Year 10 Science - Evolution
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
taxonomy
the classification of organisms
biological classification order
Dear King Philip Came Over For Good Soup. Domain, kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
Binomial Nomenclature. developed by?
= scientific name. Genus than Species. E.g. Homo sapiens, Panthera tigris
developed by Carolus Linnaeus.
Species
A population of similar organisms that can breed fertile offspring with each other.
Natural Selection
“survival of the fittest” organisms best suited to their environments are favourable and more likely to breed and pass on genetic information.
Process of evolution (4 steps) and example
some inherited charictaristics will increase the chances of survival in the environment.
Increased chance of survival
increased chance of reproducing
over time they all posses the traits that make them more likely to survive.
example = peppered moths.
selection pressures
Biotic and Abiotic. Pressures of the environment that determine the chances of survival.
examples of competition
individuals in a population can have competition over food, shelter, mates, disease.
variation
genetic differences in a population. Might increase chance or survival.
Speciation
The formation of new species. needs variation within a population. Happens through reproductive isolation.
reproductive isolation
when two species live close to each other but can’t reproduce. Prevents different species form producing offspring.
Divergent evolution
same ancestor. evolved to have different traits. (E.g Darwin’s Finches. Got different beaks from different biotic selection pressures.)
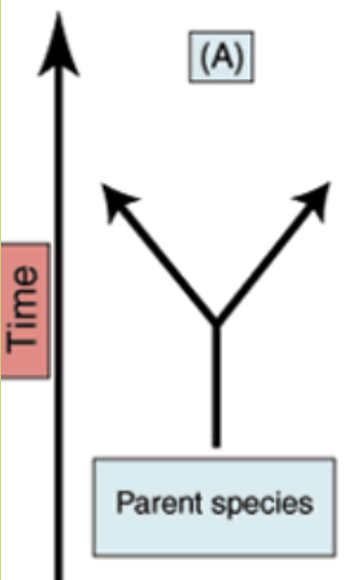
what is geographical isolation and how would it contribute to speciation.
2 populations of the same species are separated due to geographical barriers. due to different selection pressures they gain genetic differences and become 2 different species.
Convergent evolution
Species have similar traits even though they have no common ancestor. (E.g sharks and dolphine)
What are the 5 ways more variation can be introduced into a population?
Mutation, Gene Flow, Gene Drift, Adaptions, Sexual Reproduction.
Mutation
Spontaneous or induced change to the organism’s DNA. If it is in the Gametes it can effect the offspring.
Gene flow
migration. genes get carried to new species.
gene drift
catastrophic event. some traits might become lost.
adaptions (3 types)
characteristics that improves survival.
structural - e.g hair to keep warm
behavioural - e.g attracting mate
physiological - body functions
studies that are evidence for evolution. (5)
Palaeontology - the study of fossils
Comparative Anatomy - the study of the structure of different organism’s limbs and organs.
Embryology ; the development of the embryo of different species
Molecular Biology - sequencing DNA to compare genetic relationships between organisms.
Biochemistry - comparing the biochemical makeup of organisms.
radiometric dating/absolute dating
measures the number of radioisotopes and speed of decay to determine the accurate age.
Carbon-14, Uranium, Potassium.
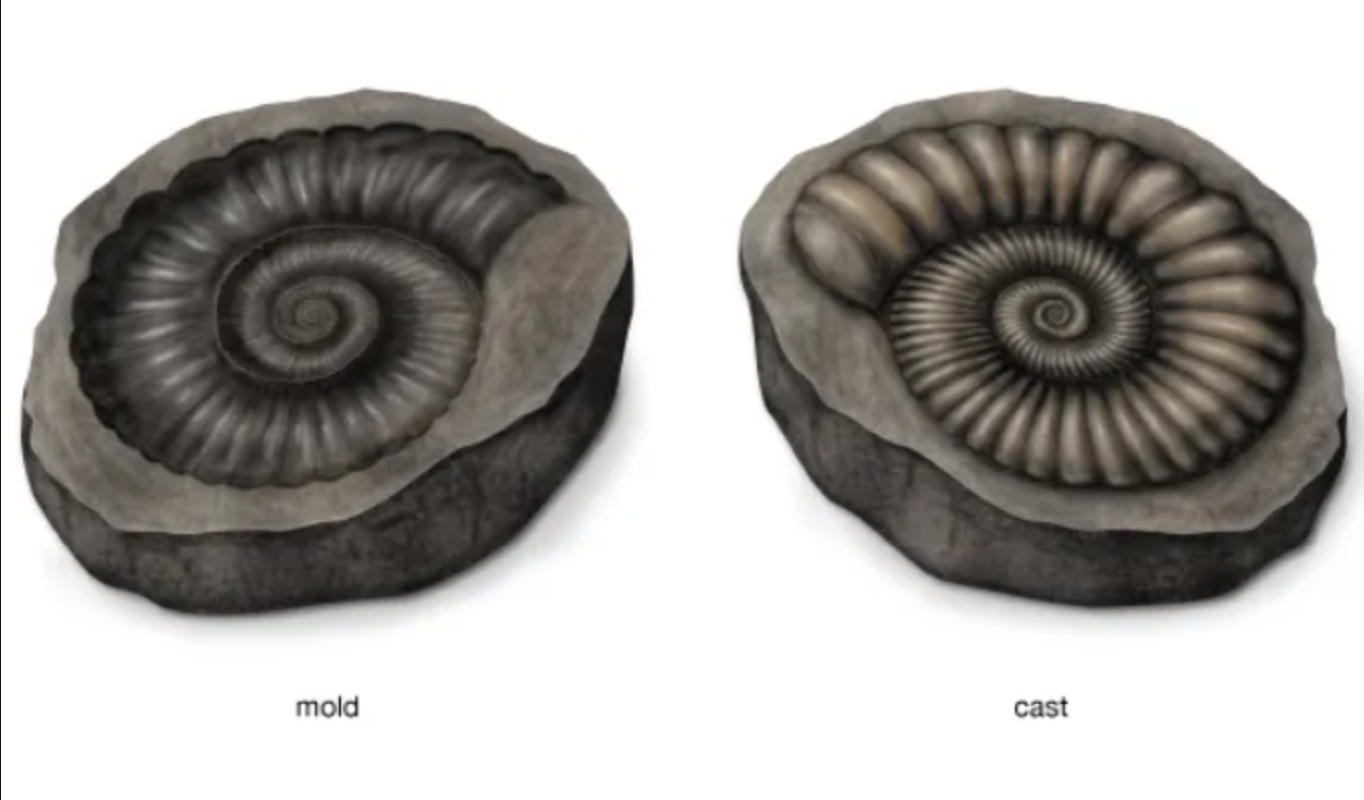
cast fossil vs mold fossil
cast = rock that’s got the shape of the organism sticking out of it.
mold = hollow imprint

Carbon imprints
organism is compressed under pressure. Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, siphor away
amber or resin fossils
Jurassic park core, organism trapped in amber then buried in the ground.
comparative anatomy (+ common example)
comparing the structural similarities of organisms. Similar structures so common ancestry. Divergent evolution. Pentadactyl limb (five fingered limb)
homologous structures
similar structure, different functions. organs or skeletal elements. suggests common ancestor. (divergent evolution)
analogous structures
different structure, similar function. no common ancestor. Shark, penguin, dolphin. (convergent evolution)
Comparative Embryology
organisms that go through similar stages in their embryonic development - prof of common ancestor.
Molecular Biology
The similarities between their amino acid sequencing in periods can determine how long ago they shared a common ancestor.
Lamarckism
Jean Baptiste Lamarck. suggested that old species died out and new ones arose. Believed if a feature is not used it will be lost. E.g. Giraffes stretching for leaves and gaining a longer neck.
vestigial structures
biological remnants from a previous ancestor that no longer serve a purpose. human appendix, wisdom teeth, tailbone.