Big bang midterm
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Order of planets
sun, mercury, venus, earth, mars, jupiter, saturn, uranus, neptune, pluto
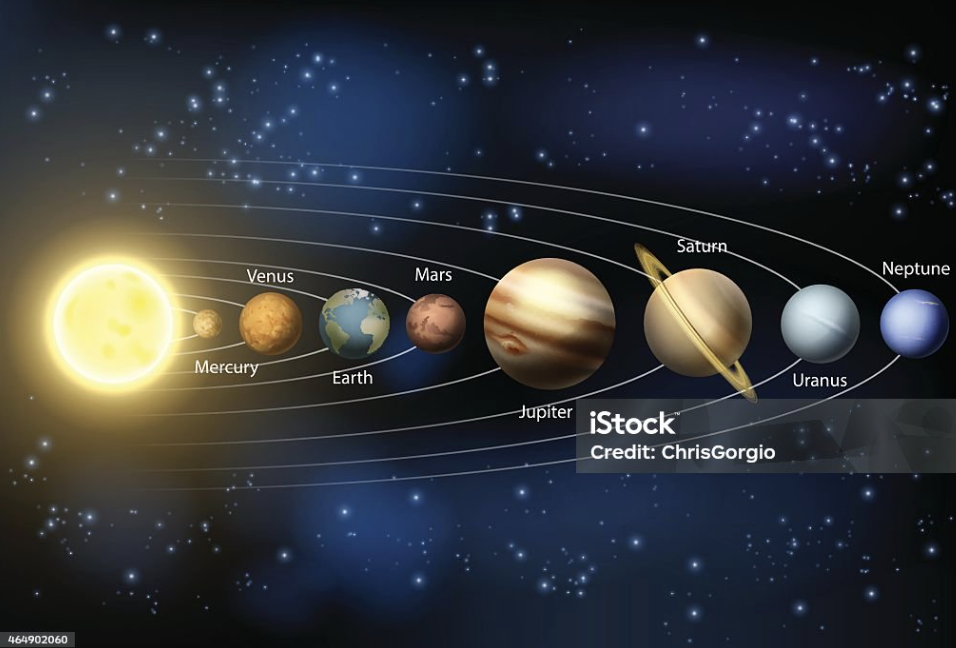
Mercury
The closest planet to the sun; fastest moving, named after the messenger god Hermes
Venus
Second planet from the sun; thick atmosphere (93x Earth's), 96% CO2, volcanic activity - sulfuric acid clouds, surface temp near 1000°F, named after the goddess Aphrodite
Earth
largest terrestrial planet; supports life, has 1 moon, atmosphere suitable for water and life
Mars
Fourth planet from the sun; polar ice caps, rust-colored surface, changing seasons, evidence of past water and possibly life, named after Ares
Jupiter
Largest planet; gas giant, hundreds of years-old storm 3x Earth's size (Great Red Spot), possible moon with life, 5 AU from Sun, named after Zeus
Saturn
Gas giant; famous for prominent rings, has moons (one may have developing life), 9 AU from Sun, named after Kronos
Uranus
Gas giant; discovered in the 1700s, slow-moving, barely visible, named after the creator god Ouranos
Neptune
Outermost traditional planet; discovered in the 1800s, 30 AU from Sun, blue color due to methane, named after Poseidon
Pluto
Dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt; formerly classified as a planet, has a moon (Charon), 40 AU from Sun, named after Hades
Charon
Pluto’s largest moon, named after the mythological ferryman to the underworld; shares its name with the discoverer's wife
Moon
Earth's only natural satellite; controls tides, shows phases, only one side is visible due to synchronous rotation;
acutal size (diameter) = 2000 miles, r = 1000 miles
Sun’s mass
m☉=1.94x10^33 grams
Alpha Centauri
Closest star system to Earth;
contains three stars (A, B, C/Proxima);
visible from southern hemisphere;
brightest star centaurus constellation
Astronomical Unit (AU)
about 149 million km/94 million miles; standard unit in astronomy
Jovian planets
largest, outermost planets in solar system (Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune, Saturn); made of gas
Terrestrial planets
Earth-like worlds with rock/solid surfaces (Earth, Mercury, Venus, Mars)
Moon’s distance from earth
d = 238,000 miles
Sun’s distance from Earth
d = 1 AU; 149 million km; 94 million miles
How many arcminutes in 1 degree?
60
How many arcseconds in 1 arcminute?
60
how many arcseconds in 1 degree?
3600
Light
Atoms - protons (2 up quarks, 1 down quark) & neutrons (1 up quark, 2 down quarks)
Quarks
components of protons/neutrons (up, down, top, bottom, charge, strange)
mass of electrons
m = 9.10910^-28 grams
light travel problem
can’t see things contemporaneously because of light travel - light travel causes delay
*The further we look, the further back in time we see
Sun’s light distance from Earth; duration of Sun’s light travel
d = 8.5 mins - we see Sun’s light as it was 8.5 mins ago
Speed of light’s travel around Earth
6.5x around Earth/second
Light speed (constant)
c = 299,792,458 meters/second - finite, noninstantaneous
How far back (in light years) can we see?
13.8 billion light yrs. away (because the Big Bang (creation of the universe) occurred only 13.8 billion yrs ago)
James Webb telescope
6.5m fragmented mirror (folds, expands upon launch);
shows how stars/planets form, finds life in the universe, gives structure of universe as a whole
Scintillation
stars light coming through Earth’s atmosphere– stars’ sparkle
Hubble space telescope
1990;
1.5m mirrors;
orbits around earth in 90 mins;
built to better understand what’s outside of milky way (gave previously unrealized images of universe);
$1 million/day to run
Sun as a star
100 billion stars over 120,000 light yrs. across;
Formed 4.5 billion yrs ago
Alpha centauri A
biggest star in alpha centauri;
similar (but more massive) than the Sun;
~1 billion yrs older than the sun;
Alpha centauri B
slightly smaller than the Sun;
what the sun will look like in ~1 billion yrs
Alpha centauri C (proxima)
Closest alpha centauri star to Earth (d = ~300,000 AU);
3 ½ light yrs away from Earth
Aristarchus of Samos
discovered you can’t see a shadow unless it falls on something (shadow is much bigger than actual object, but gets smaller with added distance);
saw relative size of moon with respect to Earth through exclipses–saw moon was ¼ of Earth’s size through its shadow
How do we know the Sun is further away from Earth than the moon?
Solar eclipses (moon PASSING IN FRONT OF the sun & going through Earth’s shadow);
ASSUMPTION: Shadow cast by the Earth = cone (if sun were close, the earth’s shadow would be a cylinder)
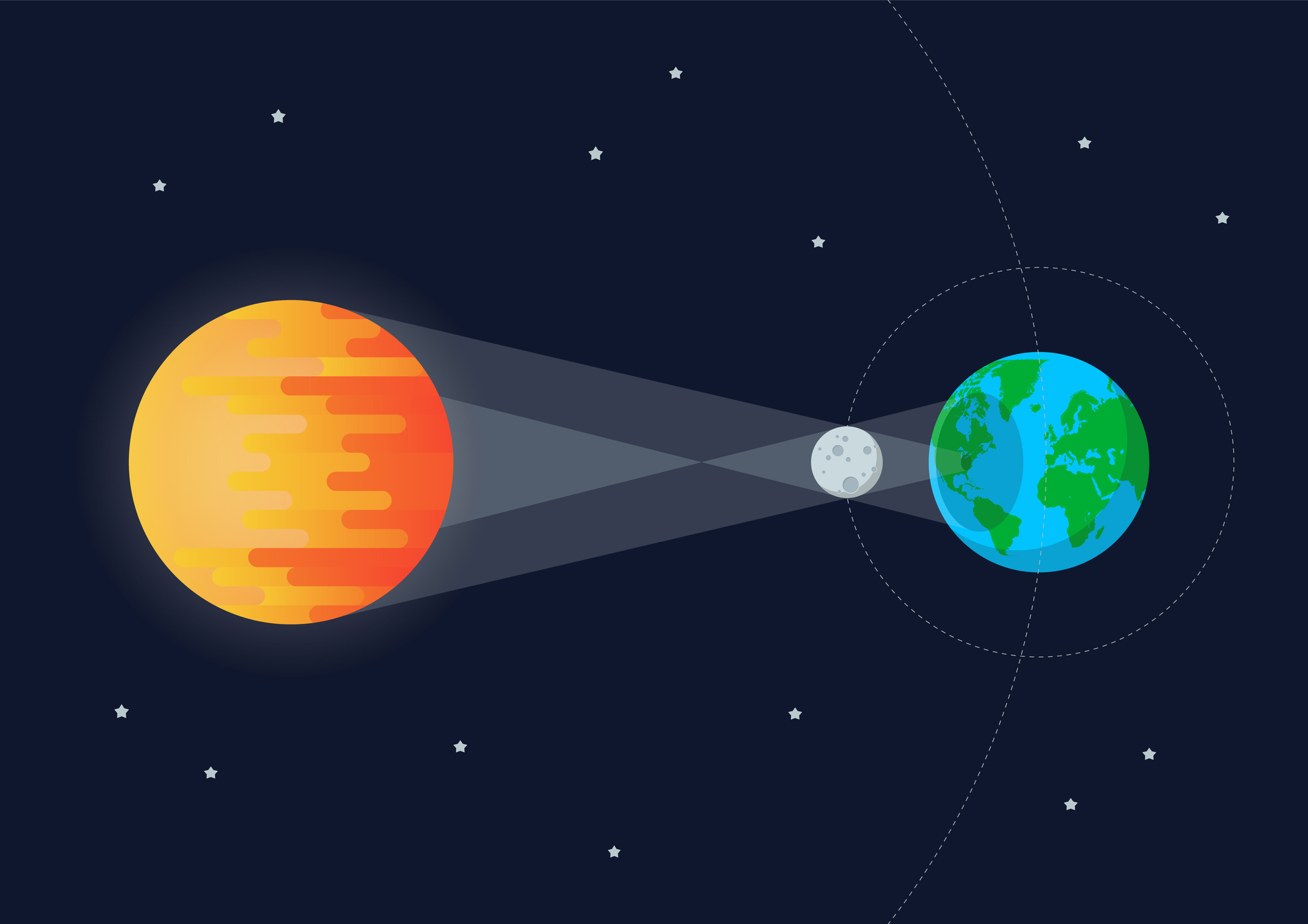
Solar eclipse - contact times
Contact time 1 = moon touching earth’s shadow;
Contact time 2 = moon fully consumed by earth’s shadow (t 1→2 = ~15 min);
Contact time 3 = moon touching opposite side of earth’s shadow (t 2→3 = ~1 hr)
Moon’s size compared to Earth
¼ of the Earth - Shadow of earth takes 15 mins to go across diameter of the moon/moon takes 1 hr to go across diameter of earth
why is 15 mins ¼ of an hour?
Shadow of earth takes 15 mins to go across diameter of the moon/moon takes 1 hr to go across diameter of earth
Aneximander’s universe model
believed Earth is a flat disc in the center of a circular surrounding universe

Babylonian universe model
believed we lived on the ground with a hemisphere dome above us (firmament) where stars/planets sat–snowglobe

How fast does the Earth go to complete a rotation on its axes?
800MPH
How long does it take Earth to rotate on its axes?
23 hrs, 56 mins
Procession
the motion of an object’s rotational axes
how long does it take for Earth’s rotational axis to form a complete circle?
26,000 yrs
How many constellations does Earth travel through every year?
12 - ZODIAC constellations (technically 13 (Ophiucus));
constant
Planet (in latin)
“wandering star”
What proved that Earth rotates on its axes
the Foccault Pendulum;
Coriolis effect;
direction of hurricanes (COUNTERCLOCKWISE MOTION);
cyclones (in southern hemisphere—clockwise motion);
setting/rising of Sun & Moon
Nova
new stars
Supernova
star gets brighter due to a catastrophic explosion–makes sky temporarily brighter;
100 billionx brighter than Sun’s eventual explosion
Asterism
a prominent pattern of stars that is NOT a formal constellation
Sirius
biggest star in the sky;
Sun is cloest to Sirius in August - warmer temps; DOG DAYS OF SUMMER
Aldeberean
“the eye of the bull”;
biggest star of taurus constellation
Betelguese
Ancient Persian(?);
big, old star - bigger than Sun
Orion constellation
soldier with shield/weapon in hand;
fighting taurus to protect the 7 sisters
Ursa major constellation
"big bear”;
Ursa Major was originally a woman with a son (Ursa Minor), ursa major gets turned into a bear, her son comes back from hunting and gets scared by her as a bear, sends Hermes (mercury) down, son drags ursa major to heaven by the tail to get her immortalized in the sky - tail gets stretched long on the journey;
big dipper;
Big dipper constellation
Ursa Major’s body and long tail
Ursa major eye test
BINARY STARS (2nd star on the tail) - only 20/20 vision or better can see it
What did Issaac Newton discover?
Force
Force
accelerating a mass (ma);
measured in Newtons (N)
Fundamental forces of nature
Gravity
Electricmagnetic
Strong nuclear
Weak nuclear
Gravity (Fgrav)
force that accelerates mass (Fgrav = ma = W);
9.81 m/s² OR 32.2 ft/s²
WEIGHT (W);
objects accelerate due to gravity at the same rate, regardless of mass—doesn’t account for friction
electromagnetic
unlike charges attract, like charges repel
strong nuclear
unlike charges repel, like charges attract
position
x;
distance & direction in space
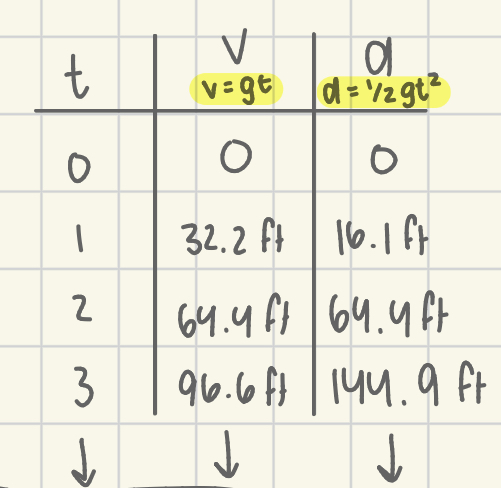
velocity
change in position with respect to time (m/s);
v = Δx/Δt;
v = gt
acceleration
change in velocity with respect to time (m/s²);
a = Δv/Δt
average velocity (speed)
distance travelled/elapsed time (m/s);
Vavg = Δv/Δt
distance (vector)
d = ½at²; ½gt²
d = vt
d = gt/at
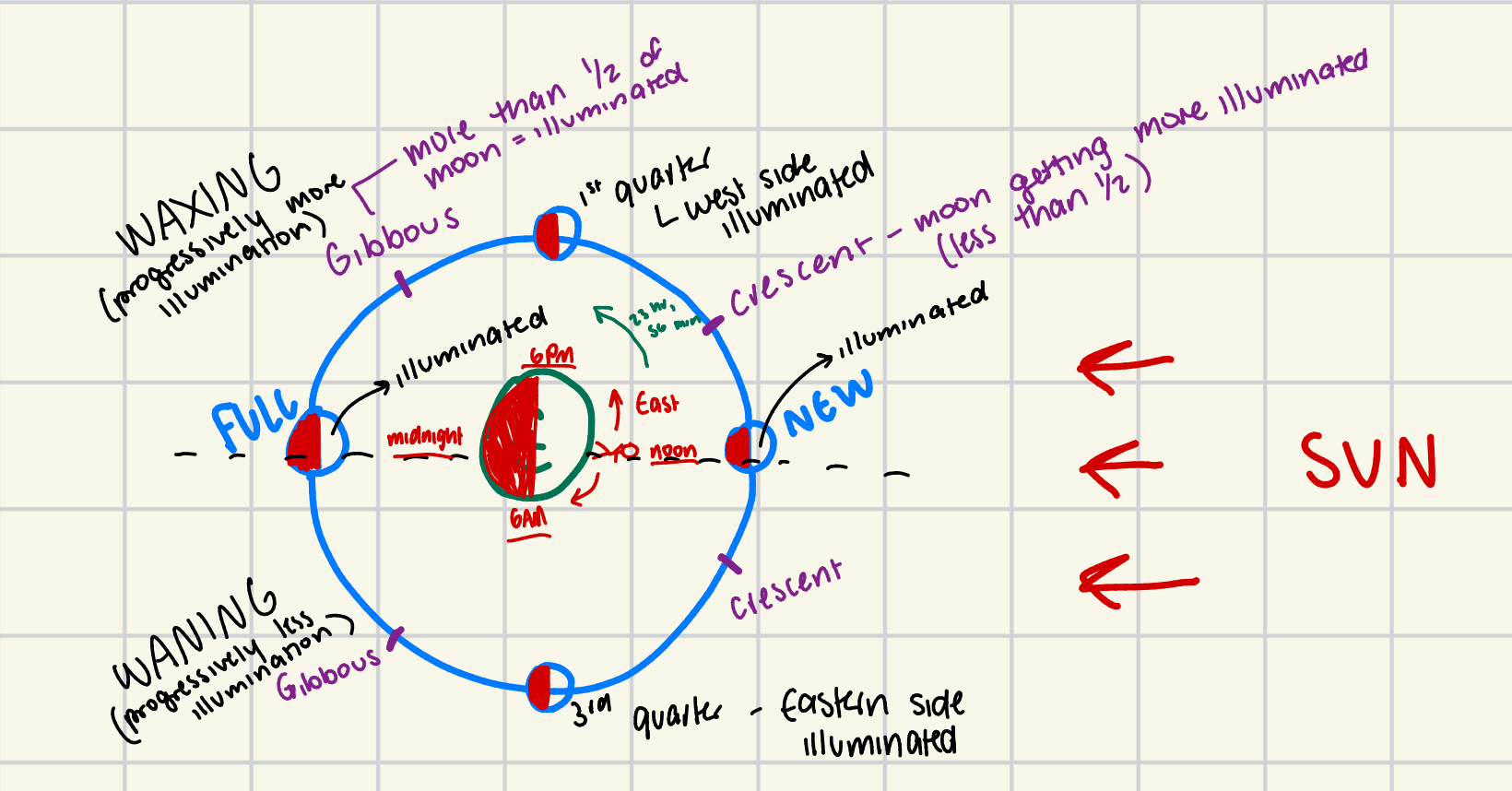
moon phase diagram
sunlight = EAST;
ORBIT = perfect circle because the size of moon and distance from earth stays constant–COUNTERCLOCKWISE/EAST
waxing phase = progressively more illumination (MOON RISING IN THE EAST/NIGHTFALL);
waning phase = progressively less illumination (MOON SETS IN THE WEST/DAYBREAK);
Full moon (midnight) = light side of moon facing earth (WEST);
New moon (noon) = dark side of moon facing earth (EAST);
equinox
“equal night”;
sun is above horizon for 12 hrs/is below horizon for 12 hrs
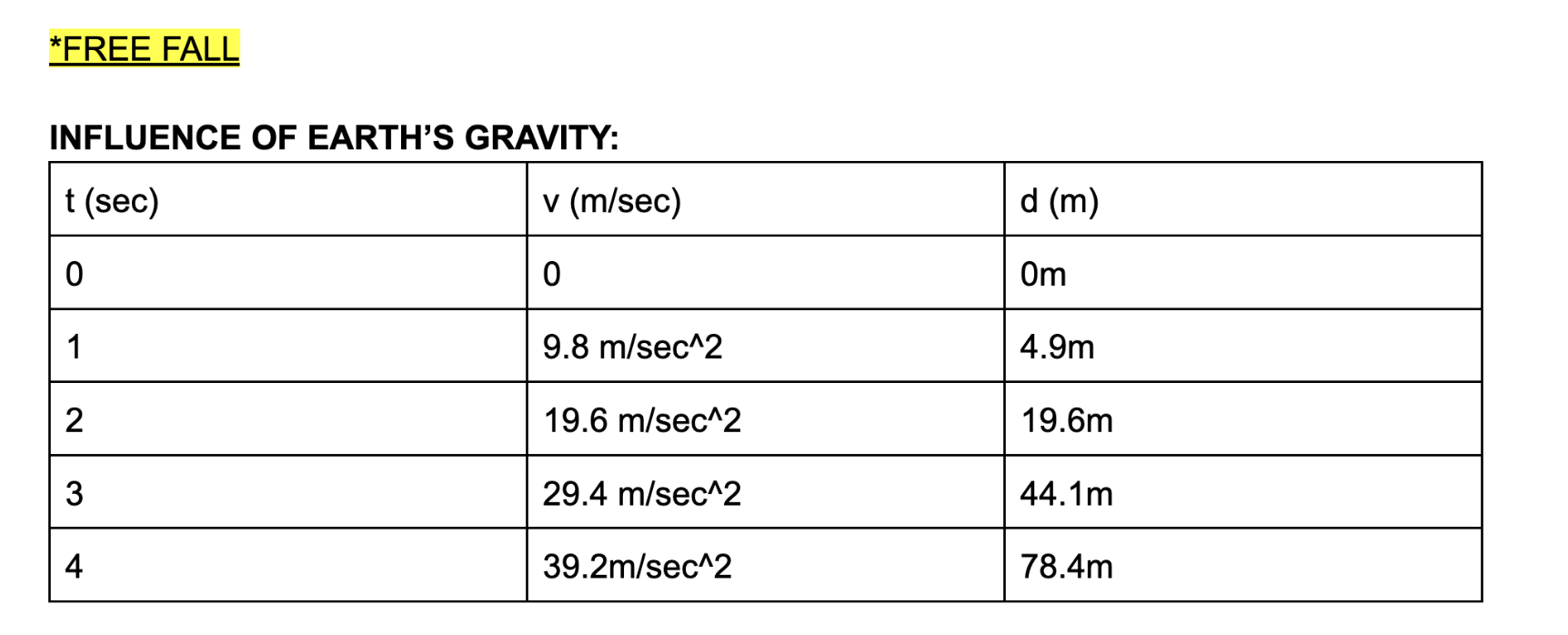
gravity (FREE FALL (m))
g = 9.8 m/s
Gravity between two masses
Fgrav = g(m1)(m2)/d²
Gravity and the distance between Sun and Moon
Double one mass → F(grav) WOULD DOUBLE–MASS EFFECTS GRAVITY LINEARLY;
Double both masses → F(grav) WOULD INCREASE 4x;
Double distance → F(grav) DECREASES 4x–INVERSE SQUARE
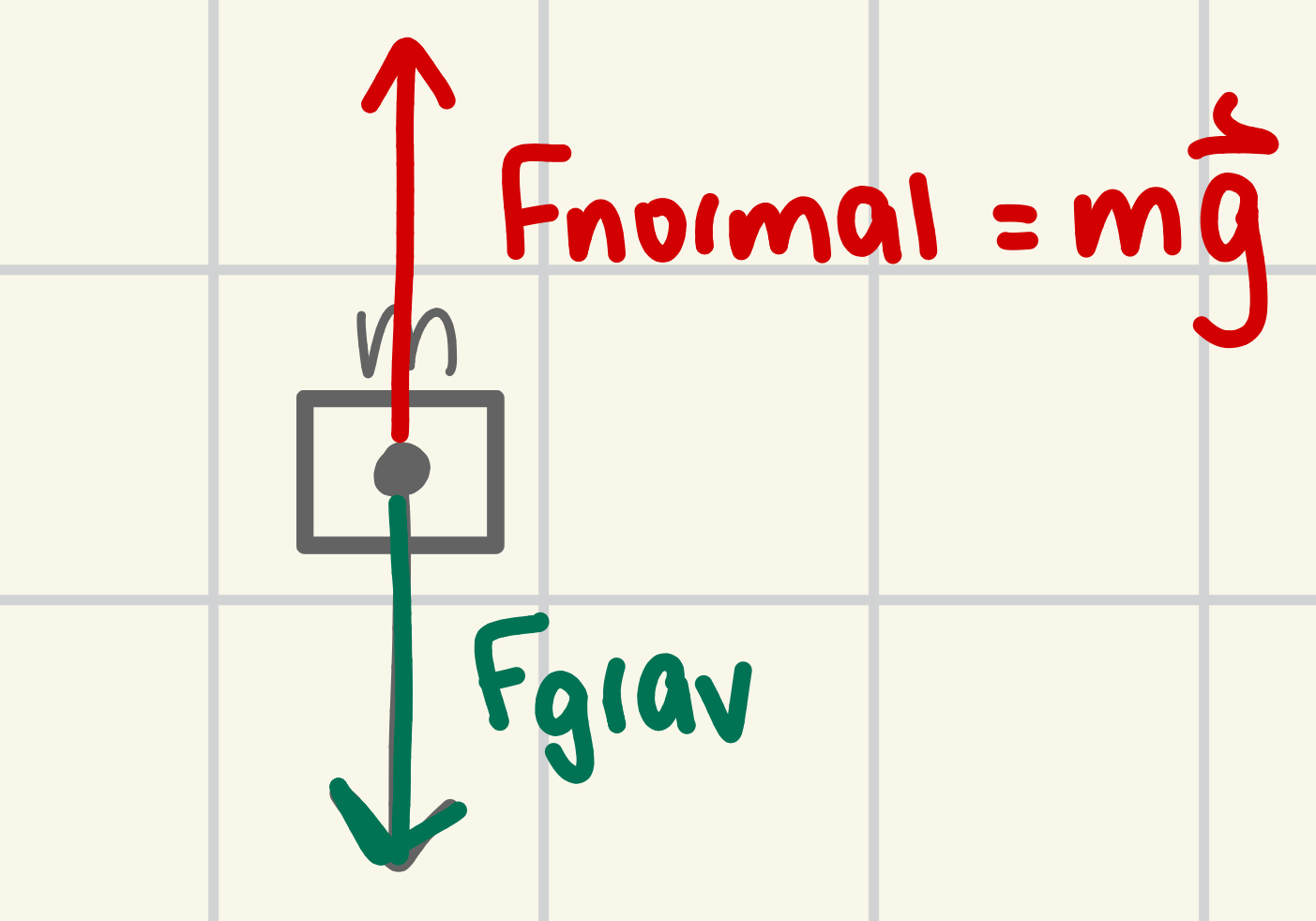
Static motion (forces)
ALL FORCES BALANCED;
Fn + Fgrav = 0
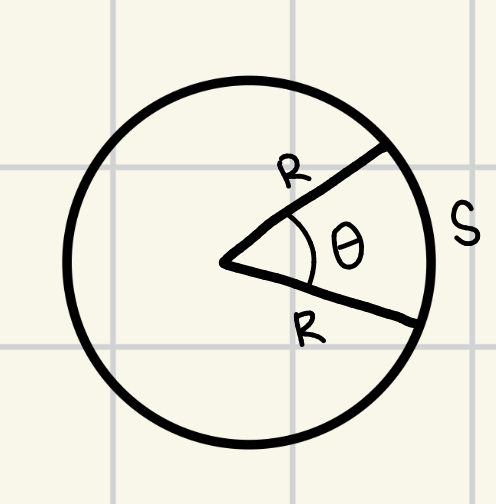
distance (arch length) (s)
s/θ = 2πR/360° → s = θ (2πR/360°)
Measuring planet radius (arc length): R = radius (degrees); θ/a = relative size (degrees); s = arch length/distance
s/θ = 2πR/360° ; R = 180(s)/πθ
dynamic motion
FORCES = UNBALANCED (tension, etc)
GUESS method
Givens
Units
Equation
Substitue
Solve
gravity (FORCE (ft))
tan(θ)
opp(θ)/adj(θ)
sin(θ)
opp/hyp
cos(θ)
adj/hyp
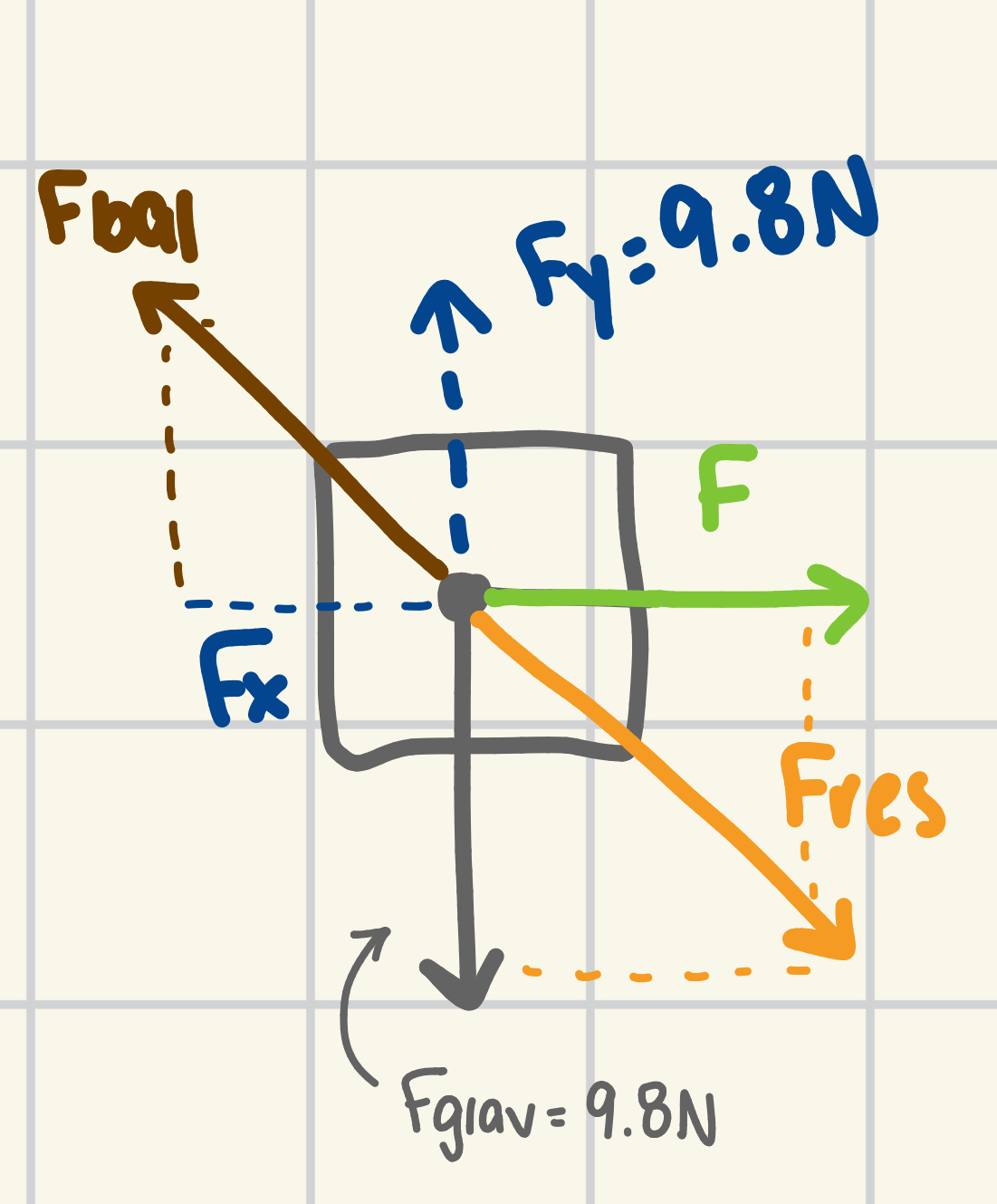
forces & formulas
Fbal² = (Fx)² + (Fy)²
θ (angle) → trig functions
Coriolis effect
deflection of a moving object's path caused by the rotation of the Earth or another rotating system
veering Eastward from equator
veering westward from North pole
What direction is earth’s motion?
COUNTERCLOCKWISE
Foucault pendulum - how it works
Pendulum hanging 4 stories down;
Pendulum stays in motion, area around it shifts with earth’s rotation
12 hrs = 180 degree rotation
Earth’s radius
4000 miles
Earth’s circumfrance
24,000 miles
Apex (top of motion) velocity
v = 0
Net force
difference between (unbalanced) opposing forces
use when solving for acceleration in motion problems—Fnet=ma
Friction in motion problems (v and a)
acceleration (a) = CONSTANT
velocity (v) is NOT constant
Friction
force that opposes/resists motion–drag; air
the faster objects move, the sronger it gets
intertia
object’s tendency to resist change in motion (mass)
Smaller mass = faster acceleration
More mass = more inertia
Earth’s diameter
8000 miles
Proofs the Earth orbits the sun
parallax
abberation of starlight
tides
seasons
What was Aristotle’s proof that the Earth orbits the Sun?
parallax