EXAM 4: Chapter 12 The Nervous System I: Nervous Tissuec単語カード | Quizlet
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
central nervous system (CNS)
consists of the brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
consists of nerves and ganglia, which are all the nervous tissues structures external to the CNS
afferent (sensory) division and efferent (motor) division
What does the peripheral nervous system (PNS) divide into?
afferent (sensory) division
sensory impulses are carried from sensory receptors through the PNS TOWARDS the CNS
efferent (motor) division
motor impulses are carried AWAY FROM THE CNS, through the PNS, to the EFFECTORS (muscles and glands)
somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
What does the efferent (motor) division further divide into?
somatic nervous system (SNS)
voluntary control over skeletal muscle contraction
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
automatic control, involving regulation of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles and glandular activity
(involuntary)
somatic
outer body
visceral
inner body
general
widespread
special
localized
branchial innervation
refers to the motor innervation of the pharyngeal (branchial) muscle
proprioception
refers to a series of senses that monitor the degree of stretch in muscles, tendons, and joint capsules
sensing the position and movement of our body parts
neurons
long lived, non-dividing cells
has a cell body, axons and dendrites
nissl bodies (chromatophilic substance)
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and free ribosomes in neurons
in the CNS except for those found in ganglia of the PNS
Where are all neuron cell bodies found?
axon hillock
specialized region of an axon, which connects the initial segment of the axon to the cell body
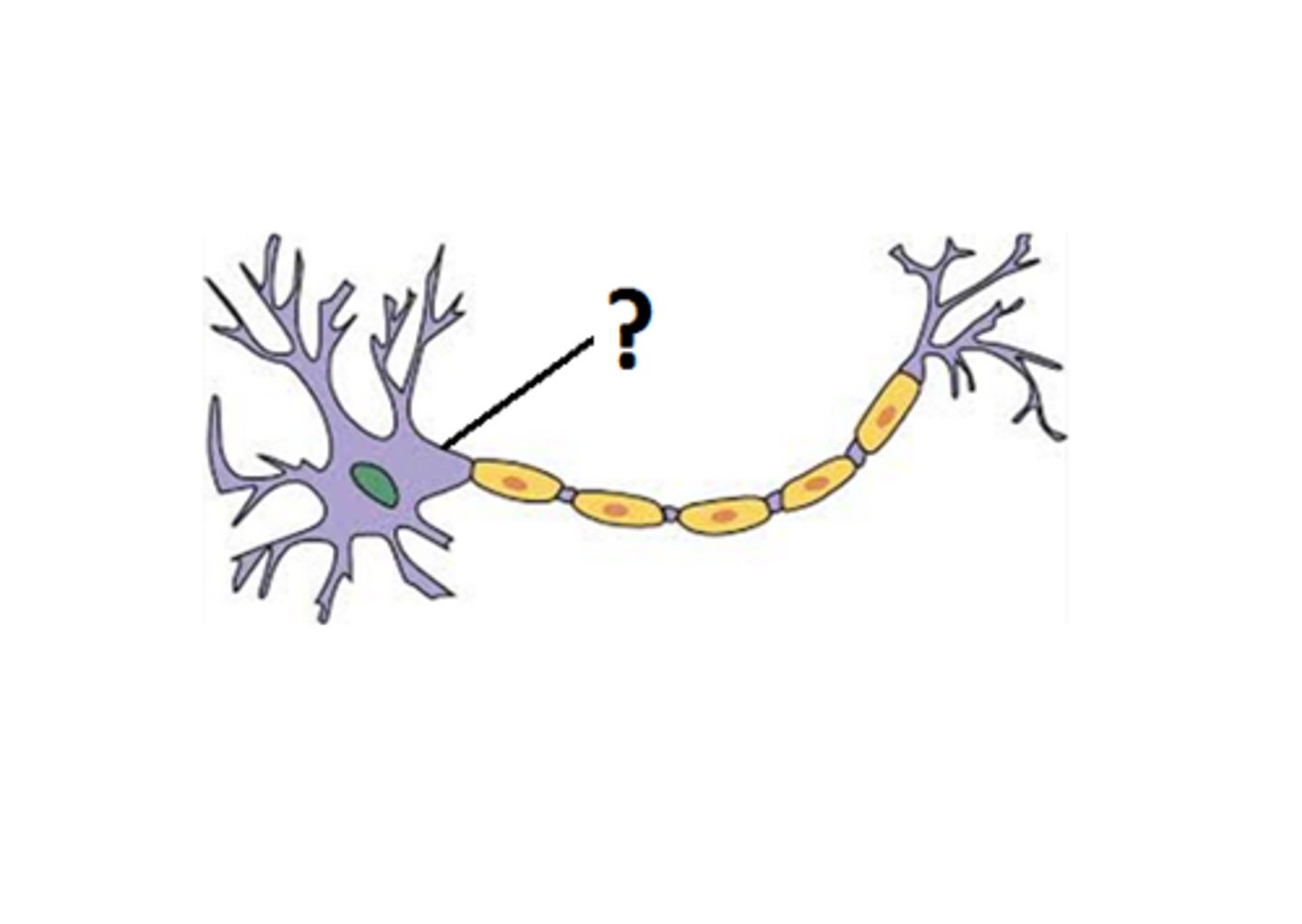
axoplasm
cytoplasm of axon, which contains numerous organelles
collaterals
side branches of the axon
terminal arborization
a series of fine, terminal extensions, which branch from the tip of the axon and end at synaptic terminals
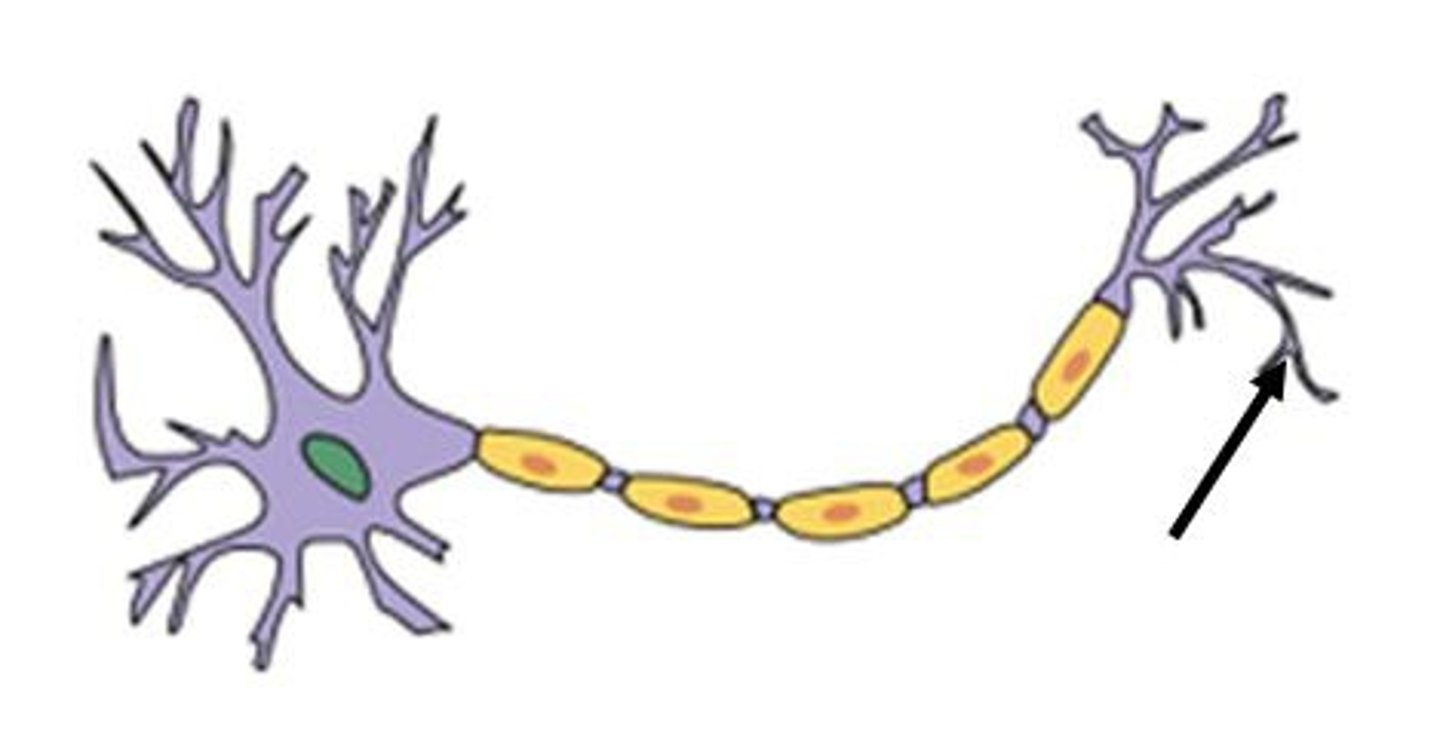
terminal bouton
the area where one neuron synapses on another
axolemma
plasma membrane of axon
ganglia
clusters of cell bodies in the PNS
nerves
bundles of axons in the PNS
dendrites
branched receptive sites that conduct signals from other neurons TOWARD the neuron cell body
axon
neuron structure that generates and conducts nerve impulses AWAY FROM the neuron cell body
synapse
a functional junction between neurons (or between a neuron and another cell) at neuroeffecter junctions
- site of intercellular communication
- occurs on dendrites, cell body, or along axon)
vesicular synapse
chemical synapse that involves neurotransmitters
nonvesicular synapses
electrical synapse that involves direct contact between cells
1. sensory neurons
2. motor neurons
3. interneurons
What are the 3 functional groups that neurons can be categorized in?
sensory (afferent) neurons
conduct impulses TOWARD THE CNS
motor (efferent) neurons
conduct impulses AWAY FROM THE CNS
Interneurons (association neurons)
neurons that lie in the CNS between sensory and motor neurons
neuroglia or glial cells
supporting cells of the nervous system
- astrocytes
- microglia
- ependymal cells
- oligodendrocytes
What are the neuroglia/glial cells of the CNS?
astrocytes
largest and most numerous type of glial cells
- controls interstitial environment
- repairs damaged neural tissue
- creates 3D framework for CNS
- guides neuron development
- maintain BLOOD-BRAIN barrier
microglia
phagocytic cells of the CNS (engulf cellular debris, waste products, and pathogens)
immune defense
ependymal cells
cuboidal to columnar epithelial cells that line the central canal and ventricles of the brain
creates and secretes CSF
oligodendrocytes
glial cells that maintains cellular organization in the gray matter AND PRODUCES MYELIN to completely sheath areas of white matter (myelinated axons)
- schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)
- satellite cells
What are the neuroglia/glial cells of the PNS
schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)
myelin-forming cells that cover all peripheral axons, whether myelinated or unmyelinated
satellite cells
enclose neuron cell bodies in the peripheral ganglia;
- regulate the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the neuron cell body and the extracellular fluid
speeds impulse conduction
What is the function of myelin?
myelin sheath
a coat of supporting-cell membranes wrapped in layers around the axon
Nodes of Ranvier (Neurofibral Nodes)
gaps in the myelin sheath
peripheral nerves, or simply nerve
a bundle of axons wrapped in connective tissue in the PNS
epineurium
surrounds the whole nerve
perineurium
surrounds each fascicle of axons
endoneurium
surrounds each axon
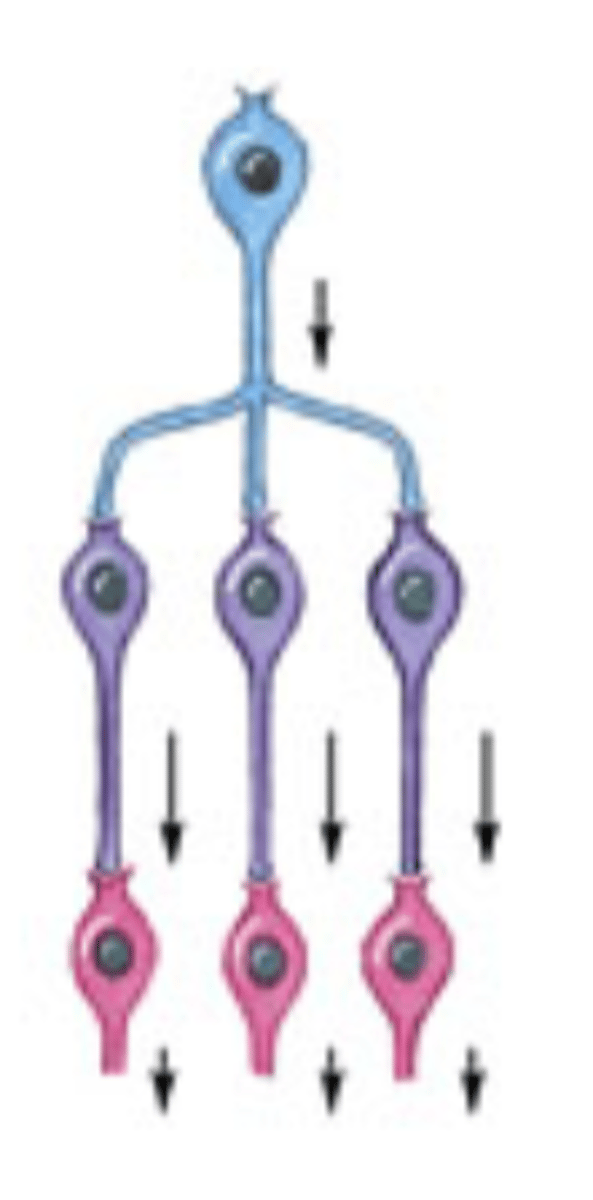
divergence of neurons
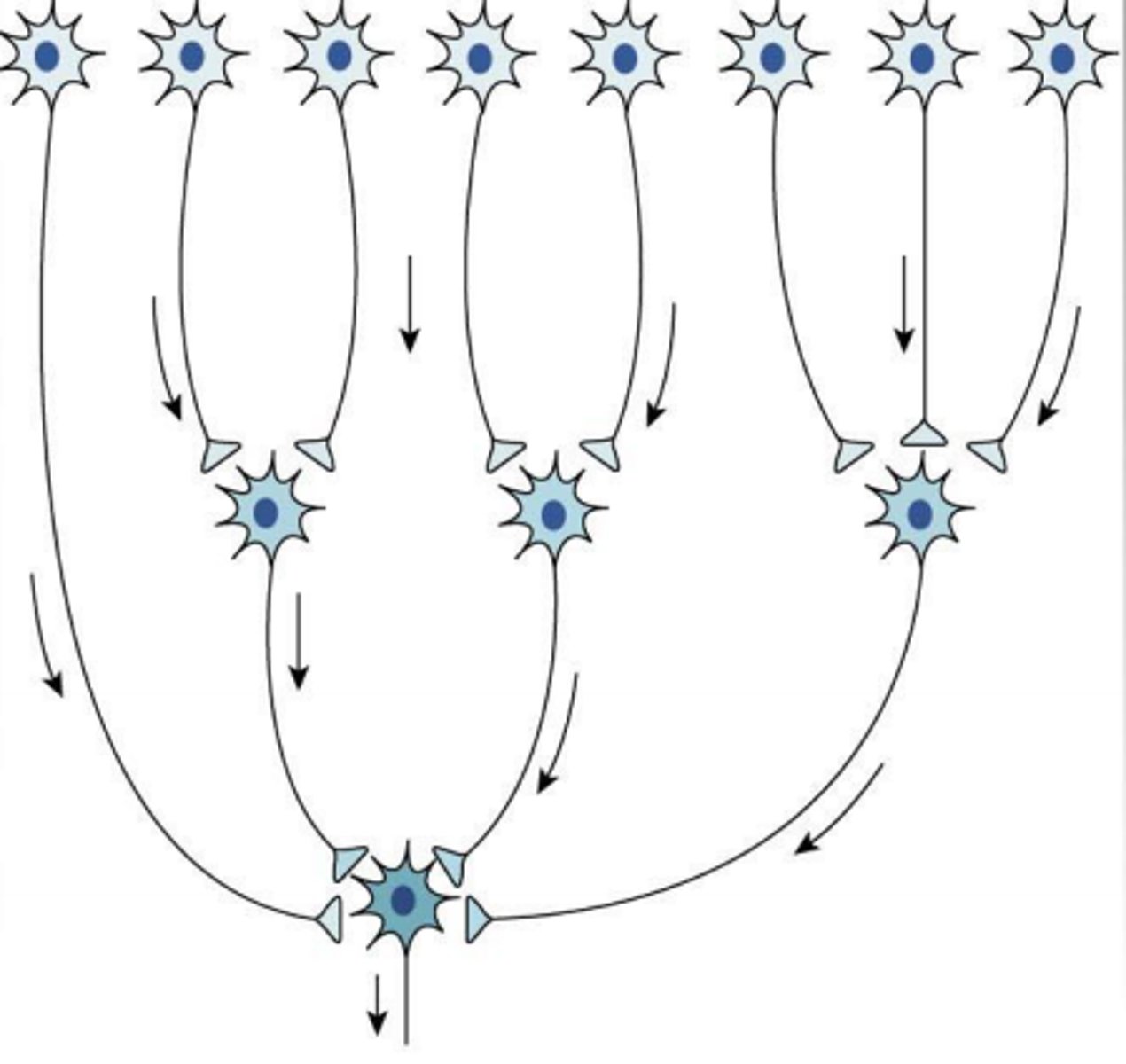
convergence of neurons
serial processing neurons
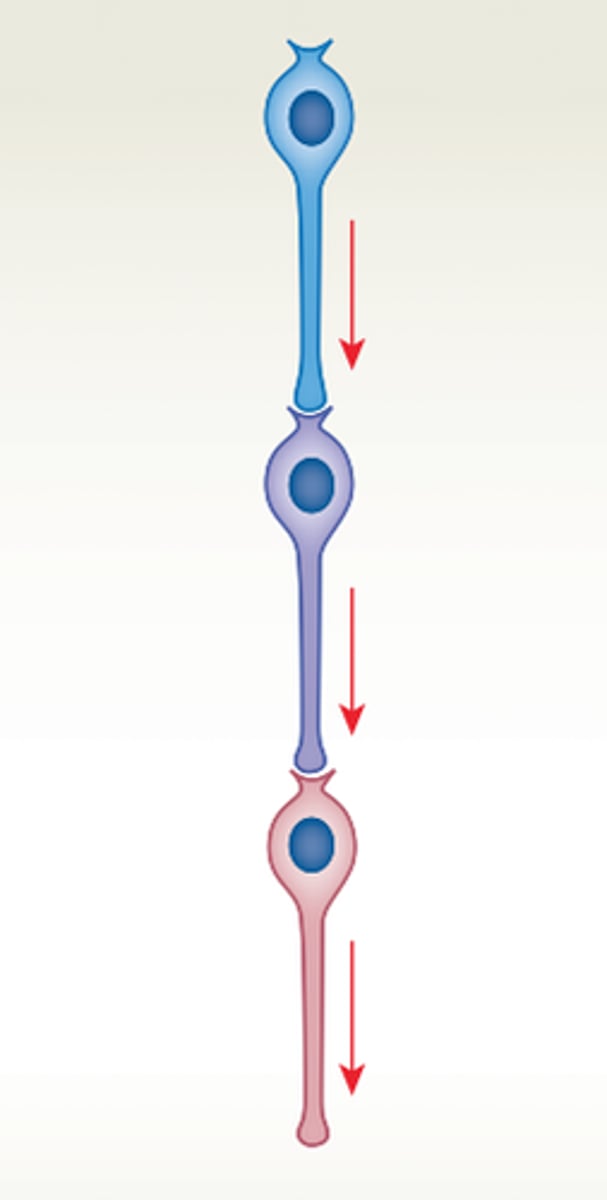
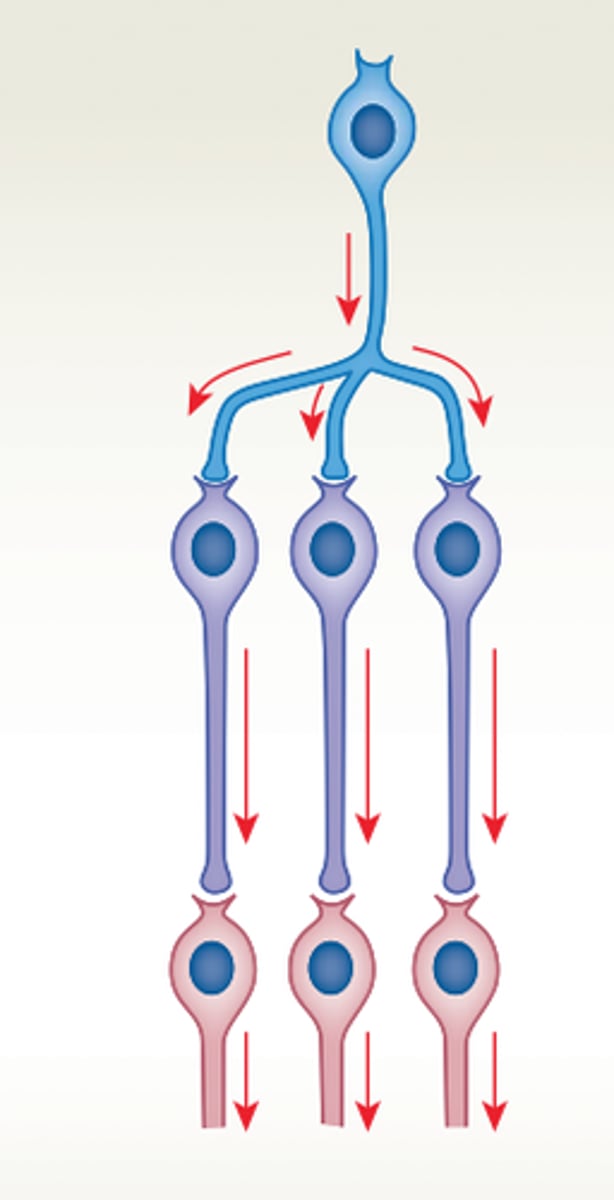
parallel processing neurons
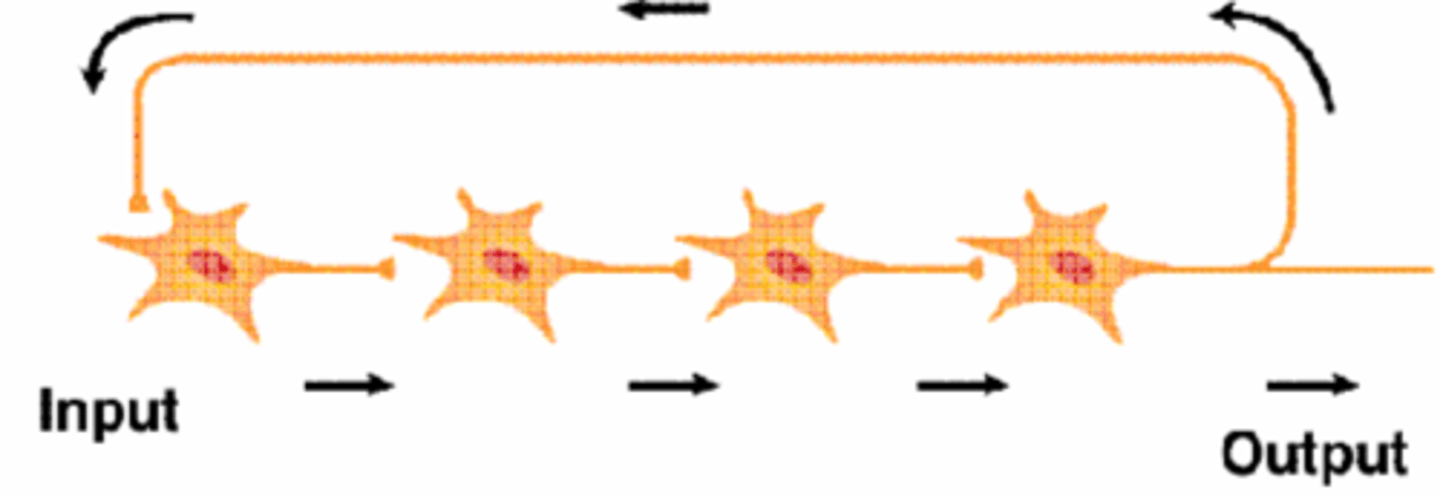
Reverberation neurons
neural circuit - homeostasis; balance; biofeedback
Exteroceptors
provide information about the external environment
Interoceptors
monitor internal organ activity
Exitability
ability of plasmalemma to conduct electrical impulses
action potential
an electrical impulse that develops after the plasmalemma is stimulated to its threshold
nerve impulse
an action potential traveling along an axon
- presence/absence of myelin sheath
- diameter of axon
The rate of impulse conduction depends on what properties of the axon?
reflex
an immediate involuntary response to a specific stimulus
can be either somatic or visceral
reflex arc
a neural "writing" of a single reflex