Ch9: Pt1 DNA structure and analysis
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part I: How did people figure out that DNA is the molecule of heredity?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Search for the material of heredity
what was before mendel
define pangenes
-Before Mendel: Some substance passed from generation to generation contains information necessary for heredity of traits
-Pangenes: substances produced in all body parts, and transferred to germ-line cells
what are the necessary qualities of genetic substance
1.Must contain information regarding traits
2. Information must be expressable by the cell.
3. Must replicate accurately
4. Must be subject to occasional change
the search for genetic material
what did Friedrich Miescher discover in 1869
Discovers DNA in bandage pus
-Contains C, H, O, N and P: Not a protein
-Appears in nucleus of all cells: named nuclein
the search for genetic material
what happens in early 1900’s
-Early 1900’s: Cytological studies show that chromosomes are passed from generation to generation.
-Chromosomes contain both protein and nucleic acid
Proteins: 20 amino acids, diversity of side chains, and chemical structures
what are the 9 important amino acid diversity
-Glycine
-Alanin
-Valine
-Leucine
-Isoleucine
-Proline
-Methionine
-Phenylalanine
-Tryptophan
DNA: 4 nucleotides, Two chemical classes, (Purines and Pyrimidines)
what are the 6 nucleotide diversity
-adenine
-purines
-guanine
-cytosine
-pyrimidines
-thymine
If you were to design a new language (information
carrying system), which would be better?
DNA or Proteins
DNA
At the outset of the 1920’s scientists were betting that
proteins carried genetic material.
what did frederick griffith show
Frederick Griffith (1928): Demonstrated that traits of
bacteria could change by exposure to dead bacteria.
-Died in his lab during a London air-raid in WWII
Define IIS (smooth) and IIR (rough) in Streptococcus pneumoniae that Frederick Griffith saw
what differs between type II and type III
Streptococcus pneumoniae:
IIIS (smooth): has polysaccharide coat, virulent
IIR (rough): lacks polysaccharide coat, non-virulent, mutant of IIS
Polysaccharide structure differs between type II and type III.
Describe the mice experiment Griffith conducted with Type IIR and Type IIIS of Streptococcus pneumoniae
Type IIR (living, nonvirulent) is injected into mice: Mice survives, no bacteria recovered
Bacteria w/ polysaccharide capsule. Type IIIS (living, virulent) is injected into mice: Mice dies, type IIIS viruent bacteria was recovered
Head applied to Type IIIS (heat killed, nonvirulent) is injected into mice: Mice survives, no bacteria recovered
Type IIR (living, nonvirulent) AND Type IIIS with applied heat (heat killed, nonvirulent) is injected into mice: Mice dies, type IIIS virulent bacteria is recovered
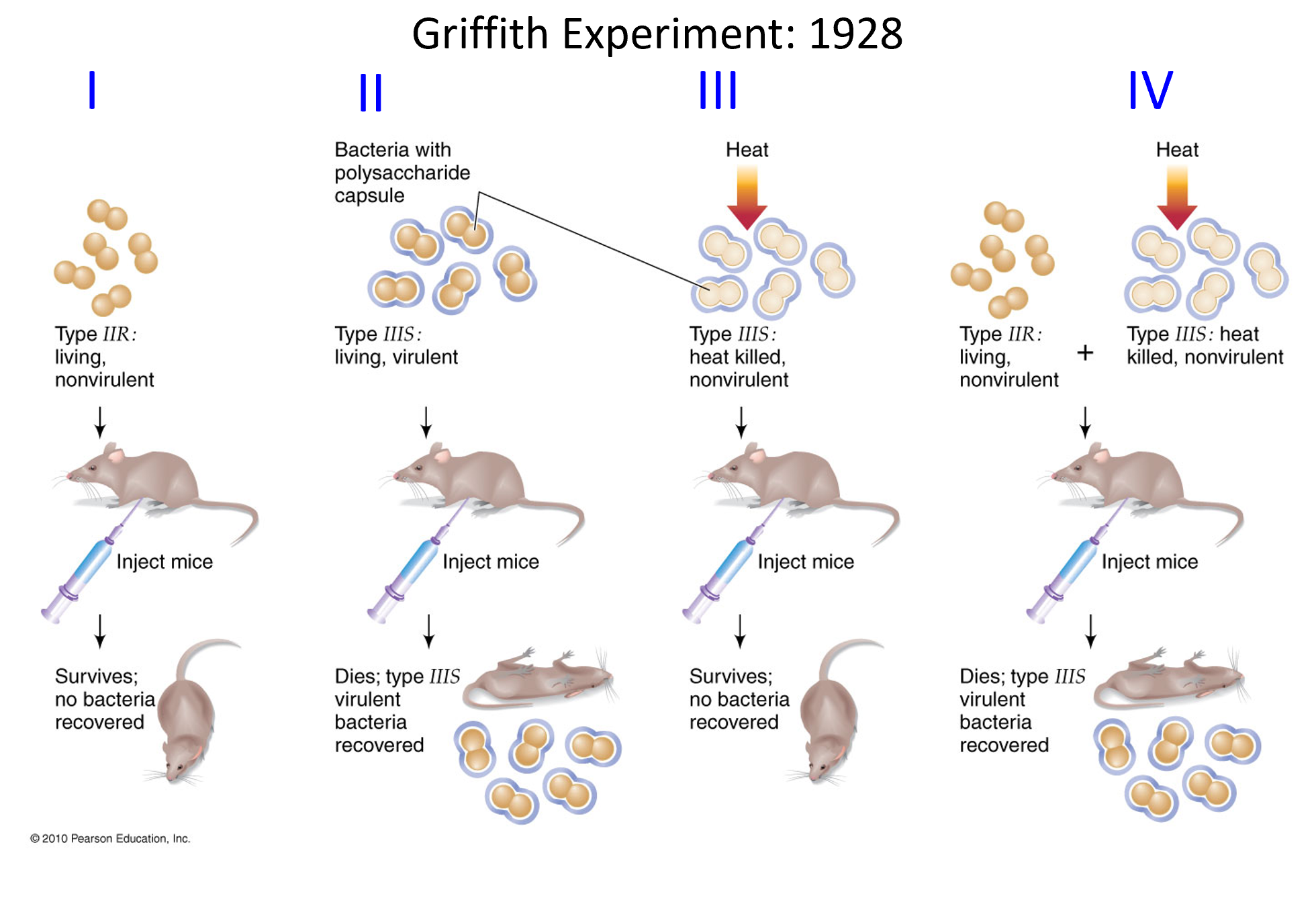
What was seen in Griffith experiment, what is it called
The killed IIIS strain passes something to the IIR strain that confers virulence AND type III coat.
transforming principle
Avery, McCary and MacLeod question:
→What material was passed from transforming to transformed bacteria
Polysaccharide wall? Protein? DNA? RNA?
what was the steps
1. Lysed IIIS bacteria, and removed cellular debris by centrifugation
2. Treat IIR with the lysate → transformation
3. Remove products selectively from the lysate and see if transforming principal remains.
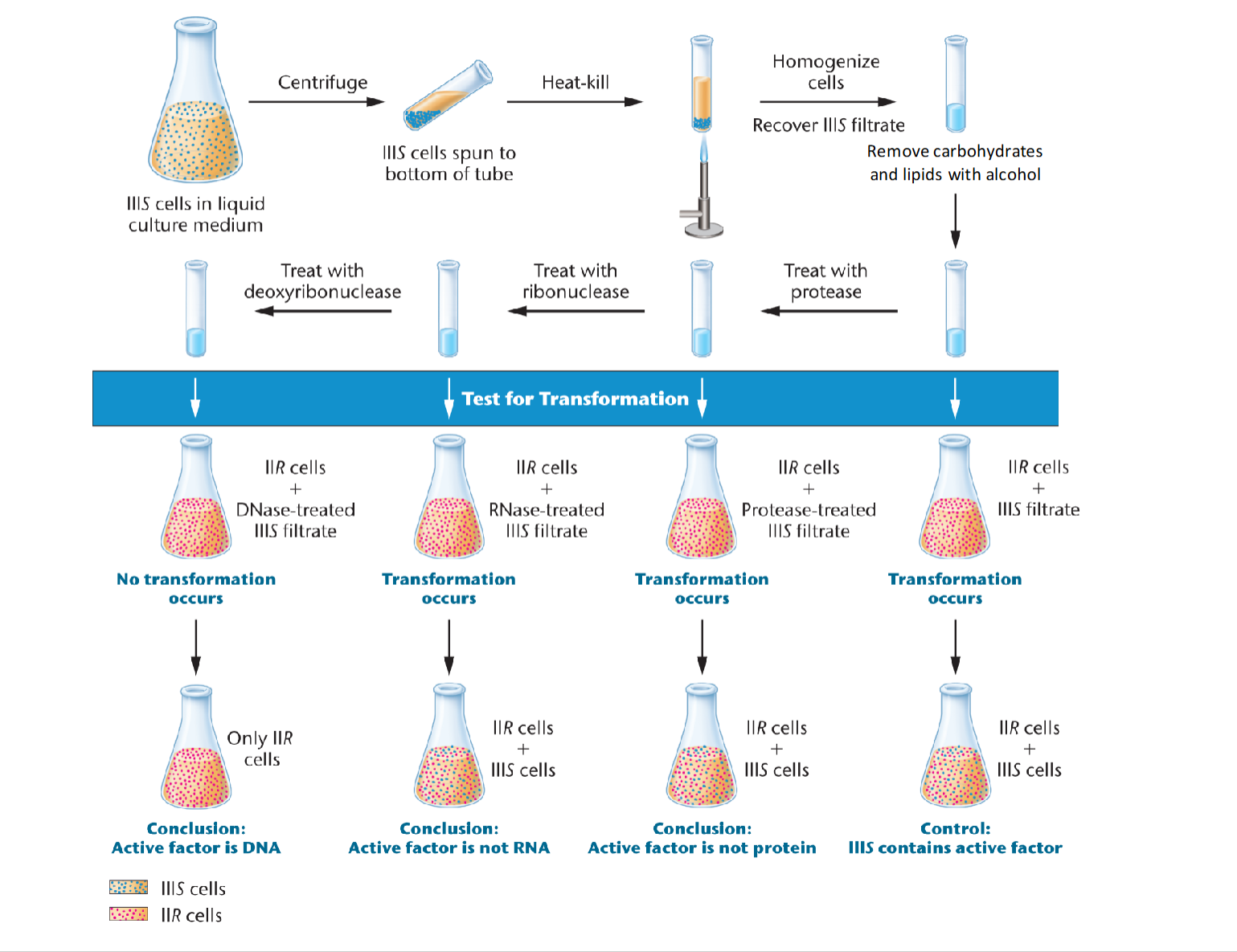
Avery, McCary and MacLeod experiment to find what material was passed from transforming to transformed bacteria
what was it?
Active factor is DNA
Hershey and Martha Chase question:
DNA is transforming factor but is it the molecule of heredity?
what did they know DNA and Protein contained, what were their differences
T2 bacteriophage*: Known to consist only of DNA and protein
-DNA contains phosphorus not found in protein
-Protein contains sulfur, not found in DNA
Hershey and Martha Chase Experiment steps
what wins?
1. When grown with 32P, phages pass radiolabel to host DNA. Radiolabel detected in further generations of phages.
2. When grown with 35S, phages incorporate radiolabel into head. Radiolabel not detected in hosts or future generations.
DNA wins it!

Without overlooking RNA
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes use DNA as molecule of heredity, what is different with RNA
what do some viruses use as molecule of heredity
-All known prokaryotes and eukaryotes use DNA as the molecule of heredity
→Higher chemical stability than RNA
→Lower mutation rate (In RNA, cytosine residues may be converted to uracil)
-Some viruses use RNA as the molecule of heredity.
TMV (tobacco mosaic virus): RNA chromosome surrounded
by a protein coat
what did Gierer and Schramm (1956) see with tobacco
-Tobacco treated with purified TMV RNA develop lesions
-Tobacco treated with TMV proteins do not develop lesions
What is the structure of DNA
what was known in 1950
-In 1950, very little was known about the chemical structure of DNA: It was composed of nucleobases + deoxyribose.
What did Erwin Chargaff discover in 1950 (Chargaff’s rule)
-Chargaff hydrolyzed DNA (broke it into nucleotides) and examined the relative quantities of the 4 nucleotides
A:T= 1
C:G= 1
what did Linus pauling see
-Determined the structure of the peptide a-helix and was working to unravel the
structure of DNA.
What happened when Watson and Crick met Chargaff in 1952 at a conference
-immediate insight into structure of DNA
-hypothesize that A shares chemical bond with T, and C with G
History on “Where are the sugar molecules?” question
who worked on it originally, who found out the two strands/what that meant
Franklin makes x-ray crystallography, which Wilkin shares a secret copy to Watson
-Watson discerns two strands, nucleotides on the inside connected by outer backbones of sugar
Putting all the info together, who got a nobel prize?
Watson Crick and Wilkins