AP Microeconomics Unit 3
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Marginal Product (MP)
The additional output produced when 1 additional unit of a resource is employed (the quantity of all other resources employed remaining constant);
Total product (TP) or total output (Q)
total number of units of output produced by the firm per period of time
Average Product (AP)
output per unit of input
diminishing marginal product
MPP diminishes as the firm uses additional units of labor
marginal cost in output increases and the marginal product of labor decreases as each additional unit of input is added
bottom of MC curve
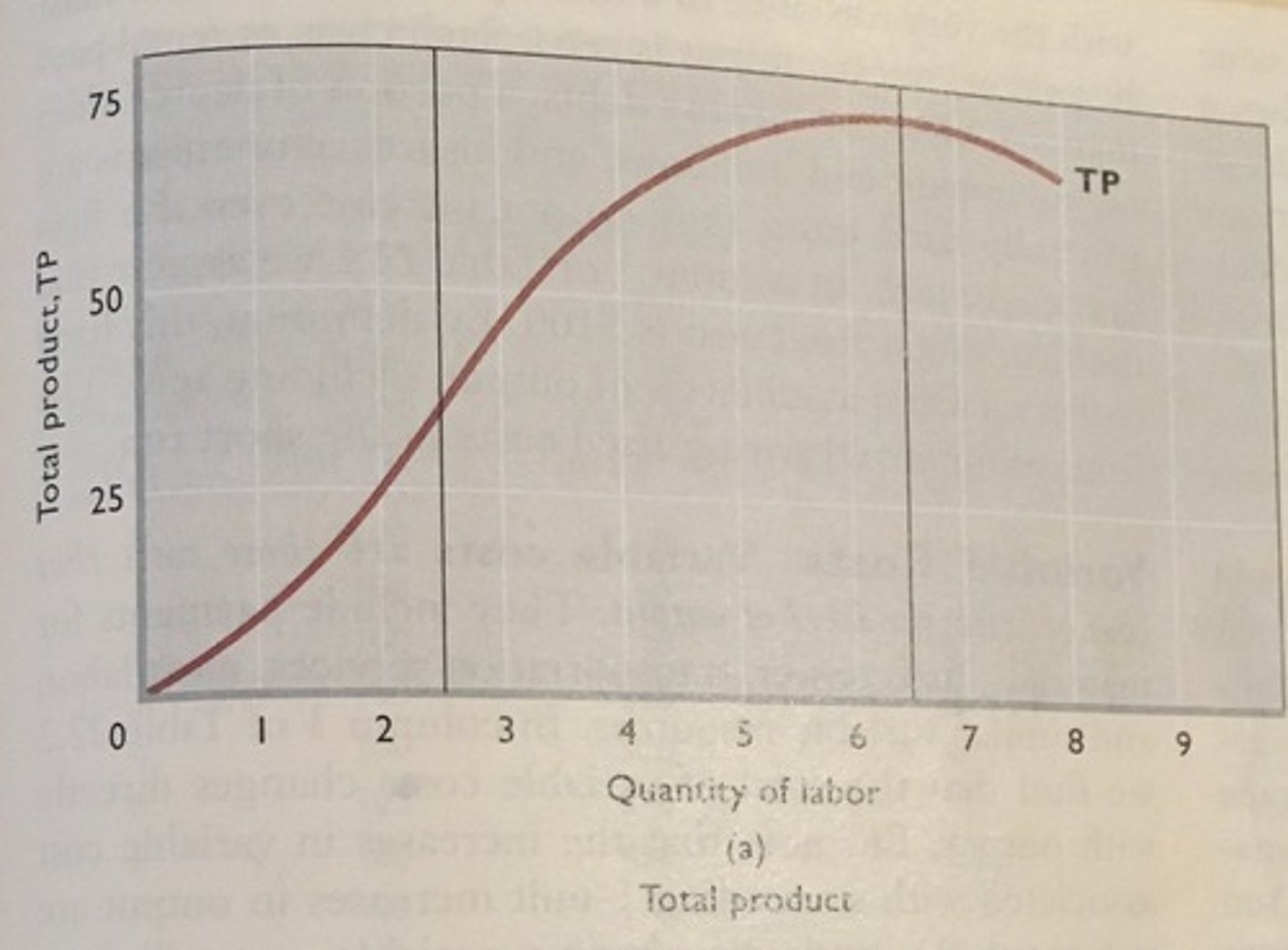
total product curve
shows how the quantity of output depends on the quantity of the variable input, for a given quantity of the fixed input
Per-unit cost curve
shows the change in per unit cost from one input extra, ceteris paribus

Total Cost (TC)
shows the change in total cost from one input extra, ceteris paribus
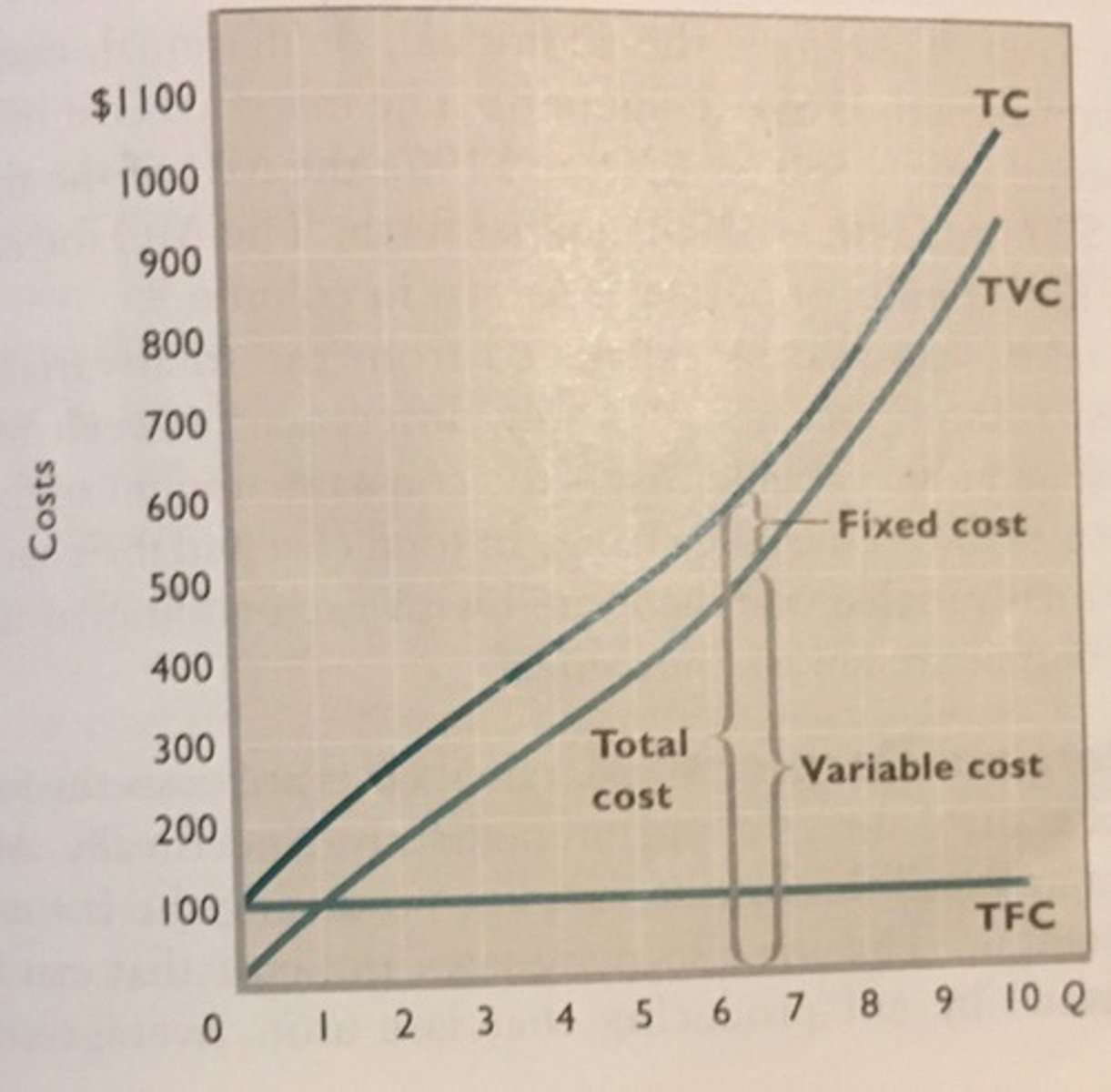
Fixed costs
costs that do not vary with the quantity of output produced
Average fixed costs (AFC)
fixed cost per unit produced
AFC = TFC/Q
AFC = ATC - AVC
Variable costs
costs that vary with the quantity of output produced
Average variable costs (AVC)
variable cost per unit produced
AVC = TVC/Q
AVC = ATC - AFC
AVC = wage/APP
Total cost (TC)
sum of fixed costs and variable costs
TC = TVC + TFC
Average total cost (ATC)
total cost per unit produced
ATC = TC/Q
ATC = AVC + AFC
Marginal cost (MC)
cost of producing an additional unit of a good (variable cost)
MC = ∆TC/MPP
MC = wage/MPP
Marginal revenue (MR)
additional income from selling one more unit of a good
MR = price of good per unit
Economic profit
price is above the minimum of the ATC curve
total revenue - (implicit costs + explicit costs)
Economic loss
price below the minimum of the ATC curve
Normal profit
price on the minimum of the ATC curve
What are the characteristics of perfect competition
many firms with no entry barriers
firms maximize profits and are price takers
identical products (perfect substitutes)
no long run profit and have perfect information
no control over price or advertisements
What are the characteristics of a pure competition graph
demand is perfectly elastic labeled MR = D = AR = P
supply is MC above AVC
ATC touches the MC at its lowest point and is always above AVC and AFC
AVC touches the MC at its lowest point and approaches (but never touches) the ATC
AFC is perpetually decreasing
MC is shaped like a swoosh

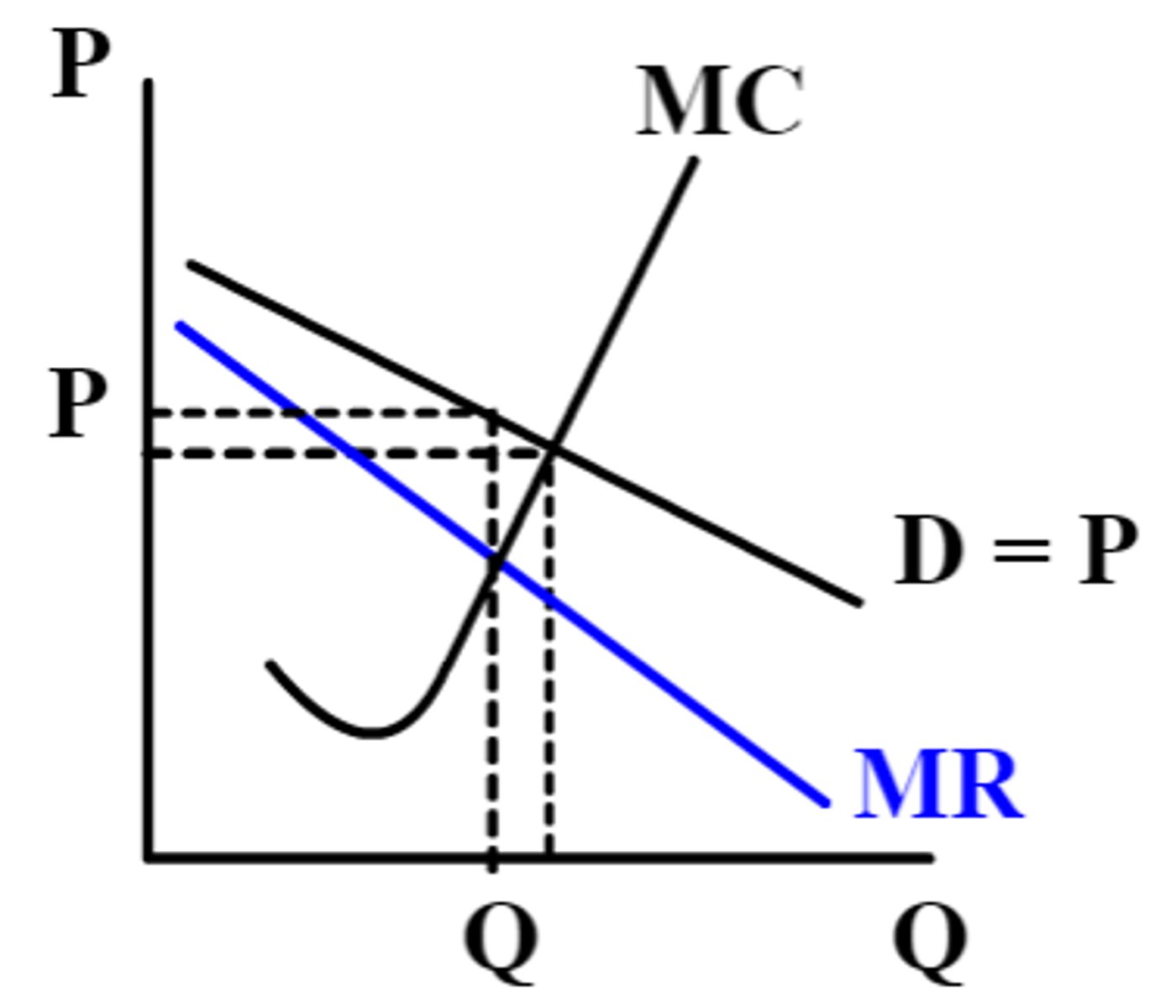
Optimal output (profit maximization)
wherever marginal revenue (MR) = marginal cost (MC)
Total revenue maximization
wherever marginal revenue (MR) = 0
Short run average total cost (SRATC)
period of time during which at least one of a firm's inputs is fixed
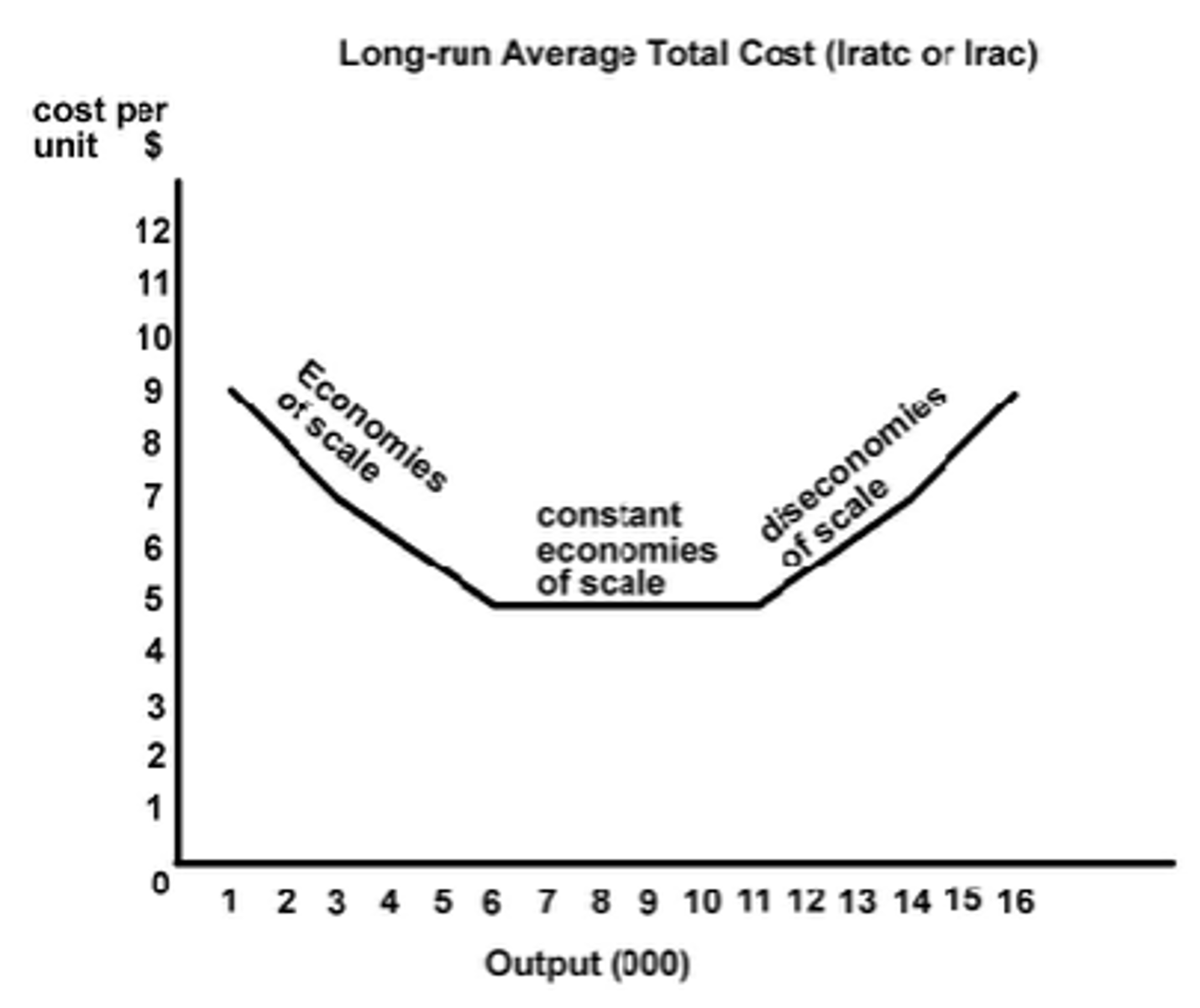
Long run average total cost (LRATC or planning curve)
period of time in which a firm has paid off all of its fixed costs
consists of many increasing then decreasing SRATC curves of various plant sizes available to a firm
price = minimum ATC
Productive efficiency
producing a good in the least costly way (minimal use of resources)
P = minimum ATC
Allocative efficiency
distribution of resources towards the production of products most wanted by society
P = MC
Shutdown point
point where price is less than minimum AVC and the firm must shut down to minimize its losses
firm should continue to produce as long as it's price is above the AVC
Increase in demand in the short run (perfect competition)
market price and market quantity increases
firm price and firm quantity increases
profit occurs

Increase in supply in the short run (perfect competition)
market price decreases and market quantity increases
firm price and firm quantity decreases
encourages entry into the market

Decrease in demand in the short run (perfect competition)
market price and market quantity decreases
firm price decreases and firm quantity decreases
loss occurs
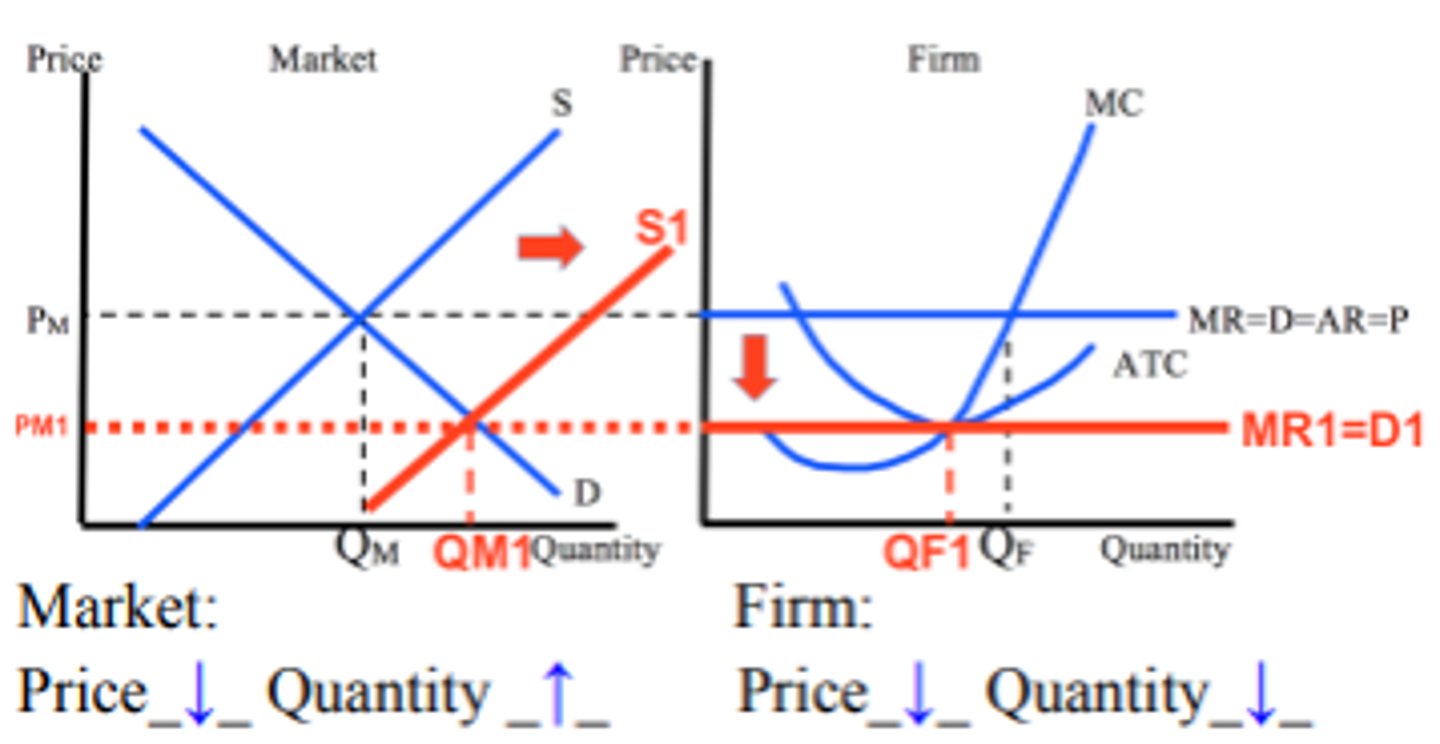
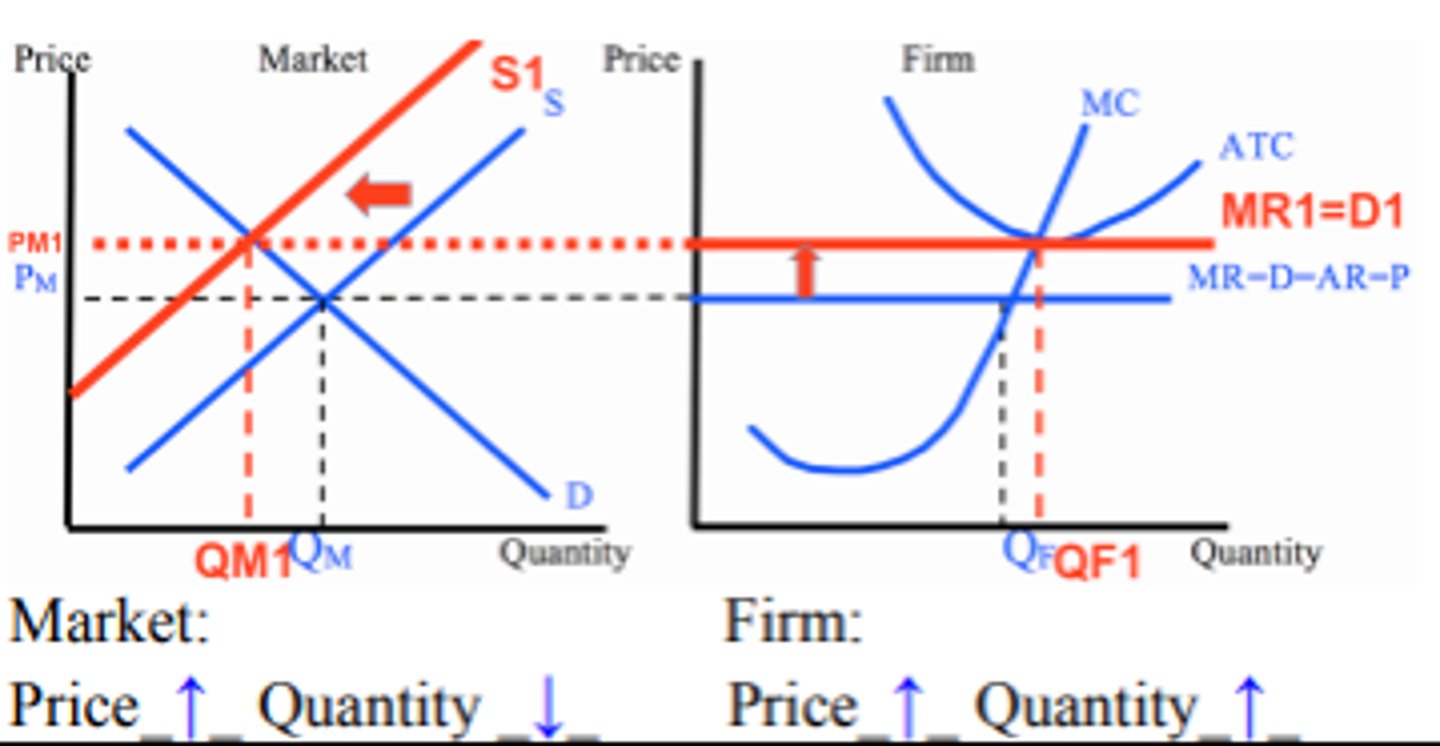
Decrease in supply in the short run (perfect competition)
market price increases and market quantity decreases
firm price and firm quantity increases
encourages exiting out of the market
When will only the ATC shift upwards
fixed costs increase once
price and quantity remain the same
When will only the ATC shift downwards
fixed costs decrease once
price and quantity remain the same
What are the characteristics of a pure monopoly
single firm that is a price searcher
firm has no substitutes
market entry is blocked (no competition)
legality dependent on government approval
earns a profit in the long run by maximizing total profit and selling where price is elastic
causes income inequality
What are the characteristics of a pure monopoly graph
MR slopes downwards from left to right at a faster rate
ATC below MR = MC
profit-maximizing price is the point on the demand curve of the profit-maximizing quantity at MR = MC
D = P ≠ MR
D = P is the demand curve and slopes downwards from left to right
no supply curve exists
creates deadweight loss, has no productive or allocative efficiency in the long run, and an unfair market price
demand is elastic where MR > 0, inelastic where MR < 0, and unitary elastic where MR = 0
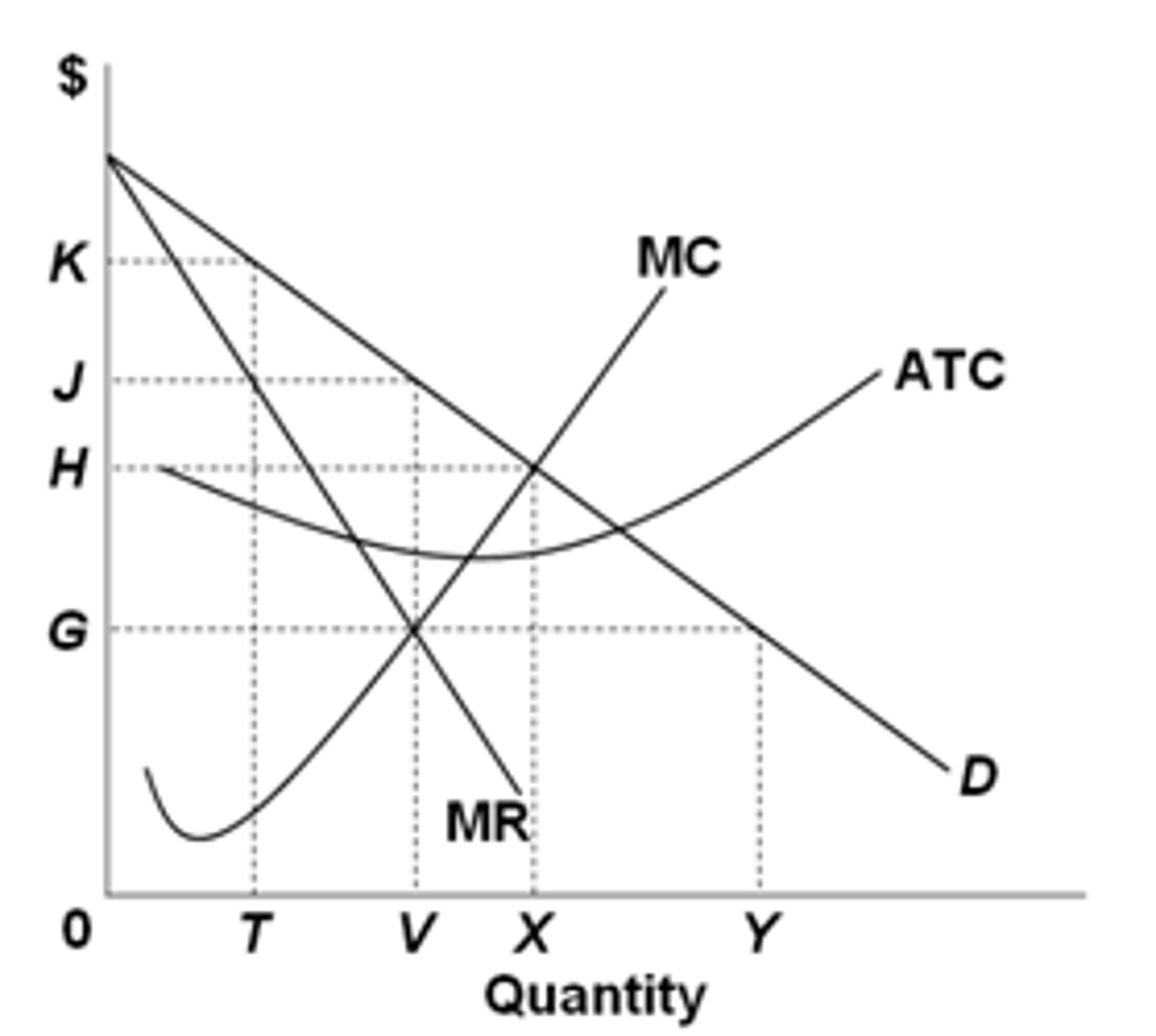
When can price discrimination be possible
monopoly power
market segregation
no resale possible
Economies of scale
factors that cause a producer's average cost per unit to fall as output rises and can alter the quantity of all inputs
LRATC decreasing
Constant economies of scale
all inputs can be increased equally to maintain the lowest cost per unit
LRATC constant
Diseconomies of scale
average cost per unit increases in the long run due to size
LRATC increasing
Accounting profit
total revenue - explicit costs
Explicit cost
cost that involves spending money for production
Implicit cost
opportunity cost when a firm uses owner-supplied resources
What are the characteristics of monopolistic competition
many firms that are price searchers
no entry barriers
products are similar but not identical
constant advertising (fixed cost that increases demand and becomes more inelastic)
normal long run profit
market demand curve different (lowering prices does not instantly mean more market share for a firm)
has no productive or allocative efficiency in the long run
What are the characteristics of an oligopoly
few firms that are price searchers
difficult entry barriers
products are similar but not identical
firms are interdependent (decisions dependent on each firm's actions)
firms make their own price
What are the barriers of entry for a monopoly
patents and copyrights
legal restrictions
control of key resources
high startup costs
Changing cost industry in the long run (perfect competition)
quantity remains the same in the firm and quantity increases in the market after prices stabilize
When will firms enter a market,
economic profit is greater than zero
When will firms exit a market
economic profit is less than zero
Decreasing cost industry
industry that faces lower per-unit production costs as industry output decreases in the long run
long run industry supply curve slopes downward
Constant cost industry
industry that faces no change in per-unit production costs as industry output stays the same in the long run
long run industry supply curve horizontal
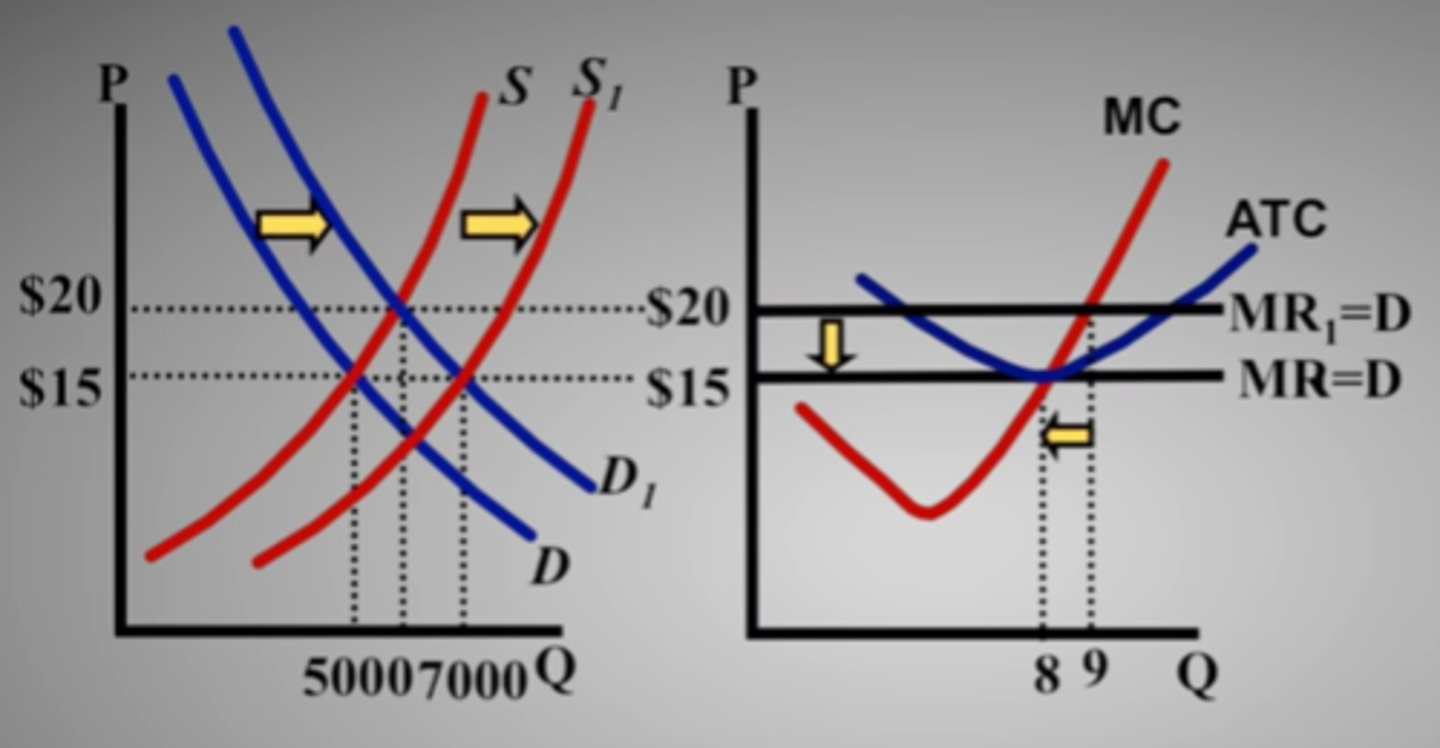
increasing cost industry
an industry in which expansion through the entry of new firms raises the prices firms in the industry must pay for resources and therefore increases their production costs