Reaction rates
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is collision theory?
Particles in liquids and gas are always moving and colliding with each other. They collide in the right direction. They need to be facing each other the right way. They collide with at least a certain minimum amount of kinetic energy
What is activation energy?
The minimum amount of kinetic energy particles needed to react
True or false Reactions with low activation energies often happen pretty easily but reactions with high activation energies don’t
True
How are particles given extra energy
By heating them
What is a Boltzmann distribution?
A graph of the number of molecules in a substance with different kinetic energies
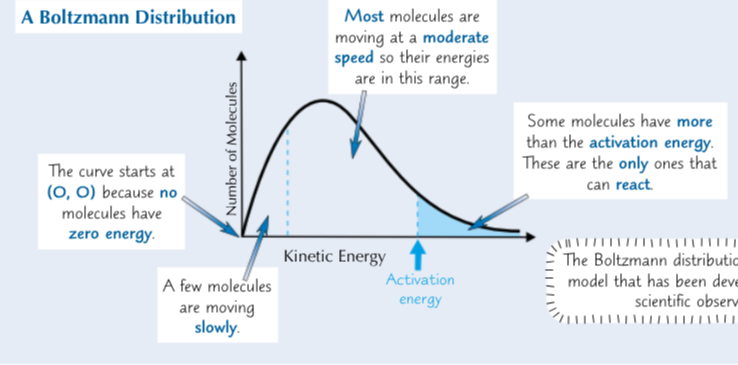
What happens to a reaction/particles if you increase the temperature? What does ti do to the Boltzmann distribution curve?
The particles will on average have more kinetic energy and will move faster. So a greater proportion of molecules will have at least the activation energy and be able to react. This changed the shape of the Boltzmann distribution curve - it pushes it over to the right. Because the molecules have more kinetic energy they’ll collide more often - so the reaction will be faster.

What are factors which affect the rate of reaction?
Temperature
Concentration
Pressure
Catalysts
How does increasing concentration speed up reactions?
If you increase the concentration of reactants in a solution, the particles will be closer together, on average if they’re closer, they’ll collide more frequently. If there are more collisions, they’ll have more chances to react.
How does increasing pressure speed up a reaction?
If any of the reactants are gases, increasing the pressure will increase the rate of reaction. At higher pressures the particles will be closer together, increasing the chance of successful collisions.
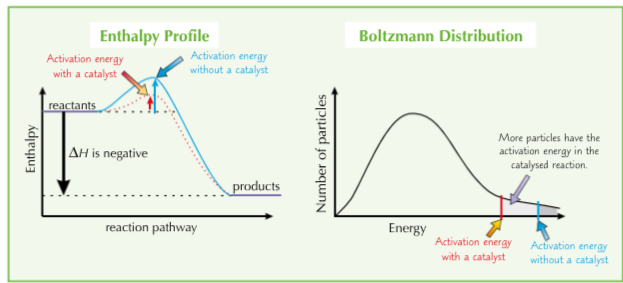
How does a catalyst speed up a reaction?
They lower the activation energy by providing a different way for bonds to be broken and remade. If activation energy’s lower, more particles will have enough energy to react. They provide and alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. The catalyst is chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction.
What does an energy profile diagram and a boltzmann distribution look like with a catalyst
What is a heterogeneous catalyst? What would increasing the surface area of the catalyst do?
One that is in a different phase from the reactants i.e. a different physical state. The reaction happens on the surface of the heterogeneous catalyst. So increasing the surface area of the catalyst increases the number of molecules that can react at the same time, increasing the rate of the reaction.
What is a homogeneous catalyst?
They are in the same physical state as the reactants. Usually they are an aq catalyst for a reaction between 2 aq solutions. They work by forming an intermediate species. The reactants combine with the catalyst to make an intermediate species which then reacts to form the products and reform the catalyst
How is iron used as a catalyst in industry- why is it good?
In ammonia production. If it weren’t for the catalyst the temp would have to be raised loads to make the reaction happen quick enough. This would be very expensive and reduce the amount of ammonia produced.
Why are catalyst benifical?
Using catalysts means that lower temp and pressures can be used. So energy is saved meaning less CO2 is released and fossil fuels reserves are preserved. Catalysts can also reduce waste by allowing a different reaction to be used with a better atom economy.
What made from alloys of platinium, palladium and rhodium reduces the pollution released into the atmosphere by speeding up the reaction 2CO + 2NO →2CO2 + N2
Catalytic converters
What is the rate of reaction?
The rate at which product is formed or a reactant is use up
What is the equation for the rate of reaction?
rate of reaction = amount of reactant used or product formed/time
Complete the method for investigating rate of reaction by investigating change in mass:
When the product is a gas its formation can be measure using a ____ _________
The amount of product formed is the mass __________ from the container
When the reaction starts, you should start a ____ ______, then take mass measurements at regular ________
Make a table with a column for _____ and a column for _____ and fill it in as the reaction goes on
The reaction is ________ when the reading on the mass balance stops _________
This method is very _______ and easy to use but does release ___ into the room which could be dangerous if the gas is ____ or flammable
When the product is a gas its formation can be measure using a mass balance
The amount of product formed is the mass disappearing from the container
When the reaction starts, you should start a stop watch, then take mass measurements at regular intervals
Make a table with a column for time and a column for mass and fill it in as the reaction goes on
The reaction is finished when the reading on the mass balance stops decreasing
This method is very accurate and easy to use but does release gas into the room which could be dangerous if the gas is toxic or flammable

Complete the sentences for measuring the rate of reaction through volume of gas given off
Use a ___ _______ to measure the volume of the ______ formed
The experiment is carries out in the same way as measuring change in mass (on the side) but you measure the _______ of ___ in the syringe rather than the ____ from the balance
This method is accurate but vigorous reactions can blow the plunger out of the syringe
Use a gas syringe to measure the volume of the product formed
The experiment is carries out in the same way as measuring change in mass (on the side) but you measure the volume of gas in the syringe rather than the mass from the balance
This method is accurate but vigorous reactions can blow the plunger out of the syringe

How can you work out the rate of reaction from a graph and a curved graph?
The gradient -change in y over change in x
Draw a tangent for a curved graph
How does dynamic equilibrium occur and where?
As the reactants get used up the forward reaction slows down and as more product is formed the reverse reaction speeds up. After a while the forward reaction will be going at exactly the same rate as the backward reaction so the amount of reactants and product won’t be changing. This is dynamic equilibrium. It can only happen in a closed system.
What happens at equilibrium?
The concentrations of reactants and products stay constant.
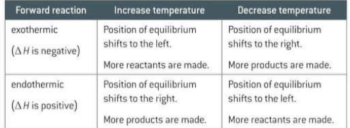
If you change the concentration, pressure or temperature of a reversible reaction what do you alter?
The position of equilibrium
What is Le Chatelier’s principle?
If there is a change in concentration, pressure or temperature the equilibrium will move to help counteract the change
What happens to the equilibrium when the conc is increased for the product and the reactants (separately). What happens if its decreased,
If you increase the concentration of a reactant, the equilibrium ties to get rid of the extra reactant. It does this by making more product so the equilibrium’s shifted to the right. If you increase the concentration of the product, the equilibrium tries to remove the extra product, this makes the reverse reaction go faster so the equilibrium shifts to the left. Decreasing the concentrations has the opposite effect.
What happens to the equilibrium when the pressure is increased and decreased? (only affects gases)
Increasing the pressure shifts the equilibrium to the side with fewer gas molecules, this reduces the pressure. Decreasing the pressure shifts the equilibrium to the side with more gas molecules. This raises the pressure again.

What happens to the equilibrium if temp is increased and decreased?
Increasing the temperature means adding heat. The equilibrium shifts in the endothermic direction to absorb this heat. Decreasing the temperature removes heat. The equilibrium shifts in the exothermic direction to try to replace the heat. If the forward reaction is endothermic, the reverse reaction will be exothermic and vice versa.
True or false catalysts have an effect on the position of equilibrium
False they speed up forward and reverse reactions by the same amount. They can’t increase yield by they do mean equilibrium is reached faster. They do not change the position of the equilibrium
Ethanol is produced via a reversible exothermic reaction between ethene and steam what are the conditons?
60-70 atmospheres temperature of 300°C and a phosphoric (V) acid catalyst
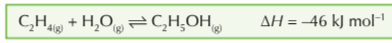
Explain the reasons for the conditions of the reaction between ethene and steam making ethanol (60-70 atmospheres temperature of 300°C and a phosphoric (V) acid catalyst)
Exothermic reaction, lower temp favours the forward reaction, so more ethene and steam are converted to ethanol at lower temp = better yield. But lower temp mean slower rate of reaction so 300°C is a compromise between maximum yield and a faster reaction
Higher pressure favour the forward reaction so a pressure of 60-70 atmospheres is used - high pressure moves the reaction to the side with fewer molecules of gas, increasing the pressure also increases the rate of reaction. High pressures can be expensive to produce, stronger pipes and containers would be needed, in this process it also causes side reactions to occur so 60-70 atmospheres is a compromise between max yield and expense.
What can you work out when you have a homogeneous reaction that has reach dynamic equilibrium?
The equilibrium constant Kc
What does the equilibrium constant Kc do?
Gives you an idea of how far to the left or right the equilibrium is
What is the expression of Kc?
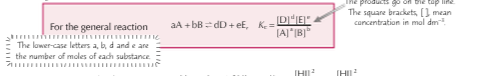
How can you estimate the position of equilibrium using Kc?
The lager the value of Kc the further to the right the position of equilibrium and the more products relevant to the reactants. The smaller the value of Kc is the position of equilibrium will lie further to the left and there will be more reactants relevant to the products.
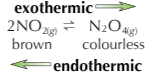
In a closed system the brown gas NO2 exists in equilibrium with the colourless gas N2O4. This reversible reaction can be used to investigate the effect of changing temperature on equilibrium position, How?
Place the 2 sealed tubes containing the equilibrium mixture in water baths, one is a warm water bath and one in a cool water back and observe the colours of the mixtures
The tube in the warm water bath will change to a darker brown colour as the endothermic reaction speeds up to absorb the extra heat, pushing equilibrium to the left.
The tube in the cool water bath will lose colour as the exothermic reaction speeds up to try and replace the lost heat, pushing the equilibrium to the right.
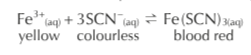
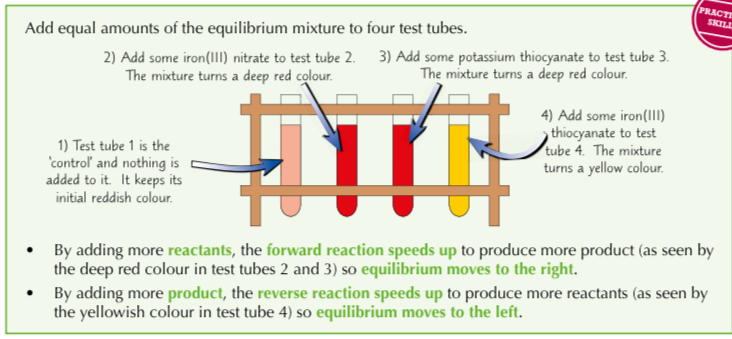
Mixing iron (III) nitrate (yellow) and potassium thicynate (colourless) results in a reversible reaction where the product is iron (III) thiocyanate (blood red). The equilibrium mixture is a reddish colour, you can investigate what happens to the equilibrium position when the concentration of reactants or products are changed by monitoring the colour of the solution. How?
What is a catalyst?
A substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent changes itself, it is not used up during a reaction and at the end of the reaction it is regenerated.
How does a catalyst increase the rate of a chemical reaction?
It provides and alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy
What are the different ways a catalyst may be used?
it may react with a reactant to form an intermediate or may provide a surface for which the reaction takes place
Draw an endo and exothermic reaction profile diagram with a catalyst
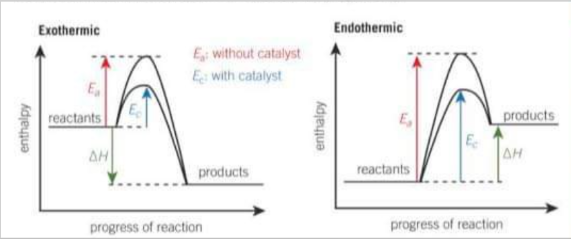
What is a homogenous catalyst?
A catalyst that has the same physical state as the reactants. It reacts with the reactants to form an intermediate, which breaks down to give the product and regenerates the catalyst.
What is a heterogeneous catalyst?
A catalyst with the same physical state as the reactants, usually solids in contact with gaseous reactants or reactants in a solution. Reactant molecules are weakly absorbed (weakly bonded) onto the surface of the catalyst where the reaction takes place. After reaction product leaves surface of catalyst by deabsorption
What does it mean when we say that collisions are elastic?
The molecules don’t slow down as a result of a collision and no energy is lost.
Complete the sentences:
Molecules in a ___ move at a _____ speed, colliding into ____ ______ and the ____ of the container. The collisions are _____ - molecules _____ slow down as a result of a collision and no ______ is lost. In any gas, liquid or solution, some molecules move _______ with ___ energy. The spread of molecular energies in ______ is shown in the ____________ distribution.
Molecules in a gas move at a high speed, colliding into each other and the walls of the container. The collisions are elastic - molecules don’t slow down as a result of a collision and no energy is lost. In any gas, liquid or solution, some molecules move slowly with low energy. The spread of molecular energies in gases is shown in the Boltzmann distribution.
In the Boltzmann distribution what does Ea represent and what does the shaded area show?
Ea represents the activation energy, the shaded area shows only a small proportion of molecules have more energy than Ea and therefore, enough energy to react.
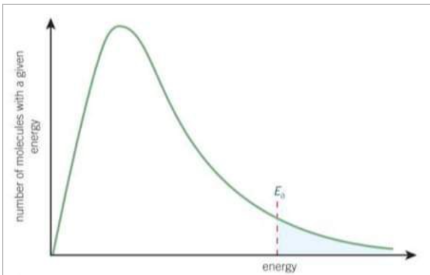
What are the features of the Boltzmann distribution?
No molecules have 0 energy - the curve starts at the origin
The area under the curve is equal to the total number of molecules
There is no maximum energy for a molecule - the curve doesn’t meet the x axis at high energy. The curve would need to reach infinite energy to meet the x axis
What happens to boltzmann distribution as temperature increases?
As temperature increases, the average energy of molecules also increases. A small proportion of molecules will still have low energy but more molecules have higher energy and the graph is stretched over a greater range of energies. The number of molecules is the same so the area is the same
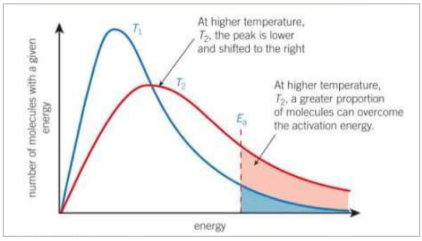
What happens to the rate of reaction at a higher temperature - in terms of particles
At a higher temperature more molecules have energy greater than or equal to the activation energy. Therefore, a greater proportion of collisions will lead to a reaction, increasing the rate of reaction. Collisions will also be more frequent as the molecules are moving faster but the increased energy of molecules is more important than the increases collisions.
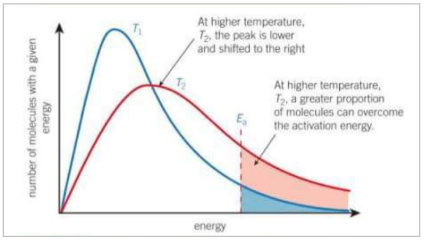
Describe how the bolzmann distribution changes as temperature increases
The peak is lower and shifted to the right, a greater proportion of molecules can overcome the activation energy.
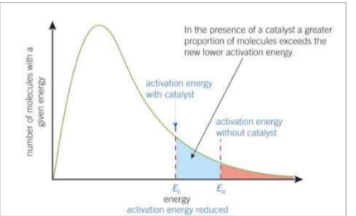
How does a catalyst affect the boltzmann distribution?
A catalyst provides an alternative route with a lower activation energy. Compares to Ea, a greater proportion of molecules now have an energy equal to or greater than Ec. On collision, more molecules will react to form products, increasing the rate of reaction.
What is dynamic equlibrium?
In an equilibrium system, the rate of the forward and reverse reactions are equal and the concentrations of reactants and products don’t change. Rate of formation of products is equal to rate of formation of reactants.
What must occur for a reaction to remain in equilibrium?
It must take place in a closed system
What is a closed system?
A system which is isolated by its surroundings so the temp, pressure and concentrations of reactants and products are unaffected by outside influences.
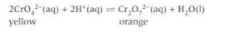
Describe how you can do this experiment - Le Chatlier’s principle
Add a solution of yellow potassium chromate to a beaker and add dilute sulphuric acid until there is no further change. The solution will turn orange. If you add aqueous NaOH until there is no further change, the solution turns back to yellow.

How can you show how Le Chatlier’s principle can be applies to concentration? Example
When you add dilute H2SO4, you increase the concentration of H+ ions in the solution which increases the rate of the forward reaction. This caused the equilibrium to shift to minimise the change in H+ concentration. The shift decreases the conc of added reactant H+. The position of equilibrium shifts to the right, making new products. A new position of equilibrium is established towards the products and the solution turns orange as Cr2O72- forms.

How can you show Le Chatlier’s principle applies to temperature? Example
Dissolve CoCl2 in water in a boiling tube, add a small amount of HCl. Place in iced water and solution should be pink. Set up a boiling water bath and transfer the tube to the boiling water. The solution will be blue. When it is transferred back to the ice, it will turn pink again.

Describe the shift in equilibrium for forward and backward reactions - exo and endothermic
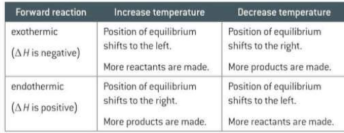
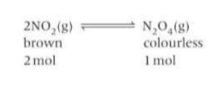
How can you show how Le Chatlier’s principle applies to pressure? Example
As there are fewer gaseous molecules on the RHS of the equilibrium, the position of the equilibrium shifts to the right, reducing the number of gaseous moles to minimise the increase in pressure. More N2O4 is formed and brown colour fades. Decreasing the pressure shifts the equilibrium in the opposite direction, to the side with more gaseous moles on the left, making the brown colour deeper.
What is the equilibrium constant?
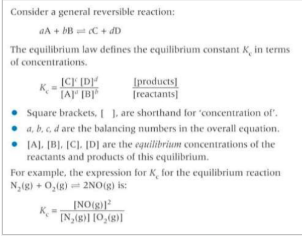
Describe what the Kc value indicates if it is 1, >1, <1
A Kc value of 1 indicated the position of the equilibrium is halfway between the reactants and the products.
A Kc value of >1 indicated the position of the equilibrium is towards the products
A Kc value of <1 indicates the positions of the equilibrium is towards the reactants
Complete the sentence:
The larger the Kc value…
The further the position of the equilibrium is to the right hand side and the greater the concentration of the products compared to the reactants.