AP World History Modern Unit 3
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Qing Dynasty of China
The last imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Ming Dynasty and succeeded by the People's Republic. Formed the territorial base for the modern Chinese state. Founded in 1644 by the Manchus and ruled China for more than 260 years, until 1912. Expanded China's borders to include Taiwan, Tibet, Chinese Central Asia, and Mongolia.
Manchus
Northeast Asian peoples who defeated the Ming Dynasty and founded the Qing Dynasty in 1644, which was the last of China's imperial dynasties.
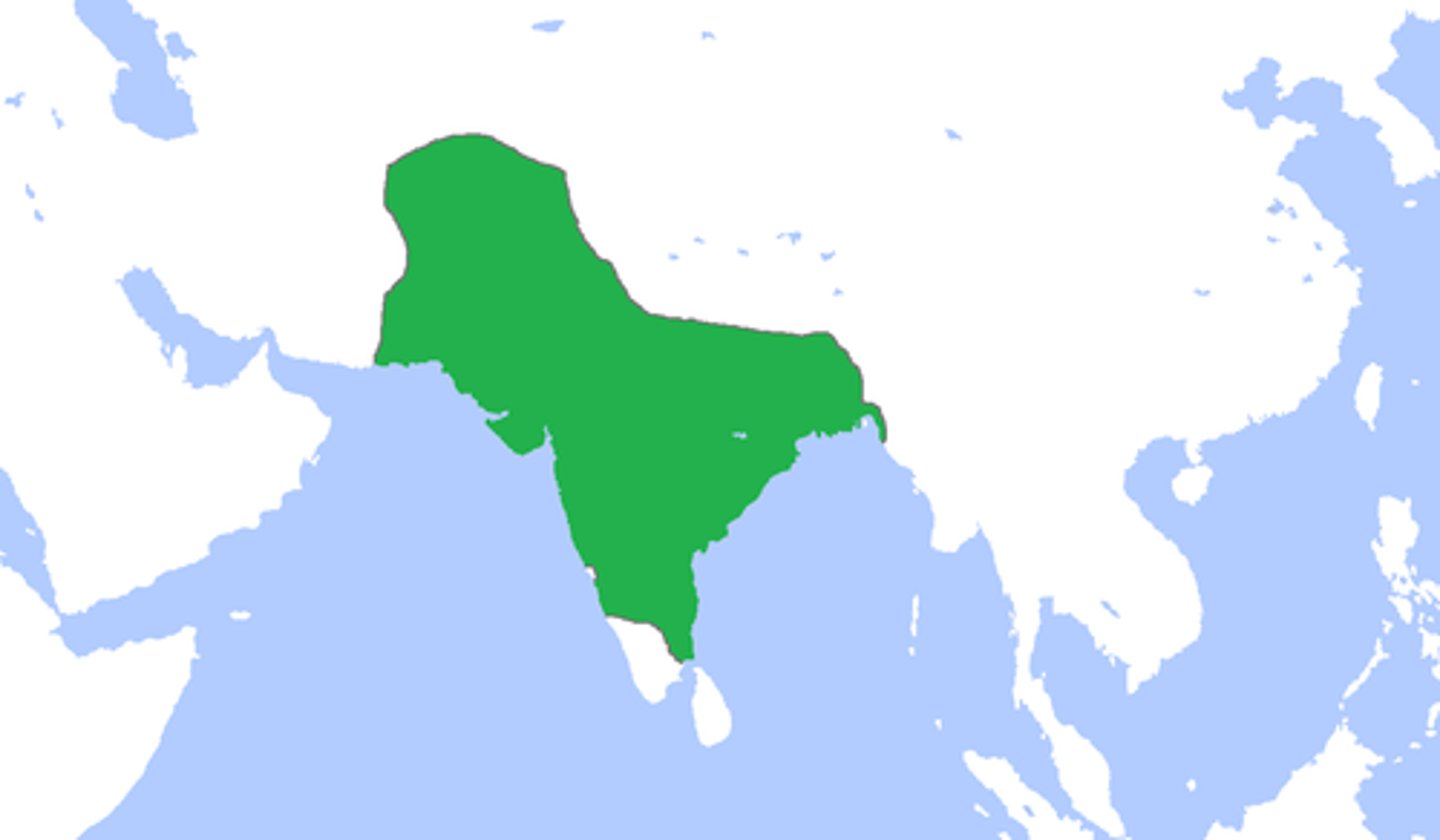
Mughal Empire
Muslim state (1526-1857) exercising dominion over most of India in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.
Ottoman Empire
Islamic state founded by Osman in northwestern Anatolia. After the fall of the Byzantine Empire, the Ottoman Empire was based at Istanbul (formerly Constantinople) from 1453-1922. It encompassed lands in the Middle East, North Africa, the Caucasus, and eastern Europe.

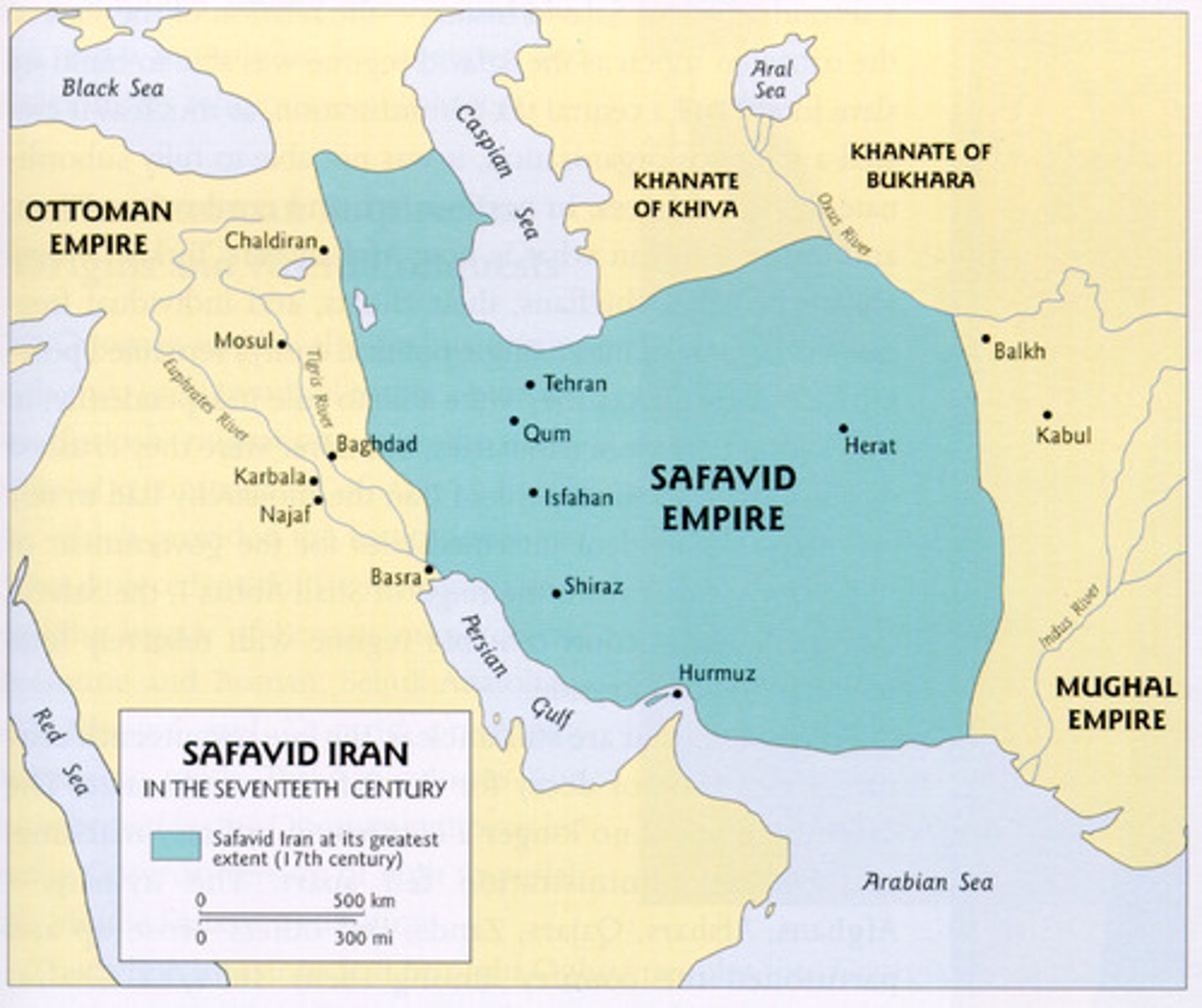
Safavids
A Shi'ite Muslim dynasty that ruled in Persia (Iran and parts of Iraq) from the 16th-18th centuries that had a mixed culture of the Persians, Ottomans and Arabs.
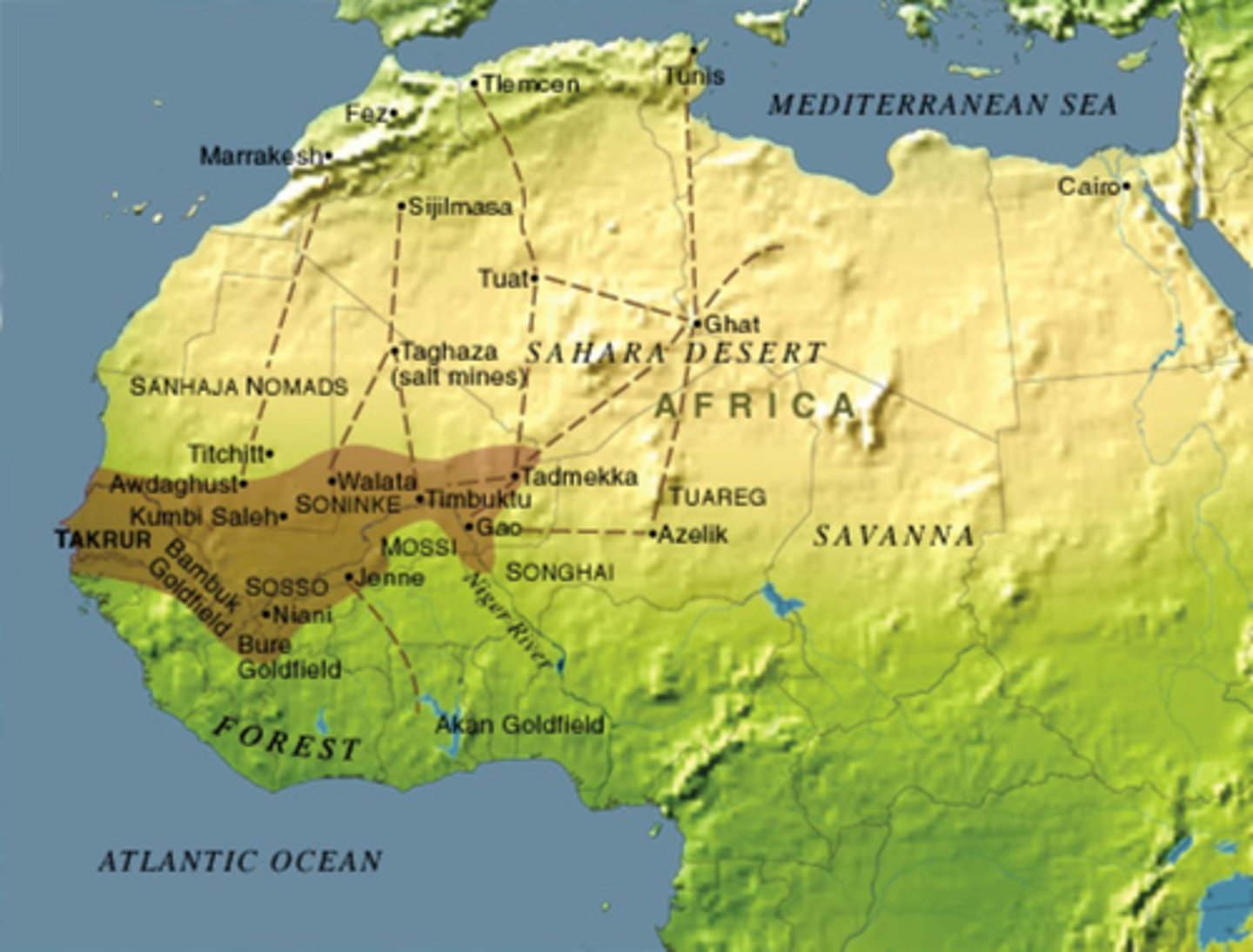
Songhai
a West African empire that conquered Mali and controlled trade from the into the 16th century; eventually defeated by the Moroccans who were broke after fighting with Portugal
Devshirme
'Selection' in Turkish. The system by which boys from Christian communities were taken by the Ottoman state to serve as Janissaries (elite military units utilized by the Ottomans)
Janissary
elite Ottoman guard (trained as foot soldiers or administrators) recruited from the Christian population through the devshirme system, that often converted to Islam
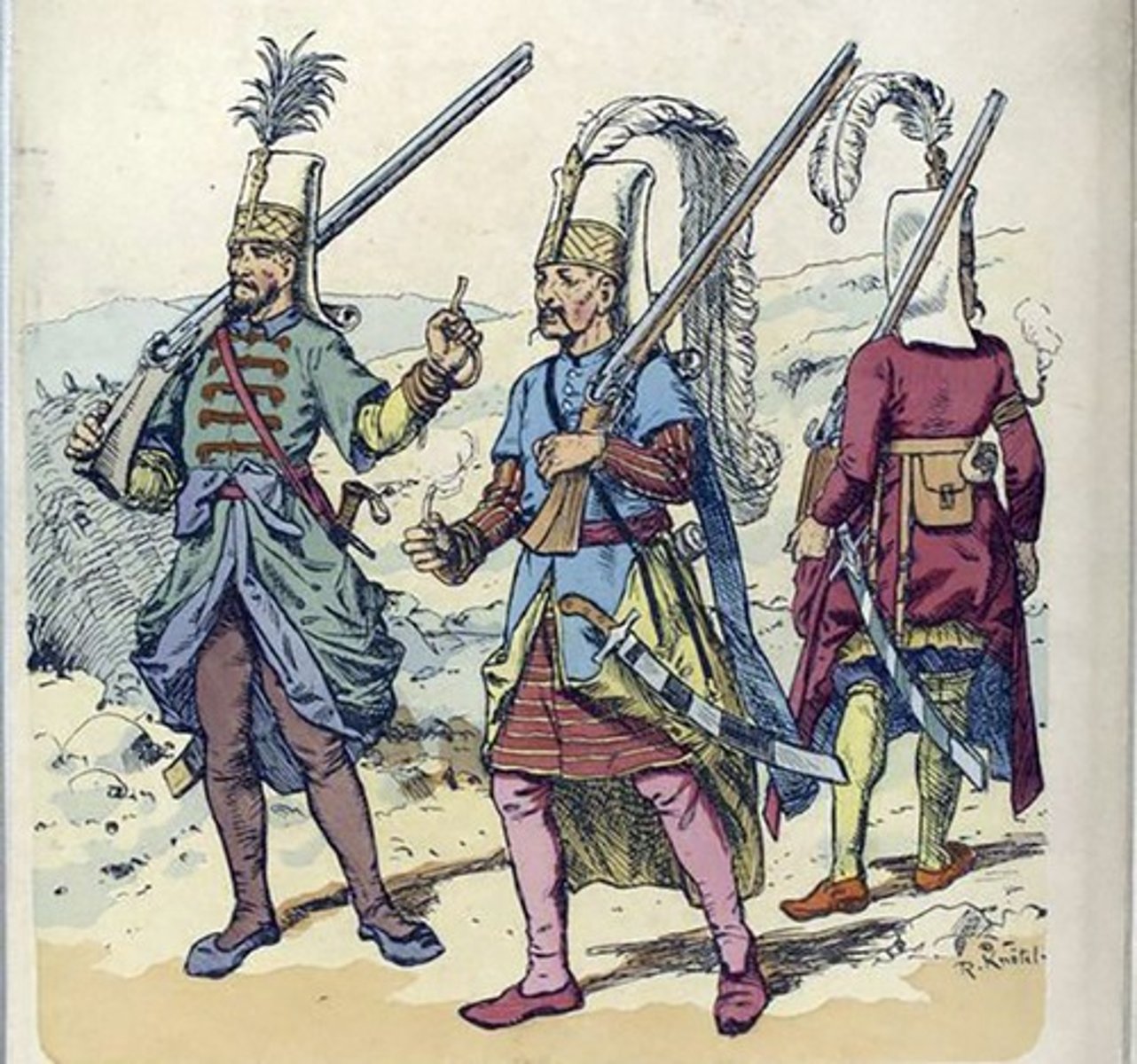

Samurai
Class of warriors in feudal Japan who pledged loyalty to a noble in return for land.

Divine Right
the idea that monarchs are God's representatives on earth and are therefore answerable only to God.

Absolute Monarchy
A system of government in which the head of state is a hereditary position and the king or queen has almost complete power
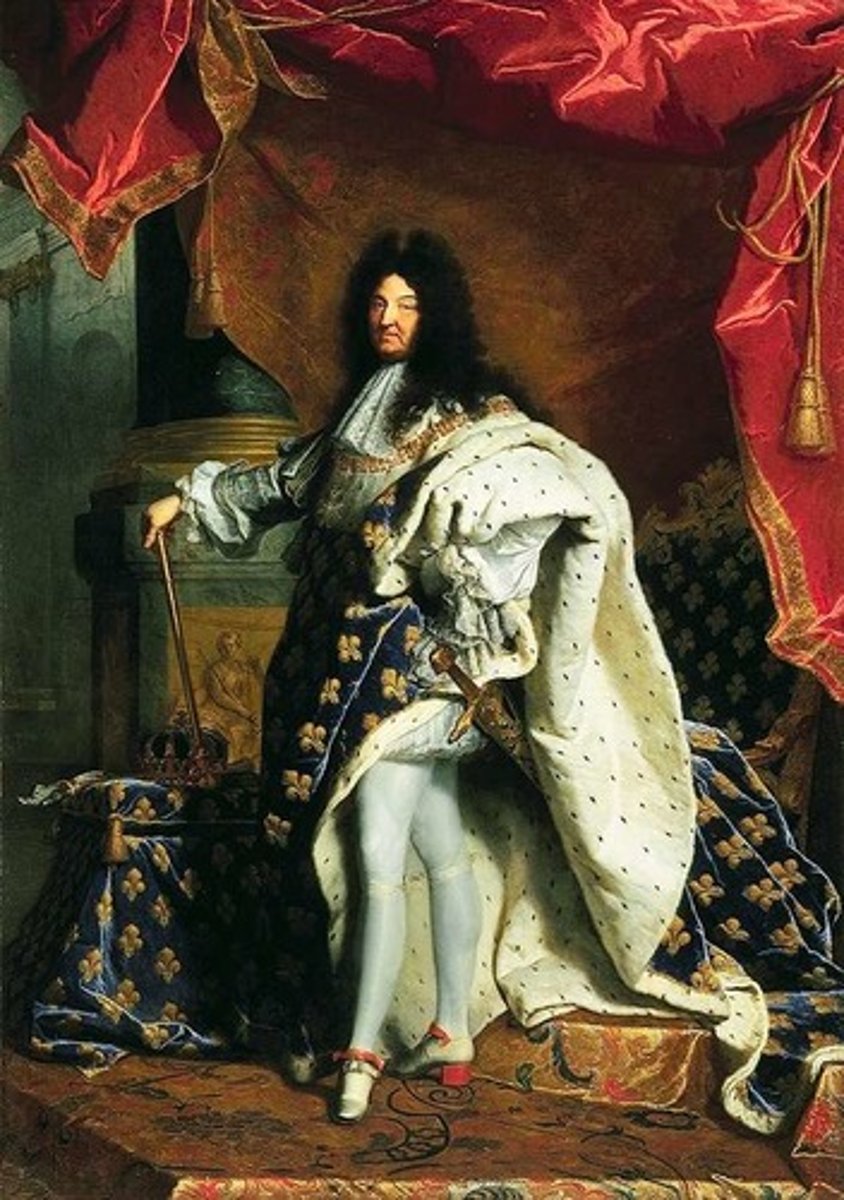

Versailles
Palace constructed by Louis XIV outside of Paris to glorify his rule and subdue the nobility.
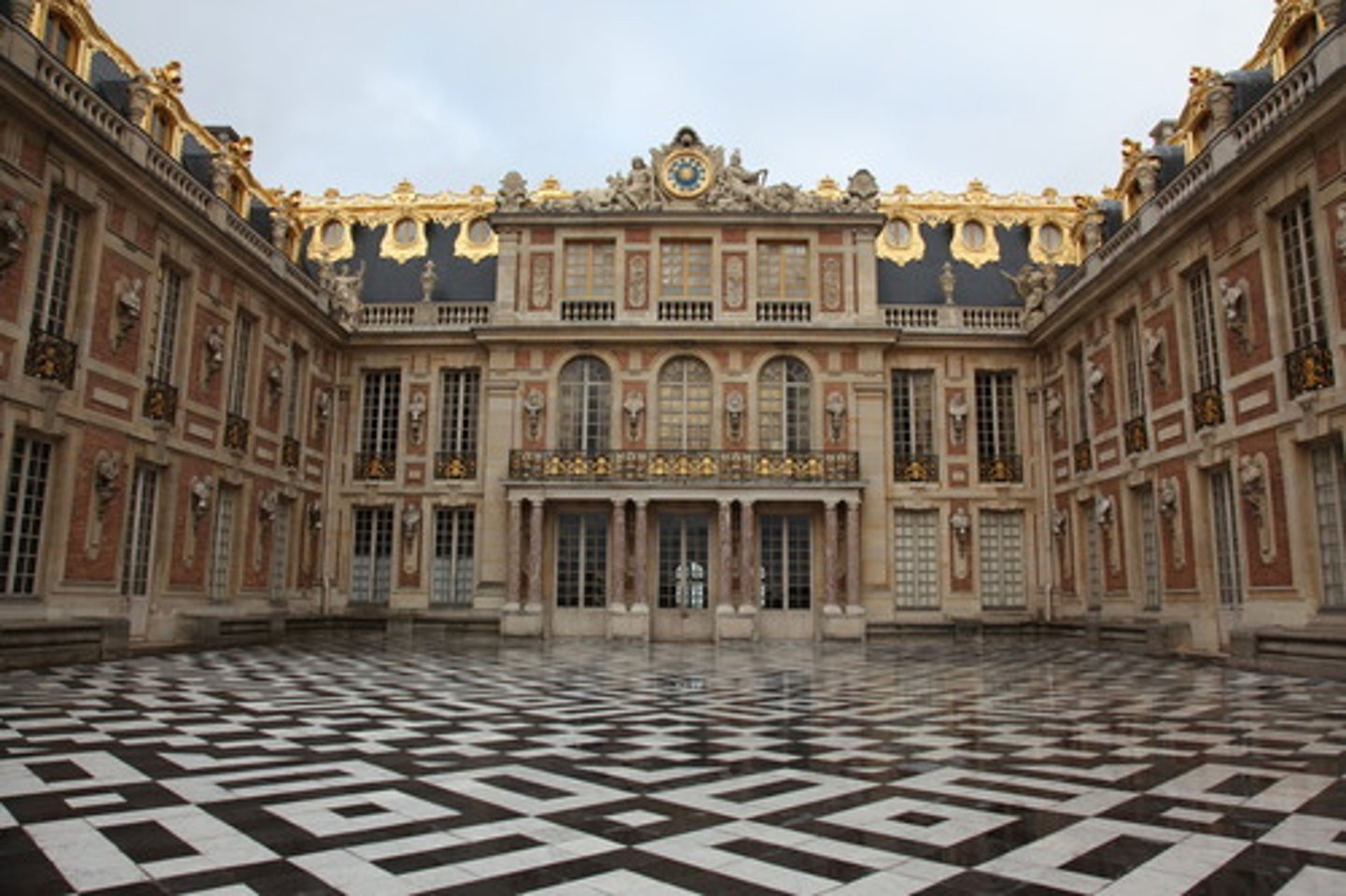

Zamindars
Archaic tax system of the Mughal empire where decentralized lords collected tribute for the emperor.
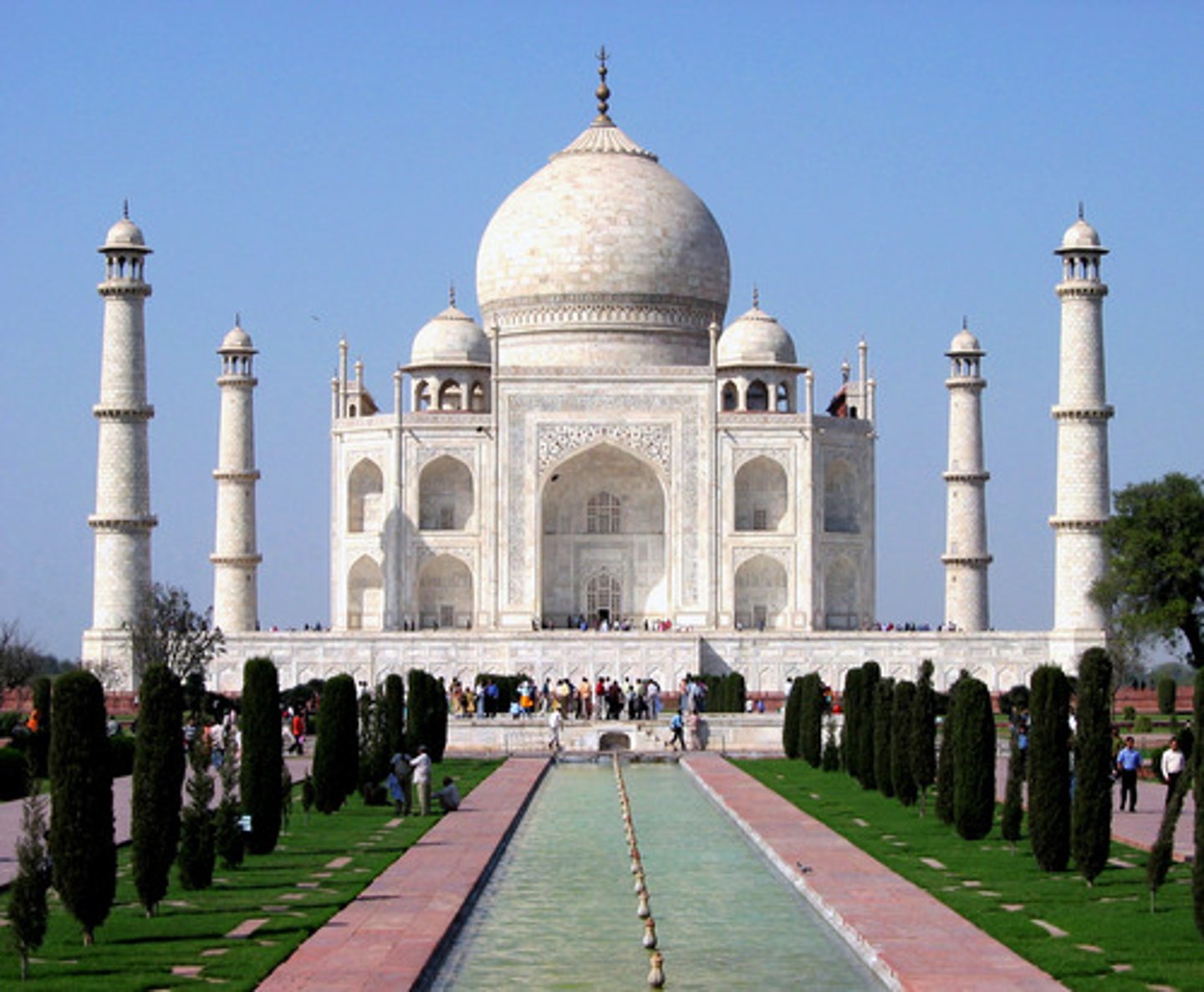
Taj Mahal
beautiful mausoleum (tomb) at Agra (India) built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan (completed in 1649) in memory of his favorite wife; illustrates syncretic blend between Indian and Arabic architectural styles

Tax farming
To generate money for territorial expansion Ottoman rulers used this tax-collection system. Under this system the government hires private individuals to go out and collect taxes for them.
Protestant Reformation
Religious reform movement begun by Catholic monk Martin Luther who began to question the practices of the Latin Christian Church beginning in 1519. It spit the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the 'protesters' forming several new Christian denominations, including the Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican Churches, among many others.
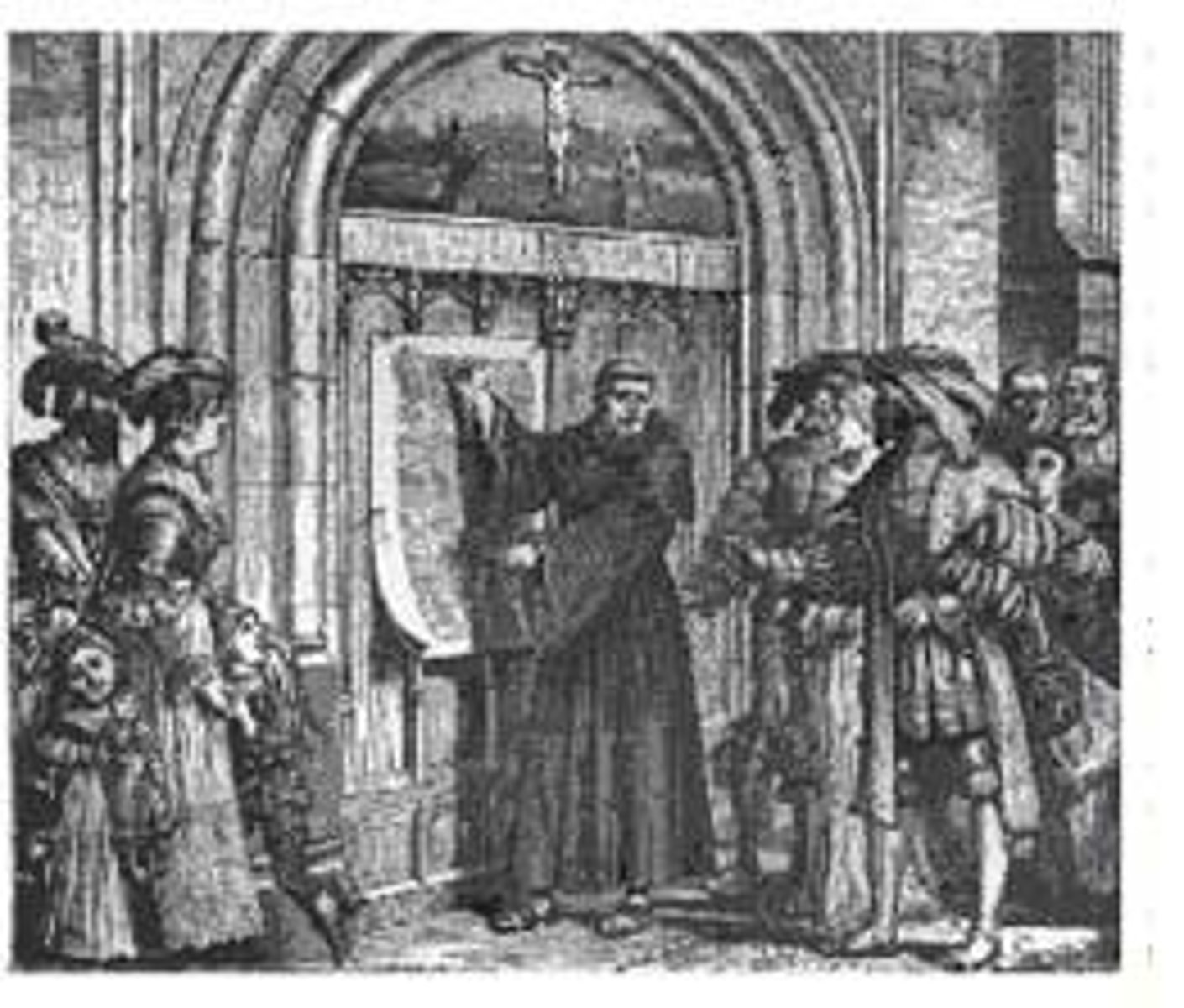

95 Theses
Arguments written by Martin Luther against the Catholic church. They were posted on October 31, 1517; ultimately led to Martin Luther's excommunication
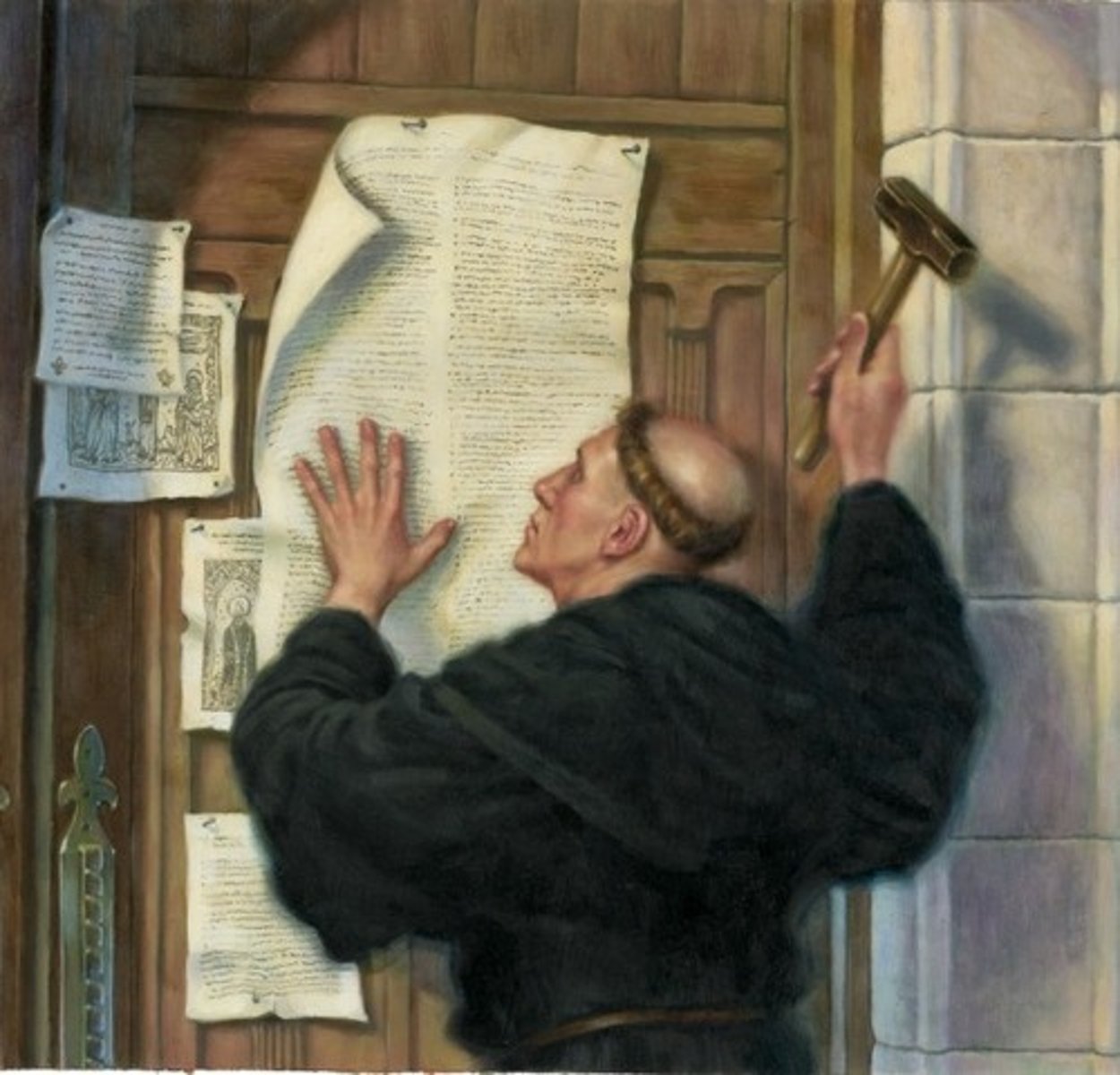

Martin Luther
a German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic Church. In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief attacking the church practices. Began the Protestant Reformation

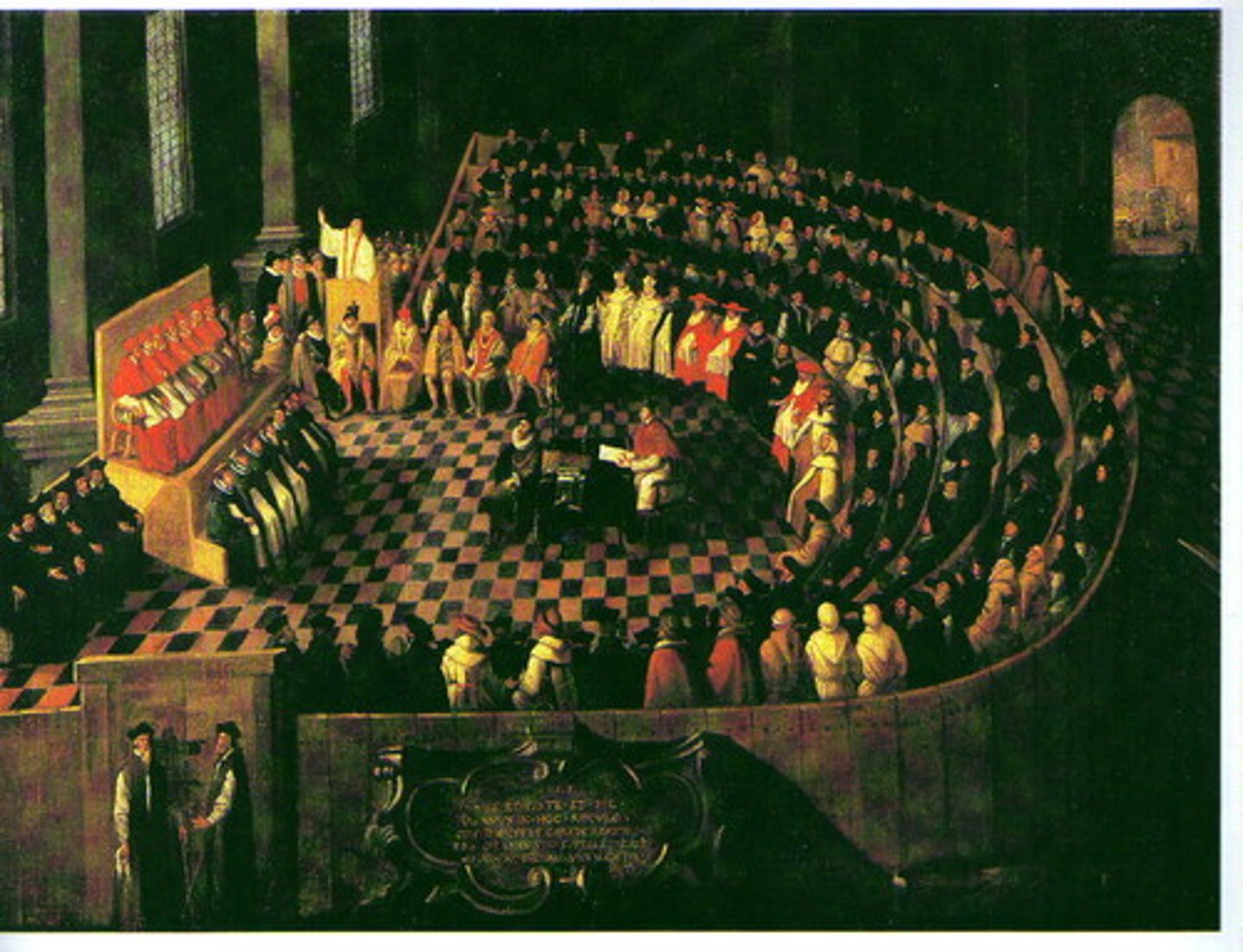
Counter or Catholic Reformation
the reaction of the Roman Catholic Church to the Reformation reaffirming the veneration of saints and the authority of the Pope (to which Protestants objected), ended sale of indulgences and simony, created Jesuits, but also the Inquisition
Jesuits
Also known as the Society of Jesus; founded by Ignatius Loyola (1491-1556) as a teaching and missionary order to resist the spread of Protestantism (a result of the Counter Reformation); were often sent to China, Japan, and around the world to gain Catholic converts

Indulgence
A pardon given by the Roman Catholic Church in return for repentance for sins
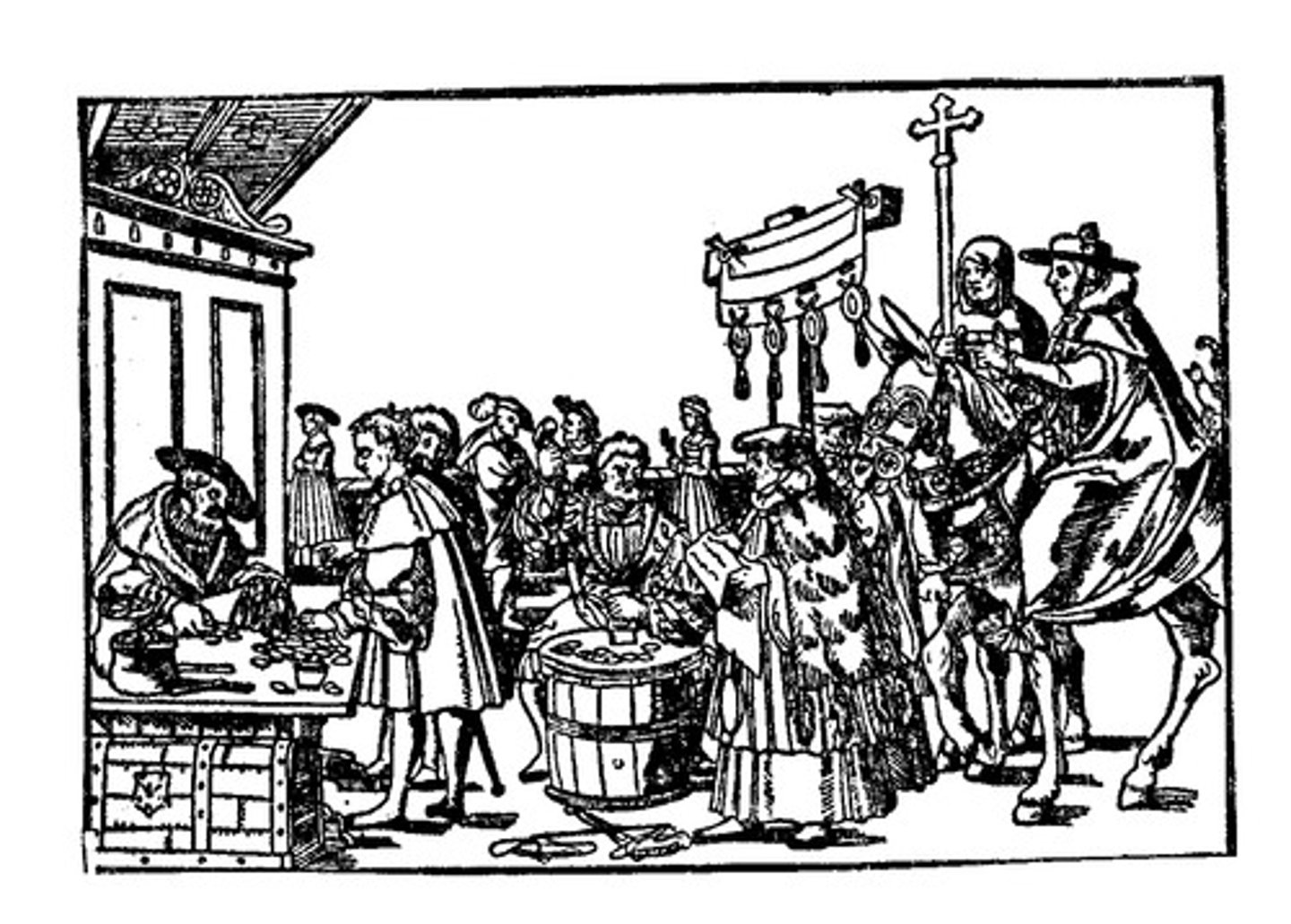

Simony
the buying and selling of church offices
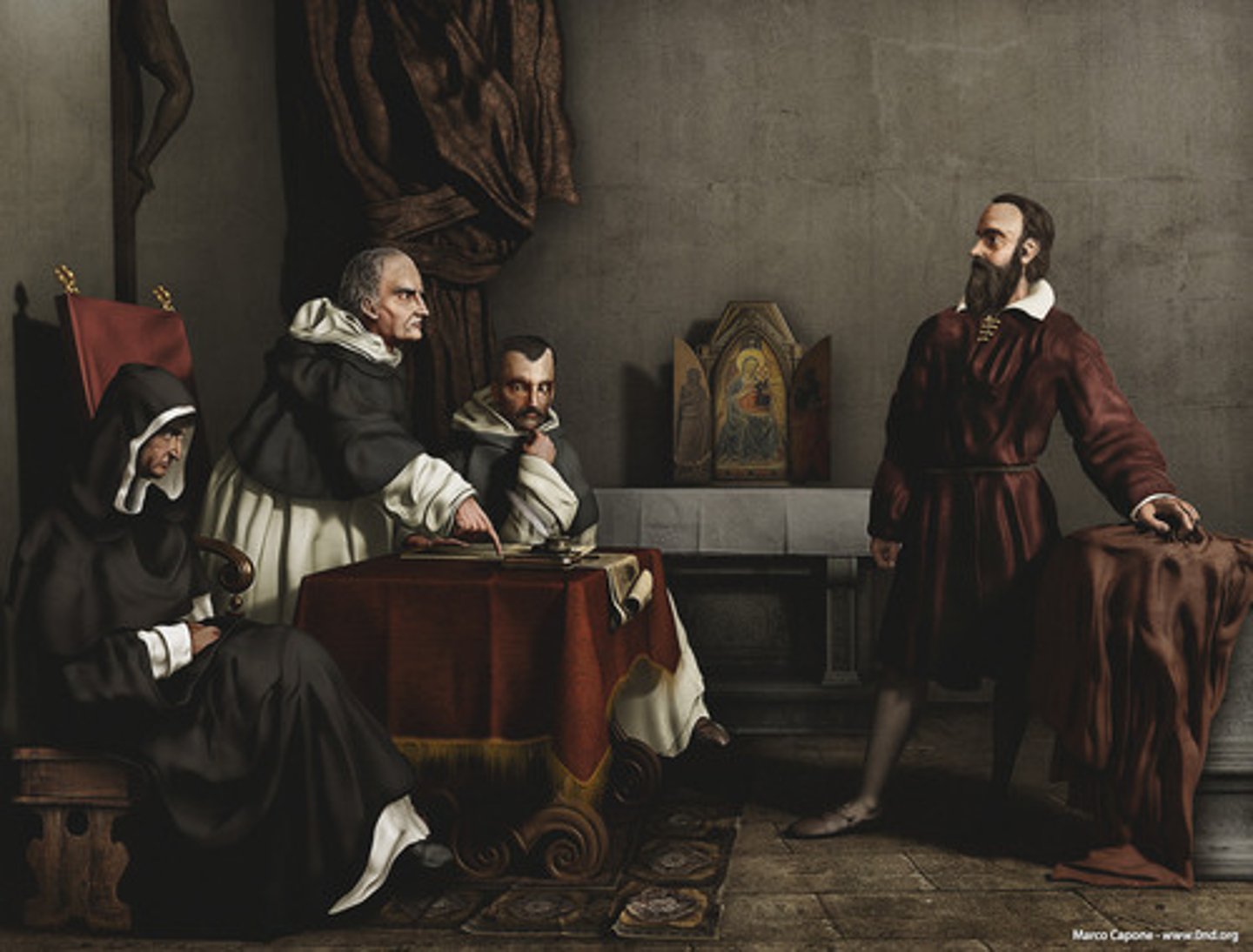
Inquisition
A Roman Catholic tribunal for investigating and prosecuting charges of heresy, a reaction to the Protestant Reformation

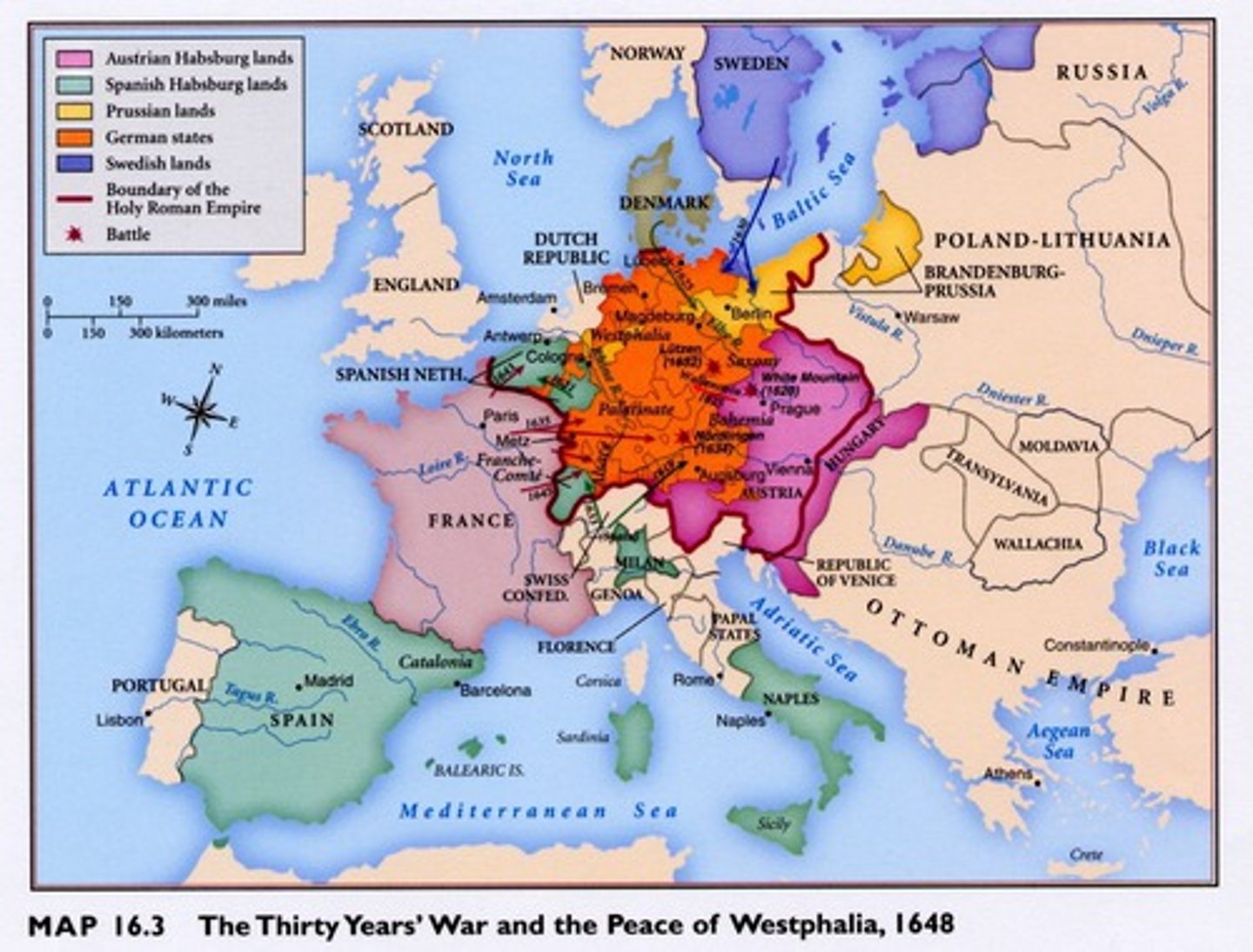
Thirty Years War
(1618-1648 CE) War within the Holy Roman Empire between German Protestants and their allies (Sweden, Denmark, France) and the emperor and his ally, Spain who supported Roman Catholicism; ended in 1648 after great destruction with Treaty of Westphalia; indicates the effects of the Protestant Reformation
John Calvin
1509-1564. French theologian. Developed the Christian theology known as Calvinism. Attracted Protestant followers with his teachings; believed in predestination

Sikhism
the doctrines of a monotheistic religion founded in northern India in the 16th century by Guru Nanak and combining elements of Hinduism and Islam; a result of the presence of the Mughal Empire in India
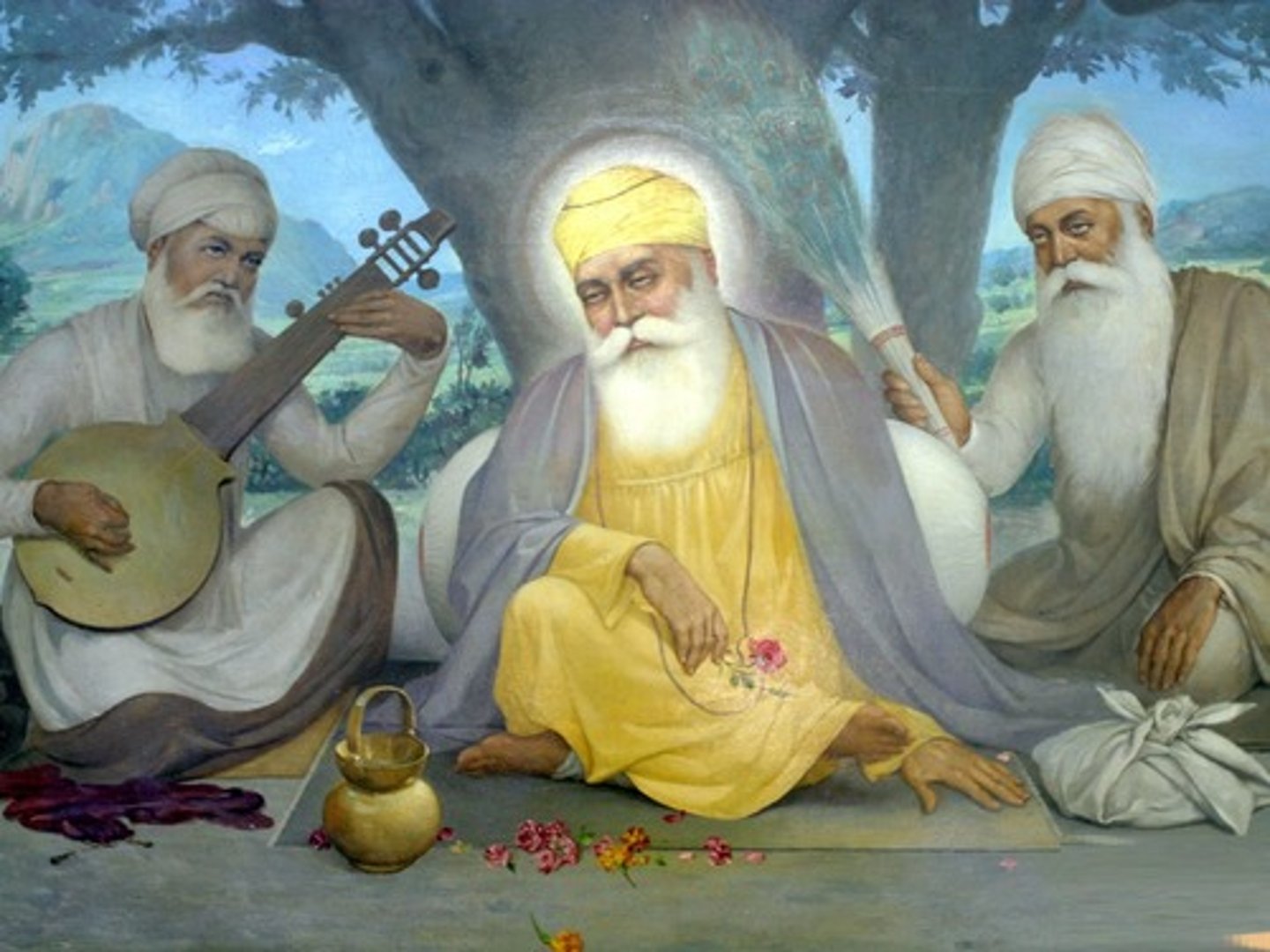

Shogunate
The Japanese system of government under a shogun (military warlord), who exercised actual power while the emperor was reduced to a figurehead.

Byzantine Empire
(330-1453) The eastern half of the Roman Empire, which survived after the fall of the Western Empire at the end of the 5th century C.E. Its capital was Constantinople - Now named Istanbul
Persians
Ethnic group that settled in what is now Iran. They were rivals for control of Mesopotamia with the Greeks, and later the Arabs.
Shia Islam
The sect of Islam practiced primarily in Persia
Sunni Islam
Most Muslims are of this denomination of Islam
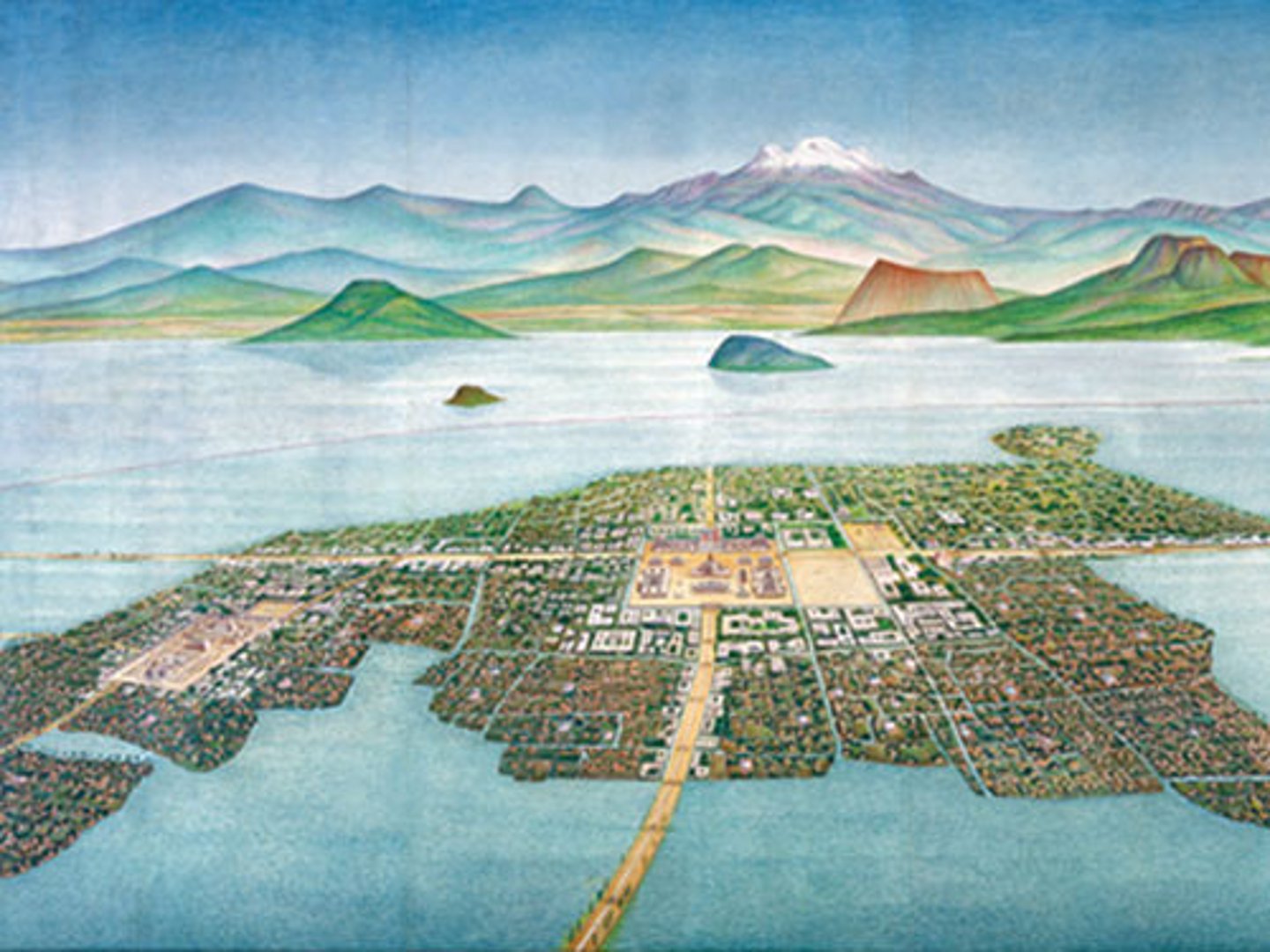
Tenochtitlan
Capital of the Aztec Empire, located on an island in Lake Texcoco. Its population was about 150,000 on the eve of Spanish conquest. Mexico City was constructed on its ruins.
Timbuktu
City on the Niger River in the modern country of Mali. It was founded by the Tuareg as a seasonal camp sometime after 1000. As part of the Mali empire, Timbuktu became a major major terminus of the trans-Saharan trade and a center of Islamic learning.
Peter the Great
(1672-1725) Russian Tsar (r. 1689-1725). He enthusiastically introduced Western languages and technologies to the Russian elite, moving the capital from Moscow to the new city of St. Petersburg.
Eastern Orthodox Church
Christian followers in the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire); split from Roman Catholic Church and shaped life in eastern Europe and western Asia
Cossacks
Peoples of the Russian Empire who lived outside the farming villages, often as herders, mercenaries, or outlaws. Cossacks led the conquest of Siberia in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.
Boyars
Russian landholding aristocrats; possessed less political power than their western European counterparts
Hagia Sophia
Most famous example of Byzantine architecture, it was built under Justinian I and is considered one of the most perfect buildings in the world. Converted into a Mosque by the Ottomans.
Shari'ah
a law code drawn up by Muslim scholars after Muhammad's death; it provided believers with a set of practical laws to regulate their daily lives
Gutenberg Printing Press
used movable type to print, increased literacy and helped spread the Reformation

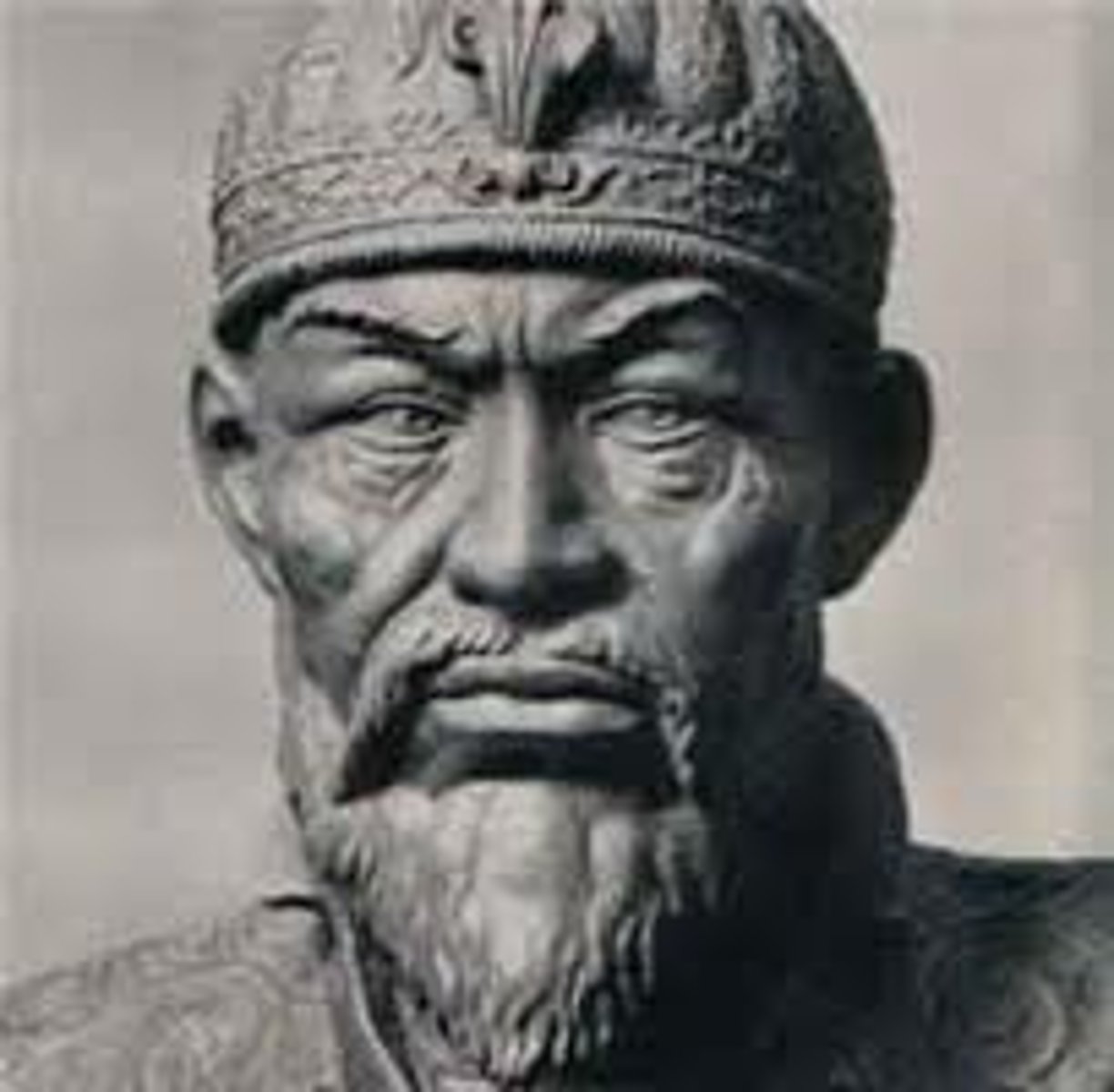
Ivan IV
Known as IVT, beat the Mongols, Tartars, and the Poles, forced nobles into service, first ruler to take the title tsar
Ming Dynasty
Succeeded Mongol Yuan dynasty in China in 1368; lasted until 1644; initially mounted huge trade expeditions to southern Asia and elsewhere, but later concentrated efforts on internal development within China.
Emperor Qianlong
Qing emperor who refused to open more trading ports to Europe. Sent Military Campaigns in lands west of China (Xinjiang) and committed atrocities against Uighur Muslims. Failed Campaigns against Burma and Vietnam.
Tamerlane
Mongol leader who conquered Persia and Mesopotamia

Ghazi ideal
a model for warrior life that blended the cooperative values of nomadic culture with the willingness to serve as a holy fighter for Islam
Mehemed II
Ottoman ruler who conquered Constantinople in 1453 and renamed it Istanbul
Suleiman
Great Ottoman leader, expanded land area of Ottomans, and restructured system of law.
Shah
Persian word for king
Abbas I
Persian Shah who ruled over the Safavids at its height. Imported weaponry and European knowledge to advise his troops. Used Shia Islam as a unifying force.
Castes
social groups into which people are born and cannot change
Harem politics
Efforts of wives and concubines who held successors to Sultan hostage to promote their own children.
Justices of the Peace
Officials selected by the landed gentry to maintain peace in English Counties. Settle legal matters and carry out monarch's laws.
English Bill of Rights
King William and Queen Mary accepted this document in 1689. It guaranteed certain rights to English citizens and declared that elections for Parliament would happen frequently. By accepting this document, they supported a limited monarchy, a system in which they shared their power with Parliament and the people.
Cardinal Richelieu
Chief minister of France who reduced the power of the nobles
Intendents
royal officials that were sent to the provinces to execute the orders of the central government. They further strengthened the power of the King in France
Boyars
Noble landowning class of Russia
Oprichnina
The secret army/police created by Ivan IV or Ivan the Terrible that he used to kill anyone who got in his way (i.e. the Boyars)
Serfdom
Peasants who could not pay debts and where attached to a piece of land to work until debt was paid off.
Peter I (the Great)
Russian Tsar who modernized Russia. Built St. Petersburg and took away power from the Eastern Orthodox church.
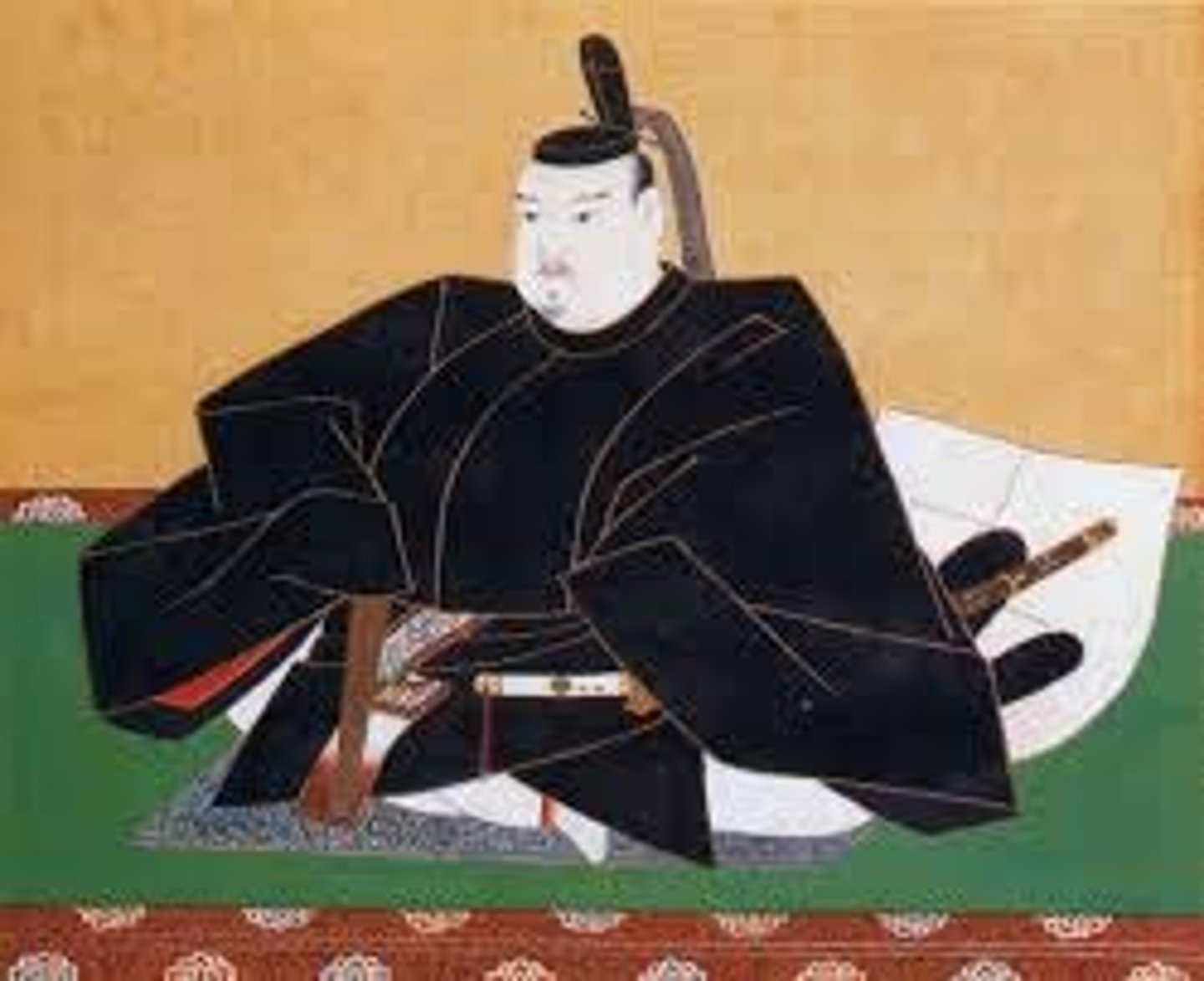
Tokagawa Shogunate
Military rulers of Japan who successfully unified Japan politically by the early 17th century and established a "closed door" policy toward European encroachment. Tough on Daiymo.
Tributes
wealth sent from one country or ruler to another as a sign that the other is superior
Henry VIII
English king who created the Church of England (Anglicanism) after the Pope refused to annul his marriage (divorce with Church approval) in order to marry Anne Boleyn.
Spanish Armada
The great fleet sent from Spain against England defeated by the terrible winds and fire ships.
Peace of Augsburg
1555 agreement declaring that the religion of each German state would be decided by its ruler to be Catholic or Lutheran
Edict of Nantes
Granted the Huguenots liberty of conscience and worship.
Peace of Westphalia
the peace treaty that ended the Thirty Years' War in 1648
Counter Reformation (Catholic Reformation)
response and reforms by the Roman Catholic Church to the Protestant Reformation
1. Inquisition
2. Jesuits
3. Council of Trent
Holy Synod
The replacement Peter the Great created for the office of Patriarch of the Russian Orthodox Church. It was a "bureaucracy of laymen under his supervision."
Council of Trent
Council who corrected abuses in Catholic Church and also banned certain readings
Predistined
The idea that you are already chosen to go to heaven. You known you are predestined by doing things like living plainly, making money, simple lifestyle.
Empiricism
the belief that data should back up a hypothesis.