AP151: Lab Exam 2
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP151 LAB
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What does a Motor Unit Consist of?
A single somatic motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates
Why does Muscle Tension eventually Plateau When Stimulation Voltage Increases?
Because all motor units have already been recruited. Once every motor unit is activated, increasing voltage can’t activate more fibers, so tension reaches a maximum and plateaus.
How did we determine the Threshold Stimulus When Increasing the Voltage of the Stimulation?
The lowest voltage that produces a visible muscle contraction (The first measurable twitch)
What Neurotransmitter is Involved In Muscle Contraction?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
What Changes take Place in the Different Regions of the Sarcomere when the Muscle Contracts?
The sarcomere shortens
The A band stays the same length
The I band and H zone shorten, causing the Z discs to move closer together
What is Motor Unit Recruitment?
An increase in the number of motor units that are activated
When does Motor Unit Recruitment Occur?
When the load increases, the muscle needs more force, so more and larger motor units are recruited
What is Wave Summation?
Increasing strength of successive contractions when the muscle is repeatedly stimulated at high frequency
What Factor is Changed to Produce Wave Summation?
The frequency of stimulation is increased
What are the Two Regulatory Proteins in Muscle Contraction?
Troponin and Tropomyosin
What is the Function of Troponin?
Binds calcium
Changes shape and moves tropomyosin
Exposes actin’s binding sites so myosin can form cross-bridges
What is the Function of Tropomyosin?
Blocks the myosin-binding sites on actin at rest
What Component of Red Blood Cells Determines Blood Type?
Surface Antigens
What Happens to Red Blood Cells if Donor Blood is Not Properly Matched?
A transfusion reaction occurs
What is the Clumping of Red Blood Cells Called in a Transfusion Reaction?
Agglutination (Clumping and subsequent death of RBCs)
What Antibodies Does Type A Blood Produce?
Anti B antibodies
What Antibodies Does Type B Blood Produce?
Anti A antibodies
What Antibodies Does Type AB Blood Produce?
No antibodies
What Antibodies Does Type O Blood Produce?
Both Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies
What Blood Can a Type A Patient Receive?
Type A and O blood
What Blood Can a Type B Patient Receive?
Type B and O blood
What Blood Can a Type AB Patient Receive?
Type A, B, AB, and O blood (Universal recipient)
What Blood Can a Type O Patient Receive?
Type O blood only (Universal donor)
What Blood Can an A+ Patient Receive?
A+, A-, O+, O-
What Blood Can an A- Patient Receive?
A-, O-
What Blood Can a B+ Patient Receive?
B+, B-, O+, O-
What Blood Can a B- Patient Receive?
B-, O-
What Blood Can an AB+ Patient Receive?
All blood types (Universal recipient)
What Blood Can an AB- Patient Receive?
A-, B-, AB-, O-
What Blood Can an O+ Patient Receive?
O+, O-
What Blood Can an O- Patient Receive?
O- only (Universal donor)
What Happens if an Rh-Positive Patient Is Exposed to Rh-Positive Blood?
Nothing happens; there is no immune reaction
What happens if an Rh-Negative Patient Is Exposed to Rh-Positive Blood?
They may produce anti-Rh antibodies, which can cause a reaction upon future exposure
What does the P Wave Represent on an ECG?
Atrial Depolarization
What does the QRS Complex Represent on an ECG?
Ventricular Depolarization
What does the T Wave Represent on an ECG?
Ventricular Repolarization
Where Would you Find the AV Nodal Delay on the ECG?
In the PR segment, between the P wave and the QRS complex
What is the Function of the AV Nodal Delay?
To allows the atria to complete their contraction before ventricular contraction begins
What is the Path through the Conduction System of the Heart?
SA Node
AV Node
AV Bundle (Bundle of His)
Left and Right Bundle Branches
Purkinje Fibers
Where is the SA Node Located?
Right atrium
Where is the AV Node Located?
Interatrial septum
Where is the AV Bundle (Bundle of His) Located?
Top of the interventricular septum
Where are the Bundle Branches Located?
Down the interventricular septum
Where are the Purkinje Fibers Located?
In the walls of the ventricles
What is an Abnormally Slow Heartbeat Called?
Bradycardia
What is an Abnormally Fast Heartbeat Called?
Tachycardia
What are the Different Flows of Blood when Measuring Blood Pressure?
Turbulent flow and Laminar flow
What Makes the Korotkoff Sounds?
The sounds of turbulent blood flow through a partially opened artery are heard when measuring blood pressure
How is Systolic Blood Pressure Determined Using Korotkoff Sounds?
It is the pressure at the first tapping sound
How is Diastolic Blood Pressure Determined Using Korotkoff Sounds?
It is the pressure when the sounds stop
Where are Baroreceptors Located?
In the carotid sinus and the aortic arch
What do Baroreceptors Respond To?
Changes in blood pressure by sensing the stretch of the vessel walls
What Happens at the Cardioacceleratory Center When Blood Pressure Decreases?
Becomes more active, increasing sympathetic output, which raises heart rate and contractility to bring blood pressure back up
What Happens at the Cardioacceleratory Center When Blood Pressure Increases?
Inhibits, reducing sympathetic output, which lowers heart rate and contractility to bring blood pressure back down
What Happens in the Ventricles During Systolic Blood Pressure?
Ventricles contract and push blood into the arteries
What Happens in the Ventricles During Diastolic Blood Pressure?
The ventricles are relaxed and filling with blood
What is Orthostatic Hypotension?
A drop in blood pressure when standing up from sitting or lying down
When might Orthostatic Hypotension Occur?
Due to dehydration, blood loss, certain medications, or when the body cannot adjust blood pressure quickly enough
What is Filtration?
Certain substances forced out of the blood into the glomerular capsule
What is Reabsorption?
Return of substances from the nephron tubules back to the blood
What is Secretion?
Selective transfer of certain substances from the blood into the nephron tubules
Where does the Bulk of Reabsorption Take Place in the Nephron?
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
What Conditions would Pepsin Best In?
Acidic Conditions and about 37 °C
What Enzymes Break Down Proteins?
Pepsin and Trypsin
What Enzyme Breaks Down Starch?
Amylase
What Enzyme Breaks Down Lipids?
Lipase
How Do pH and Temperature Affect Enzyme Activity, and Why?
Enzymes work best at their specific optimal pH and body temperature (~37°C). Too high or too low pH/temperature can denature the enzyme, reducing or stopping its activity.
What is the Optimal pH For Pepsin and Why?
Acidic pH (1–2), which matches the stomach environment where pepsin functions
What is the Optimal pH for Amylase and Why?
Neutral pH (~7), which matches the mouth and small intestine where amylase works
What is the Optimal pH for Lipase and Why?
Slightly basic pH (~8), which matches the small intestine after bile neutralizes stomach acid
How was Litmus Cream Used To Determine Lipid Digestion?
By changing color based on pH. When lipase digests lipids, it releases fatty acids, lowering the pH and changing the color
What does Color Change to Pink in Litmus Cream Indicate?
The presence of fatty acids, meaning lipid digestion has occurred
Lipase breaks fat into what molecules?
Fatty acids and Glycerol
What is the Function of Bile in Lipid Metabolism?
Emulsifies lipids, breaking large fat droplets into smaller ones so lipase can digest them more easily
What must Carbohydrates be Broken Down to be Able to be Absorbed in the Small Intestines?
Carbohydrates must be broken down into monosaccharides to be absorbed
In What Form is Pepsin Initially Released?
As pepsinogen, an inactive enzyme
How is Pepsinogen Activated Into Pepsin?
By the acidic environment of the stomach (HCl)
If ADH is Released, what would the Concentration Of Urine Be?
Becomes more concentrated because ADH increases water reabsorption in the kidneys
Where in the Nephron is Glucose Resorbed and How? What is the Presence of Glucose in the Urine Termed?
Glucose is reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule via active transport. The presence of glucose in urine is called Glycosuria
What Size Items can be Filtered at the Nephron? Could you Recognize Molecules that Should Not Be Found in the Urine?
Small molecules such as water, ions, glucose, and amino acids can be filtered. Large molecules like proteins and blood cells are too big to be filtered and should not appear in urine
What does ADH Cause Reabsorption of, and Where does it Act in the Kidneys?
ADH causes water reabsorption in the collecting ducts, making urine more concentrated
What does Aldosterone Cause to be Reabsorbed, and Where does it Exert its Effect in the Nephron?
Aldosterone causes sodium (Na⁺) reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts. Water follows sodium, Increasing blood volume and blood pressure
What is the Osmolarity of the Filtrate Entering the Distal Convoluted Tubule?
Hypotonic
How does Osmolality Change in the Kidney From the Cortex to the Medulla?
Osmolality increases from the cortex to the medulla
What Part of the Nephron Helps Maintain the Osmotic Gradient?
The loop of Henle, especially its descending and ascending limbs
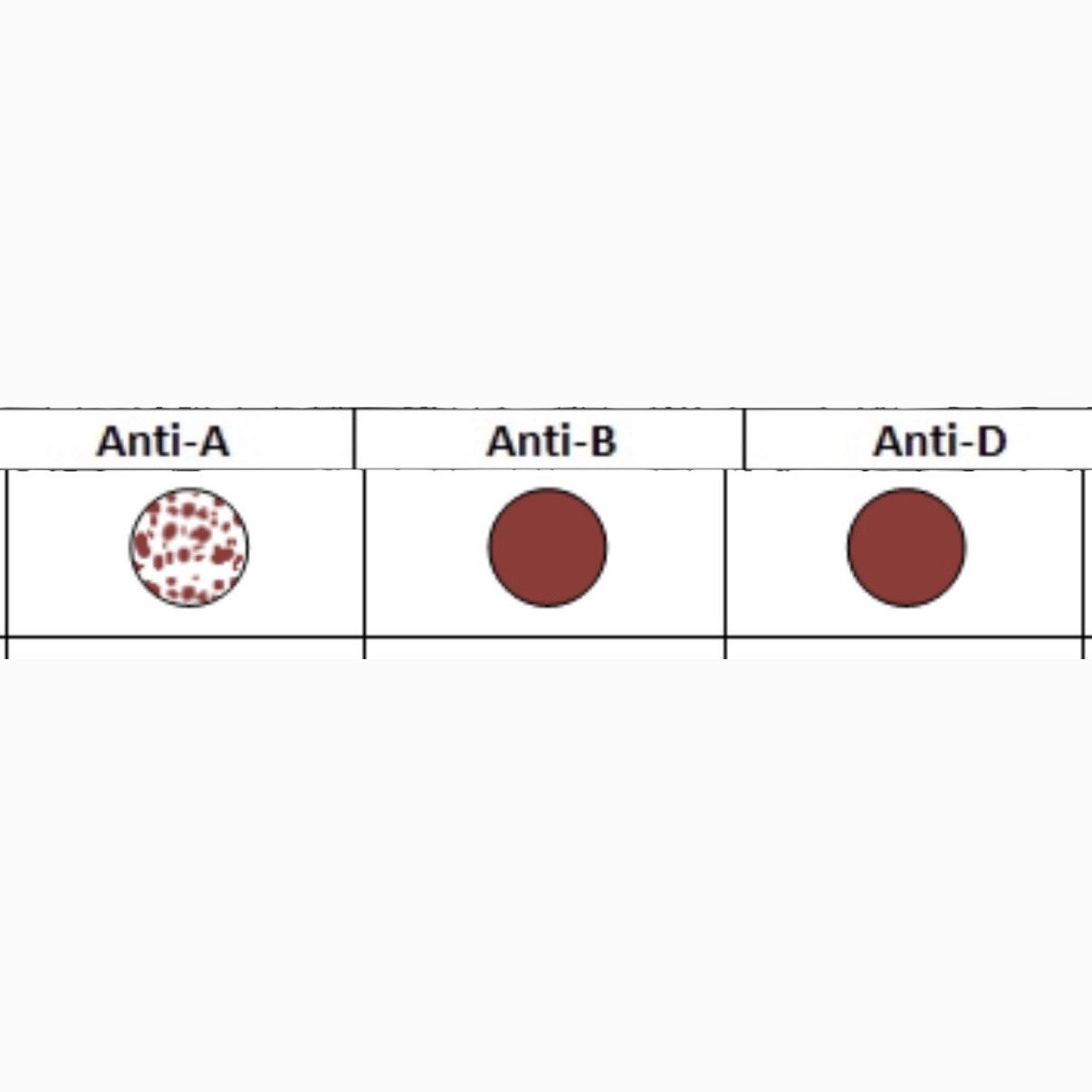
What is this Blood Type?
A-
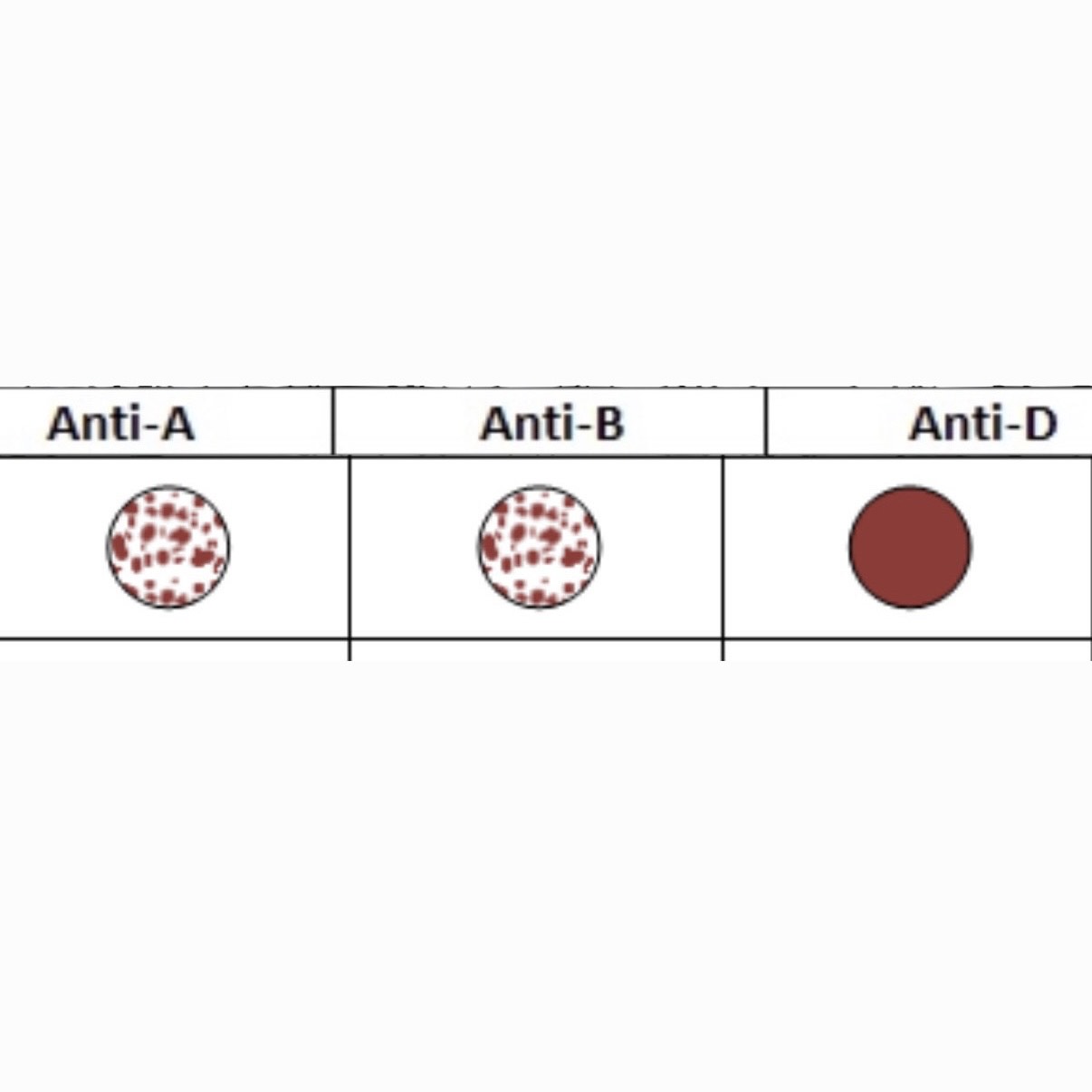
What is this Blood Type?
AB-
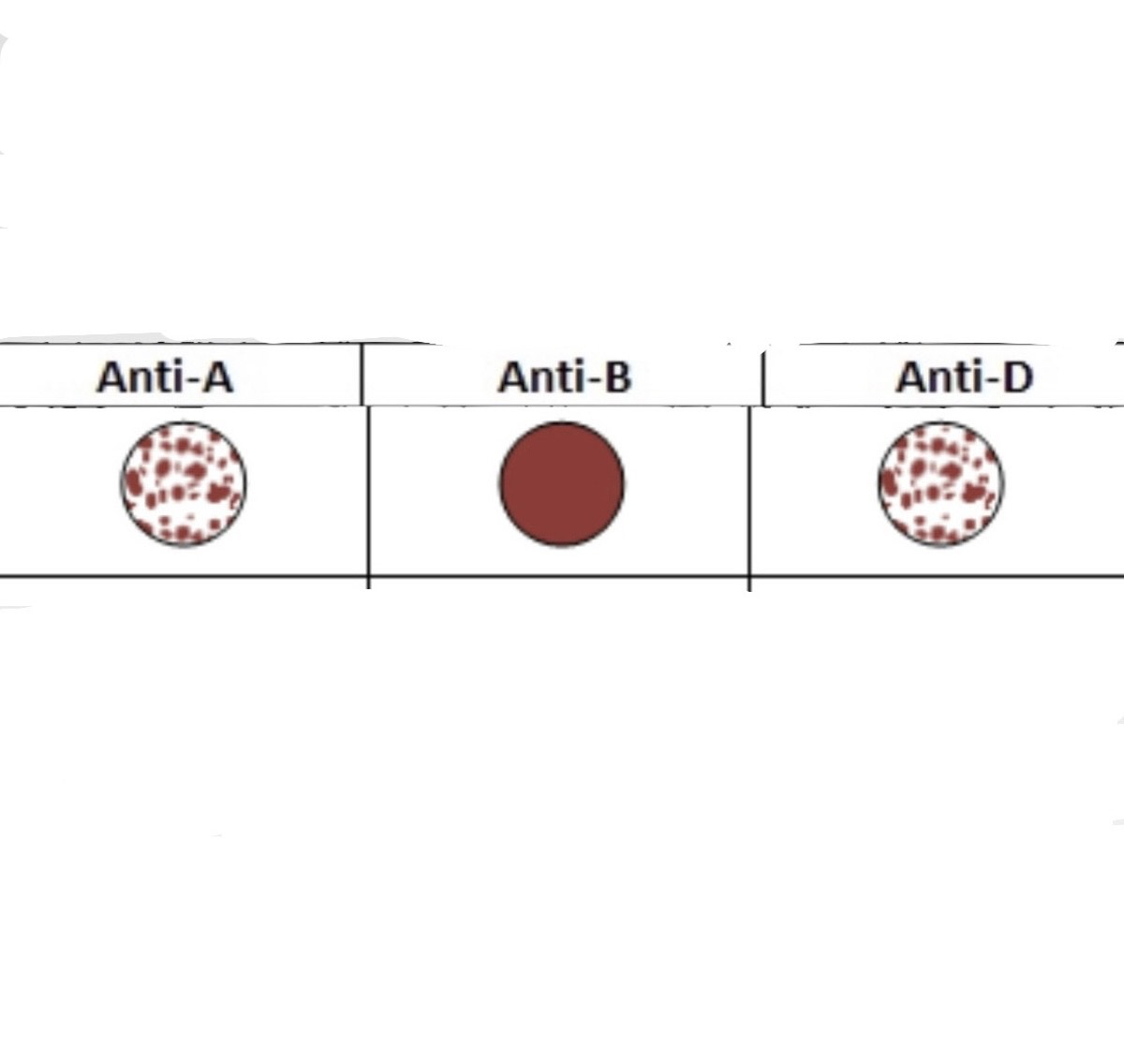
What is this Blood Type?
A+
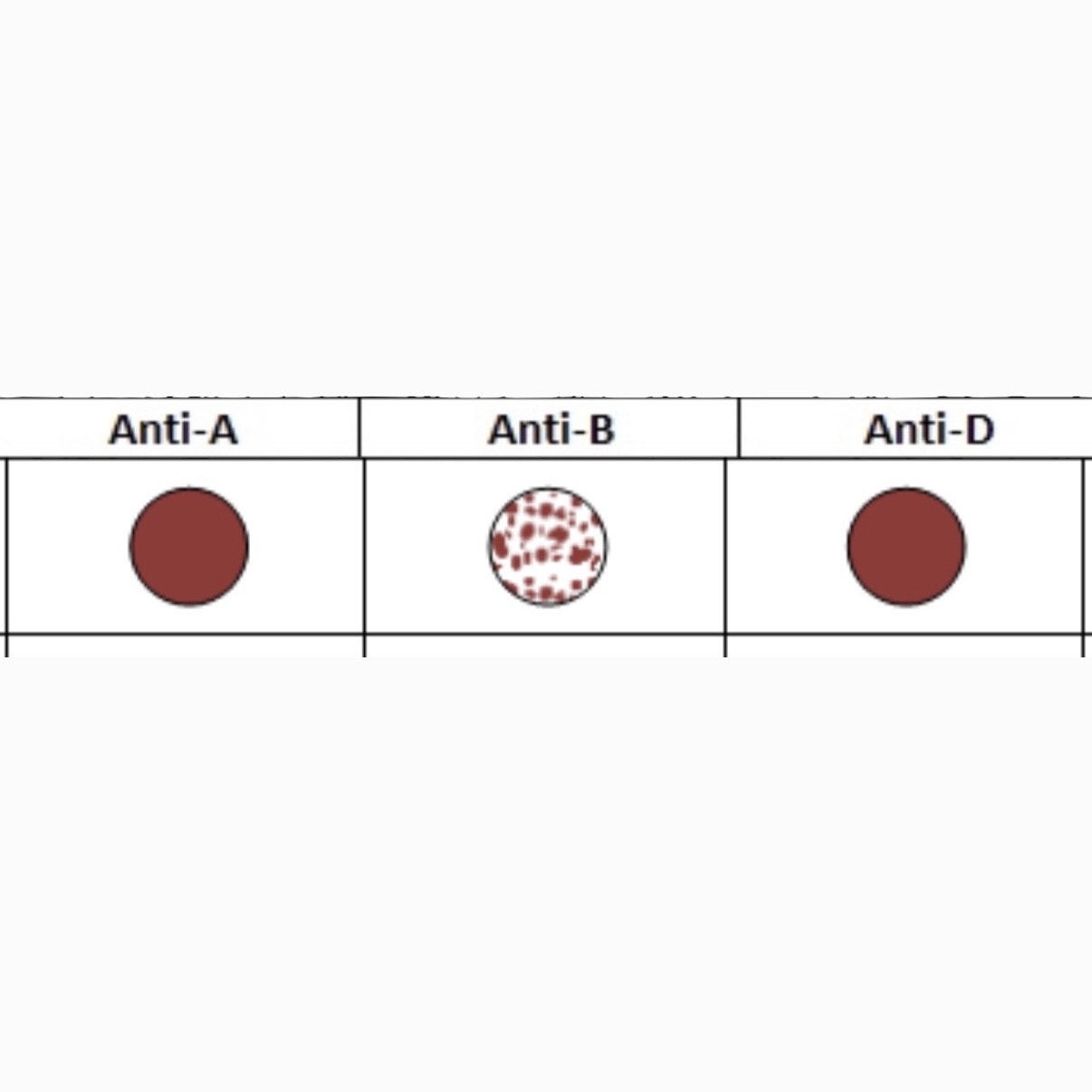
What is this Blood Type?
B-
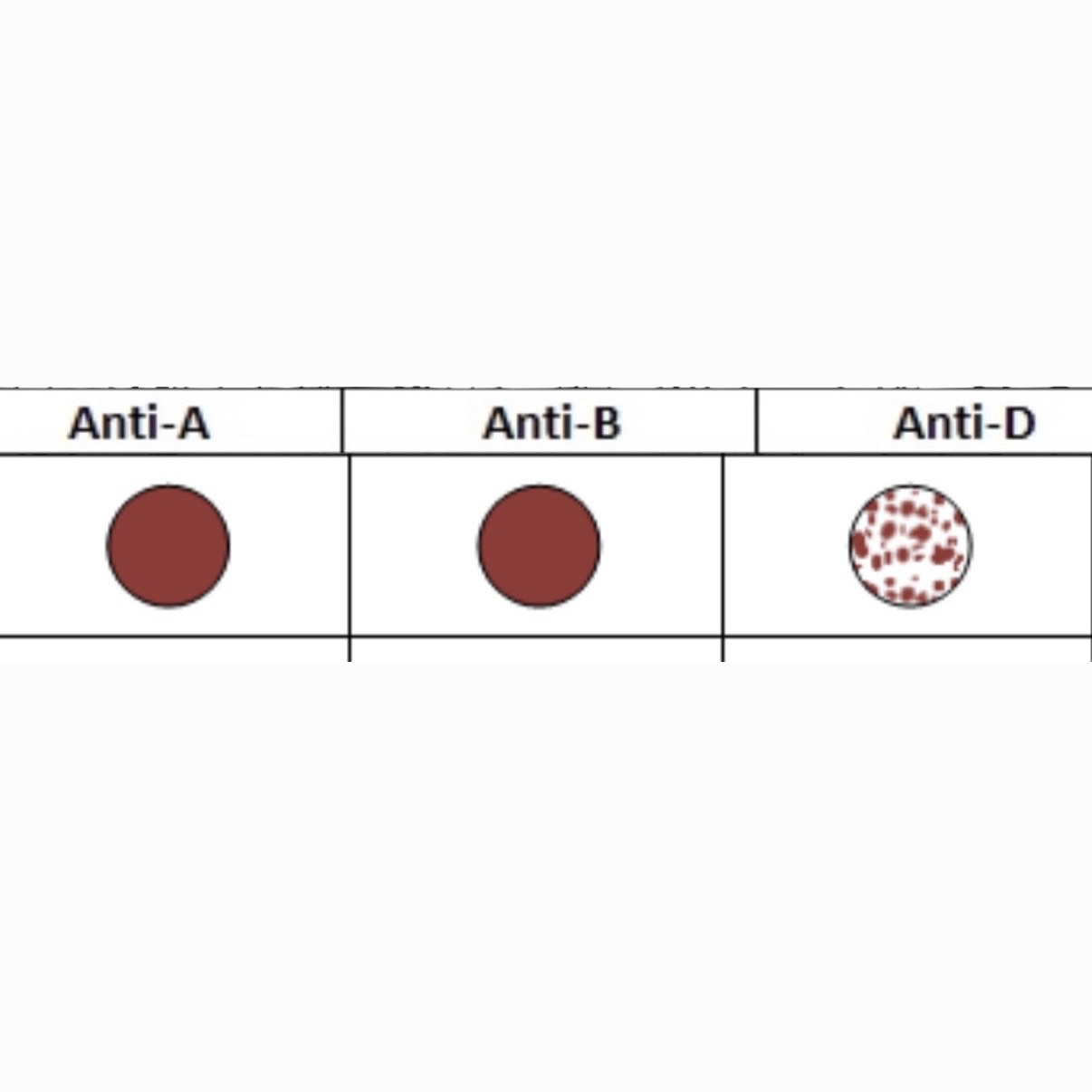
What is this Blood Type?
O+
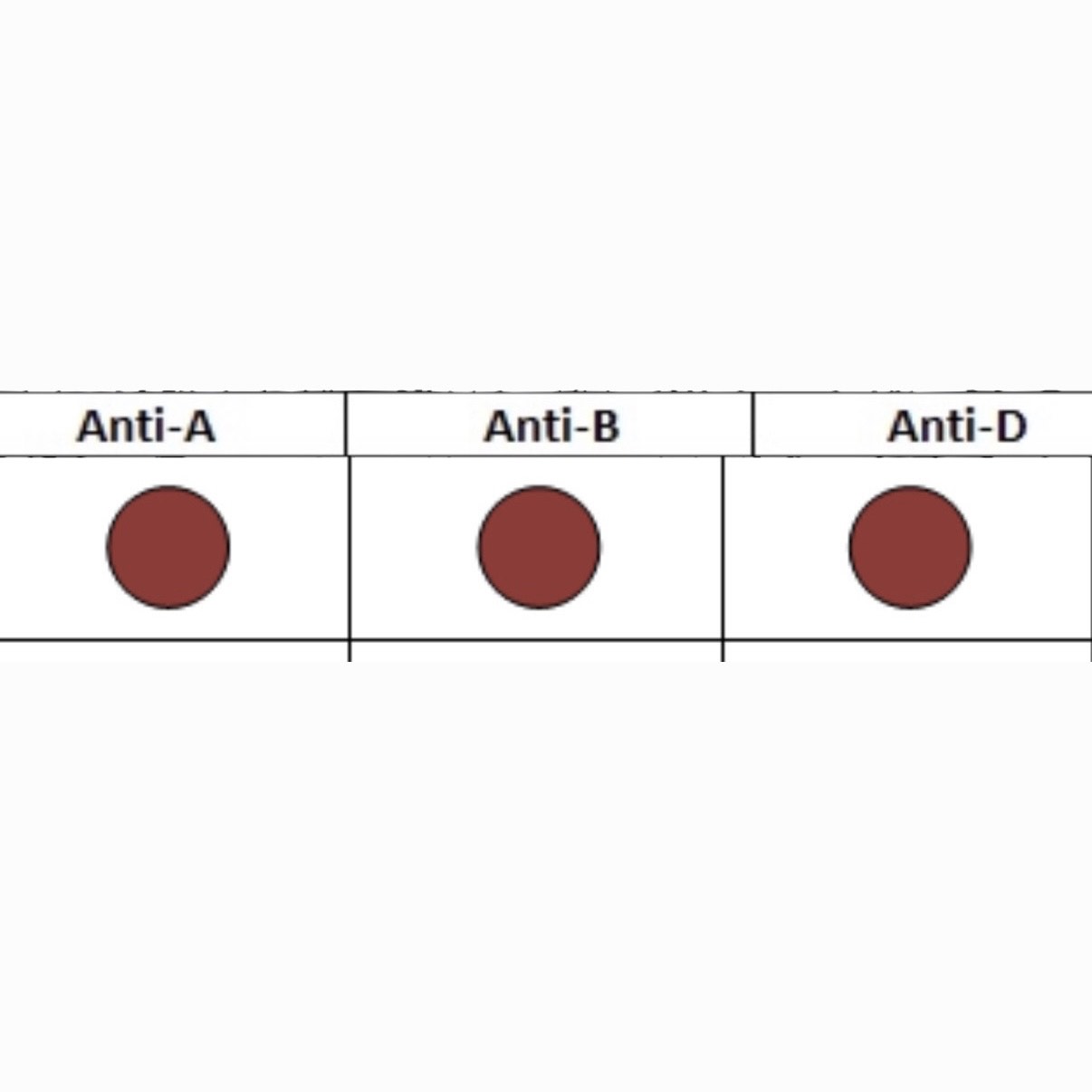
What is this Blood Type?
O-
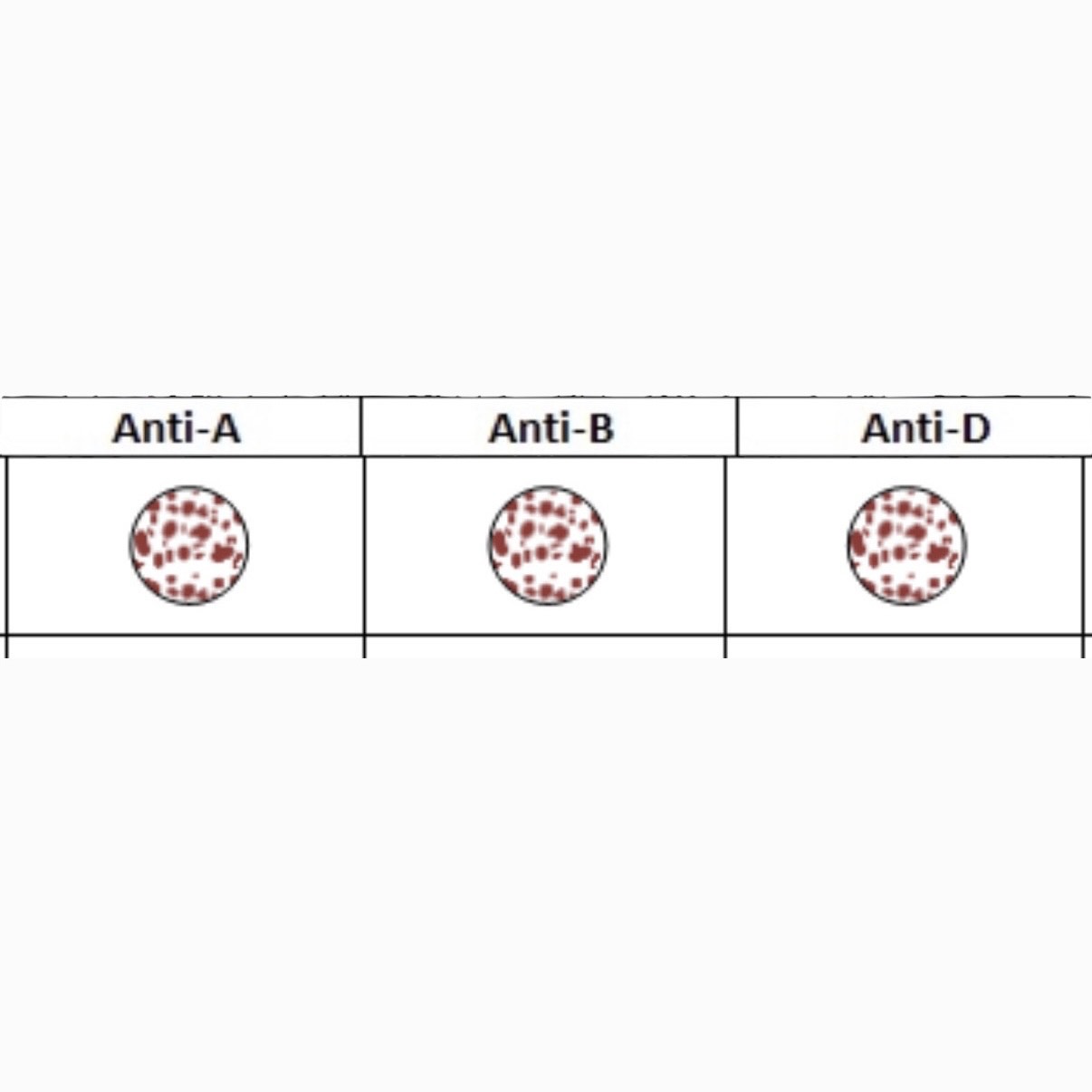
What is this Blood Type?
AB+
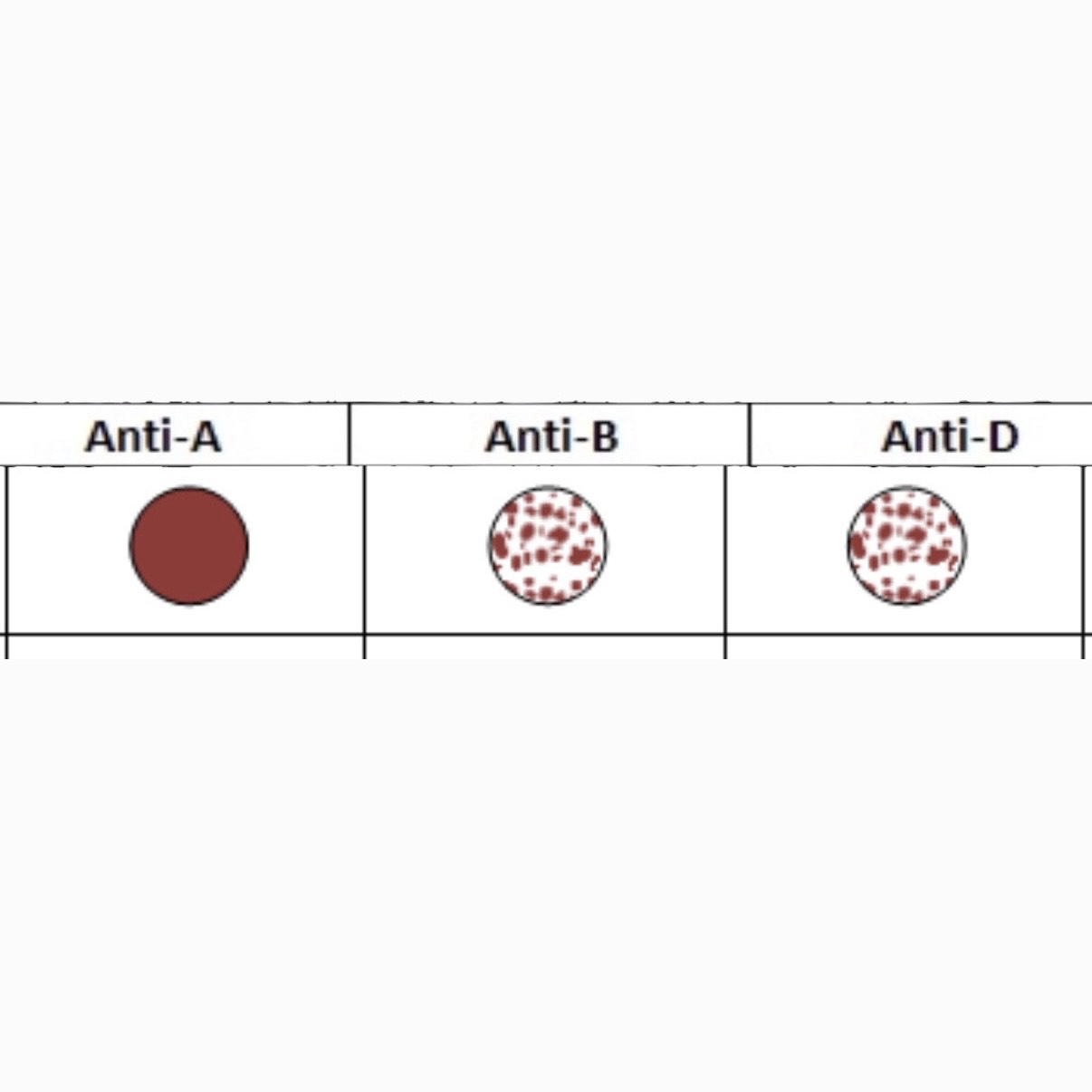
What is this Blood Type?
B+
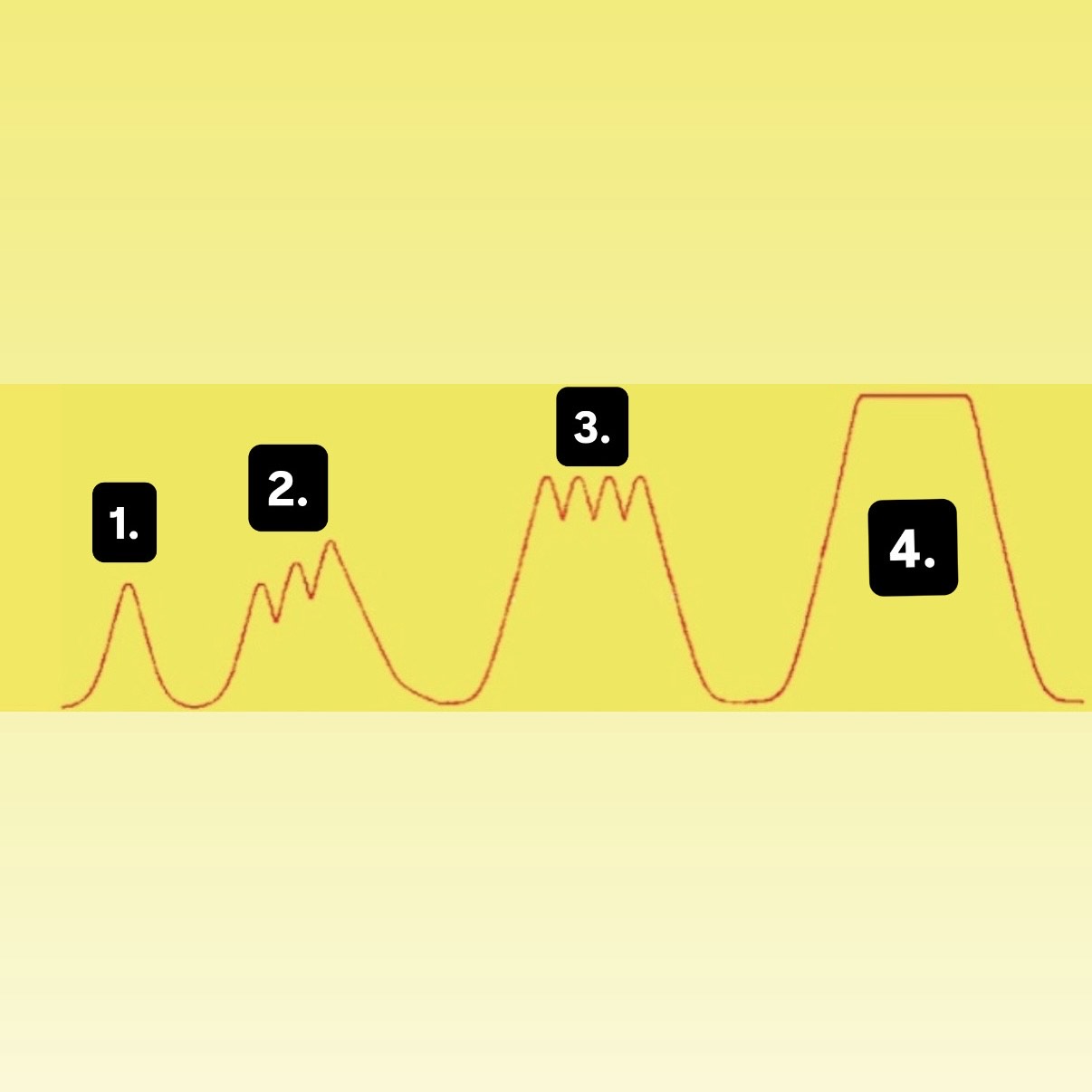
What is 1?
Muscle Twitch
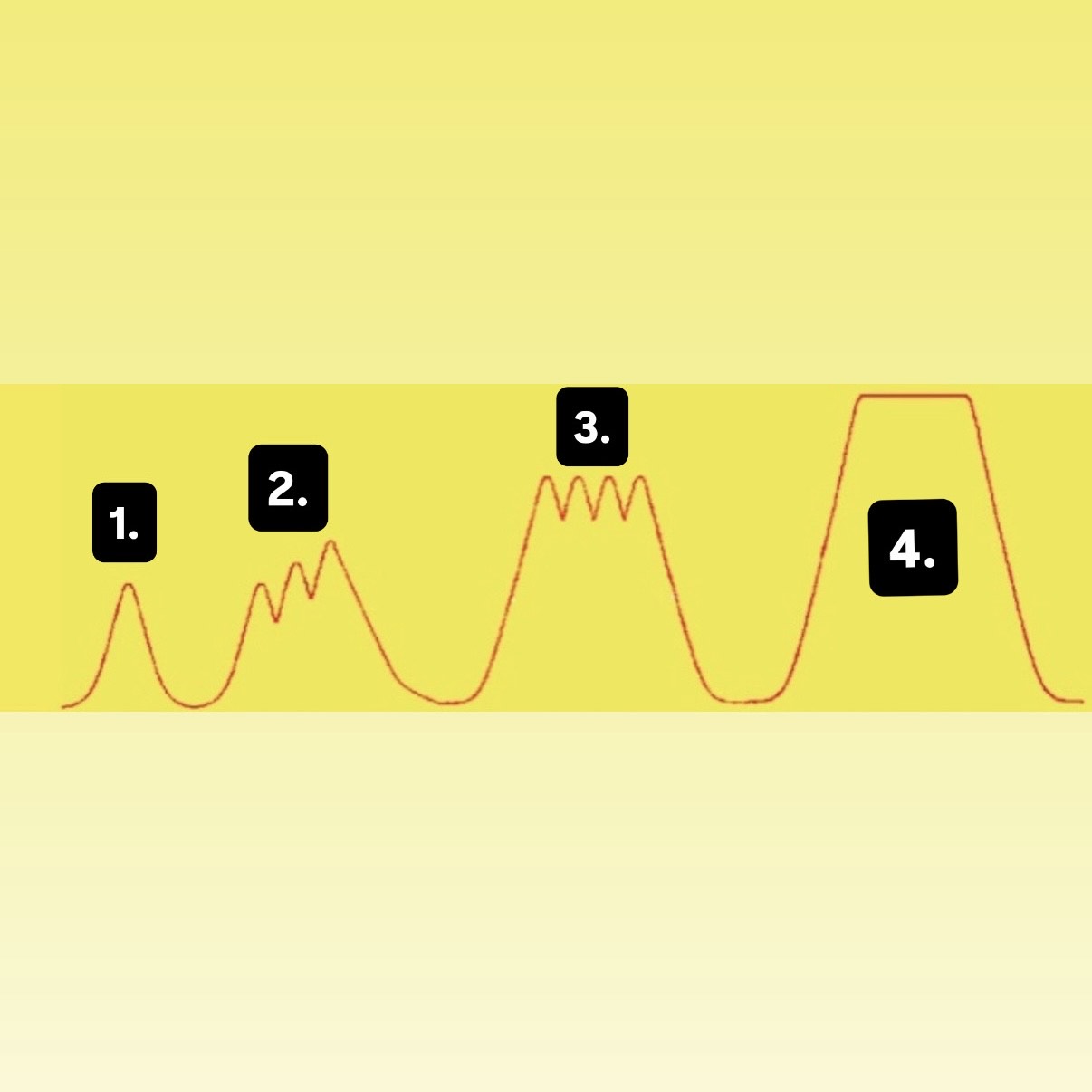
What is 2?
Summation
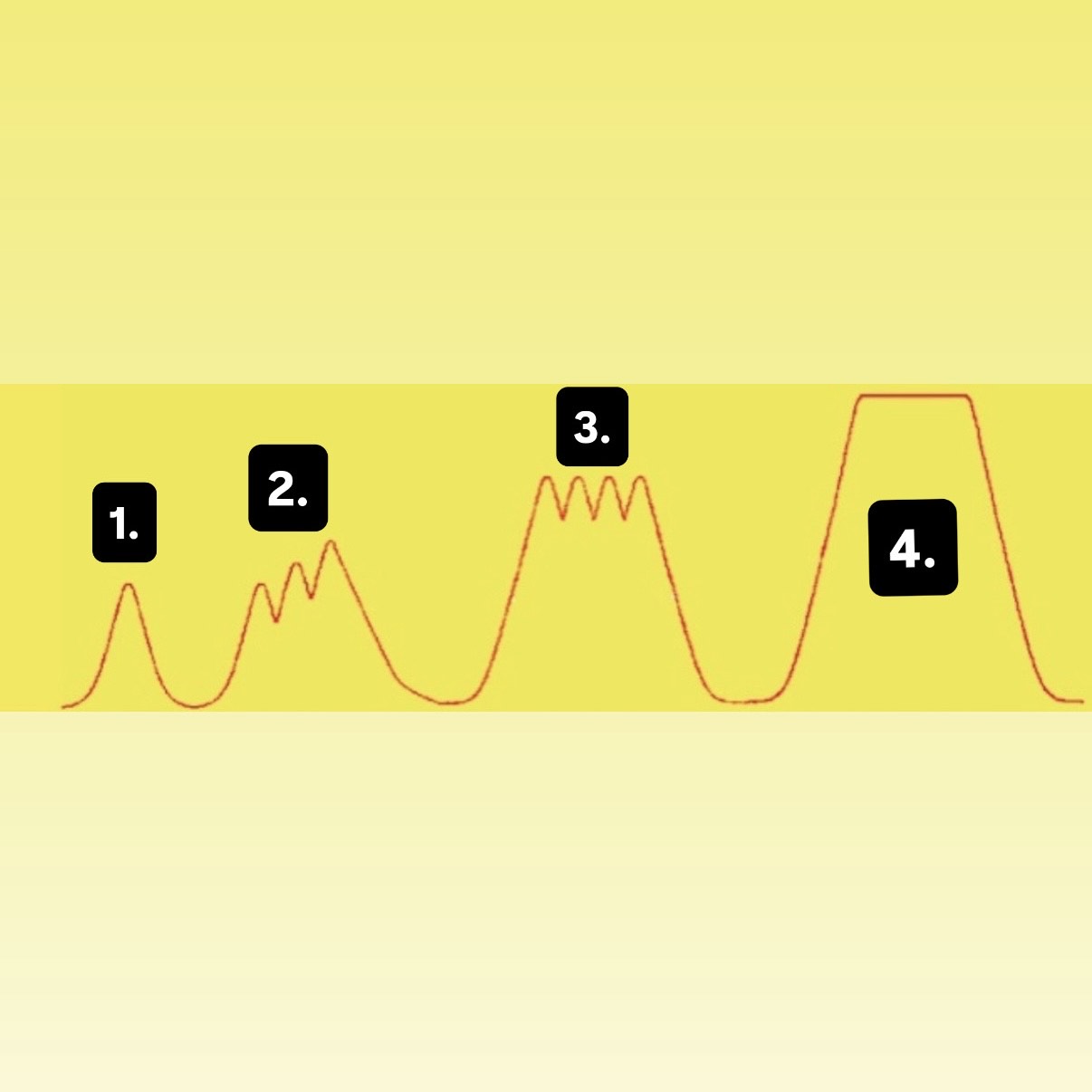
What is 3?
Incomplete Tetanus
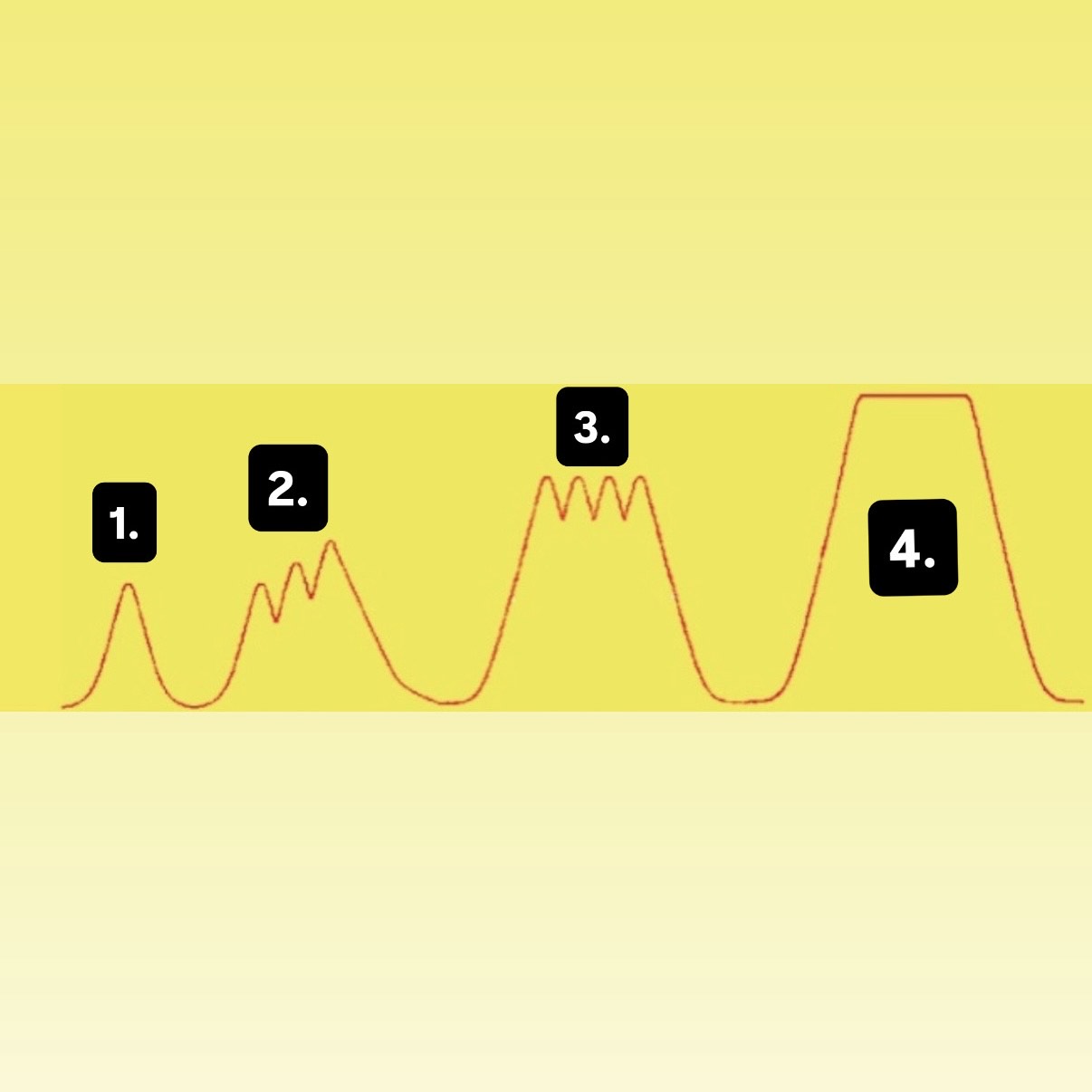
What is 4?
Complete Tetanus