Unit 9: Meiosis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
purpose of cell cycle
cell division: cells divide to:
reproduce (unicellular), grow (multicellular), repair/replace old/dead or damanged cells OR inc genetic diversity → product of meiosis is different from OG cell and eachother
asexual vs sexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction: genetically identical offspring, single parent, no sperm or egg, only uses mitosis
Sexual: genetically unique offspring, two parents, fertilization of egg w/ sperm, uses meiosis
binary fission
prokaryotic version of asexual reproduction by division in half (vs mitosis in plants also asexual)
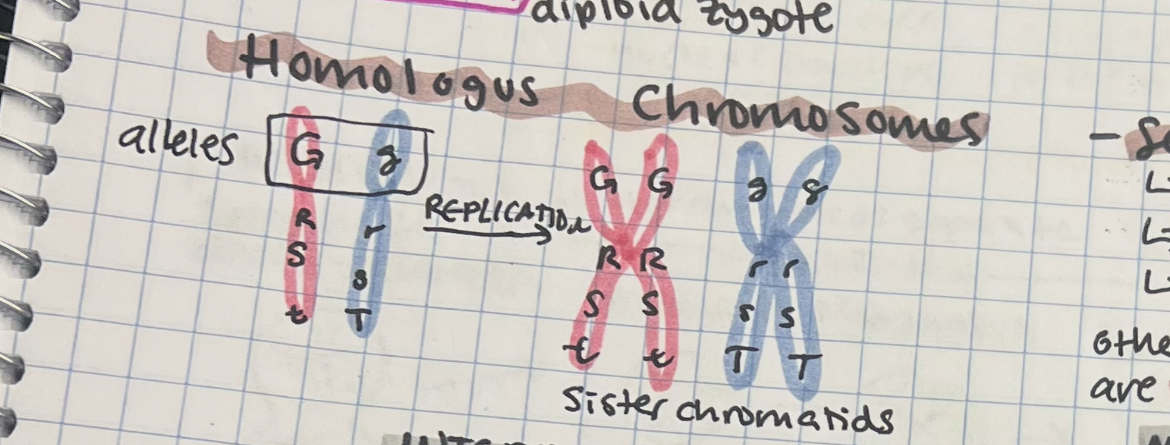
diploid cells
have 2 sets of chromosomes, 1 from each parent, and are body cells (2 versions of one gene/allele)
haploid cells
have a single set of chromosomes, and are sperm and egg cells (1 versions of one gene/allele)
sperm cells come from the
testies and have 23 chromosomes
egg cells come from the
ovaries and have 23 chromosomes
sperm and egg cells are called
gametes
sperm + egg cells make
a zygote
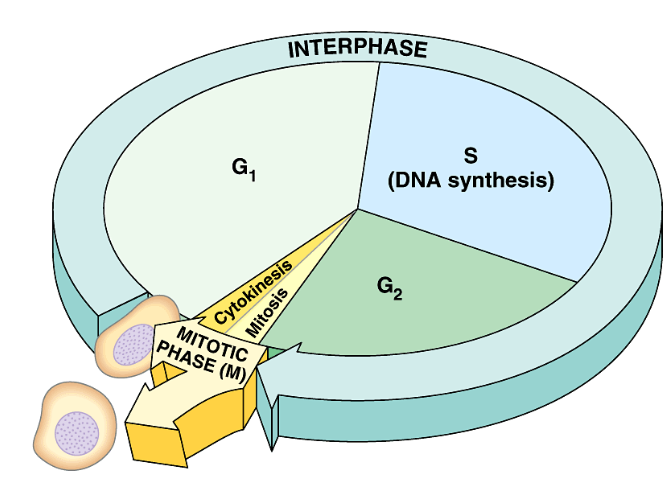
cell cycle for meiosis
cycle of growth (replication) + then division into 4 haploid cells
Interphase: 90%
G1 → growth
S → DNA synthesis (complete copy)
G2 → Growth & preparation for mitosis
Reduction Division of Cell
M I → MEIOSIS I (PMAT)
M II → MEIOSIS II (PMAT)
Division of Cytoplasm
C → continue cycle or Cytokinesis
Development of the chromosomes thru cell cycle
G1 (growth) → { } X X 46 chromosomes (homologous chromosome pair)
S (DNA synthesis) → X X X X “46” chromosomes (92 chromatids) (duplicated and linked as sister chromatids)
G2 (growth + prep) → review/ adjust chromosomes for errors
M (meiosis I & II) → division of chromosomes (anaphase) into 4 different haploid cells
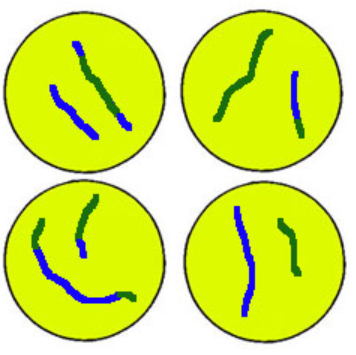
homologous chromosomes vs sister chromatids
G1 = homologous chromosome pairs from parents (not identical
S = sister chromatids are identical duplicated from 1 chromosome
Meiosis
division of nuclear material to produce gametes
5 major phases (PPMAT)
Prophase I & II
Prometaphase I & II
Metaphase I & II
Anaphase I & II
Telophase I & II
then cytokinesis (division of cytoplasm)
Prophase I
1 - before
DNA begins to condense from chromatin → chromosomes/chromatid and line up with homologous pairs → each pair undergoes crossing (2 homologous chromosomes = tetrad (a group or set of four)
nuclear membrane + nucleolus dissolves
centrioles grow spindle fibers + push centrioles to poles
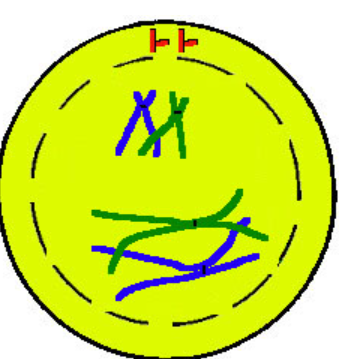
Crossing Over
part of Prophase
homologous chromosomes align in synapsis into tetrads (a group or set of four) (the pairing of homologous chromosomes)
chromosomes cross over
= recombinant chromatids
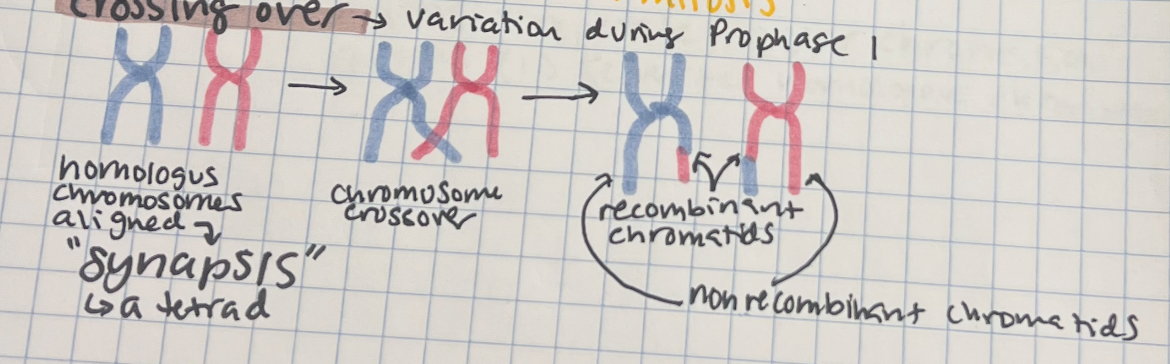
Prometaphase I
2
centriole spindles grow across cell connecting through centromere of each chromosome (forming kinetochore protein)
Metaphase I
M - middle
chromosomes moved/align in middle IN PAIRS due to microtubules/spindle fibers
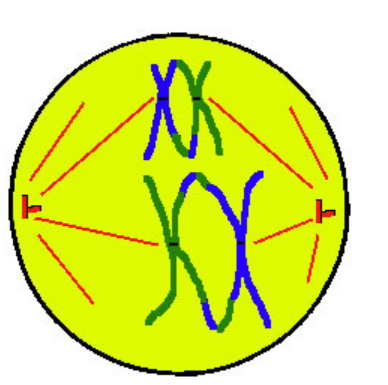
Anaphase I
A - away
spindles shorten pulling apart HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES at centromere/kinetochore (but stay w/ sister chromatids) towards opposite poles
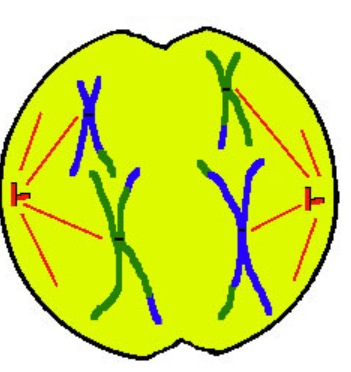
Telophase I
5
once split chromosomes unravel to chromatin
spindles shorten into centrioles
nucleolus + nuclear envelope reforms
(cell wall pinches → cytokinesis)
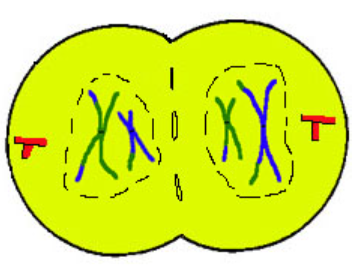
Interphase II
short resting phase for daughter cells
Prophase II
1 - before the same except no crossing
DNA begins to condense from chromatin → chromosomes/chromatid and line up with homologous pairs → (no more crossing)
nuclear membrane + nucleolus dissolves
centrioles grow spindle fibers + push centrioles to poles
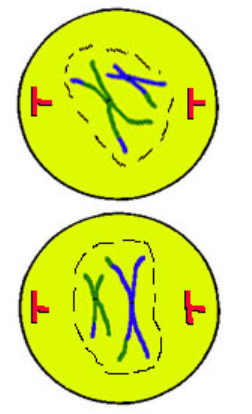
Prometaphase II
same except single file line
centriole spindles grow across cell connecting through centromere of each chromosome (forming kinetochore protein)
Metaphase II
M - middle
chromosomes moved/align in middle SINGLE FILE due to microtubules/spindle fibers
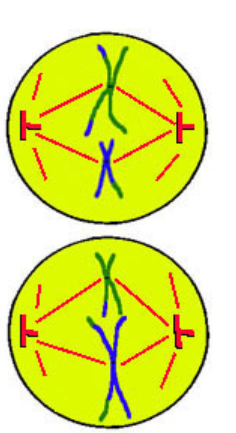
Anaphase II
A - away
spindles shorten pulling apart SISTER CRHOMATIDS at centromere/kinetochore towards opposite poles
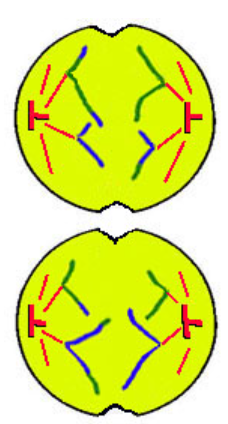
Telophase II
once split chromosomes unravel to chromatin
spindles shorten into centrioles
nucleolus + nuclear envelope reforms
(cell wall pinches → cytokinesis)