia, constipation or diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, chest pain, hemoptysis
tenderness, posterior, masses, lateral, normal
Endometriosis: Physical Exam
-Focal ____________ on vaginal examination
-Nodules in the _________ fornix
-Adnexal ______
-Immobility or ________ placement of the cervix or uterus
-Be aware that the exam can also be completely _______
biopsy, histologic, raised, discoloration, powder, clinical
Endometriosis: Diagnosis
-Imaging → TVUS, laparoscopy with _______ is the definitive diagnosis
-Definitive diagnosis requires __________ confirmation of tissue biopsy typically obtained during laparoscopy
During laparoscopy, areas of peritoneal endometriosis appear as _______ flame-like patches, whitish opacifications, yellow-brown ___________, translucent blebs, or reddish or reddish-blue irregularly-shaped islands
The appearance of some blue-brown lesions have been described as “_______ burns”
-Presumptive _______ diagnosis based on symptoms, signs, and imaging findings
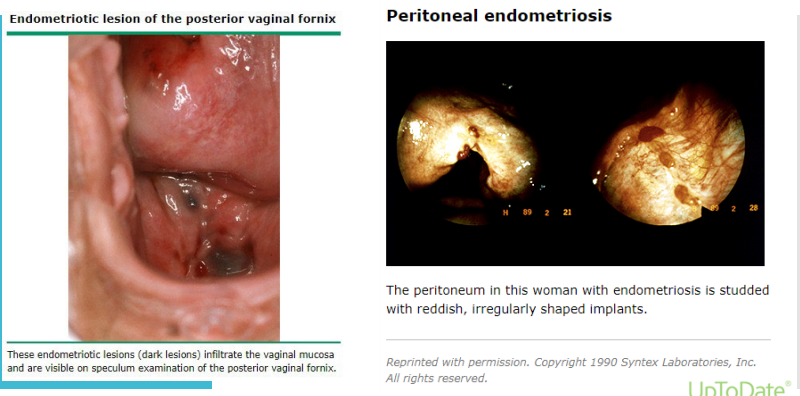
NSAIDs, ovulation, lower, GnRH, resection
Endometriosis: Treatment
-________ and hormonal therapy → hormonal regimens are designed to inhibit __________ and to _____ hormone levels, thus preventing cyclic stimulation of endometriotic implants
-Mild to moderate pain → NSAIDs and continuous hormonal contraceptives
-Severe symptoms → ____ analog with add-back hormonal therapy
-Refractory symptoms → aromatase inhibitor
-Surgical _________ of endometriosis or nerve transection procedures are offered to women who do not respond to medical therapy or who have recurrent pain symptoms
pituitary, hypoestrogenism, minimize, amenorrhea, proliferation
GnRH Agonists and Antagonists
-Agonists → bind to receptors in the _________ gland → pituitary-ovarian axis is down-regulated → ____________ results
Hormone treatment also needed to ________ hypoestrogenic side effects, typically norethindrone is used
Endometriosis-related pain is likely treated by the induction of __________ and progressive endometrial atrophy
-Antagonists → induce a dose-dependent hypoestrogenic state to inhibit endometriotic cell ___________
LH, increases, pituitary, estrogen, acne, cramps, inhibit, loss, cyst
Endometriosis Treatment: Danazol and Aromatase
-Danazol (an androgen) → inhibits __ surge and steroidogenesis and _________ free testosterone levels
Inhibits ________ gonadotropin secretion
Inhibits ovarian enzymes responsible for ________ production
Inhibits endometriotic implant growth
Has many side effects → ____, weight gain, hirsutism, voice deepening, and muscle ______
-Aromatase inhibitors → regulate local estrogen formation within the endometriotic lesions themselves
______ estrogen production in the ovary, brain, and adipose tissue
Disadvantages are bone ____ and ovarian follicular _____ development
no, mild, <, ART
Infertility and Endometriosis
-Ovulation induction and IUI only if __ infertility factors besides endometriosis, minimal to ____ endometriosis, and age _ 35 years old
-For all others, assisted reproductive technology (___)