Topic 1 Test - The Cell System
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
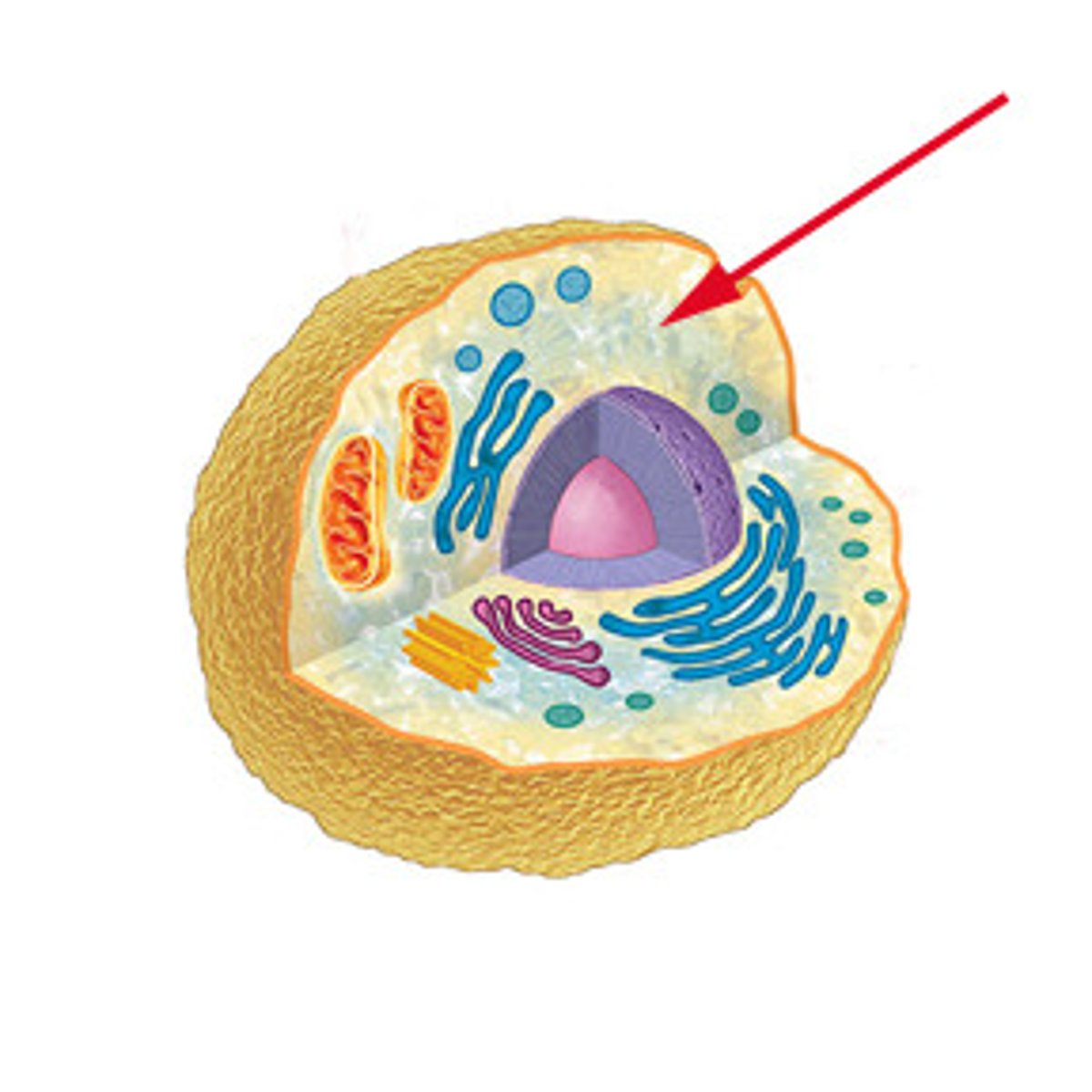
Cytoplasm
Fluid that fills the cell and keeps the organelles in place.
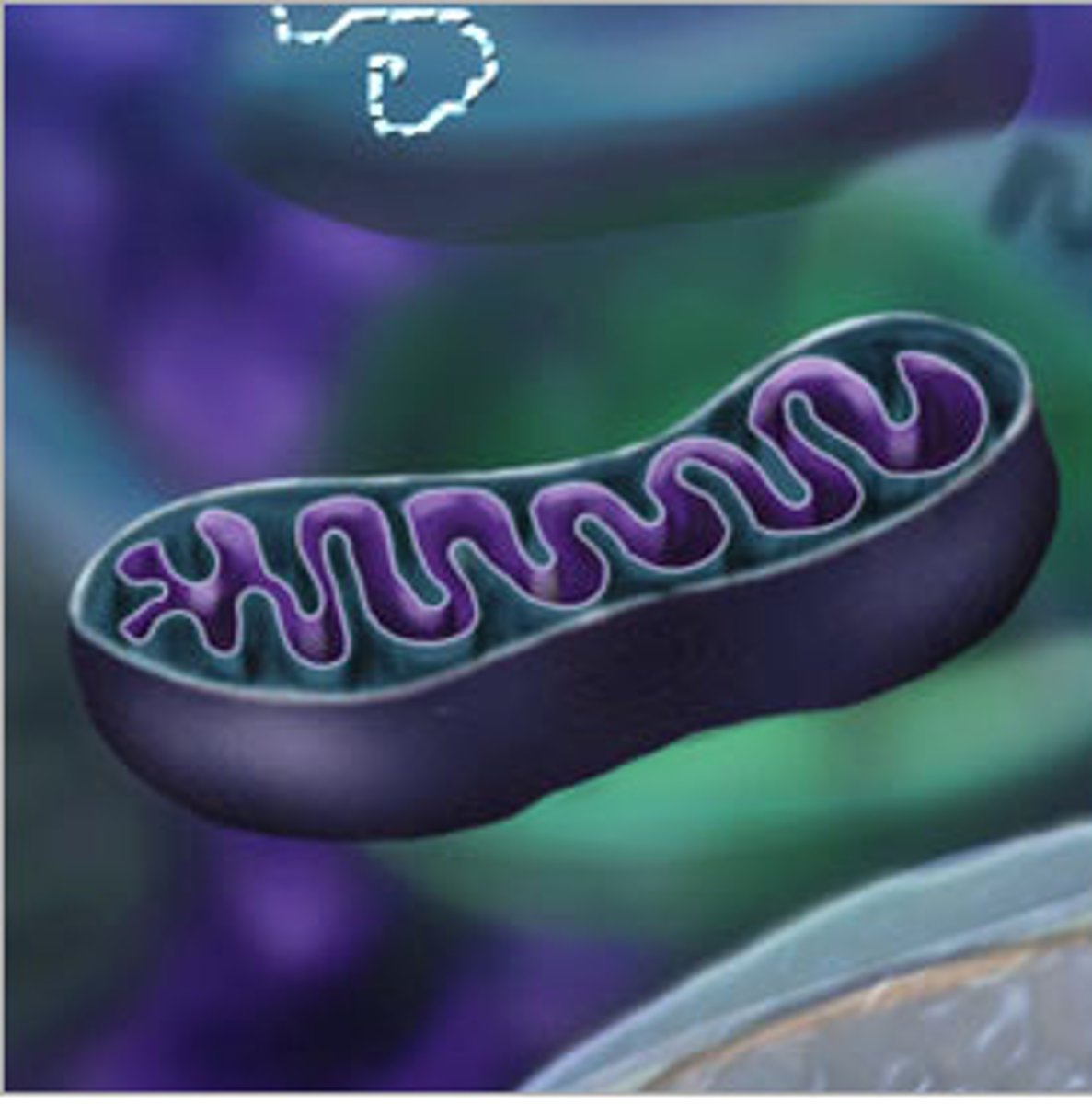
Mitochondria
Power plant of the cell. They create energy called ATP.
Cell Wall
A rigid exterior which protects and supports the cell.
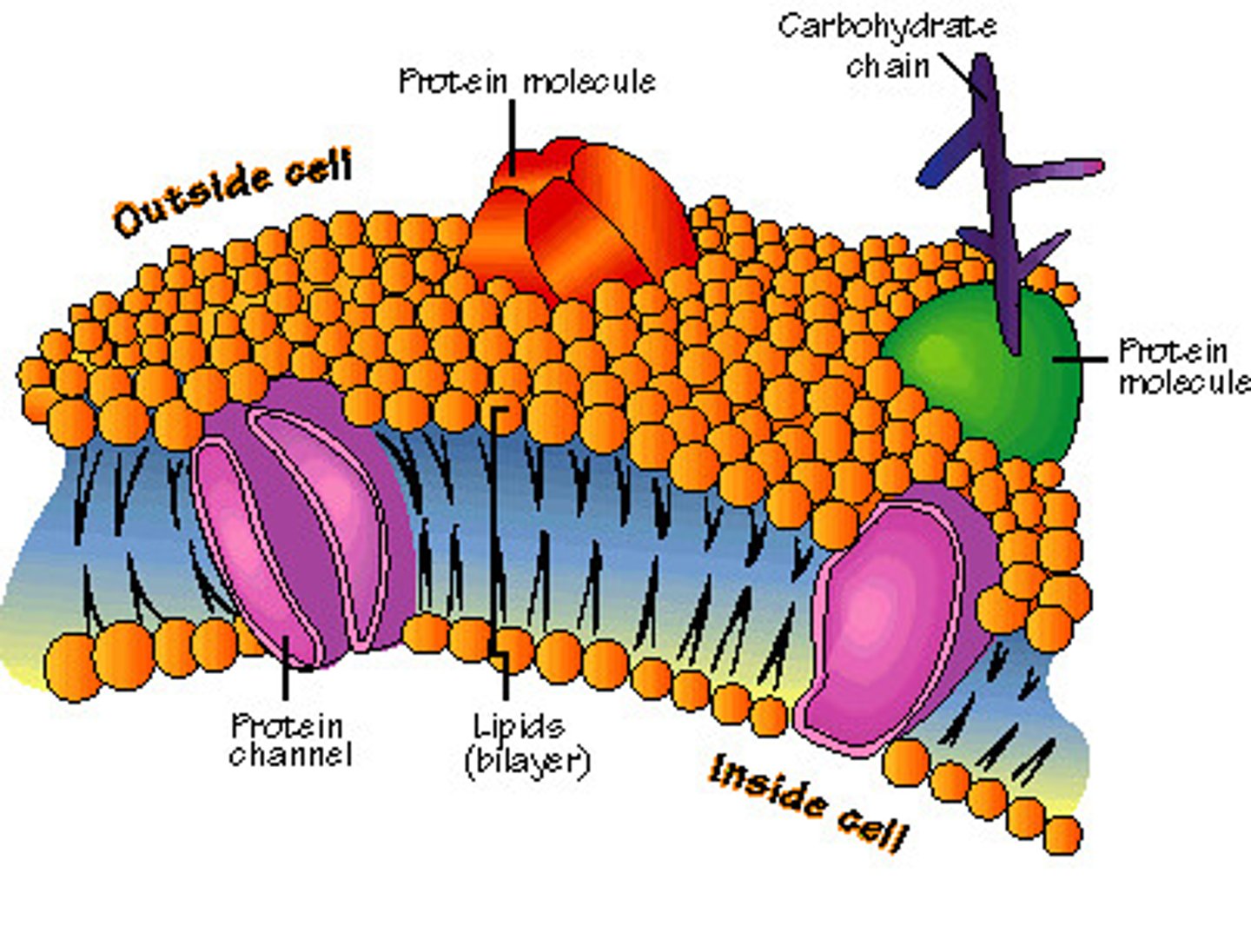
Cell/Plasma Membrane
Outer lining of cells. Controls what goes in and out of the cell.
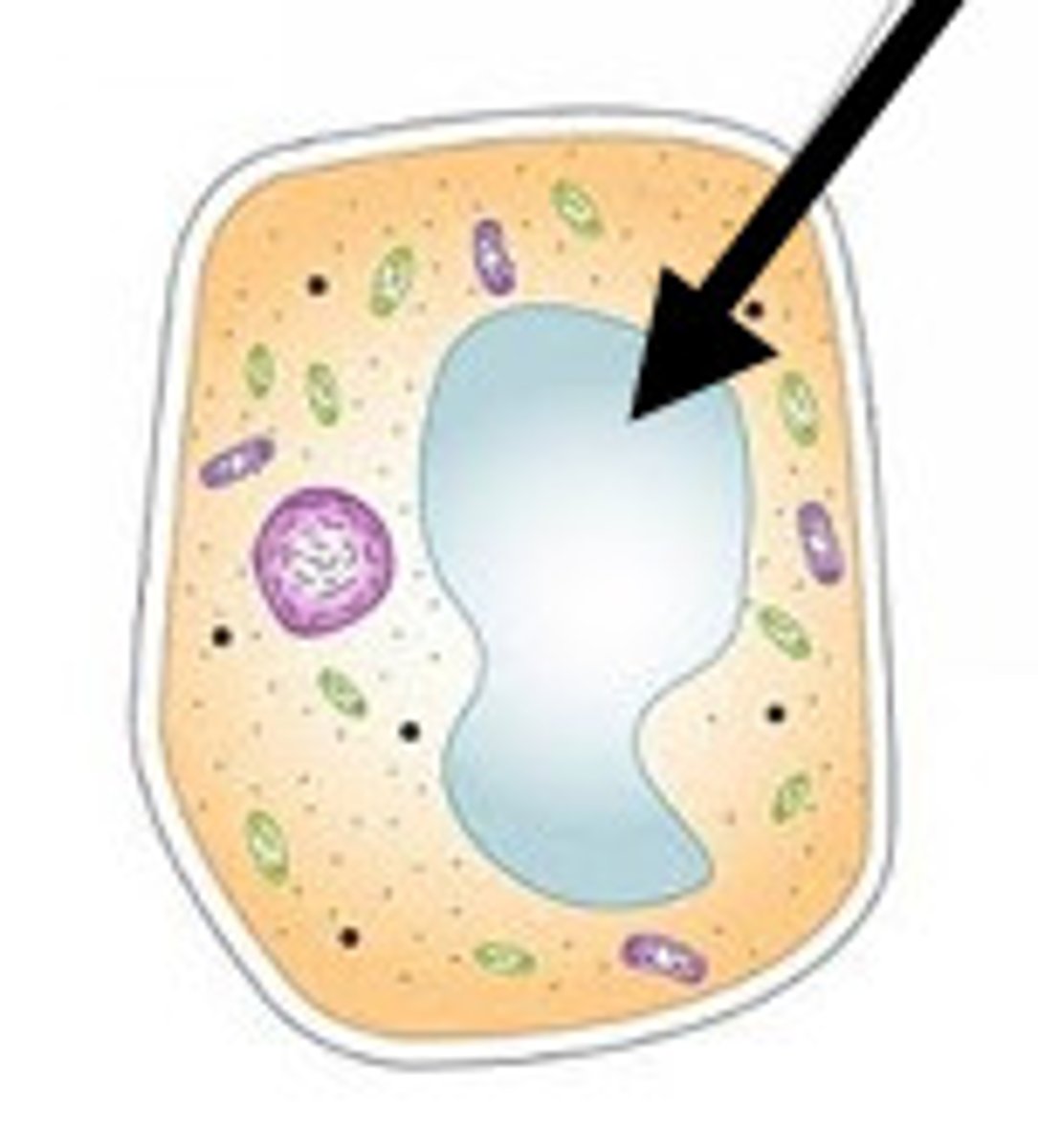
Vacuole
Stores water and nutrients for the cell to survive. In a plant cell, it also stores the wastes
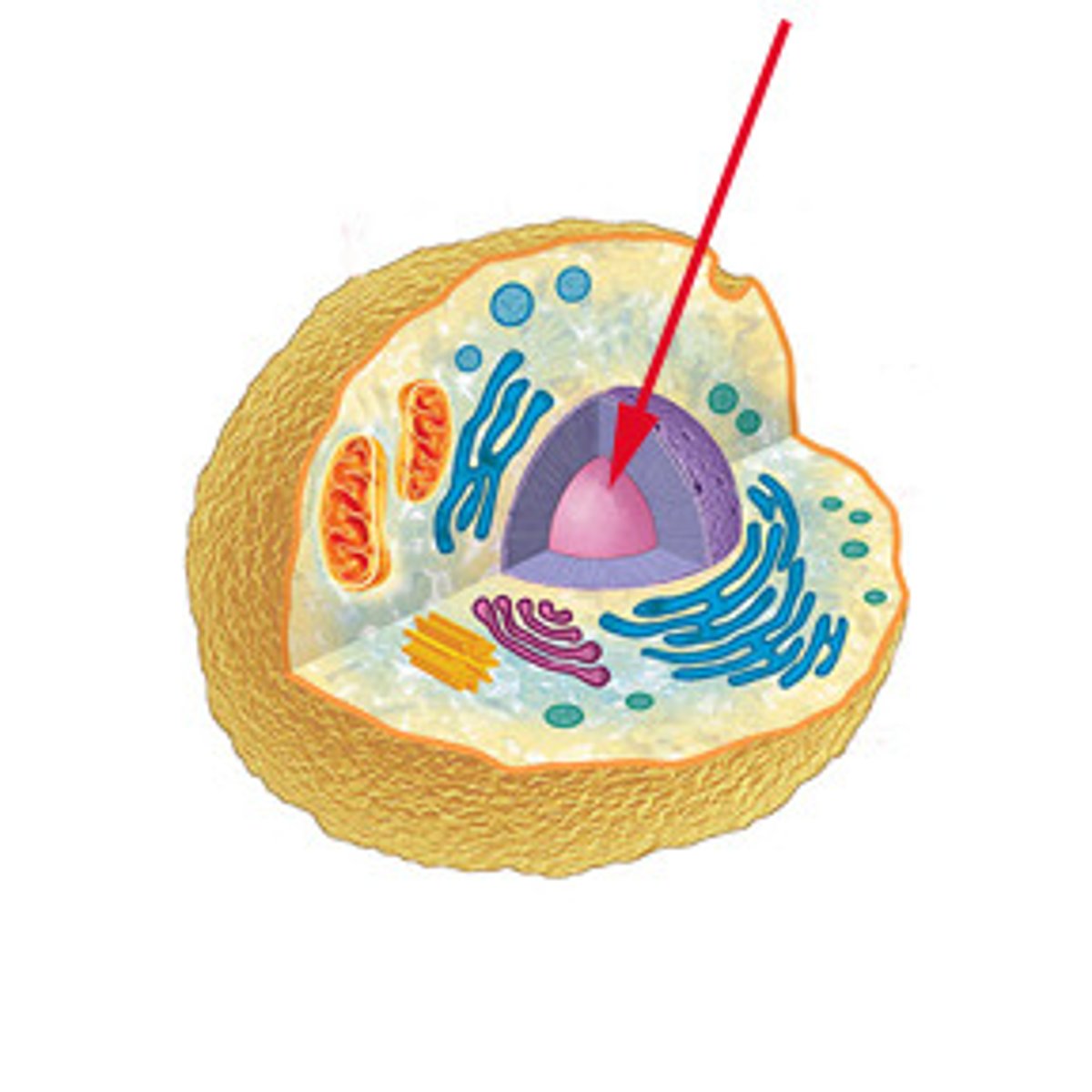
Nucleus
Controls all activity in the cell and stores DNA. (the Brain)
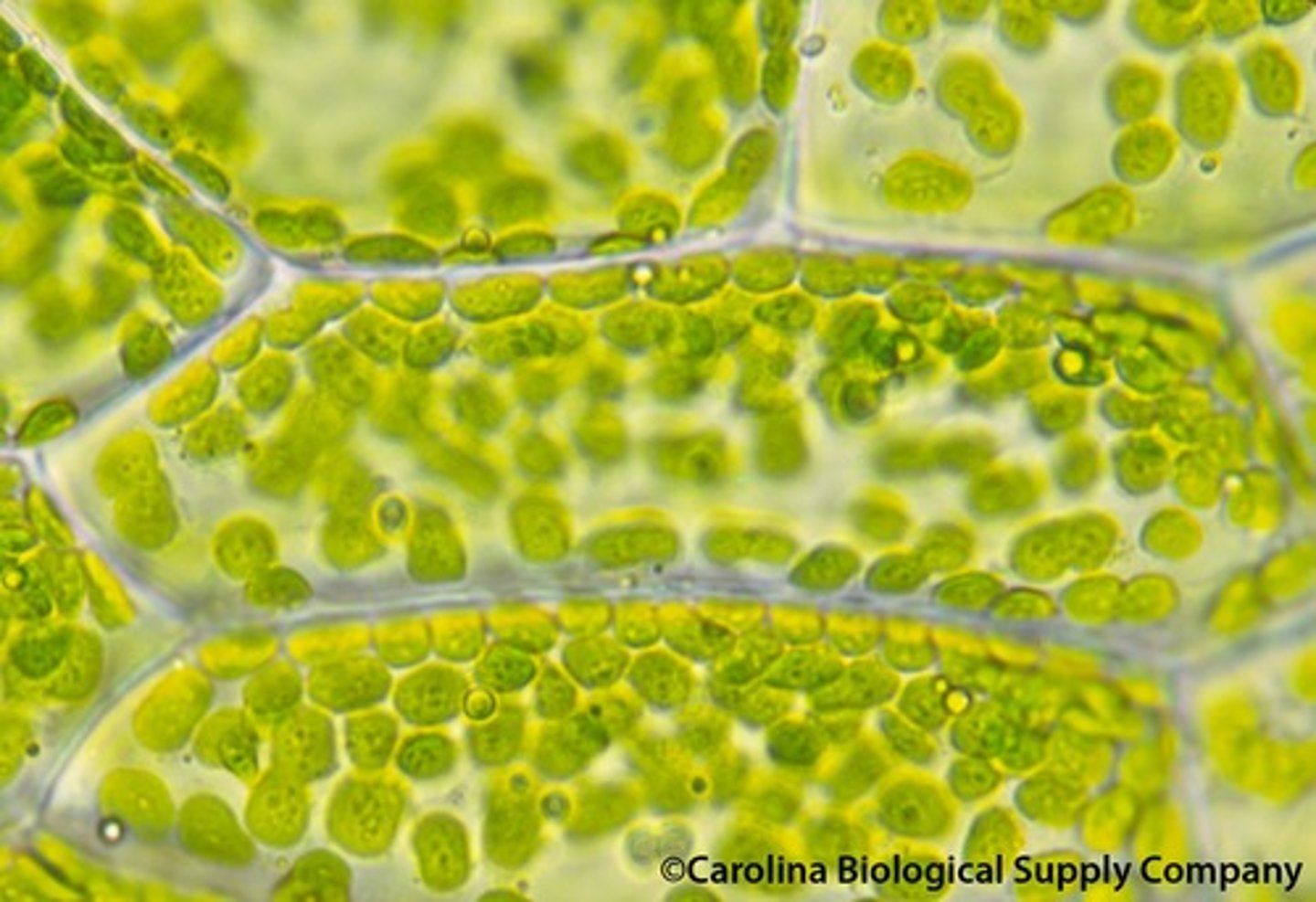
Chloroplasts
Converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose (Sugar) and oxygen in a process called photosynthesis.
Robert Hooke
Named boxes he saw under a microscope cells.

Cell Theory
All organisms are composed of cells
Cells are the basic unit of life
All cells come from preexisting cells
Metabolism
Chemical reactions inside the cell
Homeostasis
keeping conditions inside the organism within tolerable limits (balanced)
Growth
increase in size
Reproduction
producing offspring (Sexually or asexually)
cell cycle
the regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo.
replication
the process by which a cell makes a copy of the DNA in its nucleus.
Mitosis
the stage of the cell cycle during which the cell's nucleus divides into two new nuclei and one copy of the DNA is distributed into each daughter cell.
chromosome
a doubled rod of condensed chromatin; contains DNA that carries genetic information
chromatid
1 of the identical rods of a chromosome.
cytokinesis
the final stage of the cell cycle, in which the cell's cytoplasm divides, distributing the organelles into each of the 2 new cells
How does an organism increase in size?
During Interphase the cell doubles in size and produces all structures needed to carry out it's functions. Both mitochondria and chloroplasts makes copies of themselves during the growth stage.
What are the stages of the cell cycle in order?
Interphase,
Mitosis:Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase,
Telophase
Cytokinesis
What happens in each part of the cell cycle? (1st phase)
Interphase- the cell grows to its mature size, makes a copy of its DNA and prepares to divide into two cells.
What is the 2nd phase in cell cycle?
Mitosis: Prophase- The chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form chromosomes. Structures called spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell. The nuclear membrane breaks down.
What is the 3rd phase in the cell cycle?
Mitosis: Metaphase- The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Each chromosome attaches to a spindle fiber at its centromere, which still holds the chromatids together.
What is the 4th phase in the cell cycle?
Mitosis: Anaphase- The centromeres slit. The two chromatids separate. One chromatid moves along the spindle fiber to one end of the cell. The other chromatid moves to the opposite end. The cell becomes stretched out as the opposite ends pull apart.
What is the 5th phase in the cell cycle?
The chromosomes begin to stretch out and lost their rodlike appearance. This occurs in the two at the ends of the cell. A new nuclear membrane forms around each region of chromosomes.
What is the 6th phase in the cell cycle?
Cytokinesis- The cell membrane pinches in around the middle of the cell. Eventually, the cell pinches in two. Each daughter cell ends up with the same number of identical chromosomes and about half the organelles and cytoplasm.
What is the purpose of the spindle fibers?
Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell.
What is the longest stage of the cell cycle?
DNA Replication
Why is DNA replication so important?
DNA holds all the information that the cell needs to carry out its functions. The replication of a cell's DNA is very important, since each daughter cell must have a complete set of DNA to survive.
How is a cell able to produce two almost-identical daughter cells?
At the end of DNA replication, the cell contains two identical sets of DNA. One set will be distributed to each daughter cell.
How does Cytokinesis happen in an animal cell?
cytoplasm pinches in
How does Cytokinesis happen in a plant cell?
Cell plate forms
Living things are made of ____?
Cells
What is the organelle that is missing for plants that are growing underground compared to plants that grow above ground?
Chloroplasts
Osmosis, diffusion, and facilitated diffusions are examples of which type of transprort?
Passive Transport
endocytosis and exocytosis are examples of which type of transport?
Active transport
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
facillitated diffusion
when transport proteins make room for larger substances to pass through cell membrane
Endocytosis
A process in which a cell engulfs (takes in) extracellular material through an inward folding of its cellular membrane.
Exocytosis
release of large substances out a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the cell membrane.
What are the 4 reasons why a cell divides?
GROWTH by production of new cells.
REPAIR damaged cells
REPRODUCTION of new single celled organisms
REPLACING old and damaged cells
Prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
Metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
Anaphase (Mitosis)
sister chromatids are pulled apart
Telophase
After the chromosome separates, the cell seals off, Final Phase of Mitosis.