The physical landscapes of the UK
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
How are lowland, upland & glaciated landscapes distributed across the UK?
Lowland areas → south of the UK (e.g. the Midlands, London, East Anglia)
Upland areas → north of the UK (e.g. Scotland, Wales)
Glaciated landscapes → cold mountainous areas (e.g. Scotland, north Wales, the Lake District)
What is geology?
The study of rocks & their formation, structure & composition
What are the 3 main types of rock?
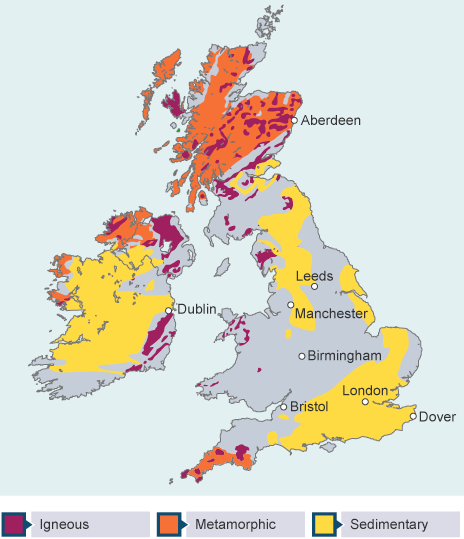
Igneous → tough & resistant rock formed from cooled magma (e.g. granite, basalt)
Sedimentary → softer & less resistance rock formed from from sediment (e.g. chalk, clay, sandstone)
Metamorphic → very tough & resistance rock formed from rocks undergoing extreme heating or pressure (e.g. slate, marble)
How are different rock types distributed across the UK?
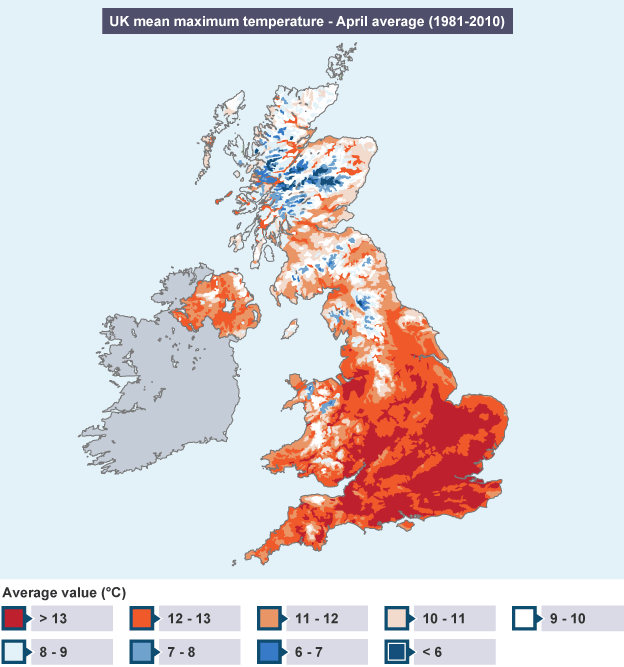
How does climate vary across the UK?
How does human activity vary across the UK?
Lowland areas → densely populated due to more infrastructure, housing, & transport links
Upland areas → sparsely populated due to the harsh climate & steep relief making the land less convenient to build infrastructure on. Land is more commonly used for animal farming, forestry & reservoirs
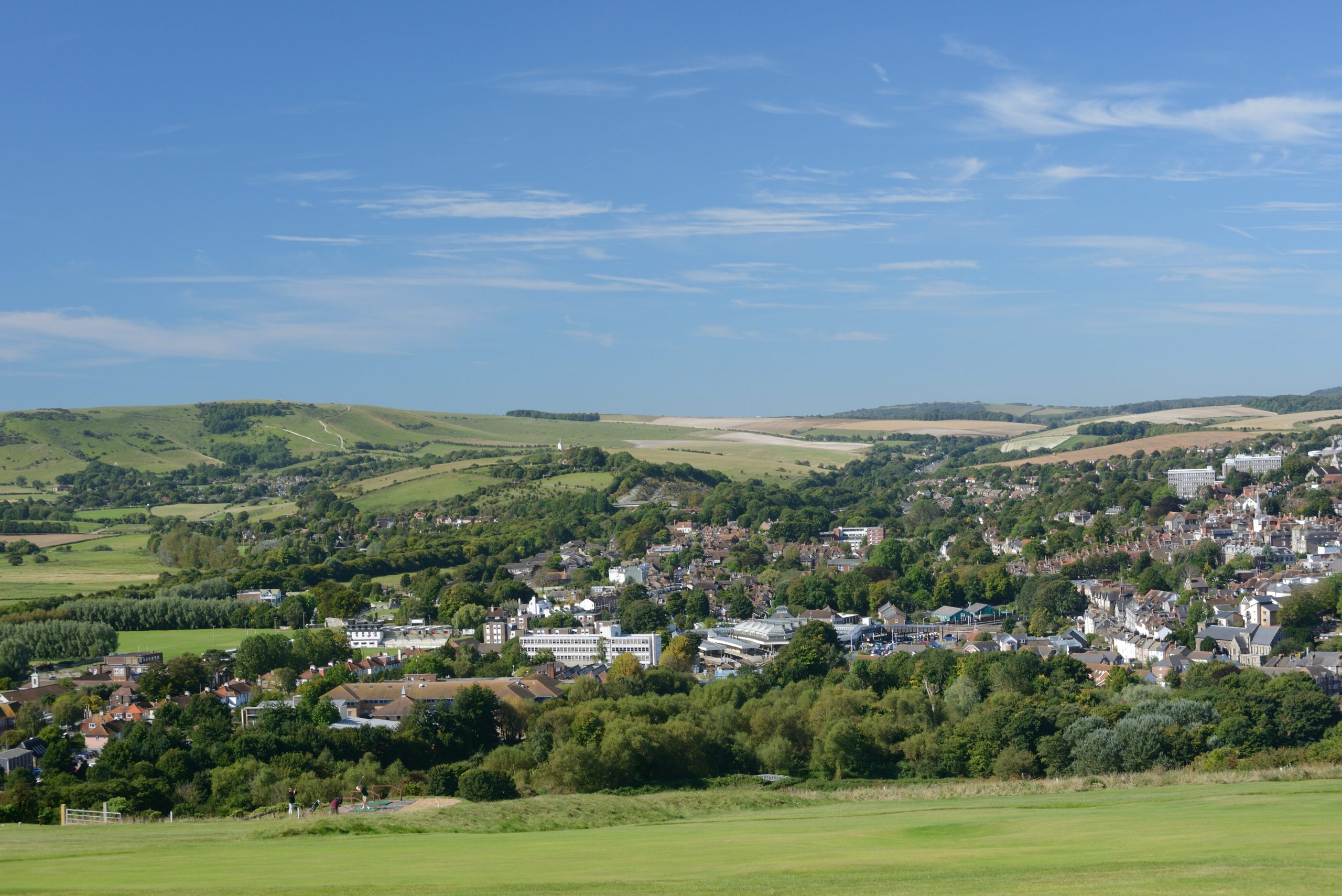
What are the defining features of lowland landscapes?
→ More human activity & infrastructure
→ Flat land & grasslands
→ Arable farming
→ Sedimentary rocks
→ Warmer & drier climate

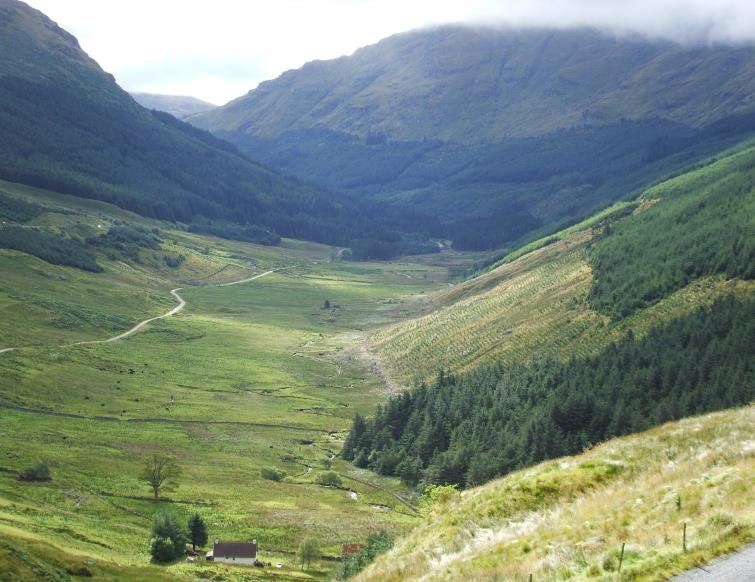
What are the defining features of upland landscapes?
→ Steep gradient & v-shaped valleys
→ Sparse population
→ Forests, waterfalls & reservoirs
→ Hill sheep farming
→ Igneous & metamorphic rock
→ Colder & wetter climate

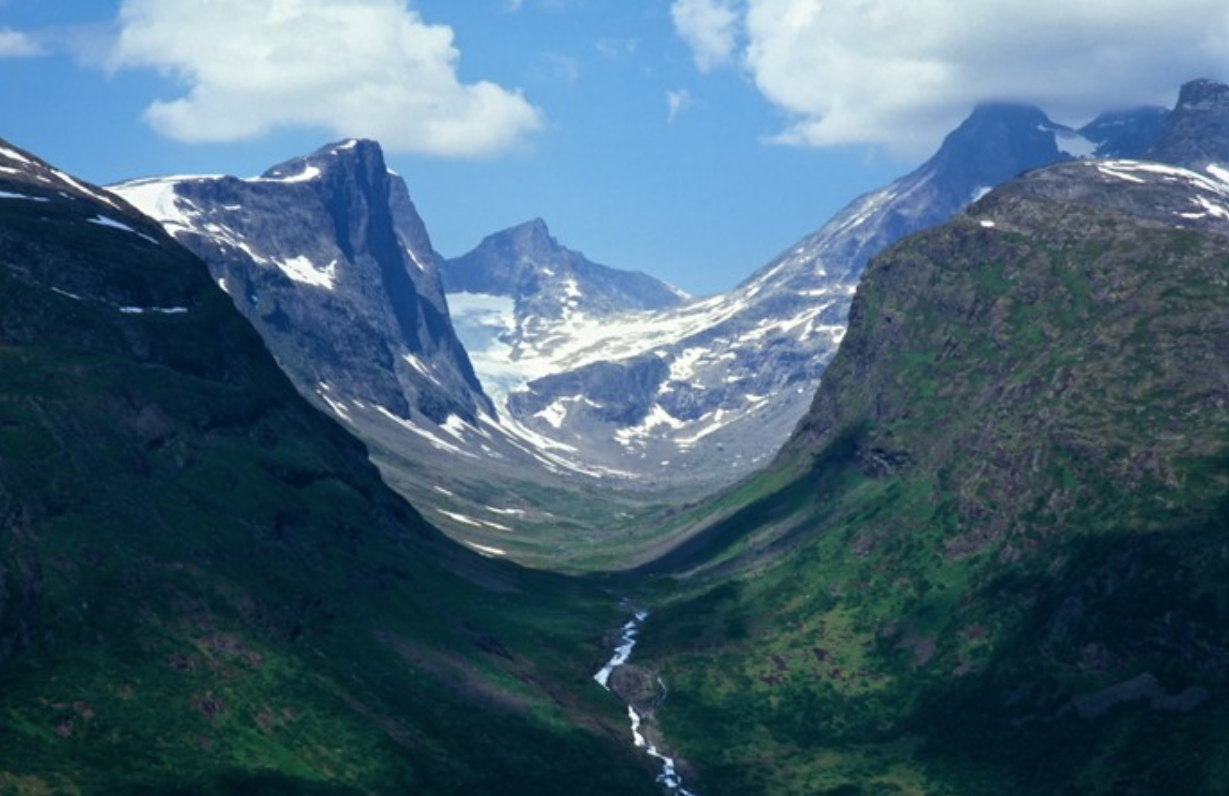
What are the defining features of a glaciated landscape?
→ U-shaped valleys
→ Truncated spurs
→ Alluvial fans
→ Little human activity
→ Miss-fit river
→ Ribbon lakes or corrie lakes
