Cell Structures Honors Biology Study Guide
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
The Cell Theory:
All living things are composed of cells.
Cells are the smallest living unit in all organisms
New cells are produced from pre-existing cells
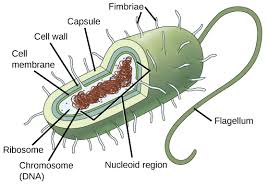
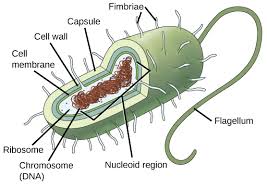
Prokaryotes don’t…
have a nucleus and don’t contain membrane bound organelles.
Prokaryotes…
Have genetic material(DNA or RNA), are smaller and simpler that eukaryotes and carry out every activity of living things.
Example of Prokaryotes…
bacteria and archaea.
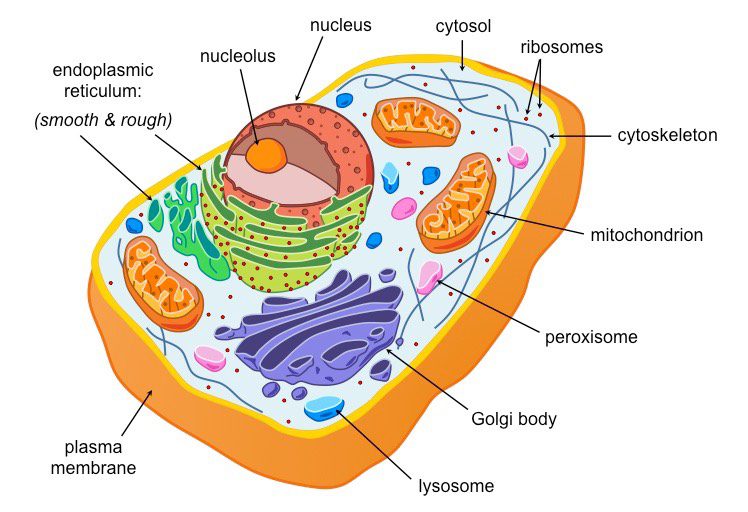
Eukaryotes contain…
a nucleus where genetic material is enclosed.
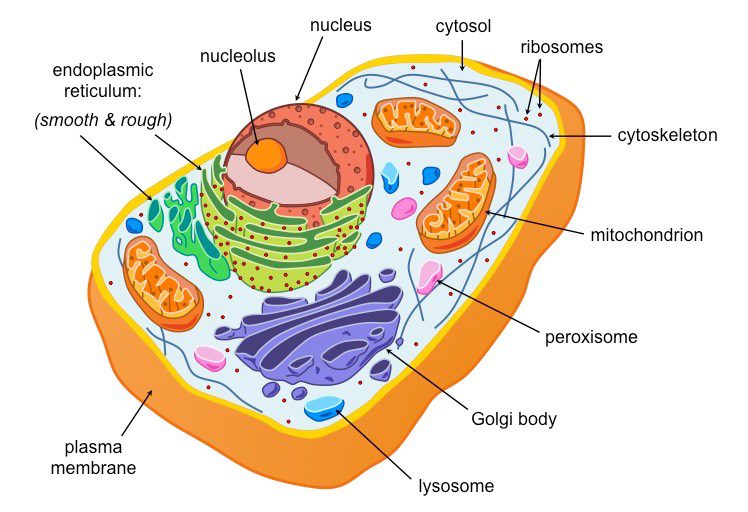
Eukaryotes
Generally larger than Prokaryotes and are more complex
Contain many specialized structures and internal membranes.
Display great variety, have membrane bound organelles.
single celled organisms to multicellular.
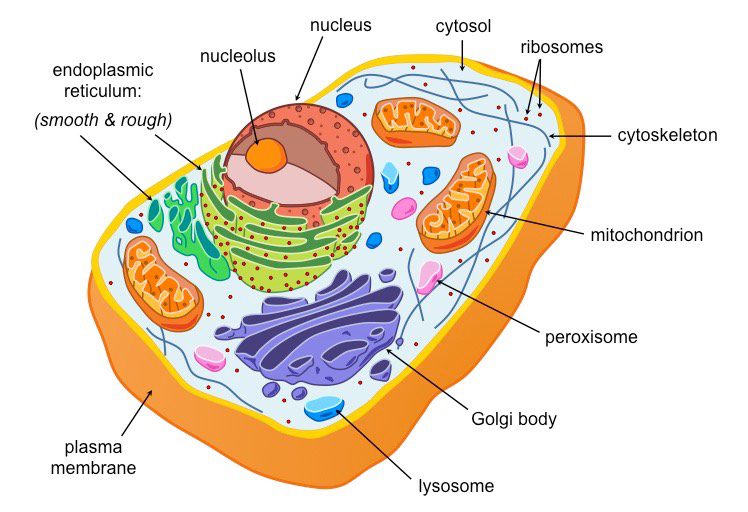
Examples of Eukaryotes
Plants, animals, fungi, protists.
Organelles are…
“little organs” within a cell that perform specific functions, they’re specialized just like your organs.
Cell(or Plasma) Membrane
A phospholipid bilayer that surrounds and protects the cell, regulating what enters and exits. (BOTH Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes and BOTH Plant and Animal)
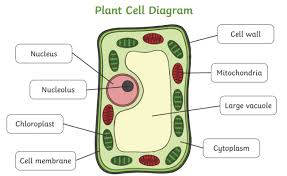
Cell Wall
Provides structure and support for plant cells, it does NOT replace the cell membrane.(BOTH Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes, Plant cells only)
Cytoplasm
the jelly-like fluid that fills a cell from the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane. (BOTH Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes and BOTH Plant and Animal)
Vacoule
stores nutrients, waste products, and helps maintain pressure in plant cells to help support plant structures. (Eukaryotes only, Plant cells typically larger, Animals cells may contain smaller ones. )
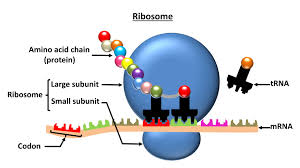
Ribosome
Site of protein synthesis( the cellular structure where amino acids are assembled into proteins. BOTH Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes and BOTH plant and Animal cells.)
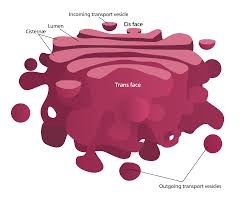
Golgi Apparatus
A series of stacked membranes that modify, package, and distribute proteins and lipids from the ER. (**Eukaryotes only, found in both plant and animal cells.)
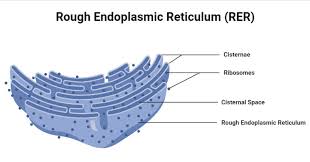
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum(ER)
Processes and synthesizes proteins, studded with ribosomes on its surface. Eukaryotes only, play a critical role in the production of proteins destined for export or for use within the cell. (Plant and Animal)
Smooth ER
Processes lipids and carbohydrates, are involved in detoxification. Eukaryotes only, present in both plant and animal cells.
Central Vacuole
A large organelle that stores water, nutrients, and waste products in plant cells. It helps maintain pressure and plays a role in cell growth. (ONLY Prokaryotes and ONLY plant cells)
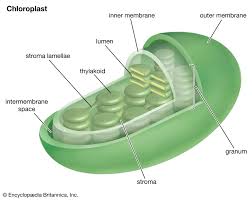
Chloroplast
Organelles that capture sunlight and convert it into chemical energy(photosynthesis), They contain chlorophyll, which is essential for this process and gives plants their green color. (ONLY Eukaryotes and ONLY Plant cells )
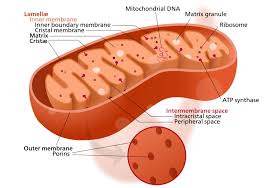
Mitochondria
Known as the powerhouse of the cell, they produce ATP through cellular respiration. (ONLY Eukaryotes and BOTH plant and animal cells)
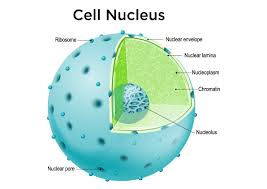
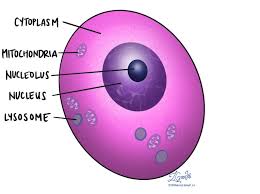
Nucleus
The control center of the cell, containing genetic material (DNA) and controls the cells activities. (ONLY Eukaryotes and BOTH plant and animal cells)
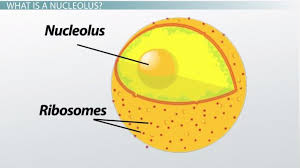
Nucleolus
Assembly and production of ribosomes(ONLY Eukaryotes and BOTH plant and animal cells).
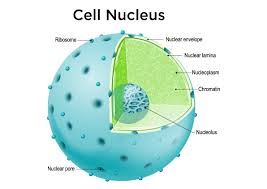
Nuclear Membrane(envelope)
The membrane that surrounds the nucleus of a EUKARYOTIC cell(BOTH plant and animal)
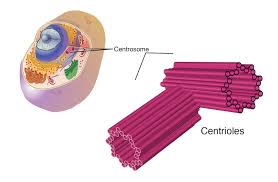
Centrioles
Located near the nucleus, have paired bundles of cylinders called microtubules that help organize the movement of chromosomes during cell division(ONLY eukaryotic animal cells)
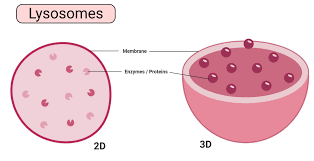
Lysosomes
Organelles that contain digestive enzymes to break down waste materials and cellular debris, found in eukaryotic cells(animal).
Cytoskeleton (microtubules)
Tubules and filaments that give the cell its shape.They provide structural support and movement.(BOTH plant and animal cells, eukaryotic).
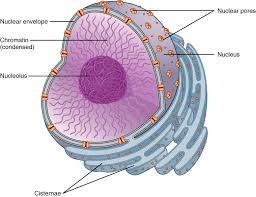
Nuclear Pores
Small openings in the nuclear envelope that allow the passage of molecules in and out of the nucleus. (Found in eukaryotic cells, animal cells).
Vesicle
The package created by the Golgi Apparatus
What kind of molecules can diffuse(go through) the cell membrane directly?
Small uncharged molecules such as oxygen and carbon dioxide.
How can some large molecules and charged ions get through the cell membrane?
They use transport proteins or channels in the membrane.
How is the nuclear pore similar to the cell membrane?
Molecules and ions enter and exit.
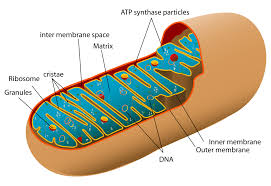
What happens inside of the mitochondria?
Small molecules and oxygen are converted into carbon dioxide and a form of energy the cell can use(ATP).
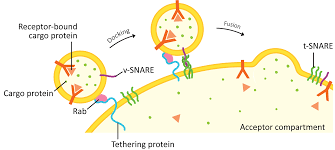
How do vesicles move through the cell?
They are pulled a long the cytoskeleton by a protein called kinsen.
What structures are present in an animal cell but not a plant cell?
lysosomes and centriols.
What structures are present in a plant cell but not an animal cell?
Cell wall, chloroplasts, and plastids.
What three structures help support the plant cell and maintain its shape?
Cytoskeleton, cell wall, and central vacoule
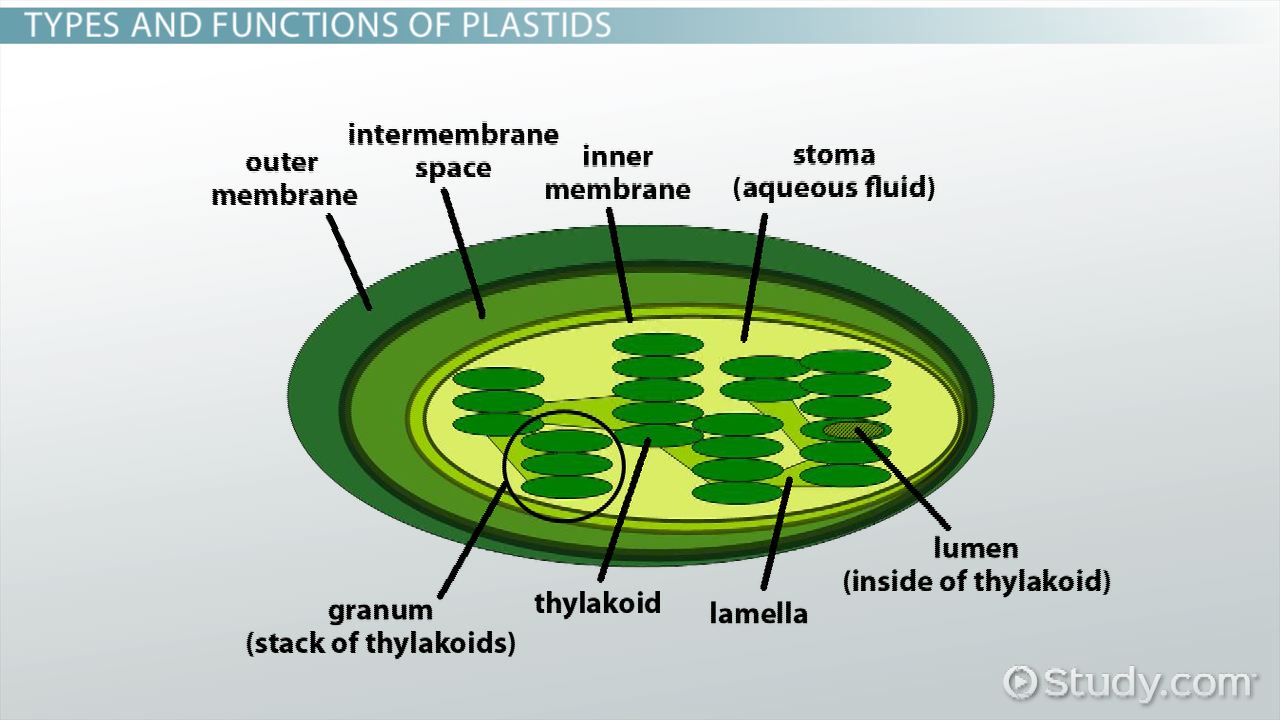
Plastids
store food or pigments
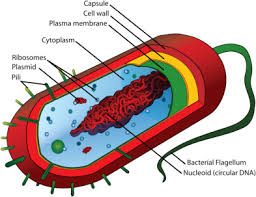
Capsule
Outermost layer of the cell that provides protection(Prokaryotes)
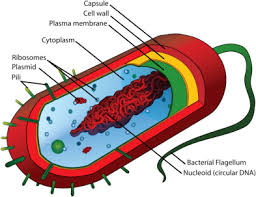
Nucleoid
Region inside the cell that contains genetic material but is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane.(Prokaryotes)
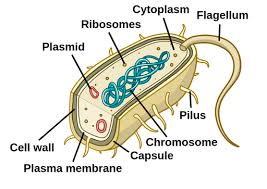
Plasmid
Circular piece of genetic material(Prokaryotes)
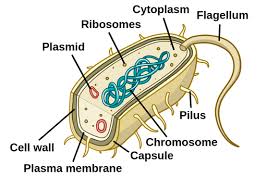
Flagellum
A long, whip/hair-like structure that the cell uses for movement.(Prokaryotes)
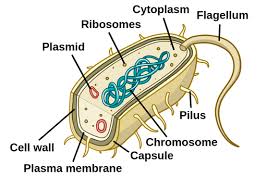
Pilius(pili)
Hair-like structure that attaches to a surface and can transfer genetic material from one cell to another.(Prokaryotes)
What structures are present in plant and animal cells, but not in a bacteria cell?
Nucleus, ER, golgi, and mitochondria.
What structures are present in a bacteria cell but not in a plant or animal cell?
Nucleoid, capsule, and plasmid
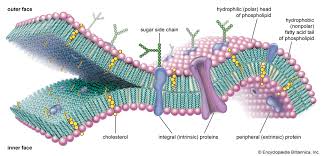
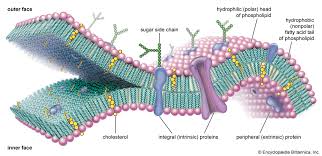
The Plasma/Cell Membrane
The thin, flexible boundary between the cell and its watery environment.
The plasma membrane allows…
nutrients into the cell AND waste to leave the cell
The plasma membrane helps maintain…
homeostasis
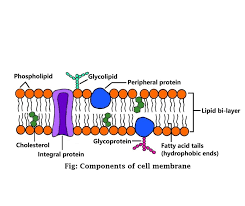
Function of the plasma membrane
Selectively permeable-
Allows some substances to pass through while keeping others out.
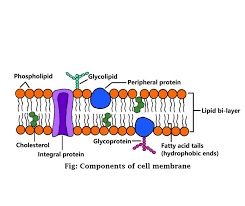
Phospholipid Bilayer
Two layers of phospholipids are arranged tail to tail.
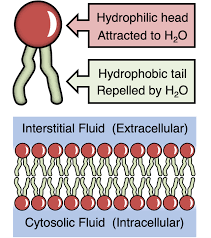
Phospholipid
Glycerol backbone; two fatty acid chains, and a phosphate group.
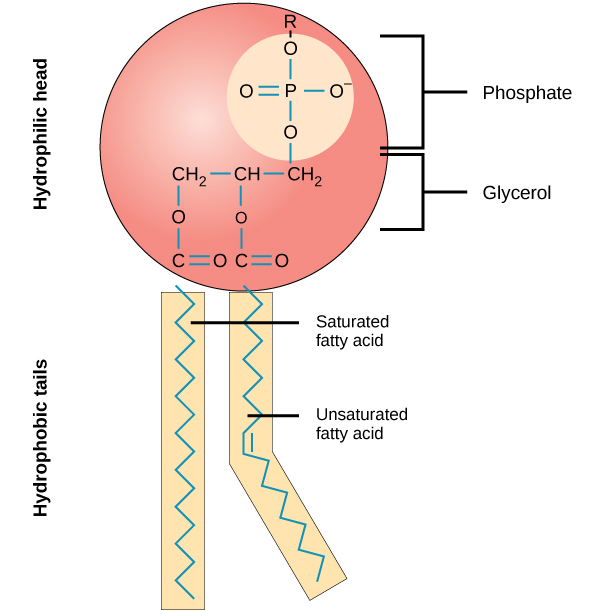
Phospholipid hydrophilic head
water loving(polar)
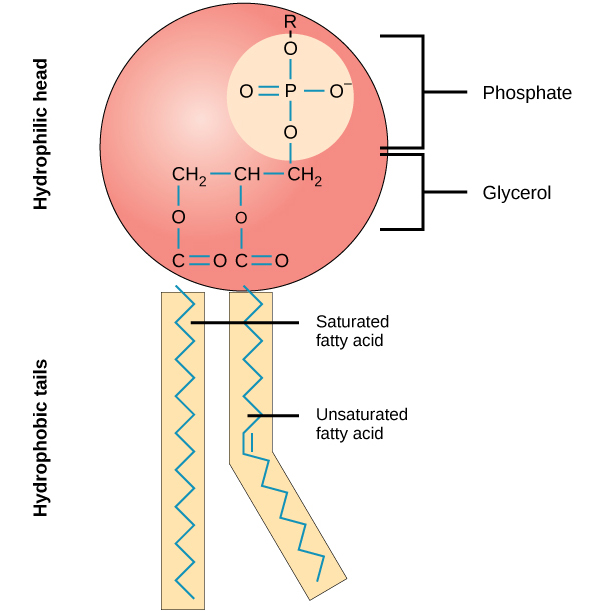
Phospholipid hydrophobic tails
water fearing(non polar)
Why can’t water soluble substances pass through the Phopholipid Bilayer?
They are stopped by the middle section(non polar tails)
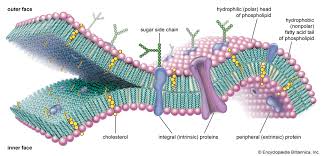
Phospholipid Bilayer protiens
transmit signals inside the cell, act as a support stucture, and provide pathways through the membrane for substances to enter and leave(transport protiens/protein channels)
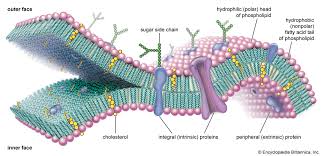
Phospholipid Bilayer cholesterol
Non polar; contributes to fluidity of membrane by preventing fatty acid chains/tails from sticking together.
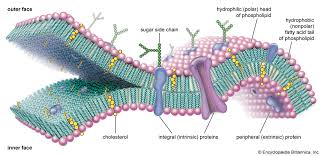
Phospholipid Bilayer carbohydrates
Identify chemical signals from other cells(communication)
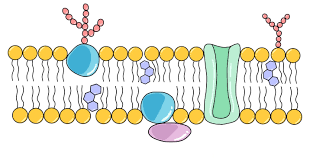
Fluid mosaic model
Components of the plasma membrane are in constant motion sliding past one another.