Anatomy: Integumentary System
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIOL-N 261 Chapter 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Integumentary system
Comprised of the integument (skin) and its accessory structures (hair, nails. sweat, and oil glands)
Skin
Largest organ of the body
Functions of the integument
• Physical protection
• Regulation of body temperature
• Excretion (and secretion)
• Nutrition (synthesis)
• Sensation
• Immune defense
Subcutaneous layer
Deep to the dermis
Epidermis
Stratified squamous epithelium layer of the skin
Dermis
Underlying loose connective tissue layer of the skin
Keratinocytes
The most abundant cell type in the epidermis that produce keratin (tough fibrous proteins) that gives epidermis its protective properties
Keratinocyte properties
• Arise from the deepest layer of epidermis from cells undergoing almost continuous mitosis
• Cells are dead, flat sacs which are completely filled with keratin by the time they reach the surface
Melanocytes
Produce melanin, a dark skin pigment
Merkel cells
Sensory cells that serve as receptors for touch
Langerhans cells
Fixed macrophages that police our outer body surface, using receptor-mediated endocytosis to take up foreign proteins
Thick skin
5 strata
Thin skin
4 strata
Stratum basale or stratum germinativum
• Innermost/deepest basal layer
• Single row of cells consists of basal cells (stem cell keratinocytes)
• Contains Merkel cells and melanocytes
Stratum spinosum
• Comprised of keratinocytes, which contain thick bundles of pre-keratin
• Also contains Langerhans cells
• Keratinocytes in this layer take on a spiky appearance due to the production of tonofibrils
Tonofibrils
Interconnecting proteins located in the stratum spinosum, which increase stability in this layer
Stratum granulosum
• Keratinocytes produce keratohyalin (helps form keratin) and keratin
• Keratin fibers develop as cells become thinner and flatter
• Gradually the cell membranes thicken, the organelles disintegrate, and the cells die
Stratum lucidum
Appears as a “glassy” layer in thick skin only
Stratum corneum
• Multiple layers of flattened, dead, interlocking keratinocytes
• Typically relatively dry
• Water resistant, but not waterproof
Properties of the dermis
• Divided into two layers: papillary and reticular layers
• Richly supplied with nerve fibers and blood vessels
• Functions in nourishment and temperature regulations
Papillary layer
Superficial portion (20%) of the dermis that is comprised of loose areolar connective tissue proper
Dermal papillae
Finger-like pegs which project into the epidermis (Ionizing radiation can make these retract)
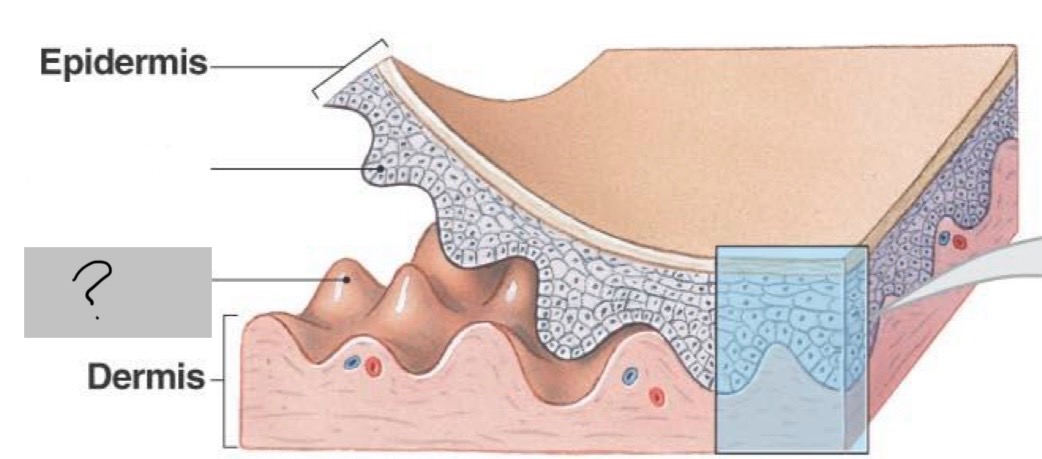
Reticular layer
Deeper 80% layer of the dermis, comprised of dense irregular connective tissue
Reticular layer properties
• Provides strength and resilience to skin
• Blood vessels, glands, muscles, hair follicles and nerves are all found in this layer
Fingerprints
Identical twins have the same DNA, but different ______
Cutaneous plexus
Network of blood vessel at the border of the reticular layer and the subcutaneous layer
Papillary plexus
Highly-branched network of blood vessels just deep to the epidermis
Tactile discs
Formed from the union of a Merkel cell and a sensory nerve ending
Free dendrites
Sensitive to pain and temperature
Factors that determine skin color
• Thickness of the stratum corneum
• Amount of pigments in the epidermis
• Carotene (yellow-orange pigment found in carrots and in green and orange leafy vegetables)
Hypodermis (subcutaneous layer, fatty layer, or superficial fascia)
Layer deep to the skin; not part of the integumentary system but shares some of the skin’s functions
Functions of the hypodermis
• Stores fat
• Anchors the skin to underlying structures
• Acts as an insulator
Arrector pili muscle
Allows movement of hairs, as in “goose bumps’
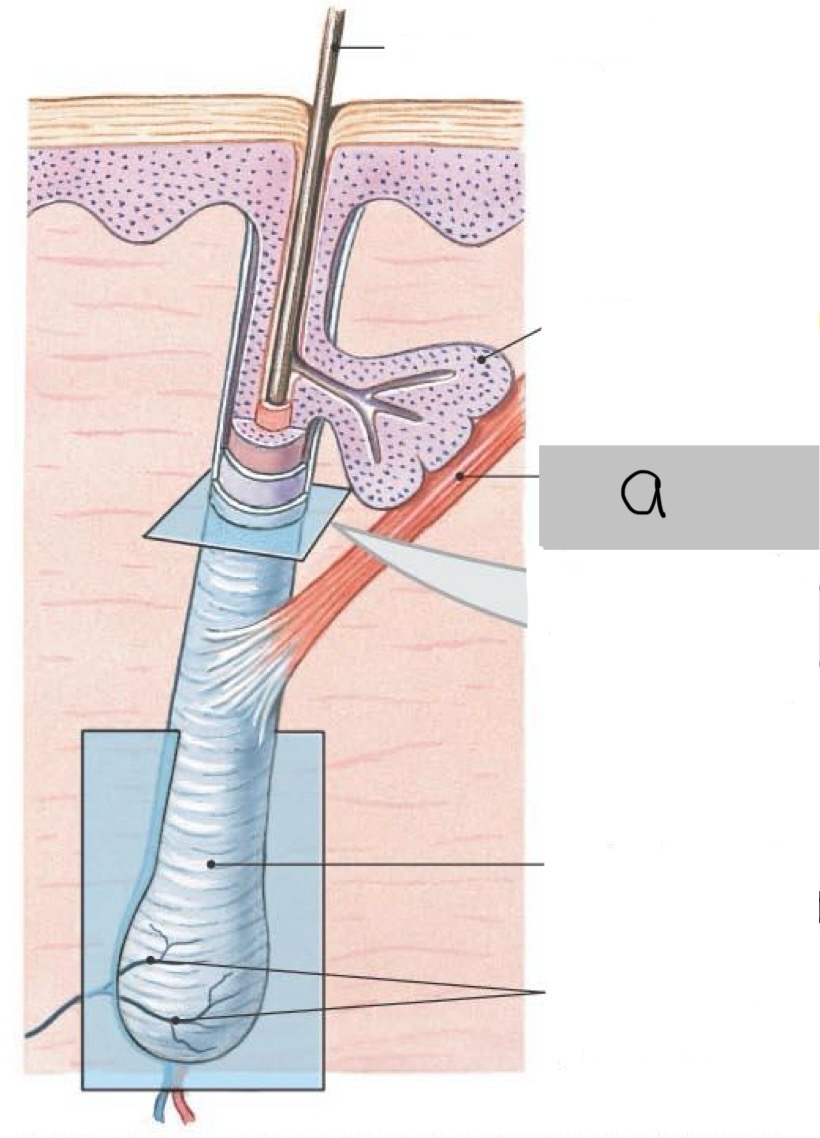
Sebaceous (oil) glands
• Secrete oily lipid (sebum) that coats hair shaft and epidermis
• Provide lubrication and antibacterial action
Sweat (sudoriferous) glands
Distributed over entire skin surface, except on the nipples and parts of the external genetalia
Myoepithelial cells
Small contractile cells that squeeze the secretion, or sweat, out of a sweat gland
Eccrine (or Merocrine) sweat glands
Most numerous type, especially on the palms and soles
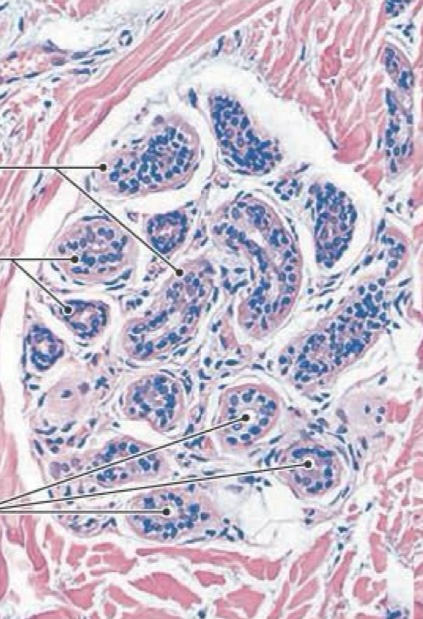
Properties of eccrine (or merocine) sweat glands
• Produce thin secretions, mostly water
• Important in thermoregulation and excretion (some antibacterial action)
• Controlled primarily by nervous system
Apocrine sweat glands
• Mostly confined to axillary, anal and genital areas
• Produce a special kind of sweat consisting of fatty substances and proteins, via merocrine secretion
Calluses
Mechanical stress can trigger stem cell divisions, resulting in these
Scar tissue
The inability to completely heal after severe damage may result in this
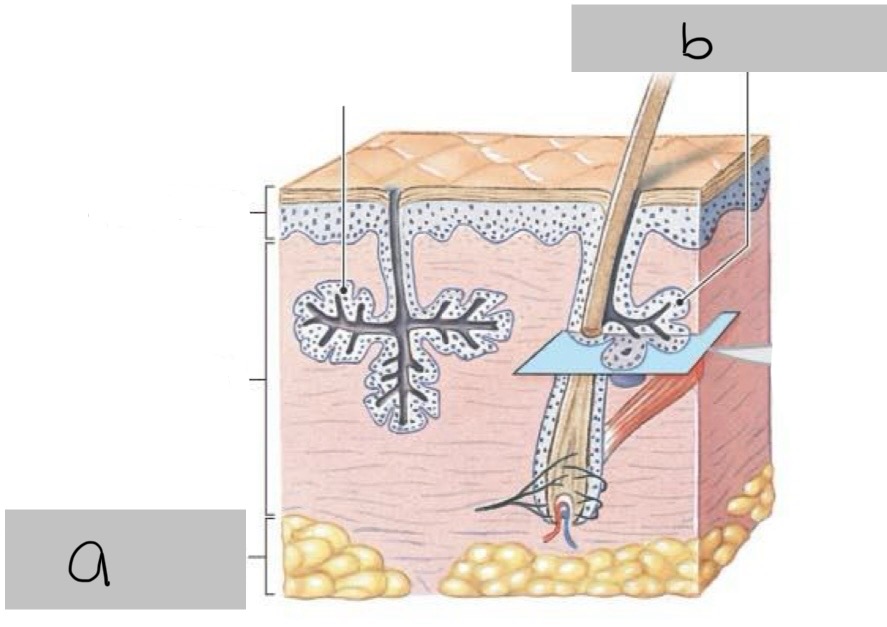
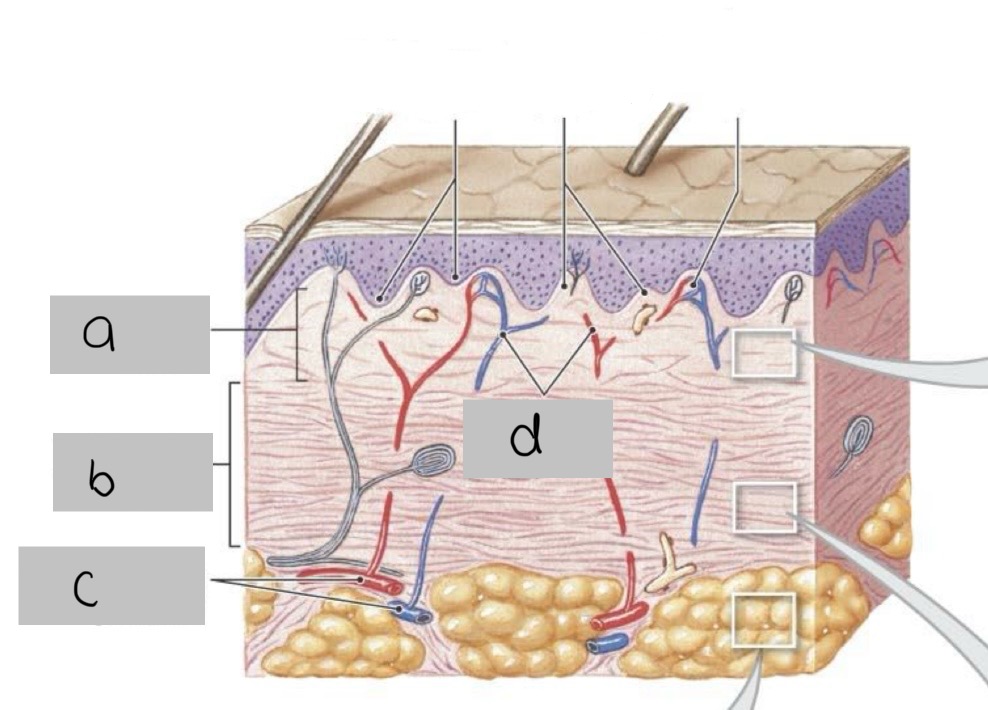
a. Papillary layer
b. Reticular layer
c. Cutaneous plexus
d. Papillary plexus
Identify structures a-d in the following image of skin
a. Subcutaneous layer
b. Sebaceous gland
Identify structures a & b in following image of skin