Study Guide 9
1/281
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 30 - Soft Tissue Trauma, Ch 31 - Chest and Abdominal Trauma, Ch 32 - Musculoskeletal Trauma, and Ch 33 - Trauma to the Head, Neck, and Spine
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
282 Terms
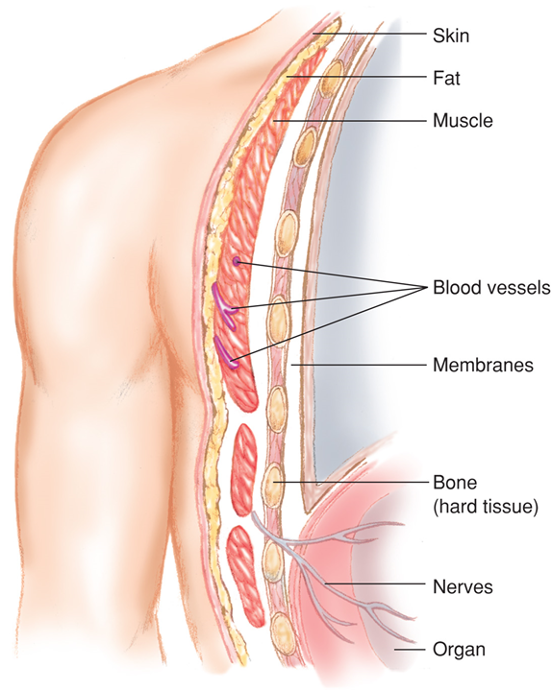
Soft tissues include:
Skin
Fatty tissues
Muscles
Blood vessels
Connective tissues
Membranes
Glands
Nerves
Major functions of the skin
Protection
Water balance
Temperature regulation
Excretion
Shock (impact) absorption
Soft Tissues
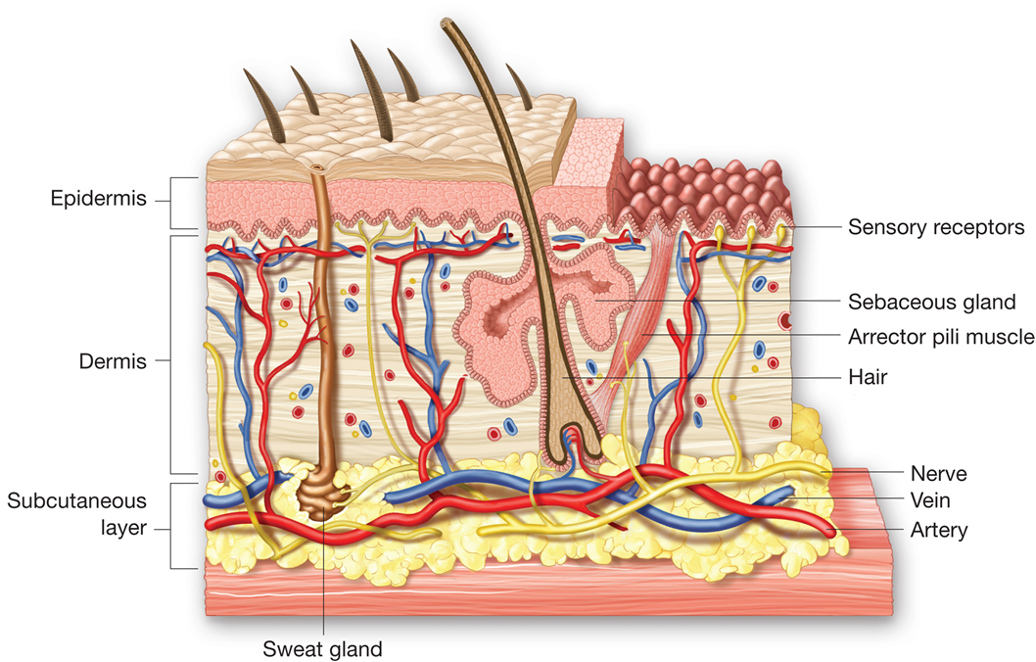
Skin layers
Epidermis
Dermis
Subcutaneous layers
Wounds often classified as closed or open.
Closed Wounds
Internal injuries with no pathway from the outside to the injured site
Although skin unbroken, may be extensively crushed tissues beneath
Range from minor to life-threatening
Closed wounds include:
Contusions
Bruise
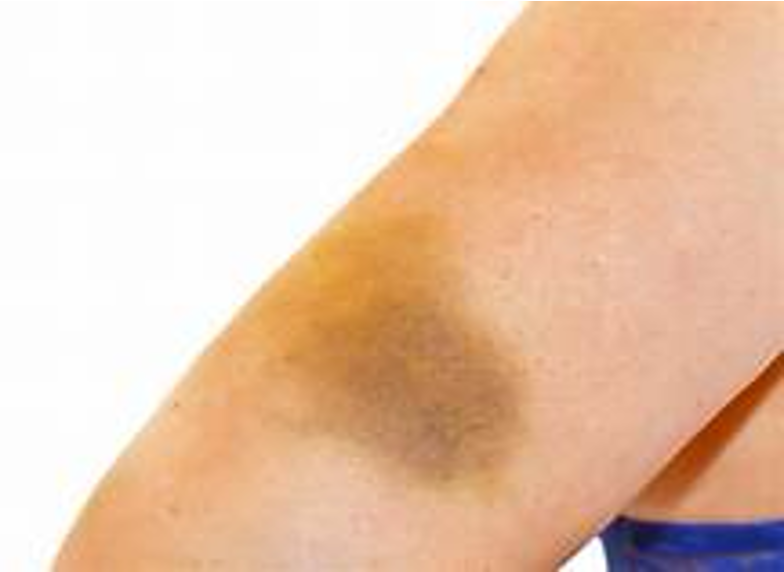
Hematomas
Similar to contusion
More tissue damage
Involves larger blood vessels
Closed crush injuries
Force transmitted from exterior to internal structures
Crush or rupture internal organs
Solid organs bleed severely and cause shock
Hollow organs leak into body cavities
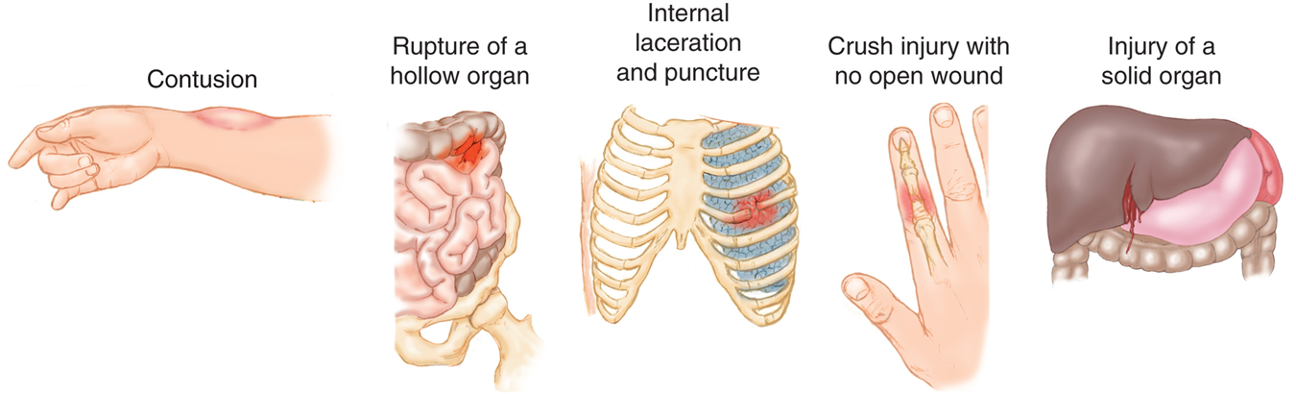
Closed wounds are what?
Contusions
Rupture of a hollow organ
Internal laceration and puncture
Crush injury with no open wound
Injury of a solid organ
Patient Assessment of Closed Wound
Bruising may be indication of internal injury or internal bleeding.
Consider mechanism of injury.
Crush injuries are difficult to identify.
Patient Care of Closed Wound
Take appropriate Standard Precautions
Manage airway, breathing, and circulation
Manage as if there were internal bleeding and shock if there is any possibility of internal injuries
Splint extremities that are painful, swollen, or deformed
Stay alert for vomiting
****Continuously monitor for changes and transport promptly
Apply cold pack to isolated injuries to manage pain and swelling
Types of Open Wounds
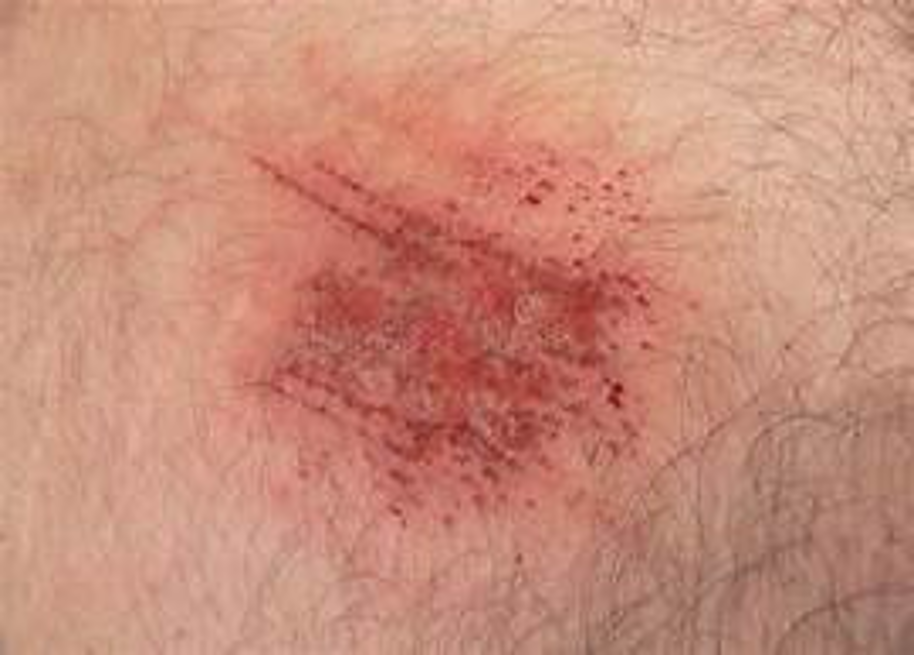
Abrasions
Lacerations
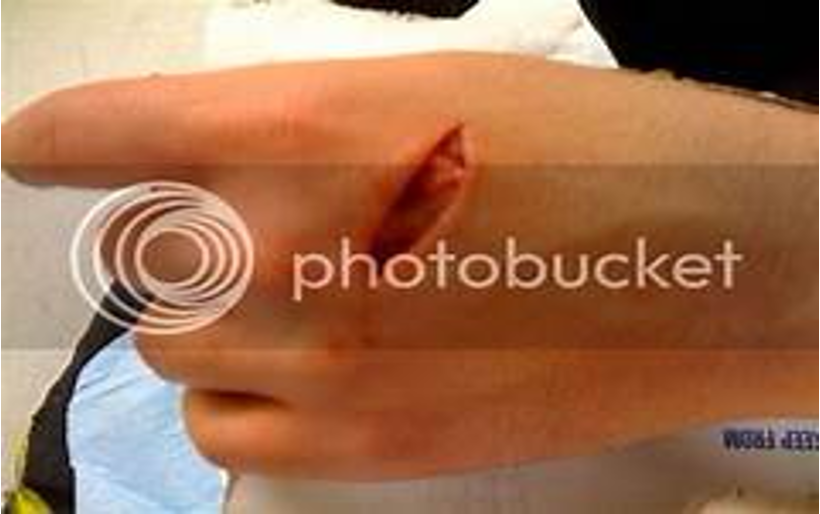

Penetrating trauma and punctures
Avulsions
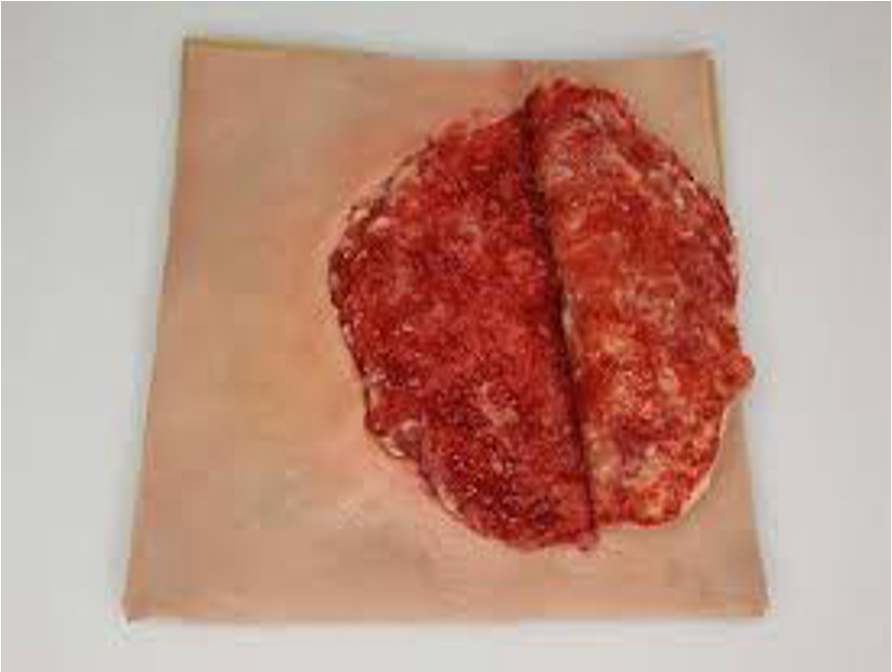
Amputations
Degloving also consistent with Avulsion
Where a large piece of skin and underlying tissue is forcefully torn away.
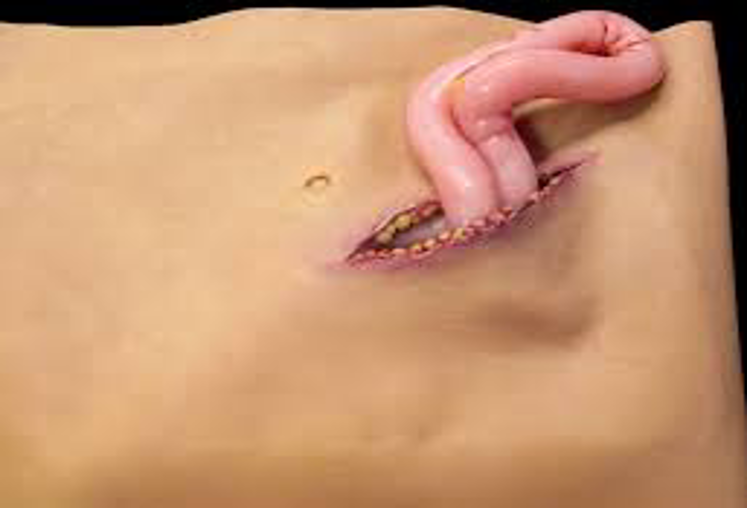
Evisceration
Removal of internal organs or viscera from the body cavity
More Types of Open Wounds
Open crush injuries
Bite wounds
Blast injuries
High-pressure-injection injuries
Blast Injuries
Can be injured multiple ways
Initial blast (High pressure wave)
Hit by debris
Thrown (landing Impact)
Closed or open injuries
Penetrating injury
Chemical burns
Blast injuries impacts
Primary
Pressure wave leading to injuries to organs like lungs, fluid filled organs like spleen etc.
Secondary
Projectiles Shrapnel
Blast injury leading to open and penetrating wounds
Tertiary
If patient is thrown, fractures, avulsions, amputations
Quaternary - Exposure to chemicals
High Pressure injury
Machinery operating at high pressures
Are used to project fluid or air into particular areas
If this pressure goes into the body what occurs
Can travel long distances
Damage tissue, bone etc.
May present with intense pain or none at all
Do not treat with ice. (Why)
Emergency Care for Open Wounds
Strict attention to Standard Precautions
In addition to wearing gloves, a gown and protective eyewear may be required.
Patient Assessment for Open Wounds
Primary assessment
–Airway Breathing
–Breathing Airway
–Circulation Circulation (Severe Bleeding)
–Severe bleeding
Care for individual wounds
Patient Care for Open Wounds
Expose wound.
Clean wound surface.
Control bleeding.
For all serious wounds, provide care for shock, including administration of high-concentration oxygen.
Prevent further contamination.
Bandage dressings in place after bleeding is controlled.
Keep patient lying still.
Reassure patient.
Treating Abrasions and Lacerations
Reduce wound contamination
Hold direct pressure to control bleeding
Always check pulse, motor, and sensory function distal to injury to assure function
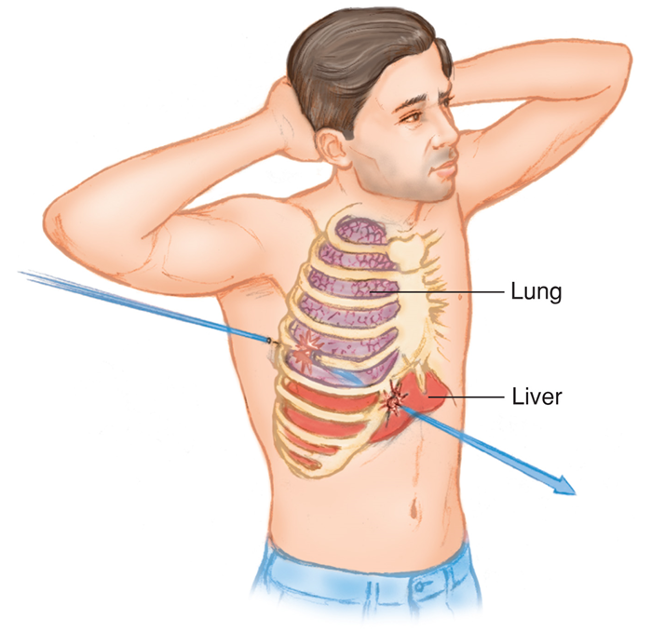
Treating Penetrating Trauma
Use caution because objects may be embedded deeper than they appear.
Check for exit wounds.
May require immediate care
Bullets can fracture bones as they enter.
Stab wounds are considered serious, especially if in a vital area of body.
More Info on Treating Penetrating Trauma
Reassure patient.
Search for exit wound.
Assess need for basic life support.
Follow local protocols regarding spinal motion restriction.
Transport patient.
Treatment: Penetrating Trauma
Bullets travel in an unpredictable path once they are inside the patient’s body, and can therefore cause damage to multiple organs and bones.
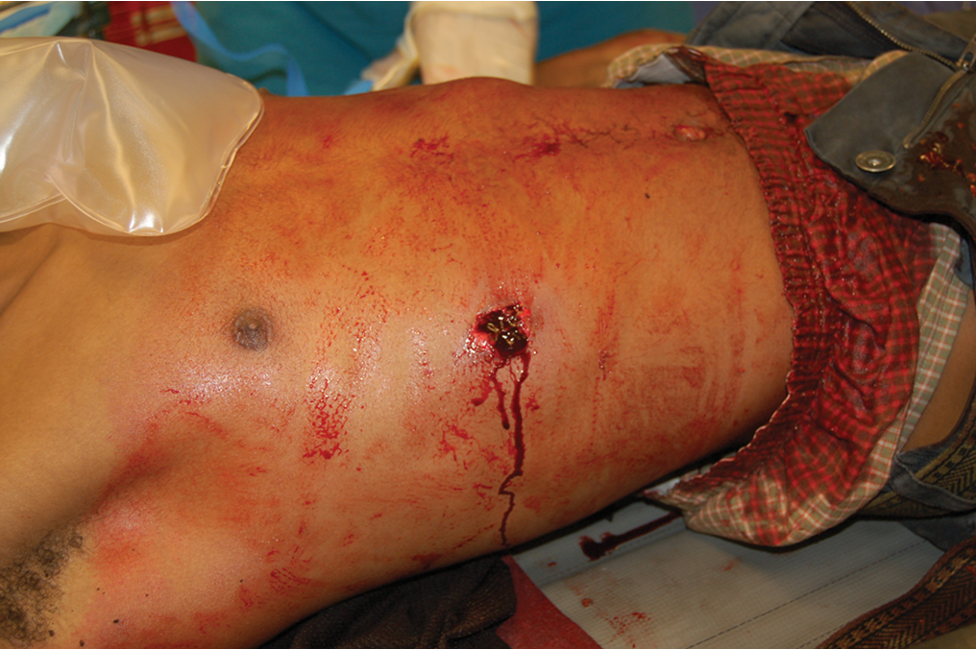
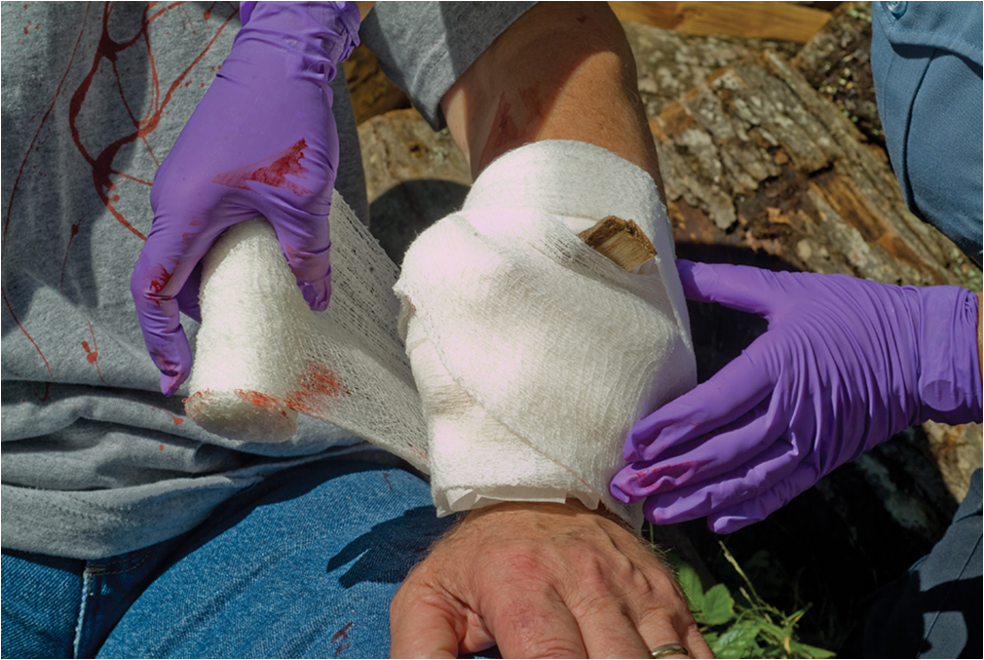
Treating Impaled Objects
****Do not remove object; may cause severe bleeding.
Expose wound area.
Control profuse bleeding by direct pressure.
Get a description of the object.
****Apply several layers of bulky dressing so dressing surrounds the object on all sides.
More Info on Treating Impaled Objects
Place bulky dressing on opposite sides of the object.
Secure dressings in place.
Care for shock.
Keep patient at rest.
Transport the patient carefully and as soon as possible.
Reassure patient throughout all aspects of care.
Treatment: Impaled Objects
Stabilize an impaled object with bulky dressings.
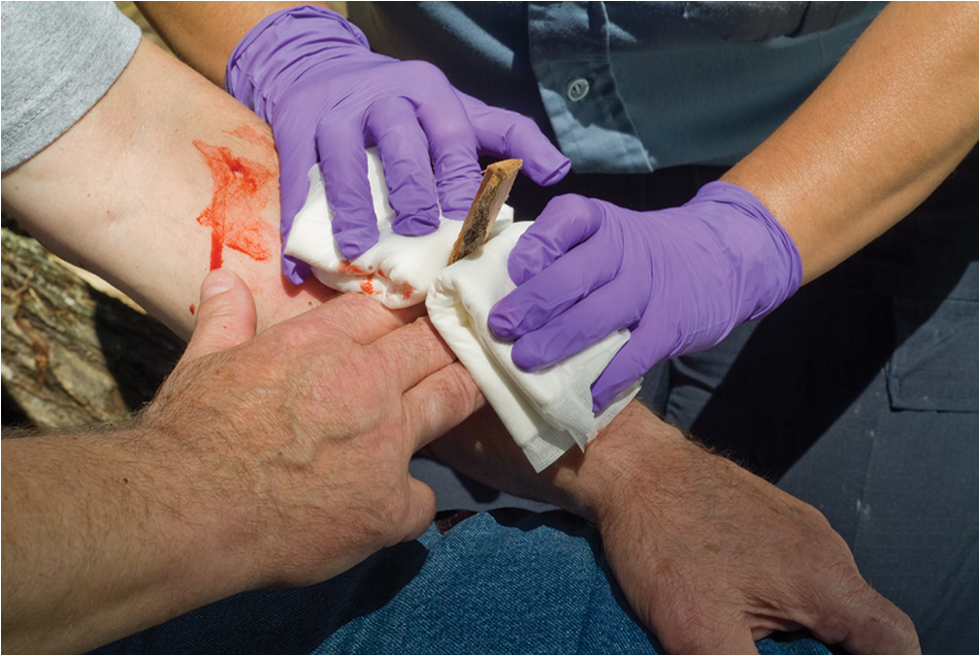
Bandage the impaled object and surrounding dressings in place.
Object Impaled in the Cheek
Object may enter oral cavity, causing airway obstruction.
If cheek wall is perforated, profuse bleeding into mouth and throat can cause nausea and vomiting.
External wound care will not stop the flow of blood into the mouth.
Examine wound site, both inside and outside mouth
****If you find the perforation and can see both ends, remove object.
If this cannot be easily done, leave object in place.
Treatment: Impaled Object in Cheek
The process of removing an impaled object from the cheek.
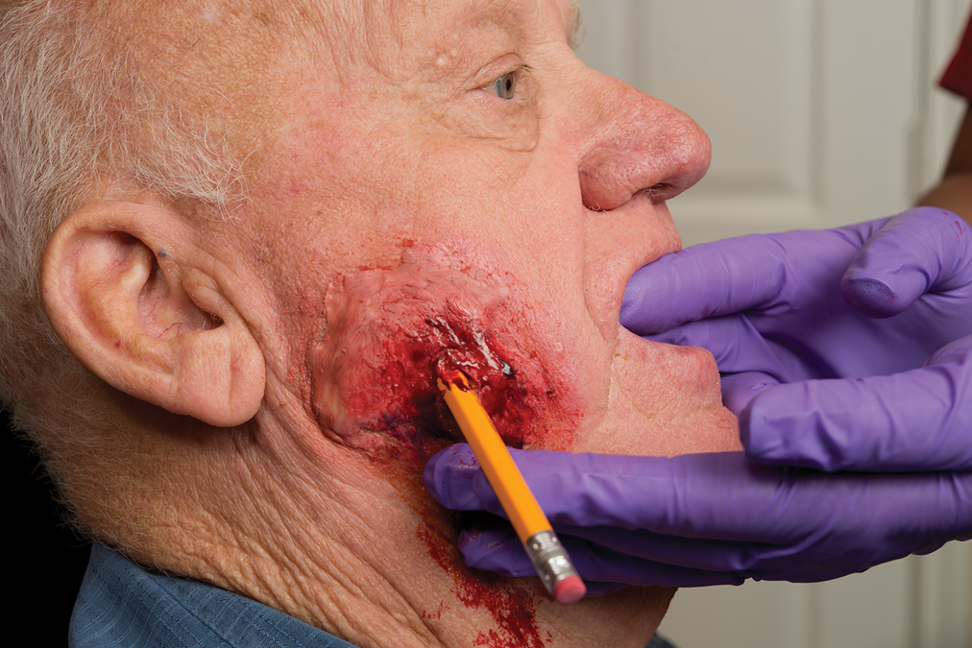
More Info on Object Impaled in the Cheek
Position patient to allow for drainage.
Monitor patient’s airway.
Dress outside of wound.
Consider the need for oxygen and care for shock.
Puncture Wound or Object Impaled in the Eye
****Stabilize the object.
Apply rigid protection.
Have another rescuer stabilize dressings and cut while you secure them in place with self-adherent roller bandage or with wrapping of gauze.
Treatment: Puncture Wound or Object Impaled in Eye
Managing an object impaled in the eye.
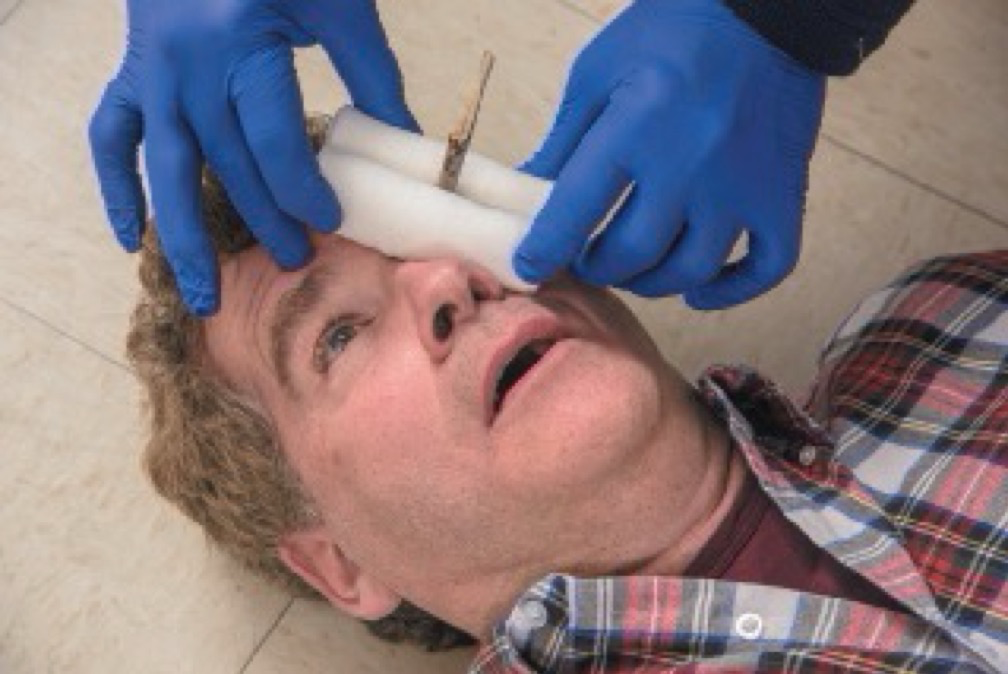
Wrap both eyes. The object is contained and immobilized.
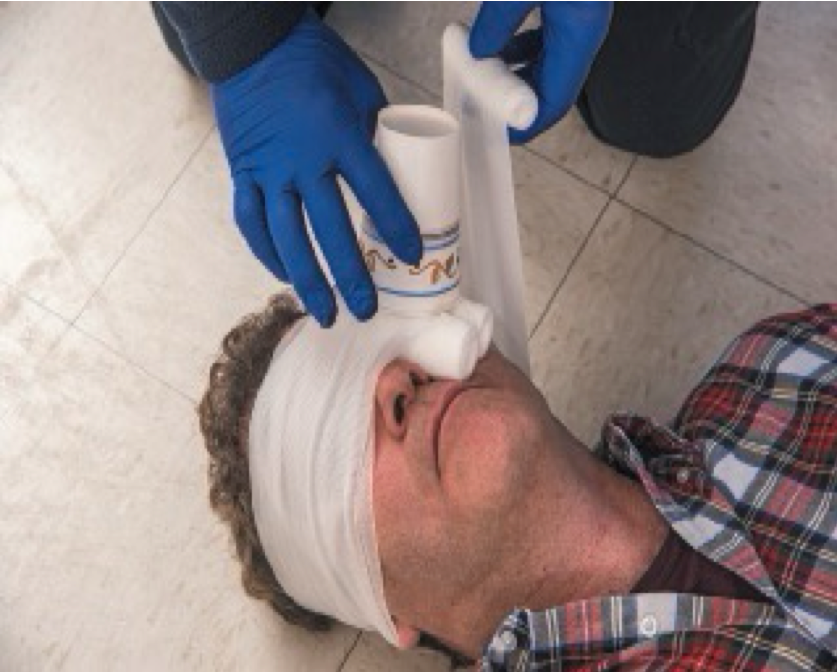
More Info on Puncture Wound or Object Impaled in the Eye
****Dress and bandage uninjured eye.
Eyes want to track together
Consider need for oxygen and care for shock.
Reassure patient and provide emotional support.
Treating Avulsions
Clean wound surface.
Fold skin back into normal position.
Control bleeding and dress with bulky dressings.
****If avulsed parts are completely torn away, save in sterile dressing and keep moist with sterile saline.
Treating Amputations
Take steps to control hemorrhage immediately.
Apply direct pressure to control bleeding; use tourniquet only if all other methods fail.
Do not place directly on ice. Care for an amputated part. The amputated digit sits on sterile gauze, awaiting reimplantation at the trauma center.
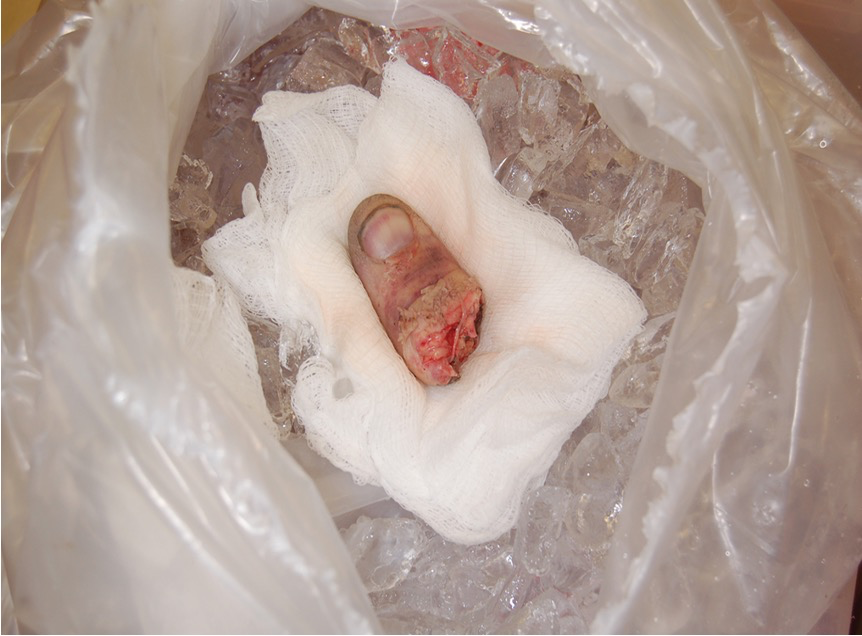
More Info on Treating Amputations
Wrap amputation site in sterile dressing, and secure dressing with self-adhesive gauze bandage.
Then wrap or bag amputated part in plastic bag; keep it cool by cold pack. (Not in direct contact)
****Do not immerse amputated part directly in water or saline.
Treating Genital Injuries
Control bleeding.
Preserve avulsed parts.
Consider whether injury suggests another, possibly more serious, injury.
Display calm, professional manner.
Dress and bandage wound.
Consider possibility of sexual assault.
Burns
May involve more than just skin-level structures.
****If respiratory structures are affected, swelling may occur, causing life-threatening obstruction.
Do not let burn distract from spinal damage or fractures.
Patient Assessment
Classifying burns
Agent and source
(What caused the burn)
Depth
How Deep
Severity
Where located, percentage of body, agent, age, health.
Classifying Burns by Agent and Source
Agent could be chemicals or electricity
****Report the agent and, when practical, the source of the agent.
Never assume the agent or source of the burn.
Always gather information from your observations of the scene, bystanders’ reports, and the patient interview.
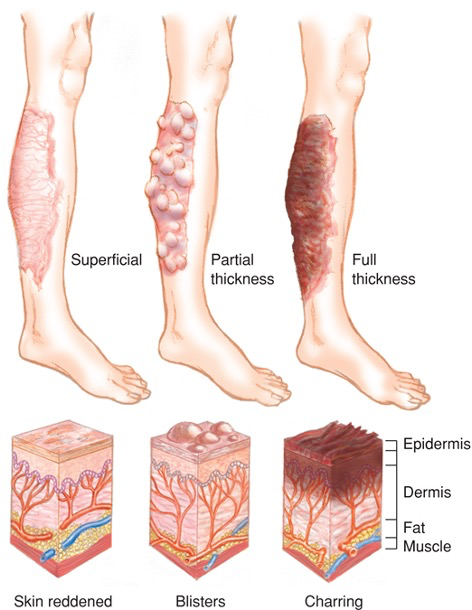
Assessment: Burns
Superficial
Skin reddened
Partial thickness
Blisters
Full thickness
Charring
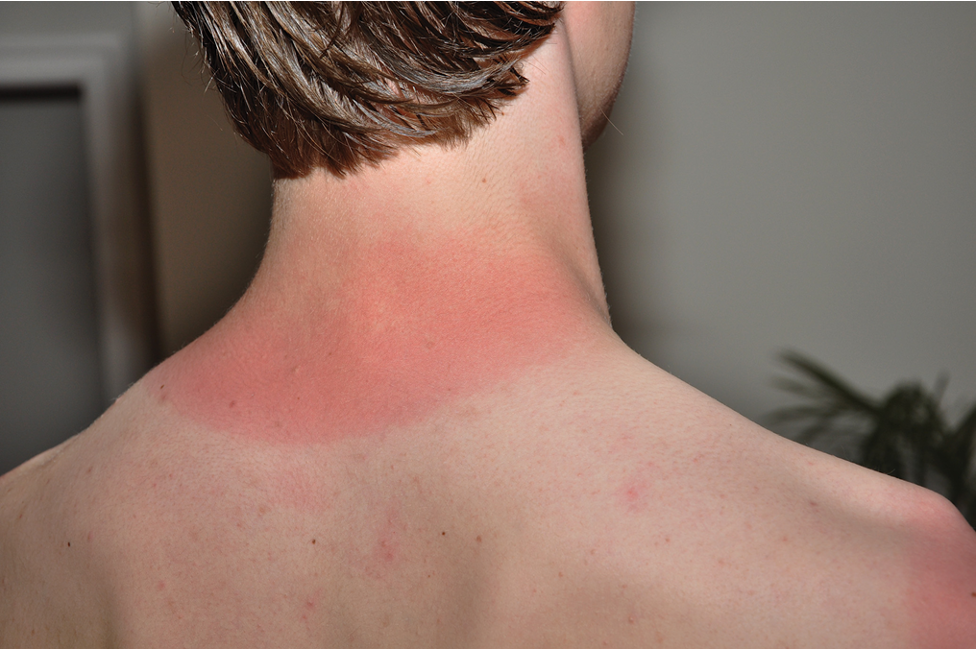
Superficial burn (1st degree)
Involves only epidermis
Reddening with minor swelling
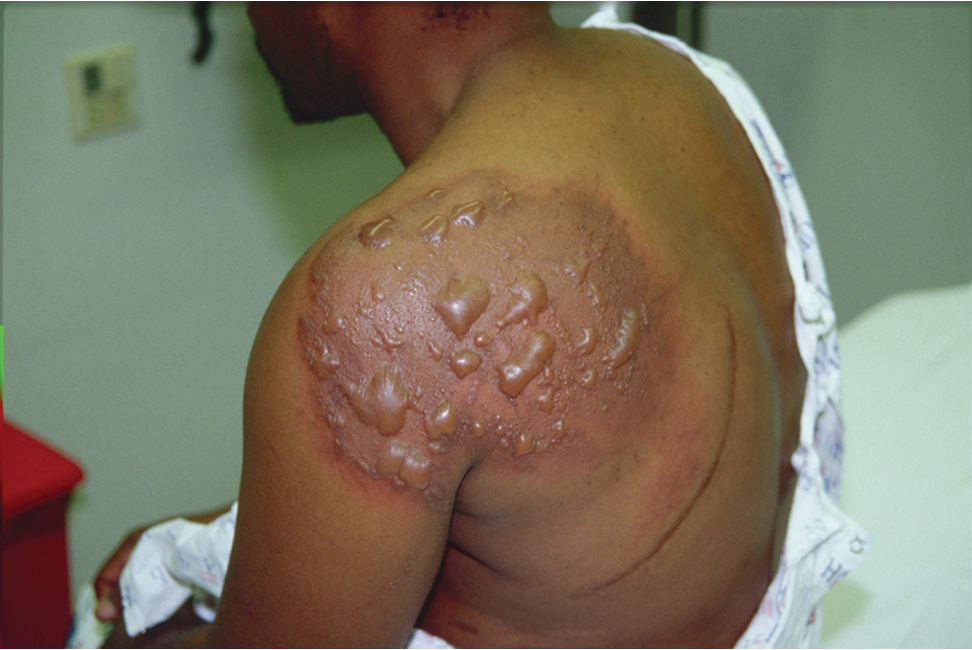
Partial thickness burn (2nd degree)
Epidermis burned through, dermis damaged
Deep, intense pain (Why)
Noticeable reddening
Blisters and mottling
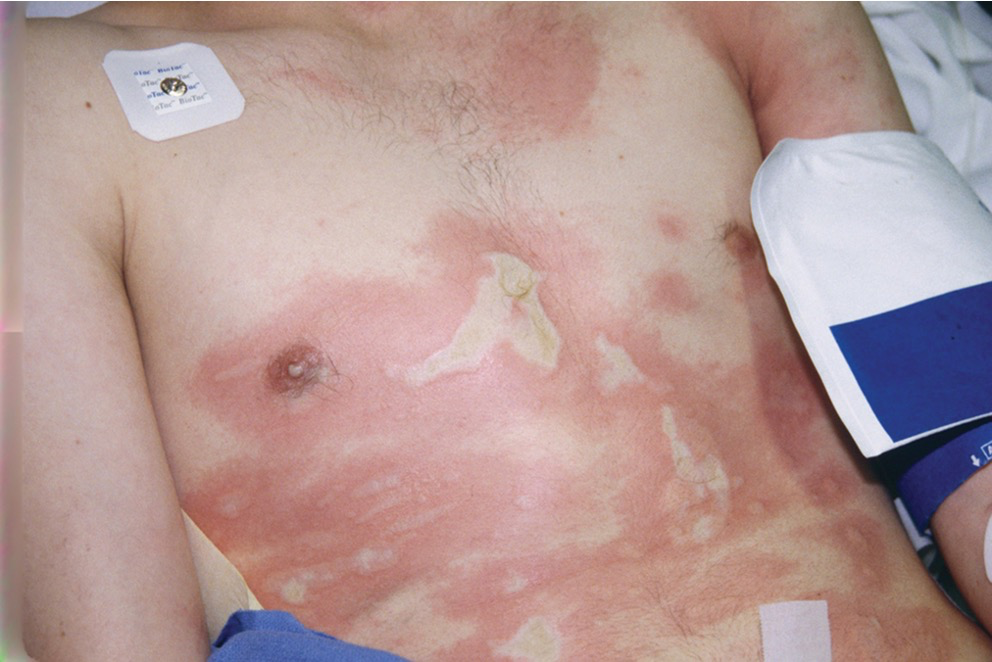
Full thickness burn (3rd degree)
All layers of skin burned
Blackened areas or dry and white patches
May not have pain at all, or may only be at the periphery. (Why)
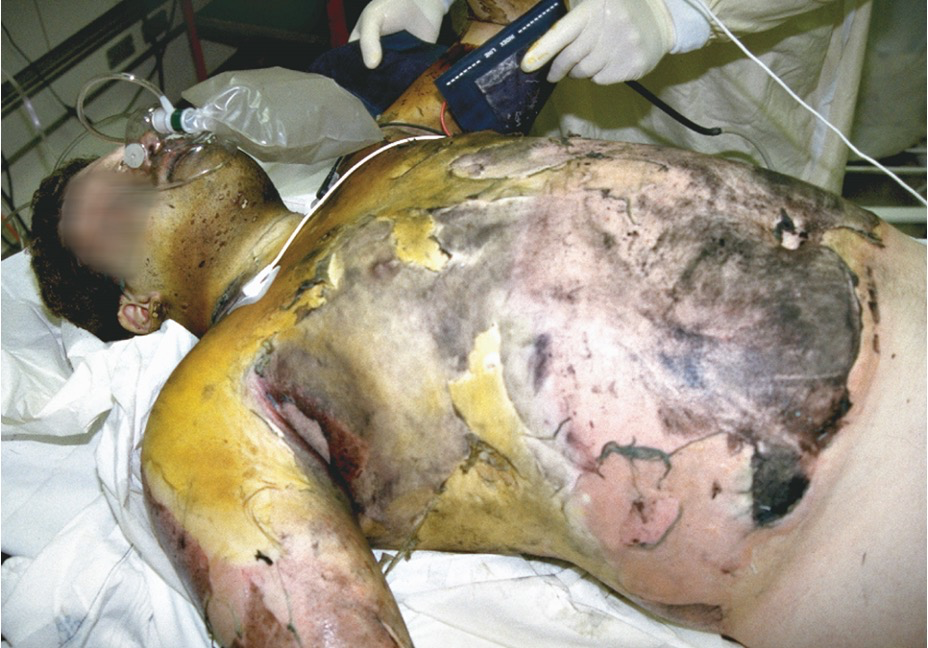
Determining the Severity of Burns
Consider the following factors:
Agent or source of the burn
Body regions burned
Depth of the burn
Extent of the burn
Age of the patient
Other illnesses and injuries
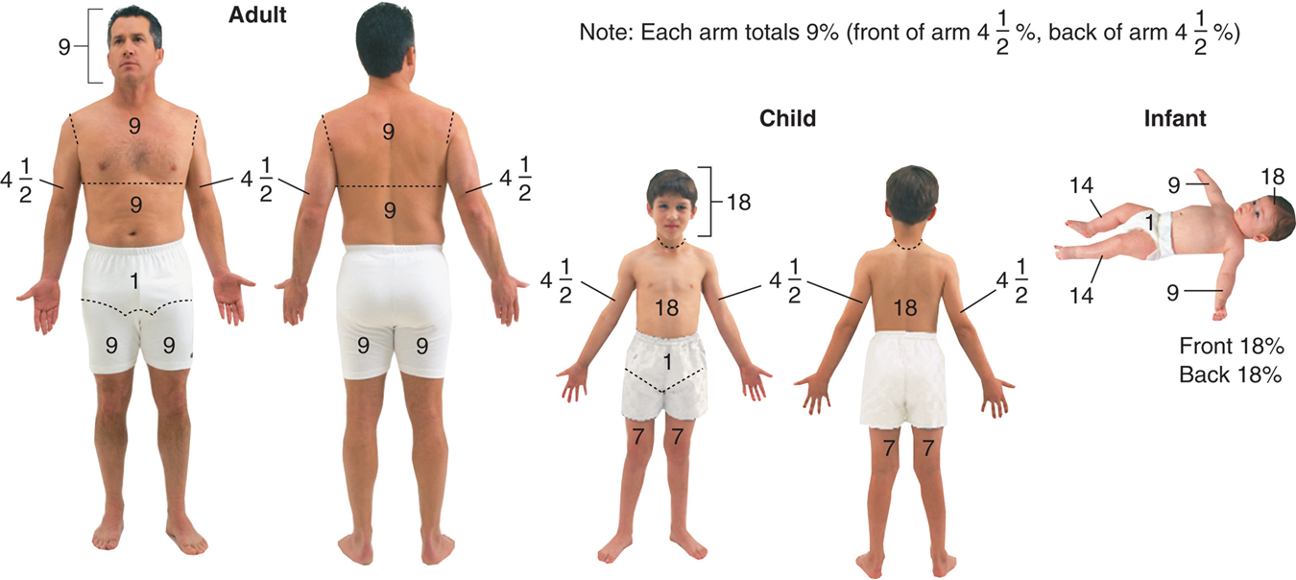
Rule of Nines
****Helps estimate extent of burn area
Adult body is divided into 11 main areas
Each represents 9 percent of body surface
Rule of palm
Helps estimate extent of burn area
****Palm and fingers equal about 1 percent of body surface area
Easier to apply to smaller or localized burns
Classifying Burns by Severity
Must be classified to determine:
Order and type of care
Priority for transport
Maximum information to provide to the emergency department.
Pediatric Note
Infants and children have a much greater relationship of body surface area to total body size, resulting in greater fluid and heat loss from burned skin.
Treating Specific Types of Burns
Patient care for thermal burns
****Stop burning process and cool burned area.
Ensure open airway and assess breathing.
Look for signs of airway injury.
Complete primary assessment.
Treat for shock.
More Info on Treating Specific Types of Burns
****Evaluate burns by depth, extent, and severity.
Do not clear debris.
Remove clothing and jewelry.
****Wrap with dry sterile dressing.
For burns to hand or feet, remove patient’s rings or jewelry and separate fingers or toes with sterile gauze pads.
What patients go to burn centers
2nd degree burns (What percentage of body)
Burns to certain body areas (Where)
3rd Degree burns
Certain agents (Which ones)
Certain types of burns (Ie. Inhalation burns)
Certain patients (Such as)
Patient care for chemical burns
****Wash away chemical with copious amounts of flowing water.
****If dry chemical, remove contaminated clothing, then flush with water.
Apply sterile dressings. → Treat for shock. → Transport.
Radiation Burns
Exposure to high levels of radiation can harm the human body both immediately and in a delayed fashion.
Great number of sources of radiation
Difficult to detect without specific monitoring equipment
Extremely harmful
Do not approach a radiological injury without protective equipment and specialized training.
See patient with a radiological burn only after they have been decontaminated.
Most will present like thermal injuries.
Electrical Injuries
****Severe damage through body along path of electrical current
****Entry and exit burns are possible.
Respiratory/cardiac arrest are possible.
Bones may fracture from violent muscle contractions.
Patient Care for Electrical Injuries
Provide airway and breathing care.
Provide basic cardiac life support; be ready to defibrillate.
Care for shock and administer high-concentration oxygen.
More Info on Patient Care on Electrical Injuries
****Care for spinal and head injuries as well as extremity fractures.
Evaluate burn sites.
Cool burning areas and smoldering clothing the same you would for a flame burn.
Apply sterile dressings.
Transport as soon as possible.
What does dressing do?
Dressings cover wounds.
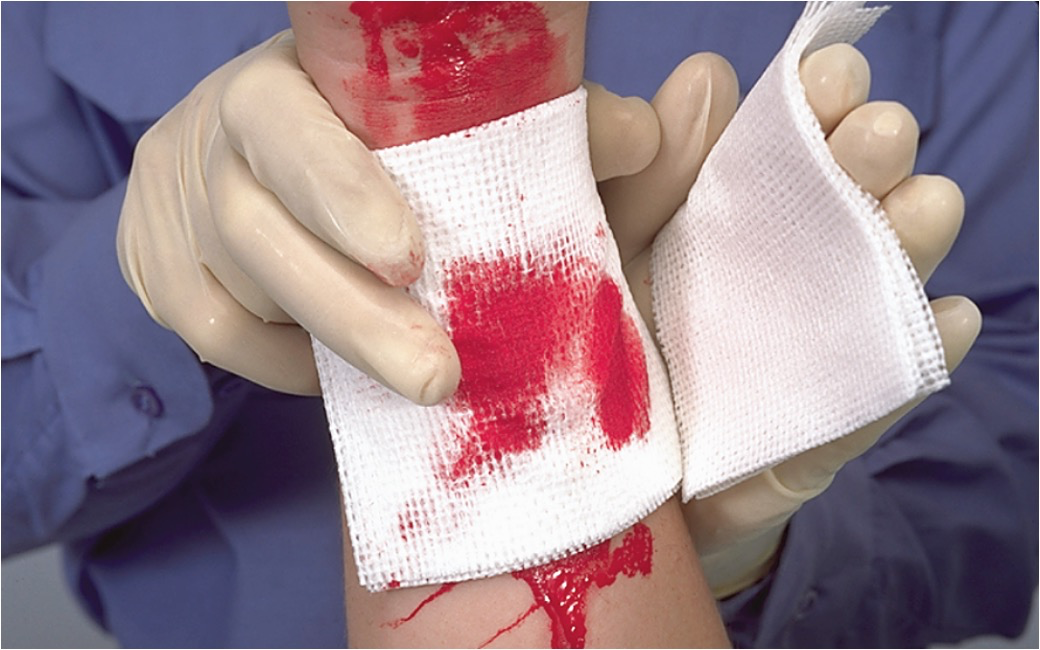
Information on Dressing and Bandaging
Universal dressing
Available for profuse bleeding, large wound
Pressure dressing
Used to control bleeding
Occlusive dressing
Used to form an airtight seal
Wounds to the abdomen, large neck veins, open wounds to chest
What does a bandage do?
Bandages hold dressings in place.
Dressing Open Wounds
Take Standard Precautions.
Expose wound.
Use sterile or very clean materials.
Cover entire wound.
Control bleeding by direct pressure and/or hemostatic agents or dressings to stop or slow bleeding.
Do not remove dressings.
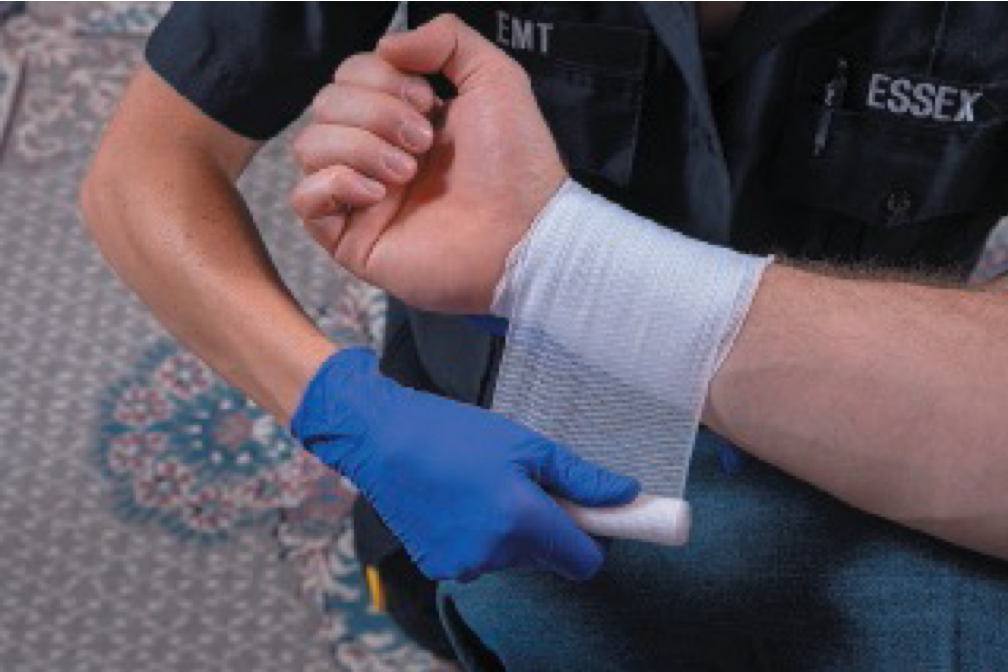
Bandaging Open Wounds
To apply a self-adhering roller bandage, secure it with several overlapping wraps.
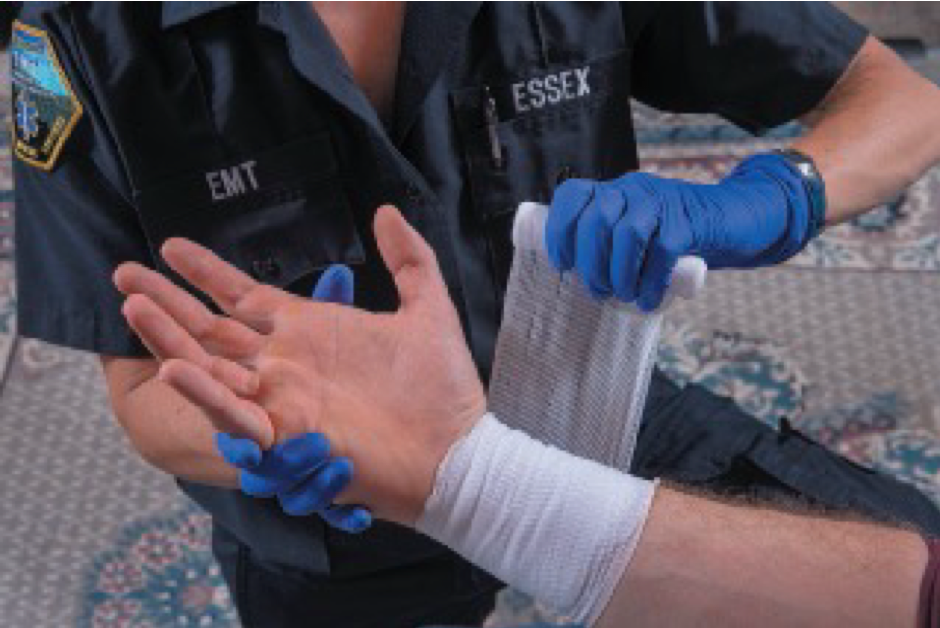
To apply a self-adhering roller bandage, keep it snug.
Review of Soft-tissue Injuries
Soft-tissue injuries may be closed (internal, with no pathway to the outside) or open (an injury in which the skin is interrupted, exposing the tissues below).
Review of Closed Injuries
Closed injuries include contusions (bruises), hematomas, crush injuries, and blast injuries.
Review of Open Wounds
Open wounds include abrasions, lacerations, punctures, avulsions, amputations, crush injuries, and blast injuries.
For open wounds, expose the wound, control bleeding, and prevent further contamination.
Open and Closed Injuries Review
For both open and closed injuries, take appropriate Standard Precautions; note the mechanism of injury; protect the patient’s airway and breathing; consider the need for oxygen by nonrebreather mask; treat for shock; and transport.
How is burn severity determined?
Burn severity is determined by considering the source of the burn, body regions burned, depth of the burn (superficial, partial thickness, or full thickness), extent of the burn (by rule of nines or rule of palm), age of the patient (children under 5 and adults over 55 react most severely), and other patient illnesses or injuries.
How do we properly care for burns?
Care for burns includes stopping the burning process (using water for a thermal burn, brushing away dry chemicals), covering a thermal burn with a dry sterile dressing, flushing a chemical burn with sterile water, protecting the airway, administering oxygen as appropriate, treating for shock, and transporting the patient to a medical facility.
How do we treat electrical injuries?
For treatment of electrical injuries, be sure that you and the patient are in a safe zone away from possible contact with electrical sources. Protect airway, breathing, and circulation. Be prepared to care for respiratory or cardiac arrest. Treat for shock, care for burns, and transport the patient.
We must remember that soft tissue is what?
The soft tissue of the body is made up of skin, fatty tissues, muscles, blood vessels, connective tissues, membranes, glands, and nerves.
Our skin does what?
The skin provides protection, water balance, temperature regulation, excretion, and shock absorption.
Open or closed is in reference to what?
Open or closed in reference to a soft-tissue injury is dictated by whether or not the skin is still intact.
Closed injuries must be what?
Closed injuries must be evaluated with consideration to underlying anatomy and mechanism of injury.
Remember that
Open injuries typically are easier to visualize, but they often can mask underlying injuries.
Burns involve immediate destruction of tissue but also can have a long-term effect, both physically and emotionally.
Safety must be a key concern when treating a patient with a burn or an electrical injury.
The goal of dressing and bandaging wounds is to control bleeding and to prevent infection.
Chest cavity
Extends from collarbones to diaphragm
Dynamic because it depends on respiratory cycle
Packed with organs, major blood vessels, and lung tissue
Organs of the chest are well protected
12 sets of ribs
Sternum
Thoracic spine vertebrae
Scapula
Physiologic functions of the chest
Heart beats to provide blood flow
Large blood vessels enter and exit the heart
Respiratory function
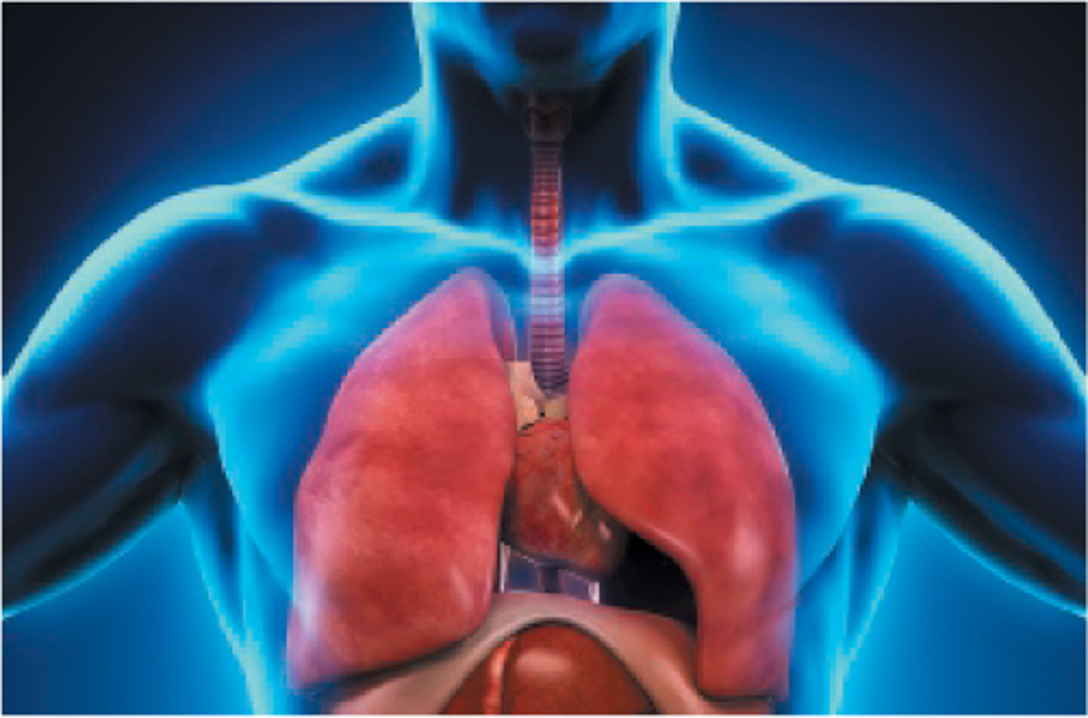
The Mechanism of Breathing
Chest wall, diaphragm, and lungs work together
Change pressure within the chest cavity
Cause air to be moved in and out
Inhalation
Active process that uses negative pressure to draw air into the lungs
Exhalation
Passive process that uses positive pressure to push air out of the lungs
Anatomy and Physiology of the Abdomen
Superior border is diaphragm
Abdominal organs extend to the lower regions of the pelvis
Described in context of location relative to four abdominal quadrants
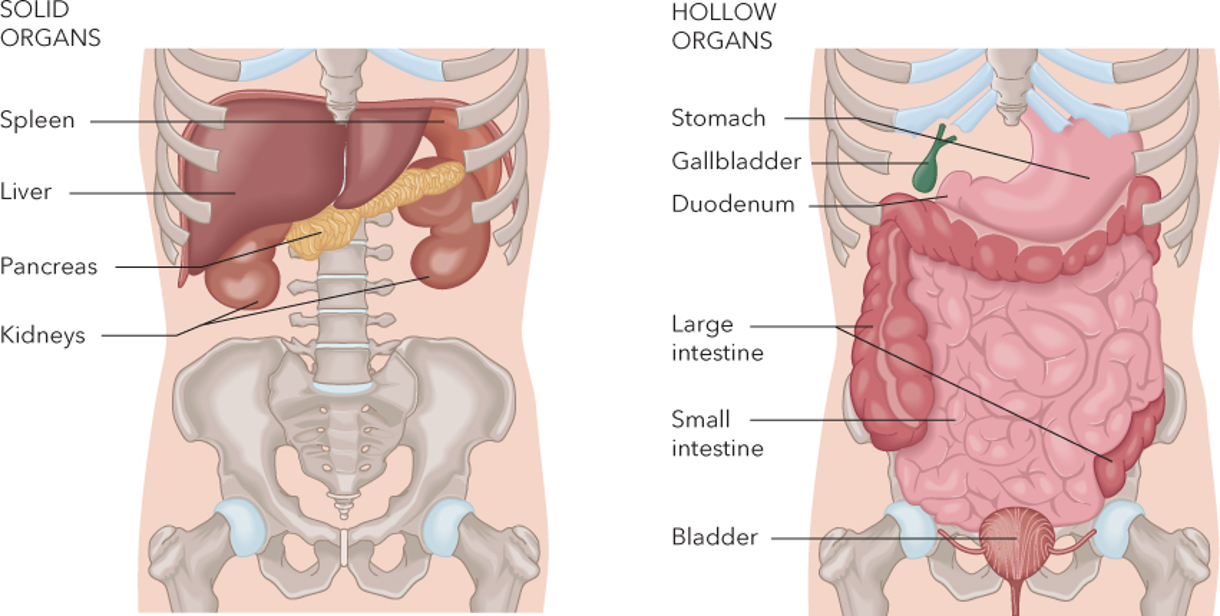
Anatomy of the Abdomen
Solid Organs
Spleen
Liver
Pancreas
Kidneys
Hollow Organs
Stomach
Gallbladder
Duodenum
Large Intestine
Small Intestine
Bladder
Information on Anatomy and Physiology of the Abdomen
Trauma assessment and care takes into consideration placement and function of abdominal organs.
Differentiate between hollow and solid organs
Hollow organs tolerate trauma well.
Bladder, intestines, stomache
Solid organs do not tolerate trauma well.
Liver, Spleen, Kidney
More Information on Anatomy and Physiology of the Abdomen
Physiology of abdominal organs is dependent on individual function.
Abdominal cavity is dynamic depending on location of diaphragm.
Organs shift location dependent on breathing cycle
There is always a large volume of blood in the abdomen.
Pathophysiology of the Chest and Abdomen
Disruption of breathing
Hemorrhage and shock
Disruption of organ function
Infection
Chest Injuries
Blunt trauma
Can fracture ribs, sternum, and costal (rib) cartilages
Penetrating trauma
Bullets, knives, pieces of metal or glass, steel rods, pipes, other objects
Can damage internal organs and impair respiration
Info on Chest Injuries
Compression and shearing injuries
Occurs when severe blunt trauma causes the chest to rapidly compress
Shearing can damage the aorta and vena cava
Chest injuries are classified as either closed or open.
Blunt Chest Injuries - Rib Fractures
Painful but usually not life-threatening
Can make breathing difficult
Can lacerate blood vessels or lung tissue
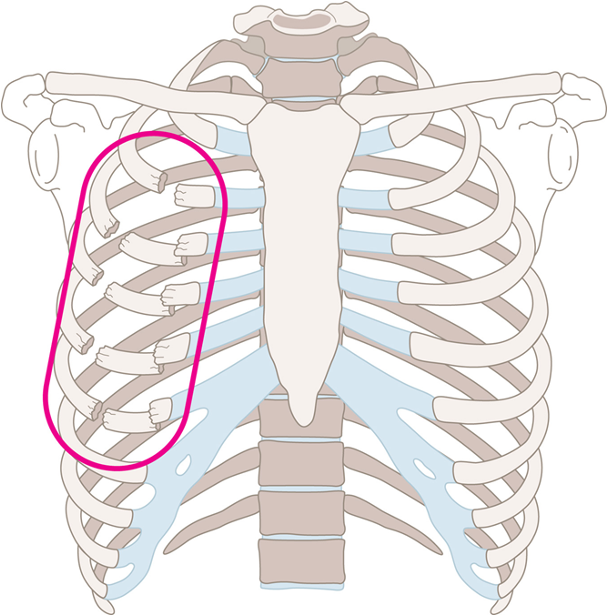
Blunt Chest Injuries - Flail Chest
****Fracture of two or more consecutive ribs in two or more places
Leaves a portion of the chest wall unstable
Leads to inadequate breathing and hypoventilation
Best way to deal with a flail chest is with O2 or ventilate.
Flail chest occurs when blunt trauma creates a fracture of two or more ribs in two or more places.
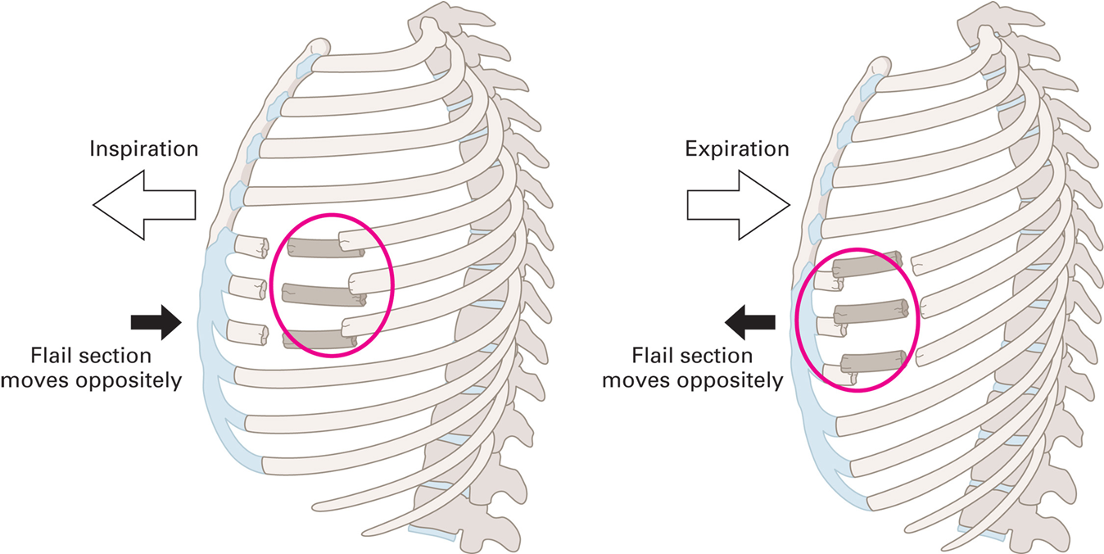
Blunt Chest Injuries - Paradoxical Motion
Movement of flail segment is opposite to movement of the remainder of the chest cavities.
Patient Assessment of a Rib Fracture
Consider mechanism of injury
Pain at the site of injury that increases with breathing
Tenderness
Redness, swelling, or bruising of skin
Respiratory distress, hypoxia, or respiratory failure
Self-splinting
Patient Assessment of Flail Chest
Mechanism of injury capable of causing injury
Difficulty breathing
Pain at injury site
Likely signs of shock and hypoxia
Chest wall muscle contraction
Patient Care of a Rib Fracture
Consider need for A L S
Allow patient to remain in position of comfort
Unless spinal precautions are needed
Treat hypoxia
Allow patient to hold pillow or cushion against chest (Not really done in the field anymore)
Patient Care of Flail Chest
Primary assessment for life threats
Administer oxygen.
If patient is breathing inadequately, assist ventilation.
Follow local protocols regarding using noninvasive positive pressure ventilations.
Info on Patient Care of Flail Chest
Request ALS for pain management.
Monitor patient carefully.
Watch respiratory rate and depth.
Do not restrict chest wall movement.
Penetrating Chest Injuries
Difficult to tell what is injured from entrance wound
Assume all wounds are life-threatening.
Open wounds allow air into chest.
Sets imbalance in pressure
Causes lung to collapse
Patient Assessment for Penetrating Chest Injuries
Determine description of object that penetrated
If one penetrating wound is found, look for others.
Visualize entire chest during assessment
Listen to lung sounds
Identify pneumothorax or hemothorax
Info on Patient Assessment for Penetrating Chest Injuries
Lung damage signs and symptoms
Difficulty breathing
Absent or unequal lung sounds
Hemoptysis
Coughing up blood
Hypoxia
More Info on Patient Assessment for Penetrating Chest Injuries
Other signs and symptoms
Shock
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Pale skin
Low blood pressure
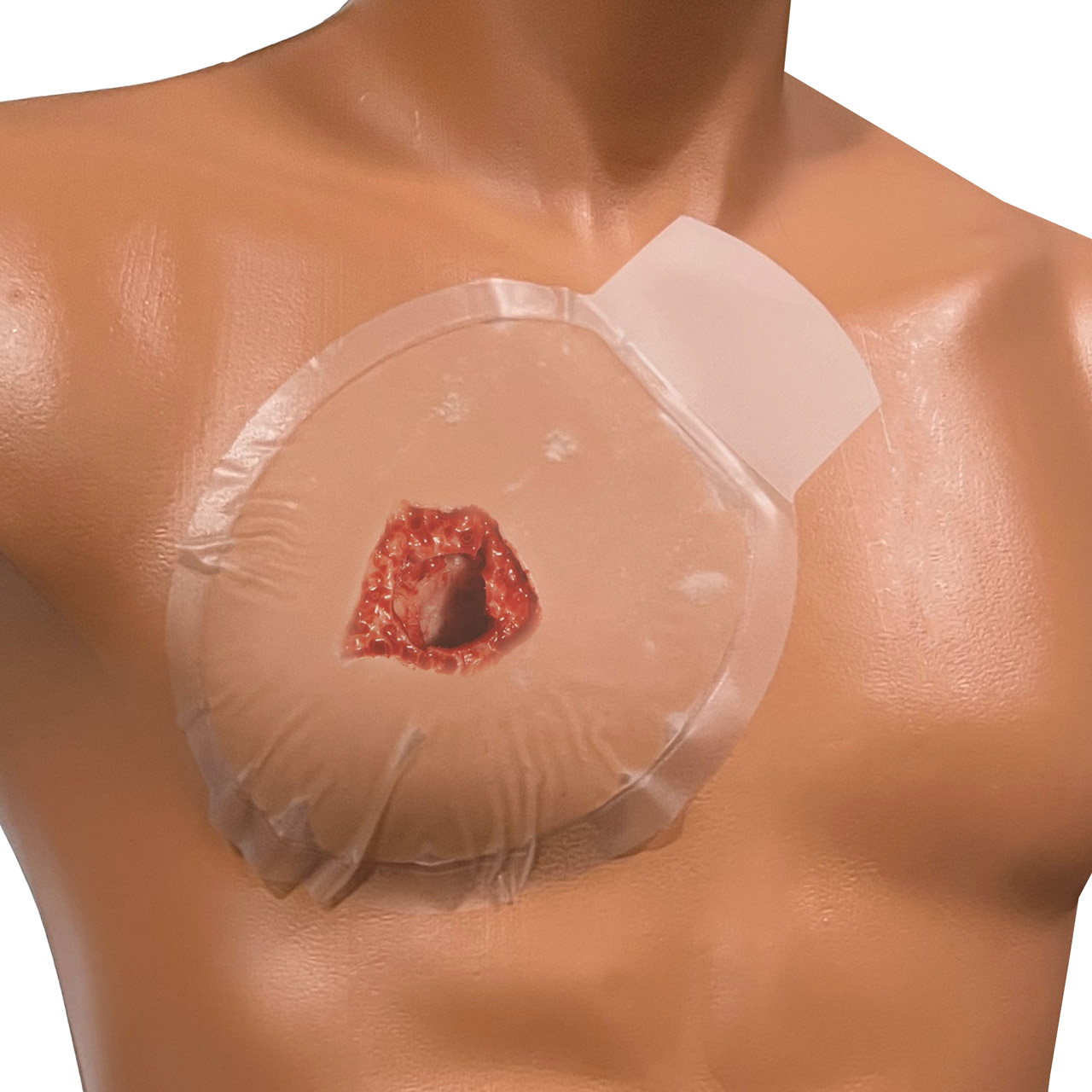
“Sucking Chest Wound”
Air drawn in through hole
Wound to the chest
Sucking sound
Small air bubbles within wound
Patient may gasp for air
Patient Care for “Sucking Chest Wound”
Allow law enforcement to render scene safe.
Consider A L S.
Maintain open airway.
****Seal wound.
****Apply occlusive dressing.
Info on Patient Care for “Sucking Chest Wound”
Allow patient to remain in position of comfort if possible.
Administer high-concentration oxygen.
Treat for shock.
Immediate transport.
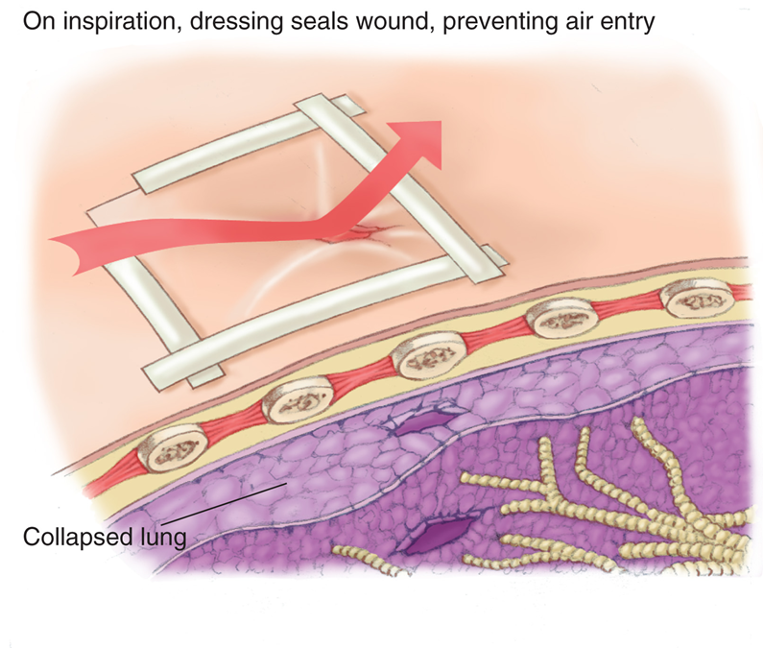
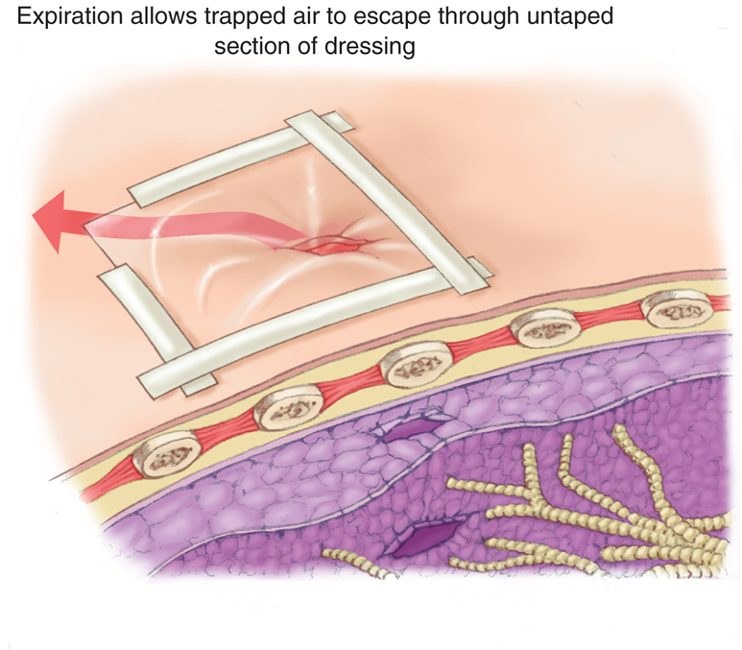
Occlusive and Flutter-Valve Dressings
Occlusive dressing seals wound to stop movement of air.
Flutter valve dressings involve taping dressing in place and leaving a side or corner of dressing unsealed
As patient inhales, dressing will seal wound.
As patient exhales, free corner or edge acts as flutter valve to release air trapped in chest cavity.
Creating a flutter valve to allow air to escape from the chest cavity.
Creating a flutter valve to allow air to escape from the chest cavity.
Injuries Within the Chest Cavity
Pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax
JVD hyper resonant tympanic sound on percussion
Hemothorax and hemopneumothorax
Hypo resonant, dull sound no jvd
Traumatic asphyxia
Pressure pushes blood into the jugular veins
Cardiac tamponade (JVD, Narrowed pulse pressure)
Aortic injury