MSK II Exam 2 review: Hip pt.1
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
what is the traditional definition of hip OA?
Wear and tear due to increased load
Caused by cartilage loss
what is the contemporary definition of hip OA?
Whole joint disease
Affects labral, cartilage, and subchondral bone, synovial inflammation, and muscles
Many risk factors, including physical inactivity
The runners' knees are actually healthier compared to those who don't run
what are the extrinsic factors that causes hip OA?
the type and amount of activity
body mass
what are examples of extrinsic factors for type and amount of activity that causes hip OA?
High impact sports
At elite levels
Physically demanding work
Sedentary lifestyle
what are examples of extrinsic factors for body mass that causes hip OA?
obestiy
what does obesity do to cause hip OA?
Increased joint load
Systemic inflammation
Metabolic changes are prone to systemic inflammation
what are intrinsic factors that cause hip OA?
they start from age
hip morphology
strength
ROM
gait biomechanics
what is hip morphology?
FAI
Labral tears
Chondropathy
Dysplasia
what are the different types of FAI?
CAM or pincer
what is hip dysplasia?
The hip joint does not develop properly, causing the ball of the femur to fit loosely or incompletely into the acetabulum of the pelvis.
what is typically weak for patients with hip OA?
Weak hip extension/abduction/ER
Weak knee extension
Weak posterior compartment of the leg
what ROM is reduced with hip OA?
Reduced hip flexion and IR ROM
Reduced hip extension ROM
what is effected with gait biomechanics in hip OA?
Midstand → increased external flexion/adduction/IR movement
Terminal stance → decreased hip extension
what is effected during midstance in gait for hip OA?
increased external flexion/adduction/IR movement
what is effected during terminal stance in gait for hip OA?
decreased hip extension
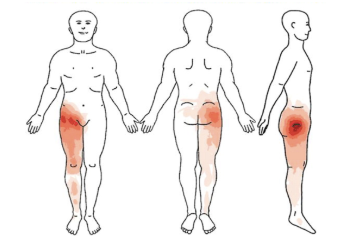
what is the subjective for hip OA?
Age (50+)
Athletic history
Type of work
Previous Hx of hip pain
Pain increases with increased sitting time
Morning stiffness <1hr
Pain at rest and night (synovitis)
Difficulty donning socks/shoes
Difficulty getting out of a low chair
Pain location
what specific previous diagnosis can lead to hip OA?
SCFE (slipped capital femoral epiphysis)
DDH (developmental dysplasia of the hip
FAI (femoroacetabular impingement)
what are red flags for a patient with hip OA?
Hx of cancer (prostate, breast, gynecological mets to hip)
Female sex → gynecological issues refer to hip
Alcohol abuse (AVN)
UTI
Unexplained weight loss (CA)
Change in bowel habits (CA or other lower GI)
Corticosteroid use (AVN, stress fractures)
Acute pain with fever (infection)
what are signs and symptoms for hip OA that compare to the lumbar spine orpelvis?
Walking with a limp (7x more likely hip)
Pain in groin/anterior hip (7x more likely hip)
Reduced hip IR (14x more likely hip)
No change in symptoms with repeated movements lumbar spine (SN = 92% to rule out lumbar spine)
Negative lumbar quadrant test (SN = 100% to rule out lumbar spine)
Negative thigh thrust (SN = 82% to rule out SIJ)
No pain over SIJ → rule out SIJ
what do you exam for a patient with hip OA?
movement analysis
tests and measures
what is within movement analysis?
gait
squat
full body rotation
single leg stance
what should you see during gait for a patient with hip OA?
Pain
Decreased stride length (lack hip extension)
Early heel off
Trendelenburg (glute med problem), compensated trendelenburg
Increased knee/hip flexion mid stance
what should you see during a squat for a patient with hip OA?
Pain
Decreased hip flexion ROM
Increased hip adduction/IR
what should you see during full body rotation for a patient with hip OA?
Pain
Decreased ipsilateral pelvic rotation
Stabilize the hip to check lumbar rotation → if no symptoms, it is the hip
what should you do during full body rotation when you discover decreased ipsilateral pelvic rotation ?
Stabilize the hip to check lumbar rotation → if no symptoms, it is the hip
what should be observed during single leg stance in a patient with hip OA?
Pain
Decreased hip extension
Trendelenburg, compensated trendelenburg
what falls under test and measures for hip OA?
ROM
strength
muscle length
what specific ROM can be decreased in a patient with hip OA?
Hip flexion is 15 degrees less than the other side or <115 degrees if bilateral
Hip IR < 25 degrees
Underline → diagnostic of hip OA
May also see decreased ankle DF
what is an underlined diagnostic of hip OA?
Hip IR < 25 degrees
what are some strength deficits that can be found in a patient with hip OA
Weak glute max, glute med
May also see weak quads and posterior compartment of leg
what muscle length can be examined in a patient with Hip OA?
Tight TFL, rect fem, deep posterior hip
what are recommended interventions for patients with hip OA ?
Education combined with exercise and/or manual therapy (activity modification, weight reduction, methods of unloading the joints)
Provide impairment-based functional, gait, and balance training
Manual therapy (joint mobilization, HVLAT, soft tissue)
As hip motion improves, add exercises, including stretching and strengthening, to augment improvement
Individualized flexibility, strengthening, and endurance exercises
Use ultrasound to the anterior, lateral, and posterior hip (1MHz, 1W/cm for 5 mins each)
how should you move forward with manual therapy in a patient with hip OA?
As hip motion improves, add exercises, including stretching and strengthening, to augment improvement
which interventions is not recommended for hip OA?
Use bracing as a first line treatment
what should you educate a patient who has hip OA?
dispersion of forces
living at the end range
capcity vs load
weight loss
multiple levers we can pull
facts
what is dispersion of forces of hip OA?
Deceased mobility = decreased surface area being utilized = increased stress on a specific part of the joint
what is living at the end range for hip OA?
Decreased mobility = stress on tissues around the joint
what is capacity vs load in hip OA?
Tissue capacity is only as high as the load that is regularly placed on it. Cartilage and bone need load too
what is education for weight loss in hip OA?
10 lbs reduction in bone weight = 60lbs reduction in joint load
for education what is multiple levers we can pull, in hip OA?
Activity, weight, muscle strength, ROM, gait
FOr education what is facts we can give about hip OA?
Imaging correlates poorly with pain and disability
Pain does not equal damage
Exercise is safe and helpful
Rest and avoidance make pain worse
what is exercsies for hip OA?
Good Living with osteoArthritis: Denmark (GLA:D)
General exercises for knee and hip OA
It helps
wellness
self efficacy
which body parts do we generally give exercises for a patient who has hip OA?
General exercises for knee and hip OA
what is wellness exercise?
Pain reduction and management
Improved mobility
Improved strength
what is self-efficacy for exercise ?
Confidence
Awareness
Motivation
what test is used for ROM in hip OA?
Using Craig’s test (looks for the total arc of 90-100 degrees and bony end feel, but don't force IR with retroversion)
what is normal for femoral neck degrees?
8-15 degrees of the angle between the posterior condyles and the femoral neck → normal
what is anteversion?
increased hip IR and decreased hip ER (the angle >15 degrees)
Toes in walking as compensation
what is retroversion?
increase hip ER and decreased hip IR (the angle <8 degrees)
Toes out walking as compensation
what is surgical management for hip OA?
THA
Mainstay for the treatment of
End stage hip OA
End stage hip RA
Younger individuals with severe hip dysplasia
what is THA?
The resection of the femoral head acetabulum and replacement with metal or polyethylene components
Hemiarthroplasty where only the femoral component is replaced
May be performed after certain types of proximal femur fractures
Allow immediate full weight bearing
May be partial weight bearing of the femoral fracture occurs after THA
10 year survival rate for a THA implant is 95%
25 year survival rate is 78% → need revision later on in life
The most common reason for the failure of THA is aseptic loosening of the components
__ where only the femoral component is replaced
May be performed after certain types of proximal femur fractures
Hemiarthroplasty
what is the 10 year survival rate for a THA?
10 year survival rate for a THA implant is 95%
what is the 25 year survival rate for a THA?
25 year survival rate is 78% → need revision later on in life
what is the most common reason for THA failure?
aseptic loosening of the components
what is the procedure (approaches) for THA?
Traditional approach: posterolateral or lateral approach
anterior approach
mini open technique
joint resurfacing
what is Traditional approach: posterolateral or lateral approach?
Having a risk of dislocating the hip posteriorly
Precautions are important to limit motion that would stress the posterior capsule to prevent dislocation
what is anterior approach for THA?
More technically demanding approach
Spares direct trauma to the glute med
The femur is dislocated anteriorly, so the anterior capsule must be protected by limited hip extension and external rotation
what is mini open technique for THA?
Uses a small incision to create less tissue damage, presumably resulting in decreased pain and decreased strength deficits
what is joint resurfacing in THA?
Carefully cuts around the femoral head and places an artificial cap on to create a new joint surface
Used on younger patients to allow easier revision surgery to convert to a traditional THA
Younger and have few or no comorbidities patients are able to go home the same day as the procedure
who is joint resurfacing used on?
Used on younger patients to allow easier revision surgery to convert to a traditional THA
Younger and have few or no comorbidities patients are able to go home the same day as the procedure
what are precautions for THA?
Usually in place between 4 and 12 weeks after surgery to allow the joint capsule to heal
The research found similar rates of dislocation (~2%) between patients whose postop protocol included these restrictions and those patients whose motions were unrestricted
But clinicians should clearly communicate with the patient’s surgeon to best understand the precautions for a given patient
what is the precautions for posteriolateal approach THA?
No hip flexion over 90 degrees
No hip adduction
No hip IR
what is the precautions for anterior approach THA?
Limited hip extension
what are preoperative treatments for THA?
education
expected outcomes
recovery process
exercises to help prevent DVT and pneumonia
what should be educated for preoperative treatments of THA?
Post-op precautions
Use of assistive device
Expected functional recovery and time frame
Beginning post-op exercises
what treatment can be given to help prevent DVT and pneumonia preoperative of THA?
Wainwright et al (2020) concluded that pre-op PT may be effective in specific patient groups but it is not an essential intervention
NICE guidelines were unable to make recommendations for practice in this area
Widner et al (2022) concluded that there are no negative effects of prehabilitation on the outcomes
what are postperative treatments for THA?
PT begins the day of surgery
Restore ROM is seldom a problem, unlike TKA
Strengthening of hip and entire LE should be emphasized throughout rehab
NMES to the quads may be beneficial
Heavy strength training, working up to loads of 85-90% of 1RM, sets of 4-6 reps, is well tolerated and does improve LE strength deficits
Balance training should be included
Gait training
what occurs when the PT begins the day of surgery postoperative for THA?
Most of the time, PT is the first one to get the patient out of bed → remember to check orthostatic hypotension
Early mobilization with an assistive device
what occurs Restore ROM is seldom a problem, unlike TKA postoperative for THA?
The patient with THA appears to have less problems with pain but more difficulty with regaining hip strength
what is Strengthening of hip and entire LE should be emphasized throughout rehab for postoperative?
Should include weight bearing and nonweight bearing exercises
Heel raises
Squats
Sit to stands
Steps up
Should be progress to the use of resistance bands, weights, and machines
are we missing the mark for THA?
Sekita et al (2024) discovered that the hip and knee muscle strength on both surgical and nonsurgical knees in female patients may not recover to the same level
Winther et al (2018) study showed that maximal strength training (MST) was stronger in leg press and abduction than the conventional PT group and 6 months postoperatively
It takes approximately 1 year to achieve their prior functional activities
what is hip fracture?
One of the most common fractures
Only refers to proximal femur fractures and not to acetabular fractures or femoral head fractures
Femoral head fractures have an increased risk of AVN due to poor blood supply
Proximal femur fractures may be intracapsular or extracapsular
Femoral head fractures have an increased risk of?
AVN due to poor blood supply
Proximal femur fractures may be
intracapsular or extracapsular
what are intracapsular fractures?
Involve the femoral neck
Femoral neck has a more tenuous blood supply and these fractures and nonoperative treatment is seldom possible
Operative treatments
Closed or open reduction with internal fixation
Hemiarthroplasty
THA → when combined with preexisting hip OA
what are operative treatments for hip fractures?
Closed or open reduction with internal fixation
Hemiarthroplasty
THA → when combined with preexisting hip OA
what are extracapsular fractures?
Include intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures
The majority of proximal femur fractures are intertrochanteric
Mostly are treated with open or closed reduction with internal fixation using implants such as compression screws and intramedullary nails with or without a plate
what is postoperative hip fracture management?
Early rehab occurs in the acute setting
Patient will have limited hip strength
Progressive strength and functional training should be included
E-stim for quads strength and pain management is indicated
Weight bearing and non weight bearing exercises should be included to provide adequate muscle strengthening and decrease osteoporetic bone loss
Progressive balance exercises such as dual tasking
Aerobic exercises should be part of the rehab to maximize outcomes
The clinician should discuss any needed modifications for safety
what should early rehab focus on for hip fracture management?
Focus on pain management, early mobilization, and prevention of secondary impairments
where will a patient have limited strength in for hip fractures postoperative?
Decreases in hip extensors, hip abductors, and knee extensors common
what can patients do for hip fracture managment postoperative?
Tai chi
Chair yoga
Aquatic exercises
Silver sneakers
what should the clinic discuss post hip fracture?
Rest breaks
Performing exercises next to a secure handrail
Seated alternatives
what did the research show for postoperative hip fractures?
The research concluded that home dwelling hip fracture patients can benefit from an extended supervised strength training. The patients are capable of high intensity strength training which should optimise gains in physical function, strength, and balance. Resistance exercise training seems to influence functional performance adaptation,
what CPG’s is recommended for post hip fracture?
Additional therapies such as strength, balance, functional, and gait training to address existing impairments and activity limitations and fall risk
PT must provide recommendations to patients to maximize safe physical activity
PT must provide aerobic training to progressive resistive, balance, and mobility training in the community setting for older adults after hip fracture
what is involved for mobilization in hip?
Monitor progress - asterisk/comparable/concordant signs
Used to monitor progress within and between sessions
what is 2 subjective for hip mobilization?
Monitor between sessions
what is 2 objective for hip mobilization?
Monitor effects of manual therapy and SMPs within sessions
For hip flexion closely predicts outcome and is sensitive to change
Avoid using IR because it likely will not change with treatment
what is the goal of every treatment for hip mobilizations?
Within and between session change, associated with functional recovery
what is MWM procedure?
Test asterisk/comparable signs
Have the patient actively move the joint through the desired motion and note the patient's ROM and symptoms
Apply the desired glide to the joint
Have the patient actively move the joint through the desired motion as you maintain the glide
Observe for a change in ROM and ask the patient if the patient feels better, the same, or worse with the applied glide
If ROM and symptoms are not significantly better (>80% pain reduction)?
adjust the force of the glide, the direction of the glide or the patient’s movement
If MWM procedure is not working?
transition to a general mobilization or try a different mobilization technique or plan of motion
if MWM procedure is significantly better (>80% pain reduction)?
you can apply overpressure at the end range and have the patient continue to go in and out of the motion 6-10 times while maintaining the glide. Recheck the signs. If improved, repeat the procedure 1-2 more times.