Population Growth/Evolution/Microscopes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
POPULATION GROWTH
What is a density-dependent limiting factor?
A factor that limits population growth more strongly as population density increases.
ex) Disease spreads faster in crowded populations, reducing growth.
POPULATION GROWTH
What is a density-independent limiting factor?
Density‑Independent Limiting Factor → A factor that limits population growth equally at all densities.
Ex) A wildfire reduces population size whether there are 100 or 10,000 individuals.
POPULATION GROWTH
What are some limiting factors to population growth?
Food, Clean water, space, limited resources
POPULATION GROWTH
What instrument did we use to measure a proxy for bacterial population size in lab? What does it measure?
We used a spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance of light in a particular wavelength (600nm yellow-orange light). More light absorbed indicated more organisms in the solution.
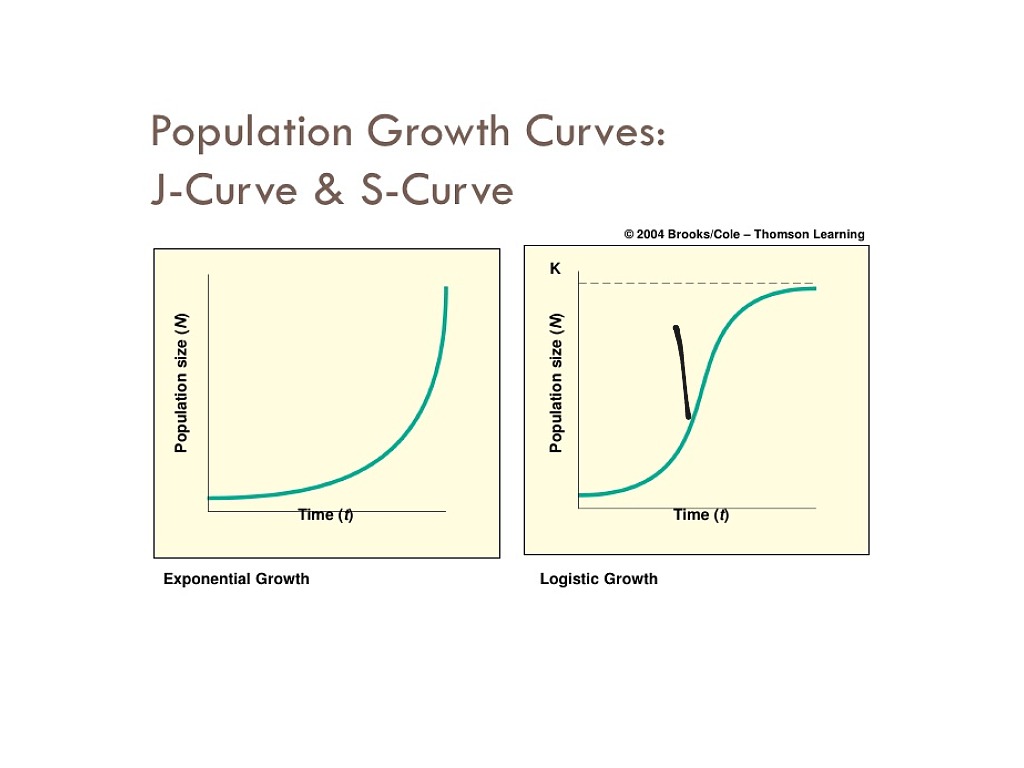
POPULATION GROWTH
Know exponential growth (J-shaped curve), logistical growth (S-shaped curve), and parts of the growth curve: lag phase, exponential phase, carrying capacity, equilibrium.
J curve: Exponential growth, beginning is the lag phase, exponential phase is the steep incline, doesn’t have equilibrium or carrying capacity.
S curve: Plateau growth, beginning is lagging phase, exponential phase is the steep incline, carrying capacity is the number it plateaus on, equilibrium is the flat plateau phase.
EVOLUTION
Define: Fossils/fossilization
Preserved remains, impressions, or traces of organisms from the past, typically found in sedimentary rock.
EVOLUTION
Define: Vestigial structures
Body parts that have lost most or all of their original function through evolution but remain present in an organism.
EVOLUTION
Define: Homologous structures
Body parts in different species that share a common evolutionary origin, even if they serve different functions today
EVOLUTION
Define: Analogous structures
Body parts in different species that serve similar functions but do not share a common evolutionary origin.
EVOLUTION
Define: Protein clock theory
Proposes that mutations in proteins accumulate at a relatively constant rate over time, allowing scientists to estimate evolutionary relationships and the time since two species diverged.
EVOLUTION
Define: Artificial selection
Intentional breeding of organisms by humans to produce desired traits.
EVOLUTION
Define: Natural selection
Process by which organisms with traits better suited to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully, passing those traits to future generations.
EVOLUTION
Define: Microevolution
Small-scale evolutionary changes within a population over time, often caused by mutation, natural selection, gene flow, or genetic drift
EVOLUTION
Define: Macroevolution
Large‑scale evolutionary changes that occur over long periods of time, leading to the formation of new species or major groups.
EVOLUTION
Define: Punctuated equilibrium
Evolutionary model where species remain stable for long periods but experience rapid bursts of change during short events, often linked to environmental shifts.
EVOLUTION
Define: Genetic drift
Random change in allele frequencies in a population, especially significant in small populations.
EVOLUTION
Define: Founder effects
Small group of individuals establishes a new population, carrying only a fraction of the genetic variation of the original population.
EVOLUTION
Define: Bottleneck effects
Happens when a population size is drastically reduced, leaving behind limited genetic diversity.
EVOLUTION
Define: Migration effects.
Occurs when individuals move between populations, introducing new alleles and increasing genetic diversity.
MICROSCOPES
You should know all the conditions your microscope should be in when put away!
Light off, cord tucked and tied, lens to the lowest setting, stage to the lowest height, magnification to the original height, iris half way.
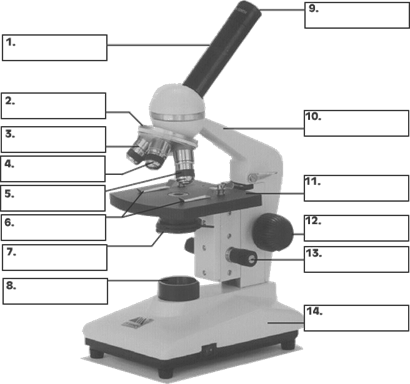
MICROSCOPES
Know the parts (names & functions) of the compound and dissecting microscopes and how to calculate their total magnification.
1/9 - Ocular Lense/eyepiece
2 - Nose Piece
3 - Scanning power objective Lense
4 - Low power Objective Lense
5 - High power Objective Lense
6 - Stage clips
7 - Iris
8 - light source
10 - Neck
11 - Stage
12 - Coarse adjustment
13 - Fine adjustment
14 - Base
MICROSCOPES
What are the proper procedures for examining a specimen in the microscope?
Have the objective Lense to scanning power, slip the slide into open stage clips before closing clips. raise stage as high until the specimen is in focus, use course adjusters or fine adjusters. As you go up you might alter the dilation of the iris or the light source in order to see the specimen.