Unit 1.1 Introduction to Economics
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Government
A political authority that decides how a country is run and manages its operations
Consumer
A person, group or organisation that directly buys and uses a good or service
Producer
A person, company or country that makes, grows or supplies goods and/or services
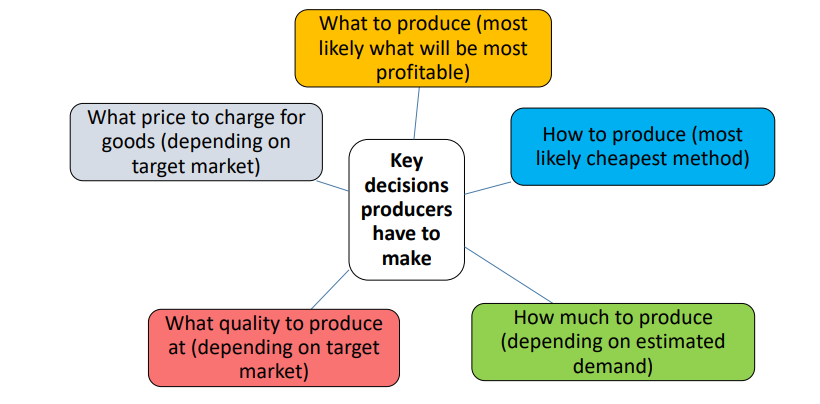
Key decisions producers have to make
Impact of the government on a country
Tax - e.g. rate of income tax and VAT to charge (to gain income)
Spending - e.g. how much spending to allocate to schools, NHS(healthcare)
Laws - e.g. passing Acts to protect consumers, workers, the environment
Redistributing income - e.g. taxing high income groups more and providing benefits to low income groups
Trade - e.g. developing free trade contracts with the rest of the world following Brexit vote
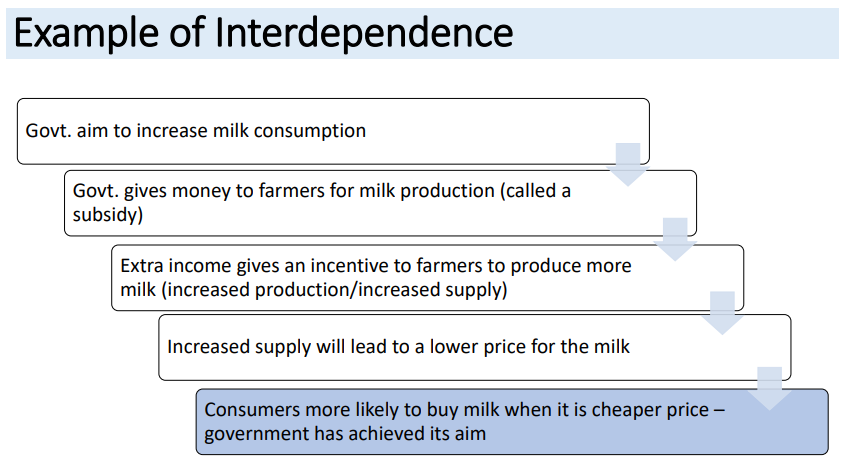
Interdependence
Where one or more economic groups respond to the actions of another economic group
Example of Interdependence
• Due to an increased population there is more demand for housing from
consumers
• This has increased house prices
• This has encouraged more house builders (eg Bovis) to increase the number of
houses they are building (increase supply)
• This has helped the government as more people are in work (eg brick layers,
plasterers) and tax revenue will rise
Good
A tangible product that can be seen or touched, e.g. a mobile phone, car, washing machine, tablet
Service
An intangible product that cannot be seen or touched, a task performed for a a payment, e.g. financial advice, haircut, train journey, holiday, meals out
Factors of production
The resources in an economy that can be used to make goods and services
Capital
Enterprise
Land
Labour
Capital
Human-made aids to production
Examples: Infrastructure includes human made capital Tractors that supports the operation of the production Robots process. E.g. roads,rail,airports
Machines
Enterprise
Where the other factors of production are organised to make goods
and services.
Entrepreneurs are the individuals who:
• Organise production
• Bear the risks of the project
Land
All natural resources in an economy.
Land includes:
• Oil
• Cotton
• Honey
Renewable resources are those that
can be replaced over time if they are
not over used eg wood/forests
Non-renewable resources are those
that cannot be replaced once used eg
coal
Labour
All human resources which make up the workforce
Labour depends on:
1.Size of working
population
2.Immigration/
emigration
3.Quality of labour
(skills, training,
qualifications and
health of workers)
Capital Intensive
Uses a large proportion of capital compared to labour to produce products, it involves the use of machines, robots, computer-aided manufacture.
Labour Intensive
Uses a large proportion of labour compared to capital to
produce products.