Intestine and Colon Disorders: Diverticular Disease, Colon Polyps, and Colorectal Cancer
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
outpouching, diverticulosis, infectious, older, diet, NSAIDs
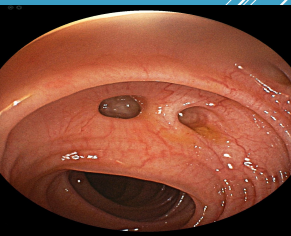
Diverticular Disease
-Diverticula → ____________ of colonic wall
-__________→ presence of diverticula and typically asymptomatic
-Diverticulitis → inflammation and/or __________ diverticular disease
-Risk Factors → _____ age, obesity, smoking, ____ (low fiber, high fat, red meat), physical inactivity, and medication use (ASA, _______, steroids, opiates)
anywhere, left, sigmoid
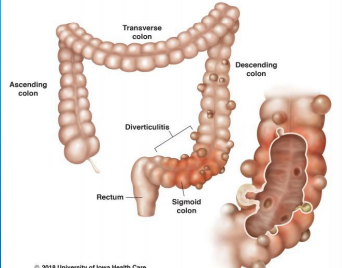
Diverticular Disease
-Can occur ____________ in GI tract
-____ colon most common in Western countries (_______ most common)
-Right colon most common in Asian countries
-Small intestines is very rare
pressure, motility, weak, vasa recta, contraction, herniation, decreases
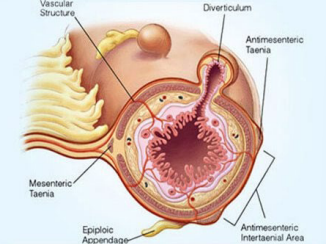
Diverticular Disease: Pathophysiology
-Associated with increased intracolonic _________, abnormal neuromuscular function, and alterations in intestinal _______
-Diverticulosis
Tend to form at ____ points in the colonic wall where ____ _____ penetrate the circular muscle layer
Exaggerated segmentation ___________ → increases intraluminal pressure → _________ of the mucosa and submucosa through the muscle layer
Laplace’s law → wall pressure increases as diameter of a cylindrical structure __________
herniates, injury, perforation, mesentery, peritonitis
Diverticular Disease: Pathophysiology
-Diverticular Bleeding
Diverticulum _______ → penetrating vessel draped over dome → exposes vasa recta to ______ → bleeding
-Diverticulitis
Erosion of diverticular wall → inflammation → necrosis → micro/macroscopic __________
Usually walled off by pericolic fat and ________ → can lead to abscess or obstruction
If not walled off then can be free perforation and __________
LLQ, guarding, constipation, obstruction, bladder
Diverticulitis: Symptoms and Complications
-Symptoms
Abdominal pain (___ most common) → constant, often present for several days. May exhibit _________, rigidity, and rebound tenderness
N/V and fever possible
Change in bowel habits → ___________ (MC) vs diarrhea
-Complications
Abscess, bowel ___________, fistula (with ______ most common), and perforation (of abscess or free)
CT, contrast, thickening, diverticula, colonoscopy, perforation, 6-8
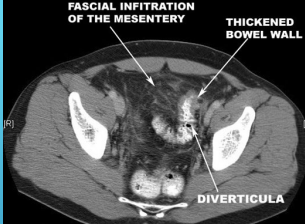
Diverticulitis: Diagnosis
-Labs → CBC
-Imaging → Abdominal __ with oral/IV ________ (preferred imaging)
Localized bowel wall ___________ (>4mm)
Increases soft tissue density within pericolonic fat (fat stranding)
Presence of _________
Can also find complications if present
-___________ should be avoided during acute diverticulitis d/t risk of _________
-After resolution of symptoms (_-_ weeks) a colonoscopy can be performed if the pt hasn’t had one within the previous year
complicated, fever, age, fluids, outpatient
Diverticulitis: Criteria for Inpatient Treatment
-CT shows ___________ diverticulitis
OR
-CT shows uncomplicated diverticulitis with pt having one or more of the following:
Sepsis, microperforation or phlegmon, immunosuppression, high _____ (102.5+), significant leukocytosis, severe abdominal pain or peritonitis, advanced ___, significant comorbidities, not able to take in _____ orally, noncompliant or unable to follow up, and failed __________ treatment
NPO, Metronidazole, emergency, uncomplicated, drainage, cancer, resection
Diverticulitis: Inpatient Treatment
-IV antibiotics, fluids, pain control, bowel rest (___)
-Uncomplicated → IV antibiotics
Cover normal GI flora (gram - rods and anaerobes)
Ertapenem or piperacillin-tazobactam or ampicillin/sulbactam
Ciprofloxacin plus ____________
-Complicated → treat the complication
Free perforation = __________ surgery
Microperforation = treated like ___________ inpatient
Abscess = percutaneous ________ vs surgery
Obstruction = affected bowel resection (r/o _____)
Fistula = affected bowel __________
rest, antibiotics, Amoxicillin/Clavulanate, 2-3, weekly
Diverticulitis: Outpatient Treatment
-Bowel ____ (clear liquid diet)
-_________ (7-10 days) in select patients
Ciprofloxacin plus Metronidazole or ___________/___________
-Follow up in _-_ days and then _______ until symptoms resolve
lower, spontaneously, 70, painless, stool, colonoscopy
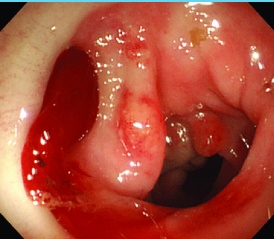
Diverticular Bleeding: Background
-Most common cause of overt _____ GI bleeding, where most bleeding stops _____________
-Risk Factors → age > __, bilateral diverticulosis, and obesity
-Symptoms → __________ hematochezia or dark/maroon colored ____
-Diagnosis/Treatment
___________ (test of choice) → provide endoscopic therapy (submucosal epinephrine injection or tamponade)
Nuclear scintigraphy with angiography → angiographic therapy (infusion of vasoconstricting meds or embolization)
Surgical intervention → segmental or subtotal colectomy
mucosa, IBD, dysplasia, benign, adenomatous, neoplastic
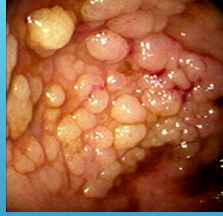
Colon Polyps: Types
-Mass or finger like projection arising from the colonic ______
-Inflammatory Pseudopolyps → seen in ___, can be associated with surrounding __________ in those with IBD
-Harmartomatous Polyps → made of normal tissue but growing in disorganized mass. May increase CRC risk in some cases
-Serrated Polyps → sawtooth appearance, larger in size. _____ (hyperplastic) to increased risk of CRC (sessile serrated and serrated adenoma)
-_____________ polyps → most common __________ polyp in the colon
Tubular (MC), villous (high risk for cancer), tubulovillous
All have some form of dysplasia
1-2, 5-10, 3
Screening in Those with Adenomatous Polyps
-Low Risk Adenomas
_-_ tubular adenomas < 10mm
Follow up colonoscopy in _-__ years
-High Risk Adenomas
3-10 adenomas or tubular adenomas
One is >6mm, villous adenoma or high grade dysplasia
Follow up colonoscopy in _ years
50, adenocarcinoma
Colorectal Cancer: Background
-Epidemiology → most common in those > __, incidence slowly rising in those 20-54
-Pathology → >90% arise from adenomatous polyps, leading to ____________
Takes 10-15 yrs
polyps, cancer, familial, IBD, ETOH, processed
Colorectal Cancer: Risk Factors
-Age
-Hx of colorectal _____ (adenomatous or serrated polyps)
-Family history of colorectal _____
-_______ adenomatous polyposis
-Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
-___ after 8-10 yrs
-Type 2 DM
-Smoking or chewing tobacco
-Obesity
-Physical inactivity
-Moderate-heavy ____ use
-High consumption of __________ meat
-Red meat consumption
-High fat-low fiber diets
screening, iron deficiency, bowel habits, diarrhea, bleeding, obstruction
Colorectal Cancer: Clinical Presentation
-Asymptomatic → found on routine __________
-Suspicious Symptoms/Signs
____ _________ anemia → fatigue, weakness, pale. Found on routine lab work, more common in right sided CRC
Change in _____ _____ (MC symptoms) → constipation, _______. More common in left sided CRC
Rectal _________ (second MC symptom) → more common in rectosigmoid CRC
Bowel obstruction

mucosa, biopsy, apple core
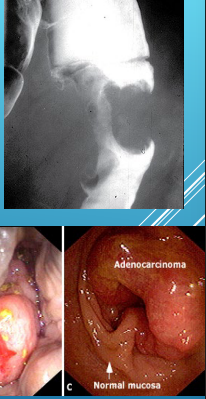
Colorectal Cancer: Diagnosis
-Colonoscopy (preferred)
Endoluminal mass arising from ______
Bleeding may be present
______ must be done to confirm diagnosis
-Barium Enema
_____ ____ lesion
-CT colonography
CT, liver, rectal, lymph
Staging of Colorectal Cancer
-Chest/Abdominopelvic __ w/ contrast
Metastases (20% at presentation)
Most common _____, lungs, peritoneum
-Pelvic MR or Endorectal US (____ cancer)
Tumors arising about 12 cm or less proximal to the anal verge
Determines depth of penetration through rectal wall and presence of perirectal ____ nodes
Stage IV
What stage of colon cancer is this?
-Metastasis to distant organs
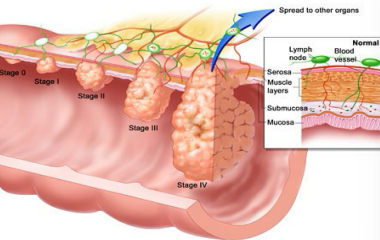
rectal
For each stage of colon cancer, ______ cancer has a worse prognosis
screening, monitor, CRC, elevate
CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen)
-Tumor marker → normal is < 5 mcg/L
-Not used for CRC ___________, low specificity and sensitivity for early disease
-Used to _______ patients with ___ → pretreatment levels compared to treatment and post-treatment levels
-Levels _________ as CRC progresses
surgery, preoperative, III, IV, metastasis
Colorectal Cancer: Treatment
-________ → treatment of choice in those with resectable lesions
Rectal cancer → recommended ______________ chemoradiation with 5-fluorouracil in node positive d/t increased risk of recurrence
-Chemotherapy
Stage I = none recommended
Stage II = may be recommended in pts at high risk for recurrence
Stage ___ and __ = recommended
-Metastasis → isolated hepatic or pulmonary __________ may be resectable
colonoscopy, 1, 3-5
Colorectal Cancer: Follow Up After Surgical Resection for Cure
-Evaluate every 3-6 mo x 2 yrs then every 6 mo for a total of 5 yrs
-____________ at _ yr s/p resection
If no adenomatous polyps can go to every _-_ years
CRC, activity, fiber, NSAID
Colorectal Cancer: Complications and Protective Factors
-Complications
LBO → MC cause is ___
Iron deficiency anemia
Endocarditis → Streptococcus bovis or clostridium septicium
-Protective Factors
Regular physical _______
Diet high in ____ and fruits/vegetables
Possibly ASA or _____ use
inherited, APC, dominant, adenomatous, 15, cancer, colectomy
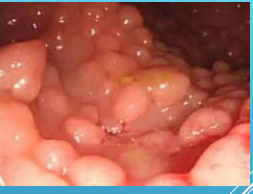
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis: FAP
-__________ condition → 90% have a mutation of the ___ gene, inherited in an autosomal _________ fashion
-Early development of hundreds to thousands of colonic _____________ polyps
Mean age of development is __y/o and _____ at 40y/o
CRC inevitable without proctocolectomy
-Recommended complete proctocolectomy or _______ with ileoanal anastomosis before 20 y/o
dominant, MLH1, MSH2, CRC, colonoscopy, gastric, ovarian, Bethesda Criteria
Lynch Syndrome
-Autosomal __________ inherited condition → 90% have a mutation in the ____ and ____ gene
-Significant increased risk of ___ as well as other cancers of the abdomen/pelvis
-Pts only develop a few adenomas, rapid progression to cancer over 1-2 yrs
-Those with positive genetic testing need ___________ every 1-2 yrs
Begin at 25 y/o or 5 yrs before the youngest affected FDR was dx
Colectomy w/ileorectal anastomosis if cancer was found
-Screen for ______ cancer every 2-3 years, begin at age 30-35
-Screen women for endometrial/______ cancer
Begin at age 30-35
Prophylactic hysterectomy/oophorectomy at age 40
-__________ ________: if one of these criteria are met, the patient should undergo genetic testing
45, 75, 10, yearly, 3, yearly
Screening for Colorectal Cancer (Average Risk)
-Routine screening recommended for everyone starting at age __ and continuing to __
-Colonoscopy every __ yrs (preferred)
-Other Screening Options
Fecal Immunochemical Test = ______
FIT-DNA test = every _ years
Guiac Fecal Occult Blood Test = ______
10, 40
Screening for Colorectal Cancer (High Risk): Family History in FDR
-Start screening __ yrs before the FDRs dx or by age __, whichever is earlier
45, 30-40, 25, 10-12, 8-10
Screening for Colorectal Cancer (High Risk)
-African American patient → colonoscopy starting at age __
-Prior abdominal/pelvic radiation → colonoscopy between __-__ y/o then every 5-10 yrs
-Fhx of Lynch Syndrome → colonoscopy starting at age __
-FAP → flexible sigmoidoscopy starting at __-__ y/o yearly, recommend colonoscopy
-Hx of IBD → colonoscopy _-__ years afte rsx onset then every 1-2 yrs