Audio Systems
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
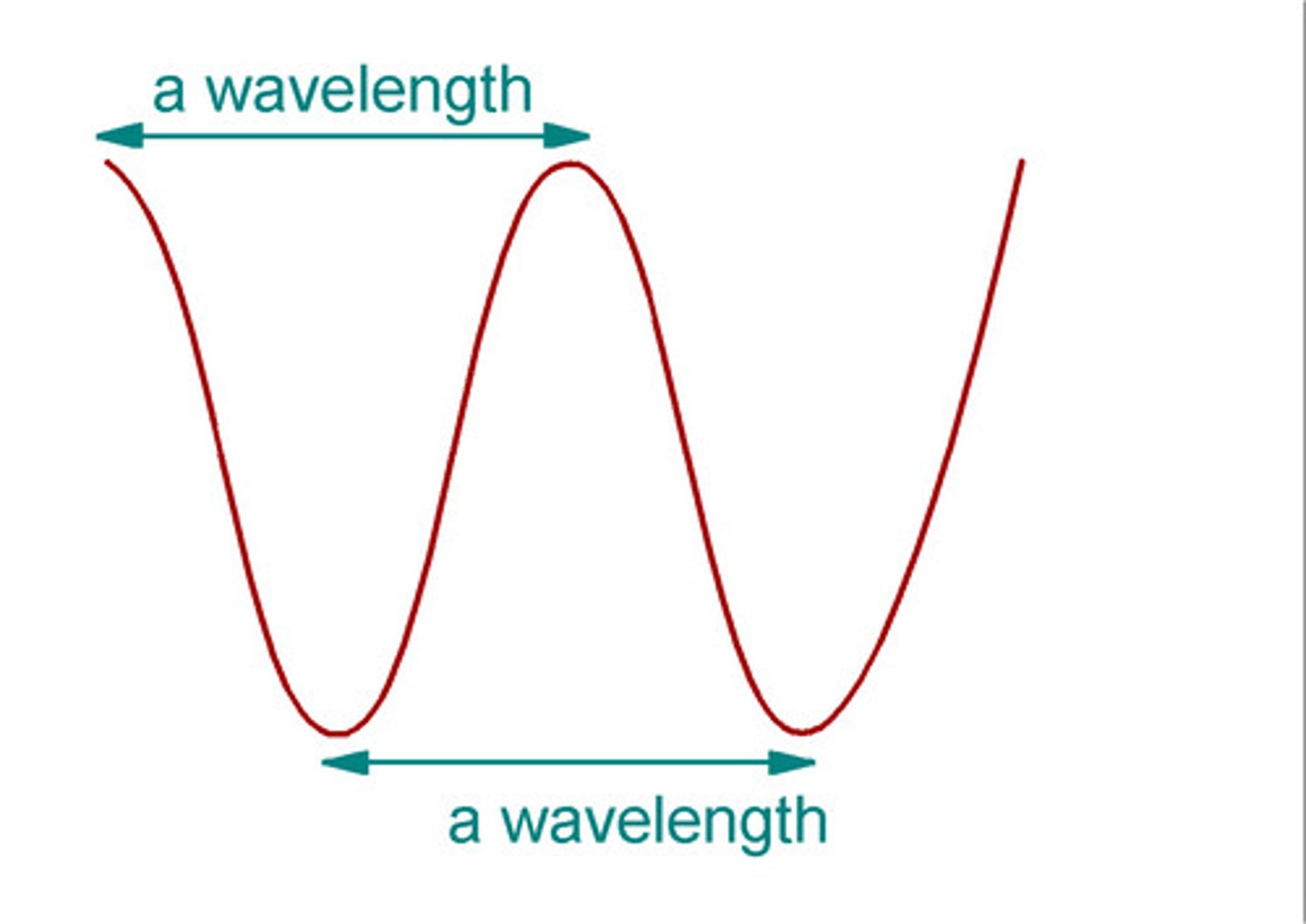
Wavelength
Distance between two points occurring at the same place in a cycle
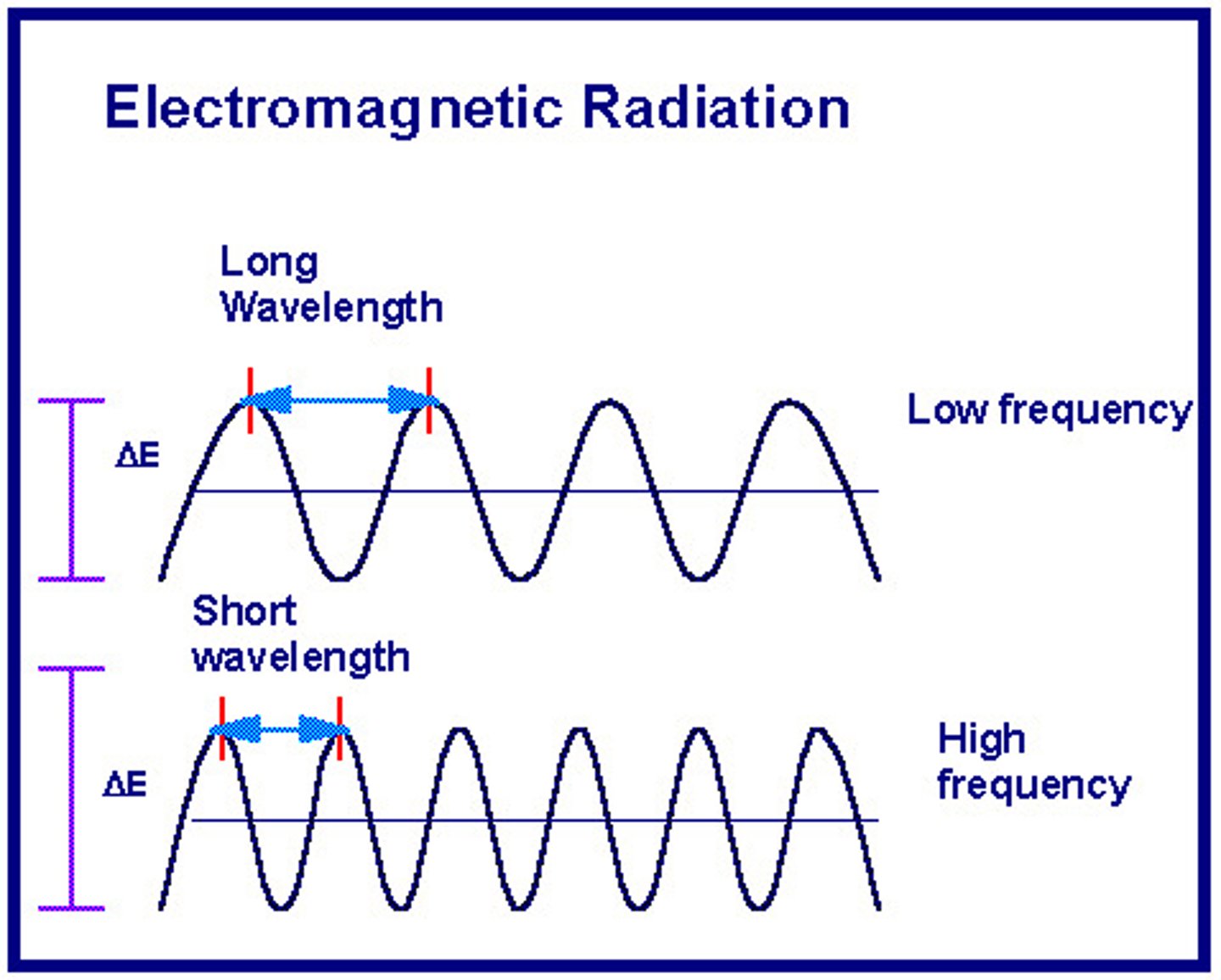
Frequency
Number of wave cycles occurring in a second (cycles per s, Hz); inversely related to wavelength
Low F - Long wavelength
High F - Short wavelength
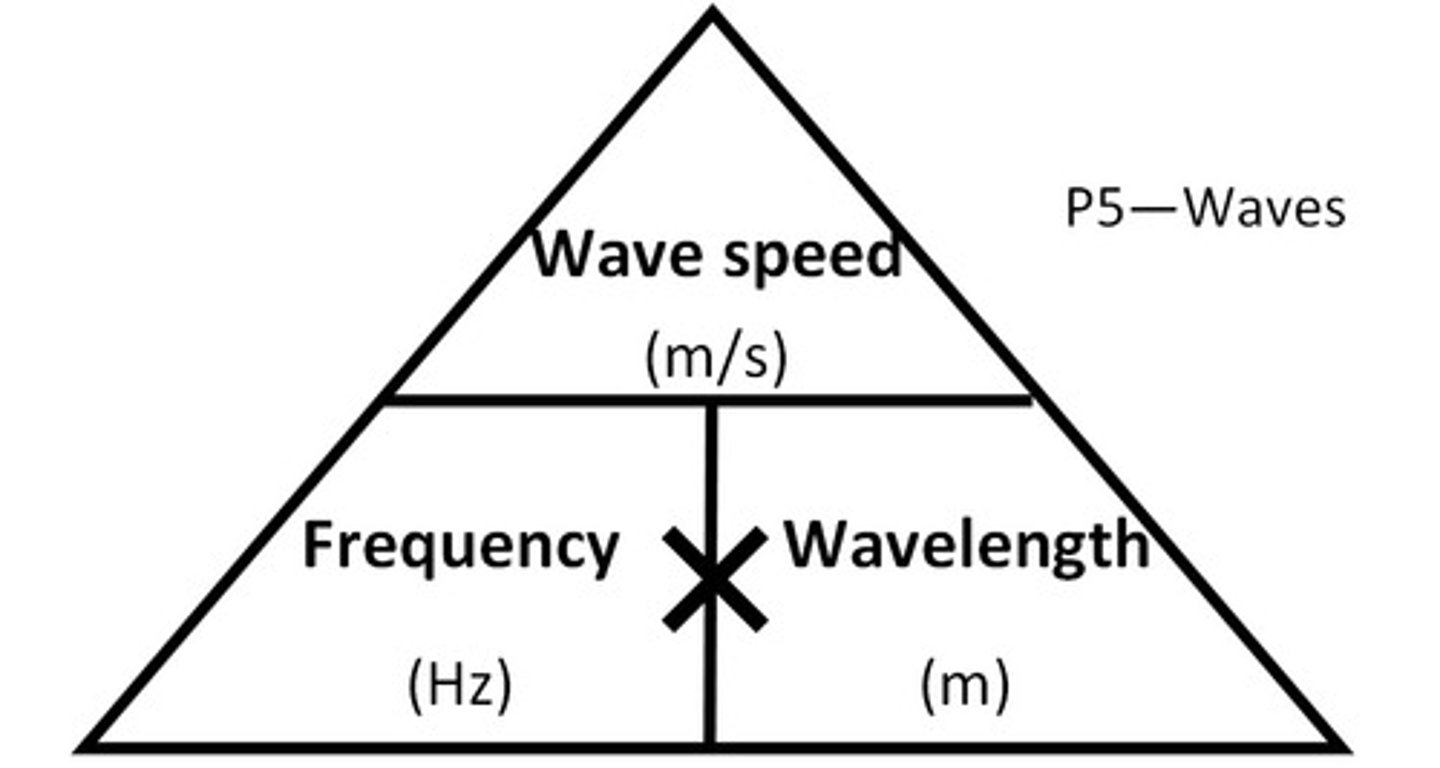
Frequency and Wavelength Formula
velocity of wave in med = wavelength x frequency
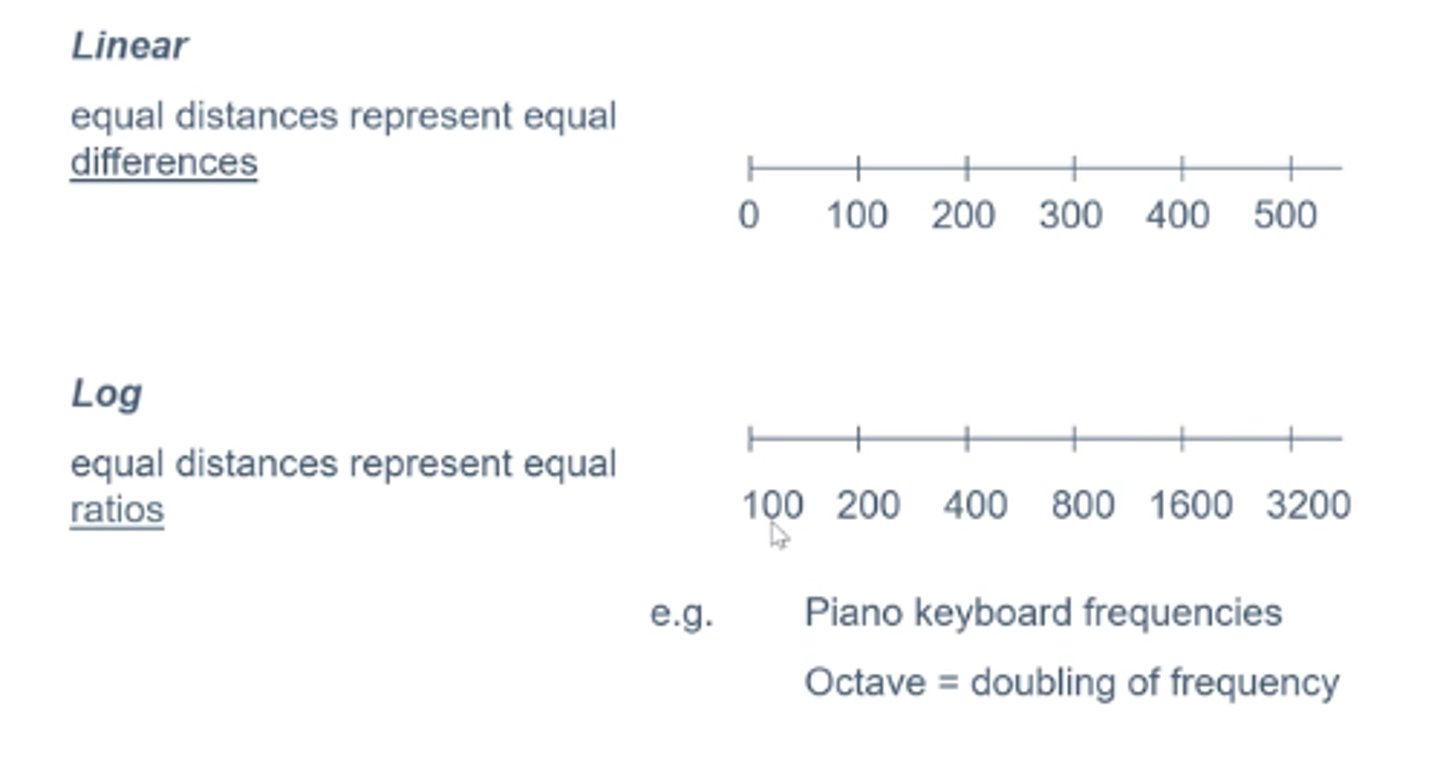
Bands
Based on the doubling of frequencies between each of them (octaves) with each divided into 8 tones
Harmonics
Complex audio waveforms include tones with frequencies that are multiples of each other (fundamental frequency)
Logarithms
Each doubling or halving of a signal sounds like the same interval - or how many times the number 10 must be multiplied by itself to get that #
10W increase = 2x loudness
Decibel
The measure of the logarithmic ratio between 2 quantities of the same physical property
Used to quantify differences in measurements of voltages, power, and sound pressure
dB = 10(log₁₀) x¹/x²
Reference Level
A known measurement to compare to, 0dB
Sound Pressure Reference Level
20 micropascals = 0dBSPL (threshold of human hearing)
Power Reference Level
10 (log₁₀) P¹/P² = X watts
Difference in power levels
1 watt reference, OR (.001 = 1mW ref)
Current/Voltage
20log(V₁/V₂)
Power is proportional to voltage²
Doubling voltage produces 4x power
1 volt reference
Sound Pressure at Distance
10log(D¹/D²)
Each time distance doubles, sound covers 4x the area and 1/4th the amount of energy
6dB per Doubling rule
Sound pressure decreases or increases 6dB every 1/2 or 2x distance
0dBu
.775 (1mw) reference = 0dBm
20log (E/.775)
0dBv
1v reference
1 dB
Smallest perceptible change
3dB
Just perceptible change
10dB
2x loudness