Volatile Oil
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
195 Terms
True about volatile oils except:
a. Do not become rancid, but resinified instead
b. Can be isolated by distillation
c. No permanent grease on paper
d. Cannot be saponified with alkali
e. None
e. None
Volatile oils that are heavier than water.
a. Sassafras
b. Clove oil
c. Cinnamon oil
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
Basic units of volatile oil.
a. Sterol
b. Fatty acid
c. Terpenes
d. Amino acid
c. Terpenes
True about fixed oil except:
a. Cannot be distilled and leave permanent grease on paper
b. Undergo saponification with alkali
c. Becomes rancid upon oxidation
d. Glyceryl ester of fatty acid
e. Has bland odor and is generally lighter than water
f. None
f. None
Glyceryl ester of fatty acid.
a. Waxes
b. Fixed oil
c. Volatile oil
d. Tannins
b. Fixed oil
Fixed oil saponification with NaOH.
a. Hard soap
b. Soft soap
a. Hard soap
Fixed oil saponification with KOH.
a. Hard soap
b. Soft soap
b. Soft soap
Characteristics of volatile oils except:
a. They are odoriferous principles of plants and animals; also known as essential oil, essences, ethereals
b. Immiscible with water
c. They are optically active
d. Easily evaporate
e. None
e. None
Form of natural camphor.
a. Dextrorotatory
b. Levorotatory
a. Dextrorotatory
Form of synthetic camphor
a. Dextrorotatory
b. Levorotatory
b. Levorotatory
Has glandular hairs or trichomes.
a. Lamiaceae
b. Piperaceae
c. Apiaceae
d. Pinaceae
a. Lamiaceae
Has modified parenchymal cells.
a. Lamiaceae
b. Piperaceae
c. Apiaceae
d. Pinaceae
b. Piperaceae
Dillweed. Oil tubers or vittae.
a. Lamiaceae
b. Piperaceae
c. Apiaceae
d. Pinaceae
c. Apiaceae
Has lysigenous or schizogenous passages.
a. Lamiaceae
b. Piperaceae
c. Apiaceae
d. Pinaceae
d. Pinaceae
Has lysigenous or schizogenous passages.
a. Lamiaceae
b. Piperaceae
c. Apiaceae
d. Rutaceae
d. Rutaceae
General method for obtaining citrus oils by rolling the fruit over through line by sharp projections, which are long enough to puncture oil glands in the epidermis.
a. Enfleurage
b. Ecuelle method
c. Distillation
d. Extraction
b. Ecuelle method
Performed using Clevenger apparatus.
a. Distillation
b. Enzymatic actions
c. Expression
d. Extraction
a. Distillation
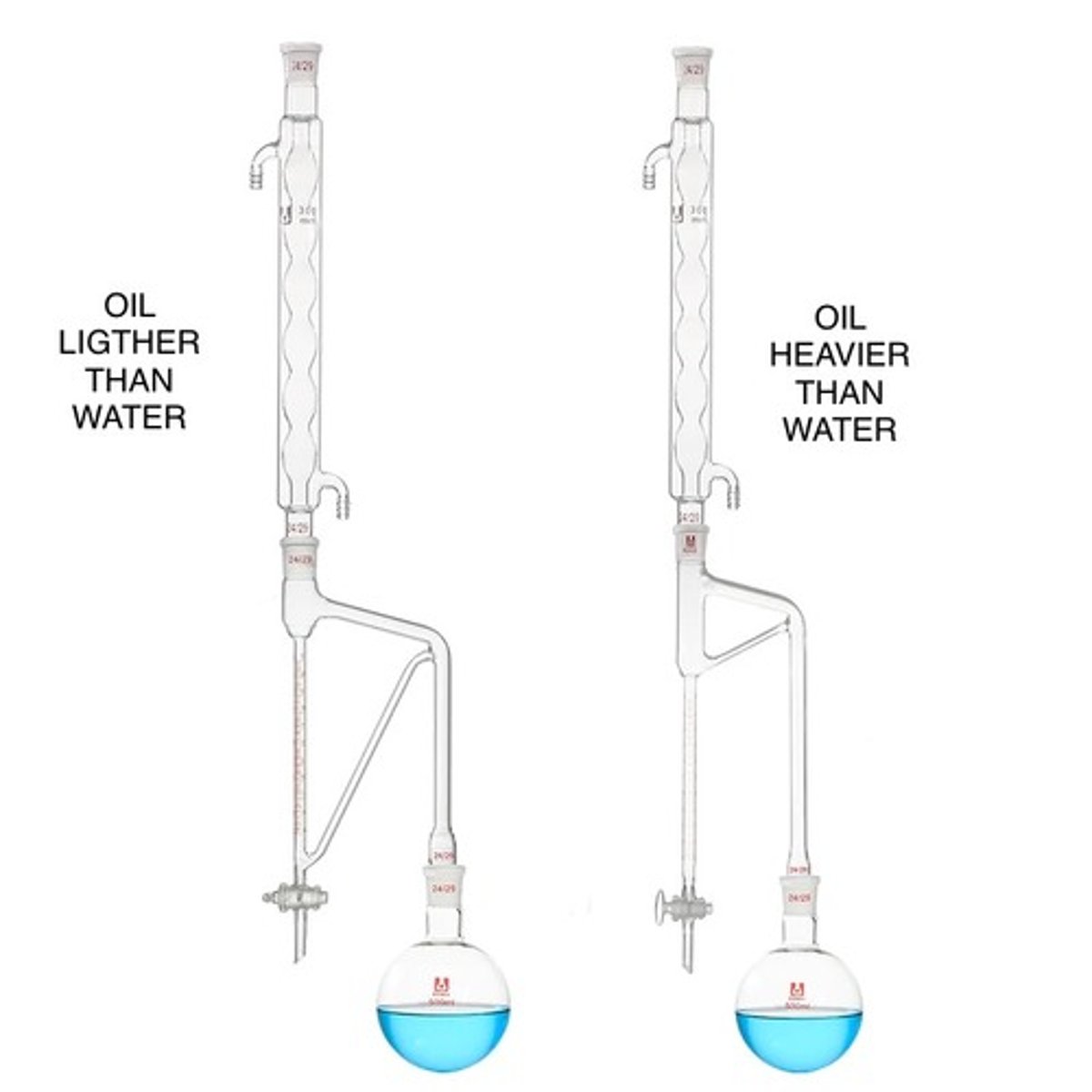
For those not injured by boiling, dried form.
a. Water distillation
b. Water and steam distillation
c. Steam distillation
d. Destructive distillation
a. Water distillation
Can be extracted by water distillation.
a. Turpentine oil
b. Clove oil
c. Cinnamon oil
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
a. Turpentine oil
Distillation for those injured by boiling.
a. Water distillation
b. Water and steam distillation
c. Steam distillation
d. Destructive distillation
b. Water and steam distillation
Extracted through water and steam distillation.
a. Turpentine oil
b. Clove oil
c. Cinnamon oil
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
e. b and c
Clove oil
Cinnamon oil
Extraction for fresh plant drugs.
a. Water distillation
b. Water and steam distillation
c. Steam distillation
d. Destructive distillation
c. Steam distillation
Extracted with steam distillation.
a. Peppermint
b. Spearmint
c. Empyreumatic oils
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
Peppermint oil
Spearmint oil
Distillation through heat without the access of air.
a. Water distillation
b. Water and steam distillation
c. Steam distillation
d. Destructive distillation
d. Destructive distillation
Extracted through destructive distillation.
a. Peppermint
b. Spearmint
c. Empyreumatic oils
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
c. Empyreumatic oils
Empyreumatic oils are from wood and resins of family:
a. Pinaceae
b. Cupressaceae
c. Rosaceae
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
Pinaceae
Cupressaceae
Empyreumatic oil.
a Oil of cade
b. Oil of tar
c. Turpentine oil
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
Oil of cade
Oil of tar
Mustard oil is extrated thrrough
a. Distillation
b. Enzymatic actions
c. Expression
d. Extraction
b. Enzymatic actions
Ecuelle and piquer and enfleurage are examples of which type of extraction?
a. Distillation
b. Enzymatic actions
c. Expression
d. Extraction
c. Expression
Rolling the fruit over a trough lined with sharp projections.
a. Ecuelle and Piquer
b. Enfleurage
a. Ecuelle and Piquer
Extraction for citrus oils.
a. Ecuelle and Piquer
b. Enfleurage
a. Ecuelle
Expression with the use of cold fat; formerly used in the perfume industry.
a. Ecuelle
b. Enfleurage
b. Enfleurage
Flower petals or small plant part on a fatty pomade is extracted by EtOH. Only works for tiny pieces of crude drug.
a. Ecuelle
b. Enfleurage
b. Enfleurage
Uses solvent systems based on volatile solvents; uses lower temperature.
a. Distillation
b. Enzymatic actions
c. Expression
d. Extraction
d. Extraction
Best extraction method for menthol from Japanese peppermint.
a. Distillation
b. Enzymatic actions
c. Expression
d. Extraction
e. Refrigeration
e. Refrigeration
Common solvent/s for extraction of volatile oils.
a. Petroleum ether
b. Benzene
c. Both
d. None of these
c. Both
Petroleum ether
Benzene
Classes of volatile oil can be
a. Terpene derivative
b. Aromatic compound
c. Sugar derivative
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
Terpene derivative
Aromatic compound
Formed via acetate-mevalonic acid pathway.
a. Terpene derivatives
b. Aromatic compounds
a. Terpene derivatives
Formed via shikimic acid-phenylpropanoid route.
a. Terpene derivatives
b. Aromatic compounds
b. Aromatic compounds
Medicinal uses of volatile oils except:
a. Carminative
b. Antiseptic
c. Counterirritant (methyl salicylate)
d. Antipruritic (camphor)
e None
e. None
Counterirritant such as methyl salicylate
Antipruritic such as camphor
Antipruritic volatile compound.
a. Camphor
b. Methyl salicylate
a. Camphor
Counterirritant volatile compound.
a. Camphor
b. Methyl salicylate
b. Methyl salicylate
Building block of terpenes.
a. Isoprene
b. Monoprene
c. Uniprene
d. Alloprene
a. Isoprene
Class of terpene mostly found in volatile oil.
a. Hemiterpene
b. Monoterpene
c. Diterpene
d. Sesquiterpene
e. Diterpene
b. Monoterpene
1 isoprene units is equal to how many carbons?
a. 3 carbons
b. 5 carbons
c. 10 carbons
d. 15 carbons
b. 5 carbons
1 isoprene, 5C
a. Hemiterpene
b. Monoterpene
c. Diterpene
d. Sesquiterpene
e. Diterpene
a. Hemiterpene
2 isoprene, 10C
a. Hemiterpene
b. Monoterpene
c. Diterpene
d. Sesquiterpene
e. Diterpene
b. Monoterpene
Limonene
a. Hemiterpene
b. Monoterpene
c. Diterpene
d. Sesquiterpene
e. Diterpene
b. Monoterpene
3 isoprene; 15C
a. Hemiterpene
b. Monoterpene
c. Diterpene
d. Sesquiterpene
e. Diterpene
d. Sesquiterpene
Abscisic acid
a. Hemiterpene
b. Monoterpene
c. Diterpene
d. Sesquiterpene
e. Diterpene
d. Sesquiterpene
4 isoprenes, 20C
a. Hemiterpene
b. Monoterpene
c. Diterpene
d. Sesquiterpene
e. Diterpene
c. Diterpene
Gibberellin
a. Hemiterpene
b. Monoterpene
c. Diterpene
d. Sesquiterpene
e. Diterpene
c. Diterpene
5 isoprenes, 25C.
a. Sesquiterpene
b. Diterpene
c. Sesterterpene
d. Triterpene
e. Tetrapene
c. Sesterterpene
6 isoprenes, 30C
a. Sesquiterpene
b. Diterpene
c. Sesterterpene
d. Triterpene
e. Tetrapene
d. Triterpene
Brassinosteroids
a. Sesquiterpene
b. Diterpene
c. Sesterterpene
d. Triterpene
e. Tetrapene
d. Triterpene
8 isoprenes, 40C
a. Sesquiterpene
b. Diterpene
c. Sesterterpene
d. Triterpene
e. Tetrapene
e. Tetrapene
Carotenoid
a. Sesquiterpene
b. Diterpene
c. Sesterterpene
d. Triterpene
e. Tetrapene
e. Tetrapene
C-10 precursor of the terpenes and is believed to play a key role in the formation of monoterpenes.
a. Geranyl pyrophosphate
b. Isopentyl pyrophosphate
c. Dimethylally pyrophosphate
d. b and c
e. All
a. Geranyl pyrophosphate
Synthetically active isoprene units.
a. Geranyl pyrophosphate
b. Isopentyl pyrophosphate
c. Dimethylally pyrophosphate
d. b and c
e. All
d. b and c
Isopentyl pyrophosphate
Dimethylally pyrophosphate
Primary precursor of volatile oil with aromatic compounds.
a. Cinnamic acid
b. p-hydroxycinnamic acid
c. Both
d. None of these
c. Both
Cinnamic acid
p-hydroxycinnamic acid
Kinds of volatile oil
Hydrocarbons
Alcohols
Aldehydes
Ketones
Phenols
Phenolic esters
Oxides
Esters
a. True
b. False
a. True
True about stearoptene except:
a. Solid portion of HC
b. Oxidized HC
c. Present in smaller quantities
d. Imparts the characteristic odor
e. None
e. None
Water soluble portion of volatile oil.
a. Stearoptene
b. Eleoptene
c. Terpinol
d. Limonene
a. Stearoptene
Liquid hydrocarbon portion of volatile oil.
a. Stearoptene
b. Eleoptene
c. Terpinol
d. Limonene
b. Eleoptene
Stearoptene except:
a. Menthol
b. Anethol
c. Thymol
d. Camphor
e. Methyl salicylate
f. None
f. None
The only liquid stearoptene:
a. Menthol
b. Anethol
c. Thymol
d. Camphor
e. Methyl salicylate
e. Methyl salicylate
Eleoptene
a. Encalyptol
b. Eugenol
c. Thymol
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
Encalyptol
Eugenol
Product formed by the action of nitric acid on rectified turpentine oil in the presence of alcohol.
a. Stearoptene
b. Eleoptene
c. Terpinol
d. Limonene
c. Terpinol
Aka terpin hydrate.
a. Stearoptene
b. Eleoptene
c. Terpinol
d. Limonene
c. Terpinol
Most volatile component of perfume thus leave the skin readily.
a. Top notes
b. Middle notes
c. Base notes
a. Top notes
Intermediate volatility and intermediate tenacity.
a. Top notes
b. Middle notes
c. Base notes
b. Middle notes
The lowest volatility
High tenacity
Fixatives
a. Top notes
b. Middle notes
c. Base notes
c. Base notes
Lemon oil
Lavender oil
Anise oil
a. Top notes
b. Middle notes
c. Base notes
a. Top notes
Thyme oil
Rose oil
Neroli oil
a. Top notes
b. Middle notes
c. Base notes
b. Middle notes
Vanilla
a. Top notes
b. Middle notes
c. Base notes
c. Base notes
Fixatives:
a. Musk
b. Civet
c. Ambergris
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Dried secretion from the preputial follicles of the male musk deer of Asia, Moschus spp which contains muskane.
a. Musk
b. Civet
c. Ambergris
a. Musk
From secretion of civet cat, Paradoxurus hermaproditus which contain civeton.
a. Musk
b. Civet
c. Ambergris
b. Civet
Most valuable material which contains ambrein.
a. Musk
b. Civet
c. Ambergris
c. Ambergris
Pathologic product formed in stomach of sperm whale when it feeds on squid or cuttlefish.
a. Musk
b. Civet
c. Ambergris
c. Ambergris
HYDROCARBON VOLATILE OILS:
I. Turpentine oil
II. Rectified turpentine oil
III. Terpin hydrate or Terpinol
a. I, II, III
b. I, II
c. II, III
d. I, III
a. I, II, III
Spirit of turpentine
From Pinus palustris
Disinfectant, deodorant, counterirritant in Vicks Vaporub
a. Turpentine oil
b. Rectified turpentine oil
c. Terpin hydrate or Terpinol
a. Turpentine oil
Distilled from an aqueous solution of NaOH
Expectorant for cough
a. Turpentine oil
b. Rectified turpentine oil
c. Terpin hydrate or Terpinol
b. Rectified turpentine oil
Used for rectifying by distillation of rectified turpentine oil.
a. KOH
b. MgOH
c. NaOH
d. CaOH
c. NaOH
cis-p-menthane-1,8-diol hydrate
Formed by action of nitric acid on rectified turpentine oil in the presence of alcohol
Used as expectorant
a. Turpentine oil
b. Rectified turpentine oil
c. Terpin hydrate or Terpinol
c. Terpin hydrate or Terpinol
Turpentine oil + NaOH.
a. Turpentine oil
b. Rectified turpentine oil
c. Terpin hydrate or Terpinol
b. Rectified turpentine oil
Turpentine oil + HNO3.
a. Turpentine oil
b. Rectified turpentine oil
c. Terpin hydrate or Terpinol
c. Terpin hydrate or Terpinol
Cinnamomum lourerri
a. Saigon cinnamon
b. Cassia cinnamon
c. Ceylon cinnamon
a. Saigon cinnamon
Cinnamomum cassia
a. Saigon cinnamon
b. Cassia cinnamon
c. Ceylon cinnamon
b. Cassia cinnamon
Cinnamomum zeylanicum
Most marketed
a. Saigon cinnamon
b. Cassia cinnamon
c. Ceylon cinnamon
c. Ceylon cinnamon
Disagreeable odor from volatile oil.
a. Resin
b. Terebinthinate
c. Phlobaphene
d. Phloroglucinol
b. Terebinthinate
Cassia, ceylon, and saigon cinnamon are used as carminatives and flavorants.
a. True
b. False
a. True
ALDEHYDE VOLATILE OILS:
I. Lemon peel
II. Lemon balm
III. Orange oil
IV. Citronella oil
V. Hamamelis water
a. I, II, III, IV, V
b. I, II, III, IV
c. II, III, IV, V
d. I, II, III
e. III, IV, V
a. I, II, III, IV, V
Citrus limon
Contain limonene and citral
a. Lemon peel
b. Lemon balm
c. Orange oil
d. Citronella oil
e. Hamamelis water
a. Lemon peel
Melissa officinalis
Contain citral
a. Lemon peel
b. Lemon balm
c. Orange oil
d. Citronella oil
e. Hamamelis water
b. Lemon balm
Citrus aurantium
Contain decanal, limonene
a. Lemon peel
b. Lemon balm
c. Orange oil
d. Citronella oil
e. Hamamelis water
c. Orange oil
Cymbopogon winterianus, Cymbopogon nardus
Contain citronellal
a. Lemon peel
b. Lemon balm
c. Orange oil
d. Citronella oil
e. Hamamelis water
d. Citronella oil
Hamamelis virginia
Astringent in the OTC hemorrhoid preparations
a. Lemon peel
b. Lemon balm
c. Orange oil
d. Citronella oil
e. Hamamelis water
e. Hamamelis water
PHENOL VOLATILE OILS:
I. Eugenol
II. Thymol
III. Carvacrol
a. I, II, III
b. I, II
c. II, III
d. I, III
a. I, II, III
Volatile oil in Eugenia caryophyllus
Used as carminative, toothache drops, dental analgesics
a. Eugenol
b. Thymol
c. Carvacrol
a. Eugenol