propedeutics small animals- respiratory system exploration
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
does it breathe normally- do you hear any sounds?
can it exercise?
is the animal coughing- when?
what questions might we ask the owner about its pet regarding respiration?
a chronic, lifelong, debilitating, primarily obstructive airway disease which adversely affects the quality of life of many popular dog breeds
characterized by stenotic nares, extended nasopharyngeal turbinates, elongated soft palate, everted laryngeal saccules, laryngeal collapse, and hypoplastic trachea
what is brachycephalic syndrome?
bulldog, pug, boxer, pekinese, shih tzu, persian, exotic, shorthair, burnese, etc
what breeds does brachycephalic syndrome commonly affect?
kennel cough
what respiratory problem might be caused by environmental conditions?
distemper, tumors, tracheal collapse
what respiratory problems might be caused by old age?
wet, cold, smooth
how should the snout appear?
fever
what does a hot, dry nose indicate?
abcesses, tumors, fractures, fistulas
what types of deformities might we see on the nose?
foreign bodies, neoplasia, polyps
what causes unilateral nasal discharge?
tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia
what can cause bilateral nasal discharge?
serosal
mucous
purulent
hermorrhagic
foamy
what are the 5 types of nasal discharge?
transparent, acellular. due to a mild, non-infectious disease (acute part)
describe a serosal nasal discharge
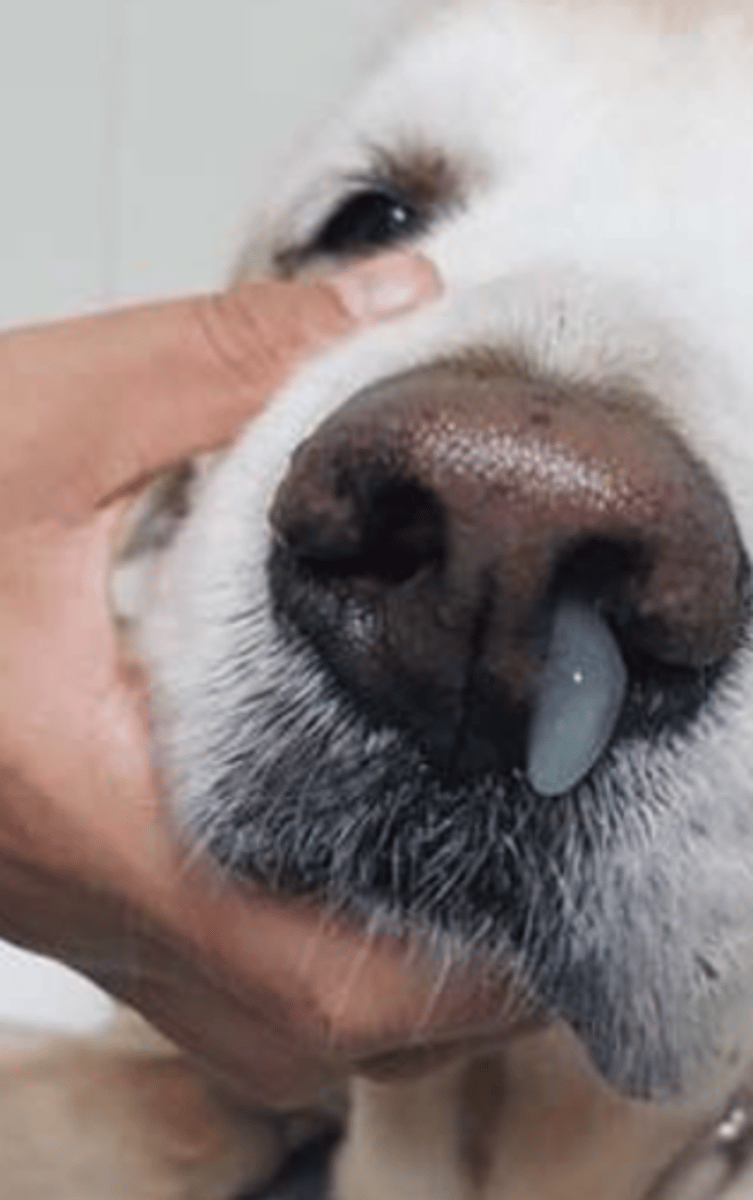
mucous discharge
non infectious, chronic nasal disease
if the animal's nose leaks clear discharge that is acellular and has a high protein content, what is this called? is it due to an infectious disease?
whitish to yellowish. neutrophils and bacteria
describe a purulent nasal discharge
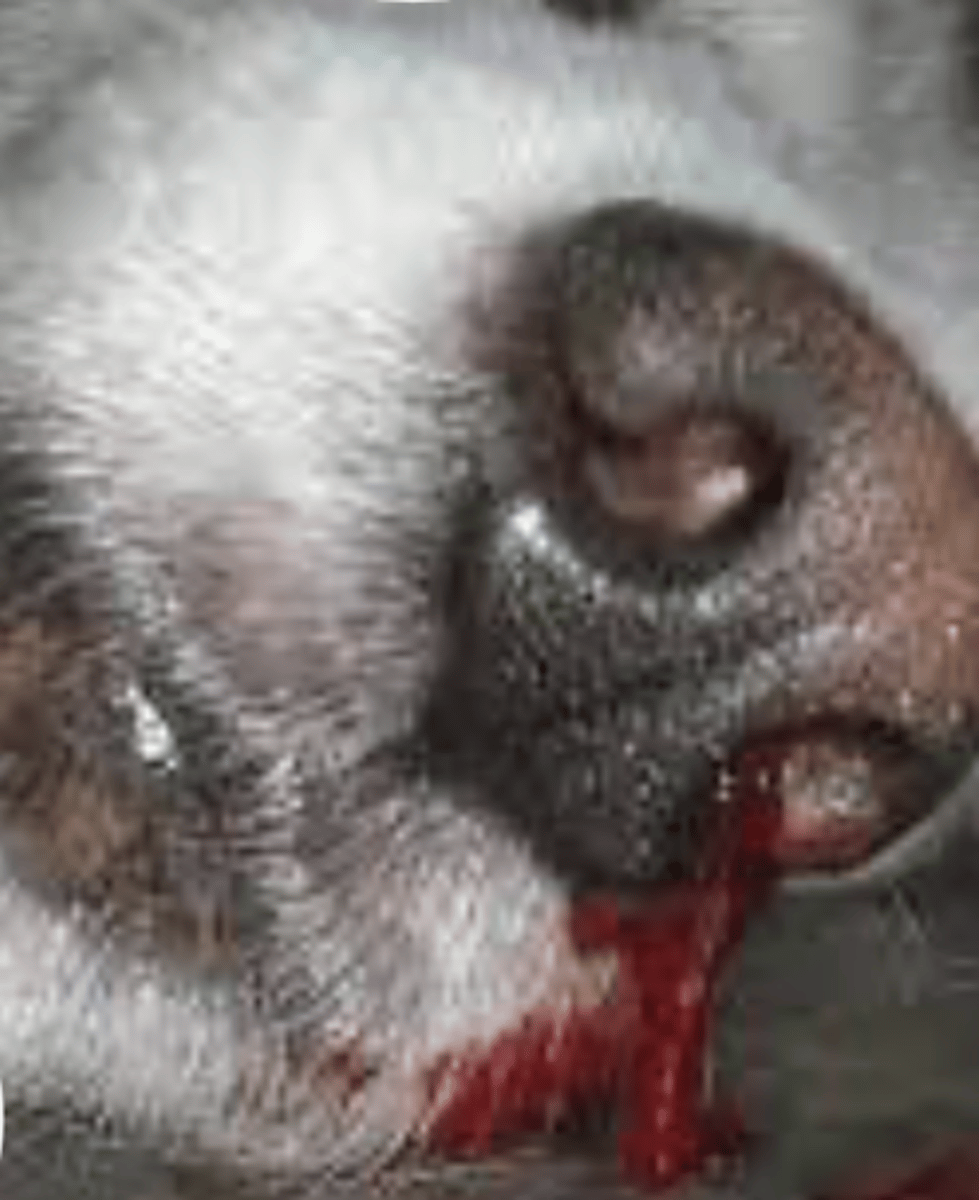
hemorrhagic
which type of nasal discharge is bloody?
epistaxis
what is the medical term for nose bleed?
pulmonary edema
what causes a foamy nasal discharge?
serous with bubbles
describe foamy nasal discharge
serosal
what type of nasal discharge would be caused by a mild, non infectious disease?
mucous
what type of nasal discharge would be caused by a chronic, non infectious disease?
unilateral
what is it called when there is discharge only from one nostril?
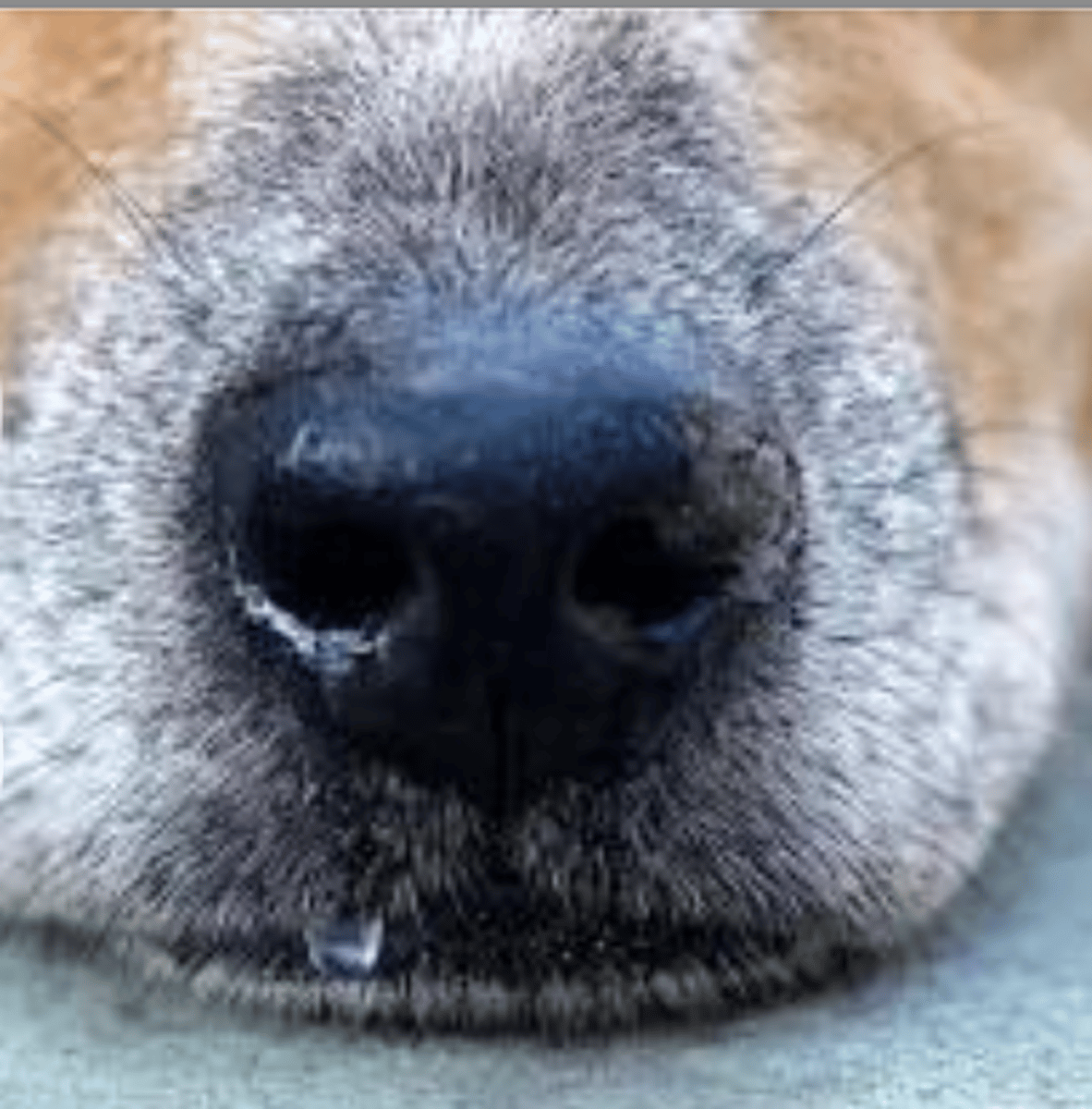
serosal
what is this discharge called?

mucous
what is this discharge called?

hemorrhagic
what is this discharge called?

purulent
what is this discharge called?

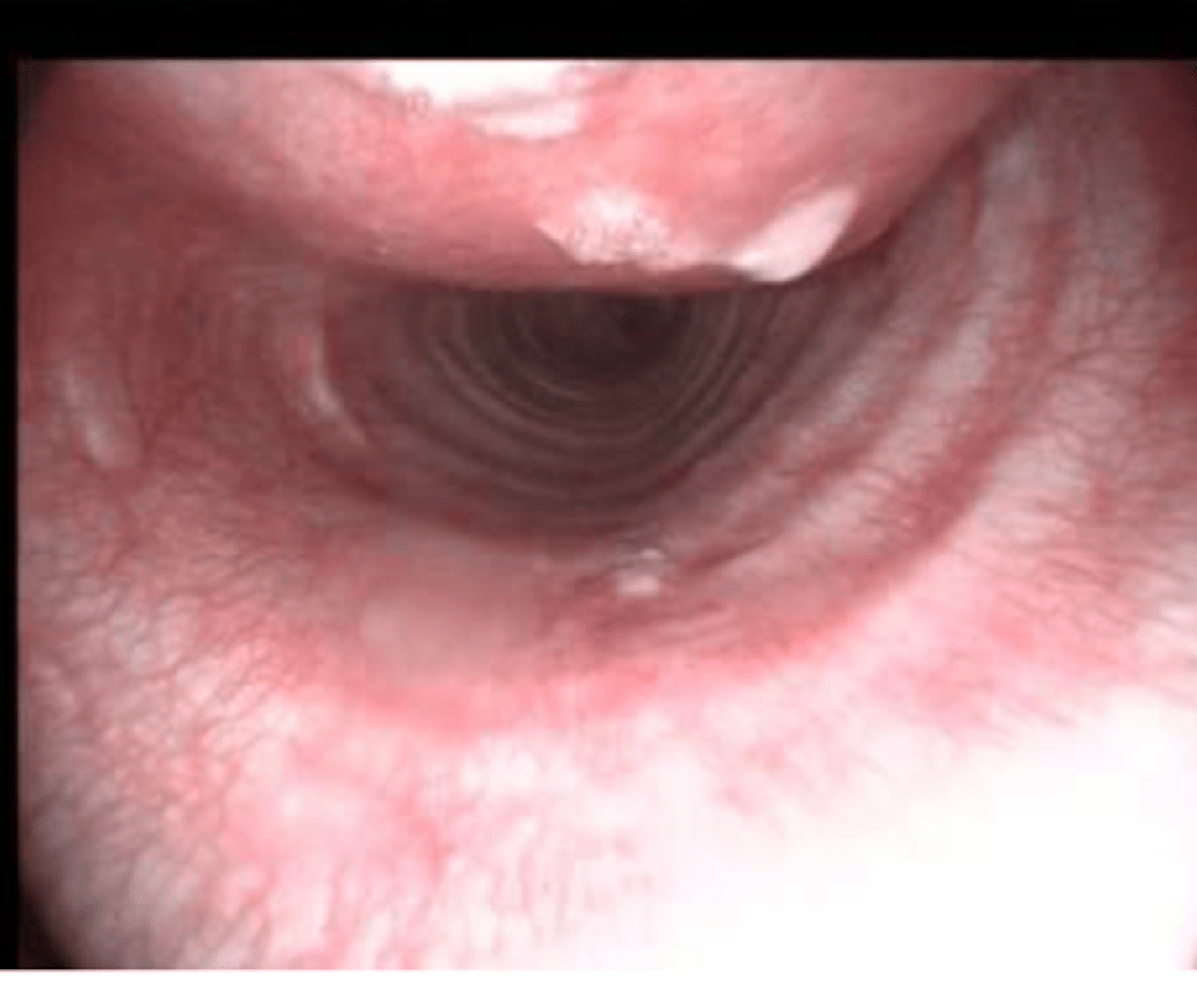
rhinoscope
what do we use to internally explore the nose?
a camera and a light that is inserted into the nose to explore the nasal cavity
what is a rhinoscope?
rhinoscope
what is this instrument?
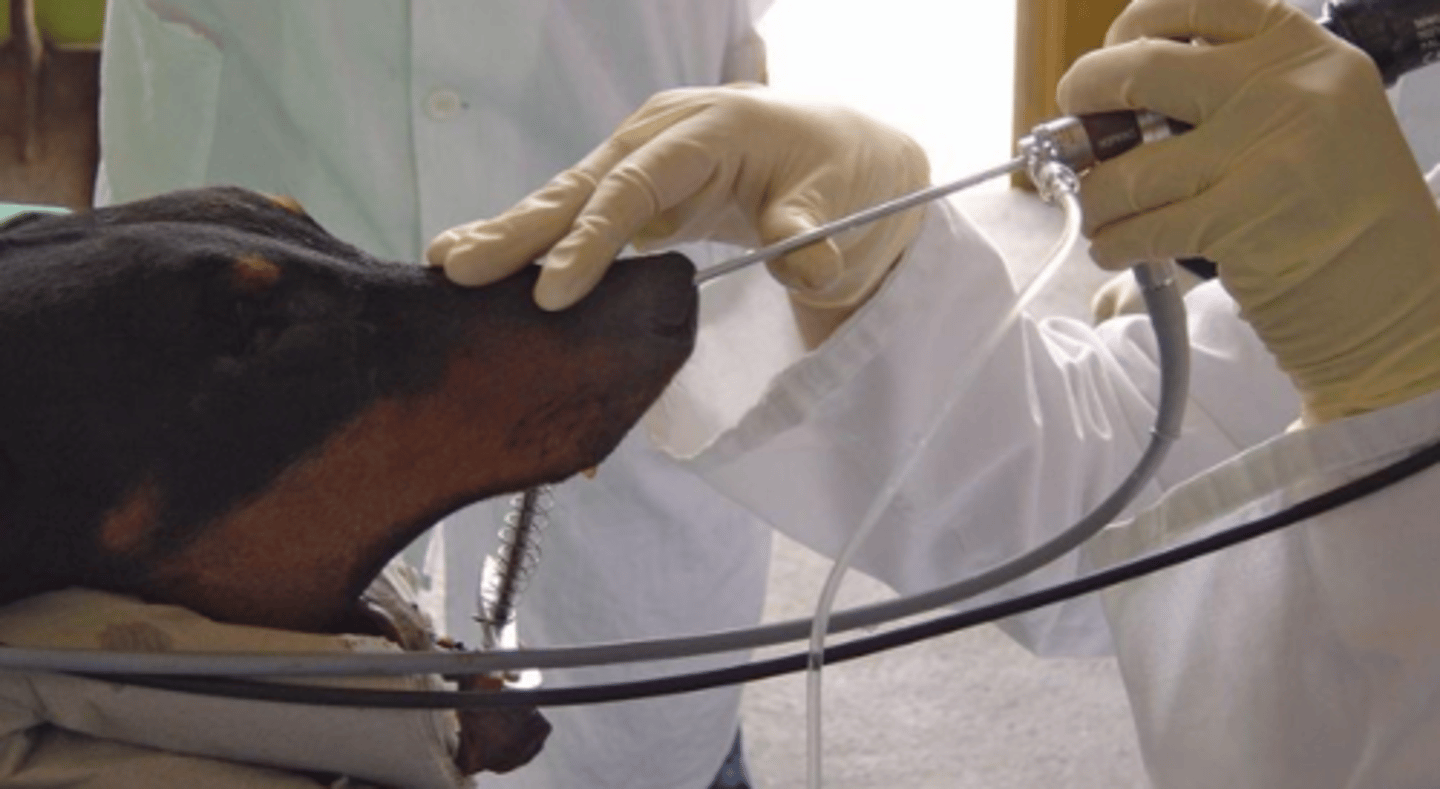
foreign bodies, tumors, nasal mucosa status
rhinoscopy can be used to check for....
sensibility, temperature, consistency, crackles
when we palpate the nose, what characteristics do we check?
1. stertors/snoring
2. stridors/wheezing
what are the 2 types of abnormal breathing sounds?
stertors/snoring
what are the abnormally deep respiratory sounds called?
stridors/wheezing
what are the abnormally sharp/acute respiratory sounds called?
-accumulation of dense exudates (fluid leaking out of blood vessels)
-membranes that vibrate as air passes
what causes the deep sounds of stertors/snoring?
-narrowing of nasal passages- due to inflammation, foreign bodies, masses, etc
-upper airway obstruction
what causes the sharp/acute noises of stridors/wheezing?
air
what are paranasal sinuses filled with?
3- frontal, maxillary, and sphenoidal, but we can only examine the frontal ones
how many paranasal sinuses do cats have?
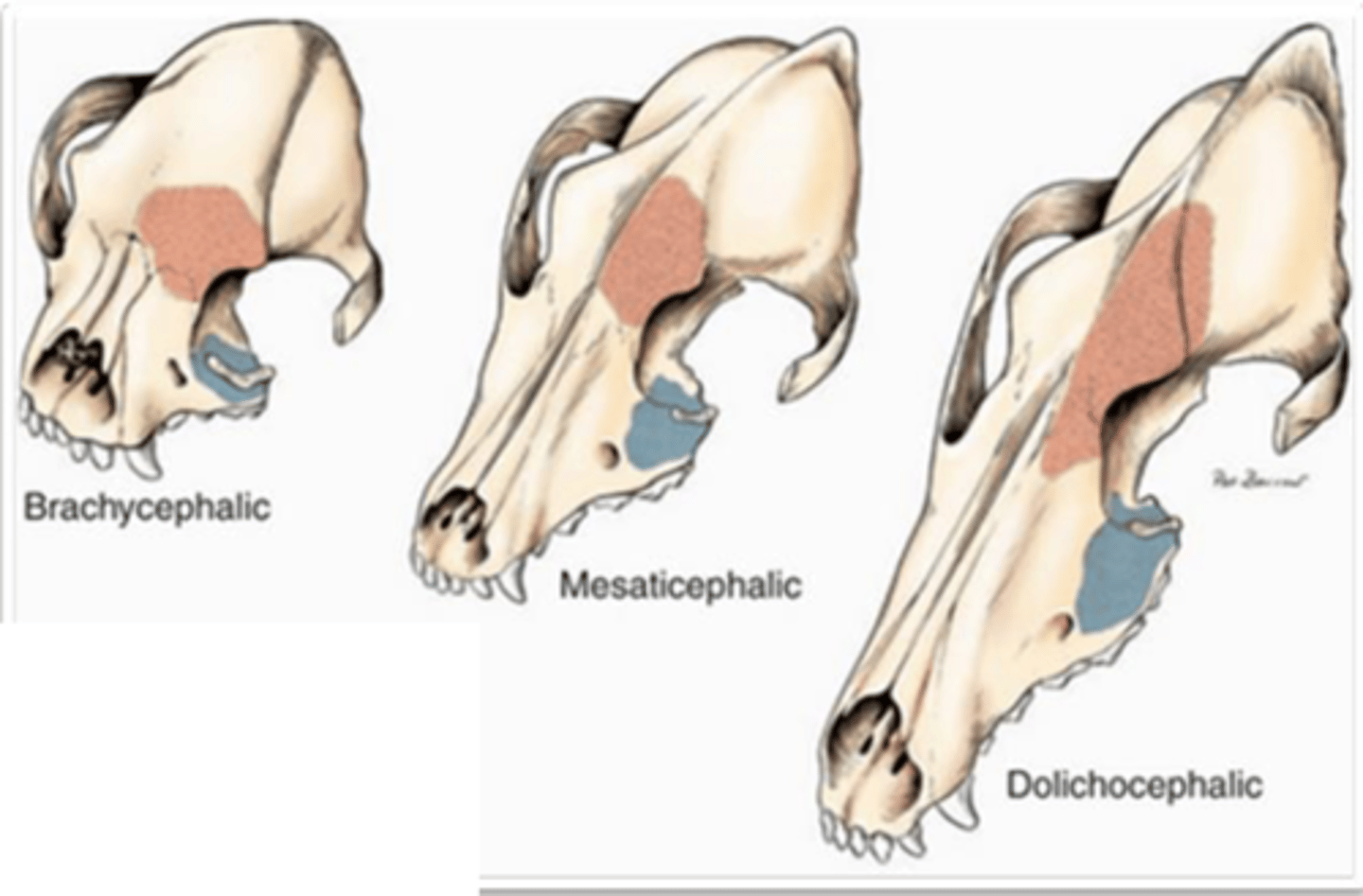
2- frontal and maxillary
how many paranasal sinuses do dogs have, and which?
rhinitis or dental problems
what causes sinusitis?
sinusitis in the maxillary sinuses
a molar infection might cause what other problem?
frontal sinus
cat- what is 1?
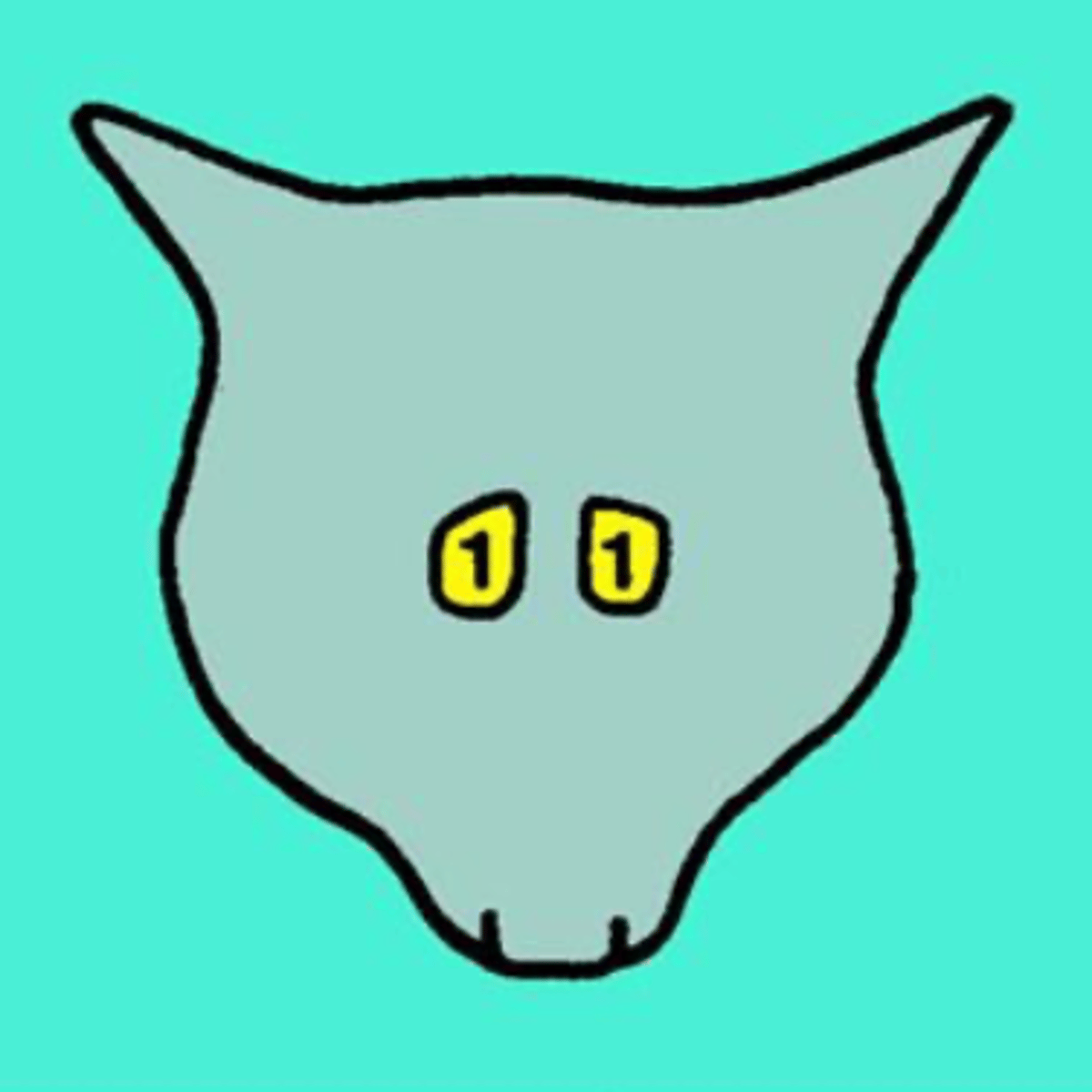
frontal sinus
dog- what is 1?
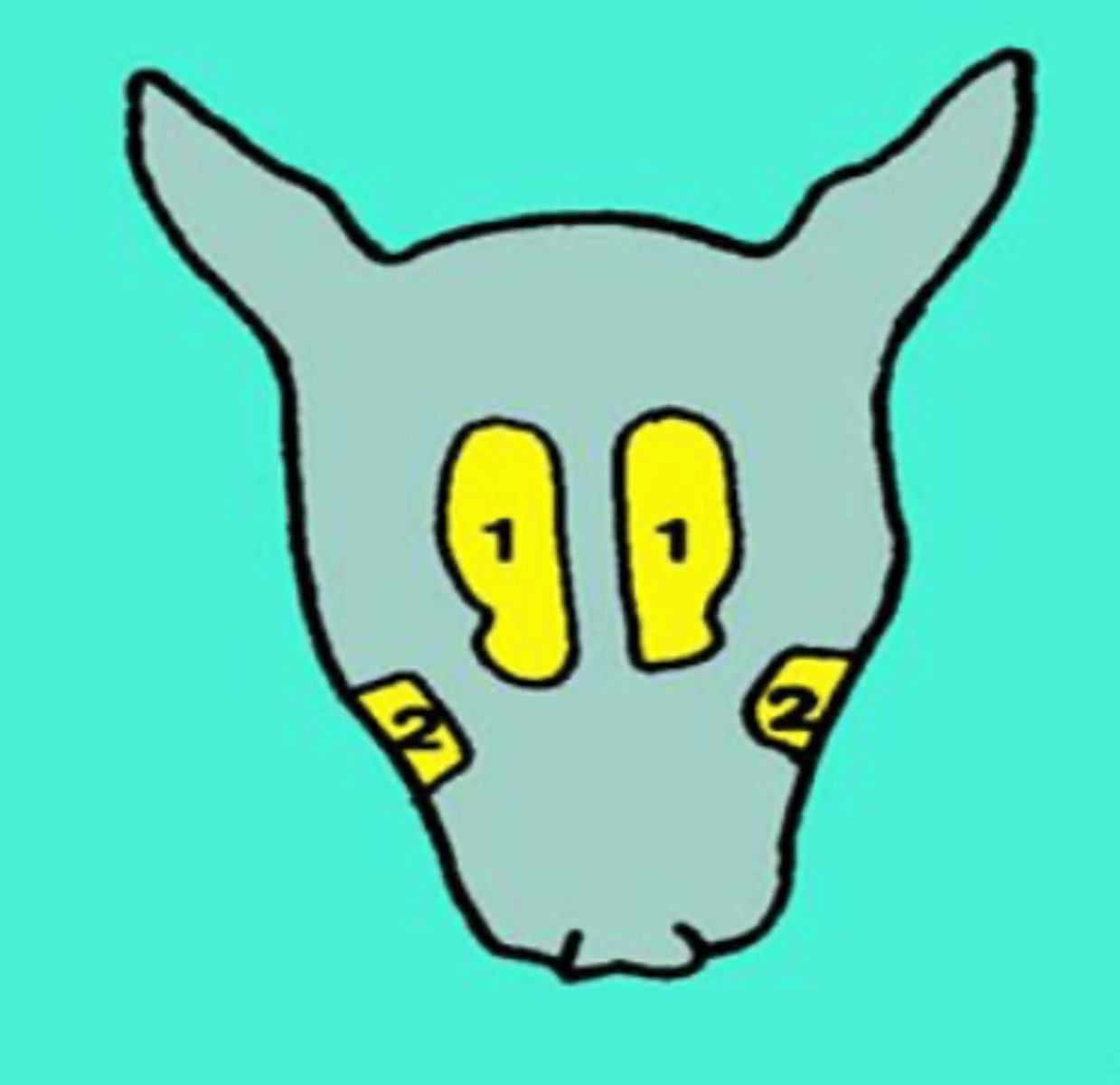

maxillary sinus
dog- what is 2?
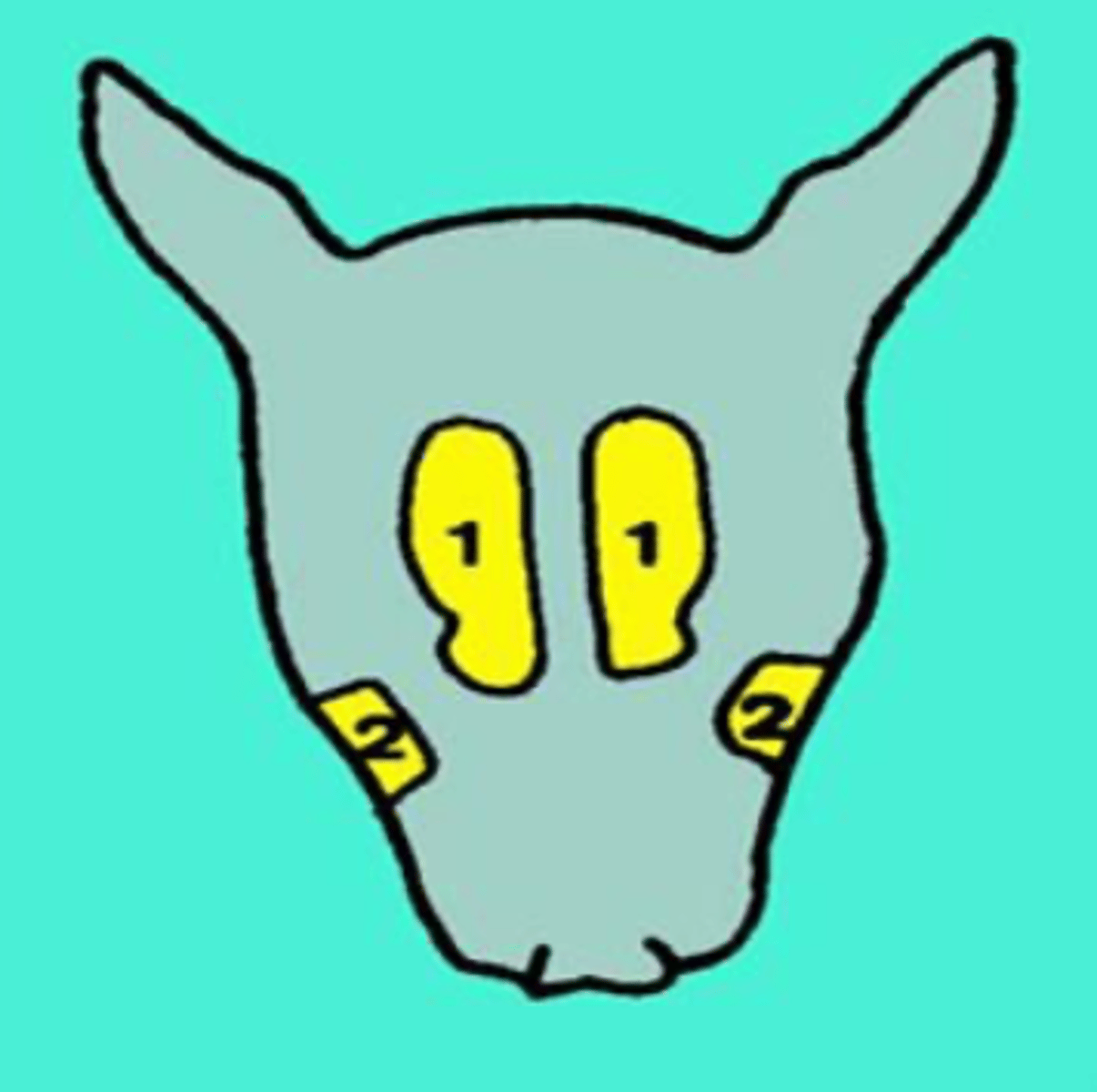

frontal sinus
what is the red part called?
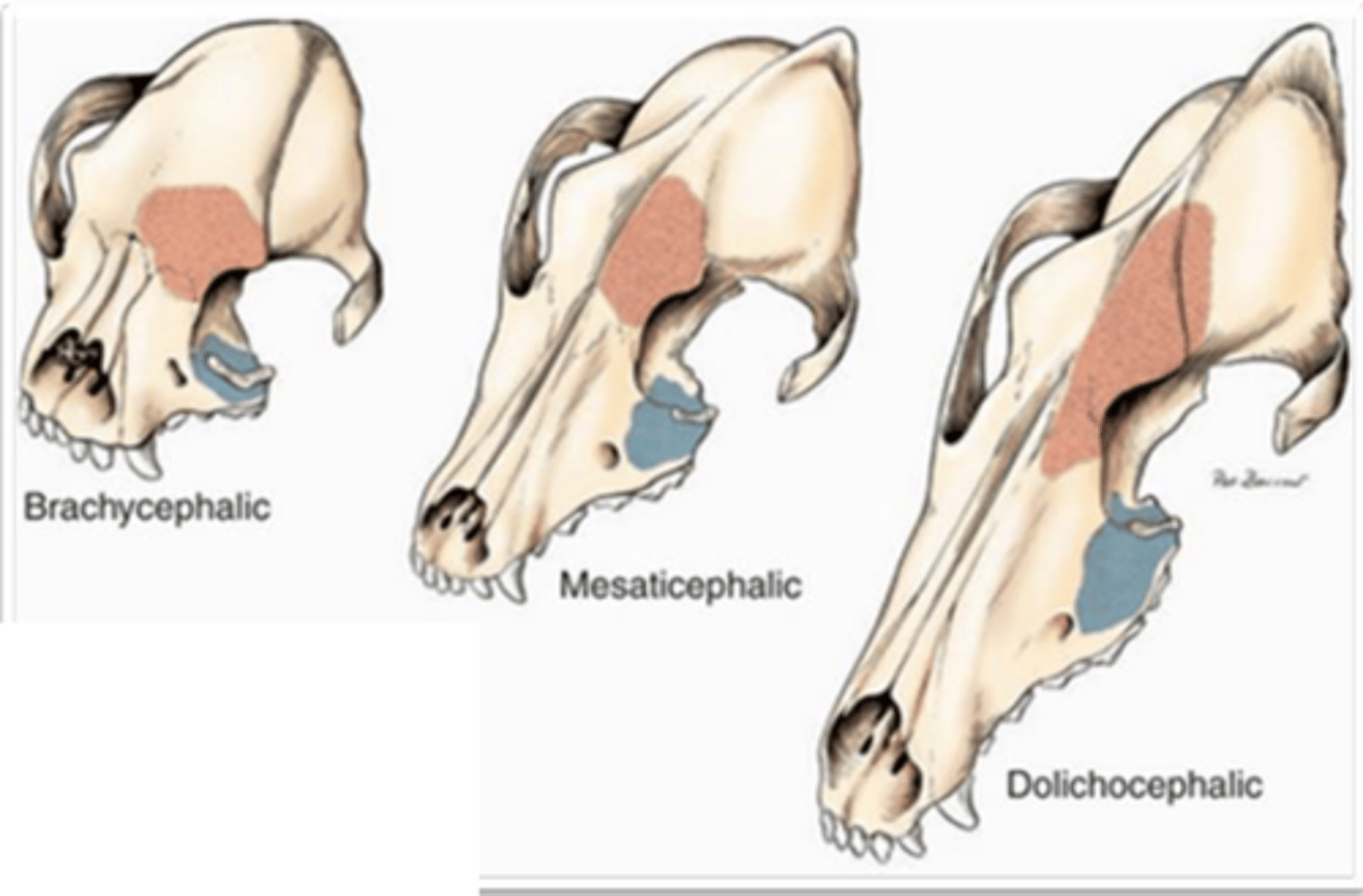
maxillary sinus
what is the blue part called?
-asymmetry/deformities
-size changes
-lesions
what do we check for when we explore the paranasal sinuses?
hypersonorus/tympanic- hollow
when we percuss the paranasal sinuses, what sound should we hear in normal conditions?
there are masses or exudate in the sinuses
we hear submatte/matte sounds when percussing the paranasal sinuses when what is wrong?
the frontal sinus
this is an issue with what part of the animal?
asymmetries, neoplasms, dysphagia, ptyalism, extended neck
by externally inspecting the pharynx, what problems can we observe?
condition of overproducing saliva
what is ptyalism?
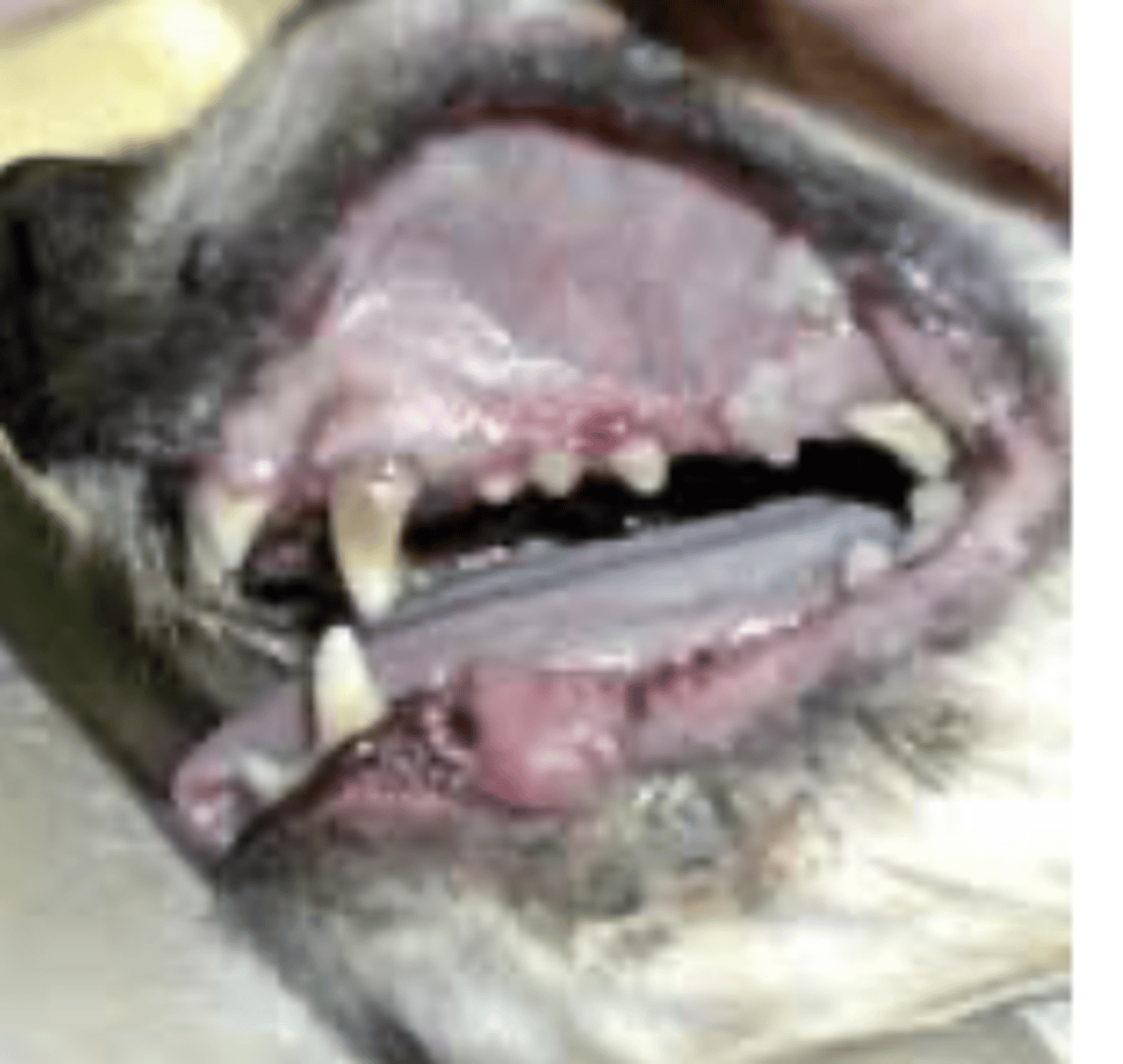
pharyngitis, ulcers, foreign bodies, tumors
by internally inspecting the pharynx, what problems can we observe?
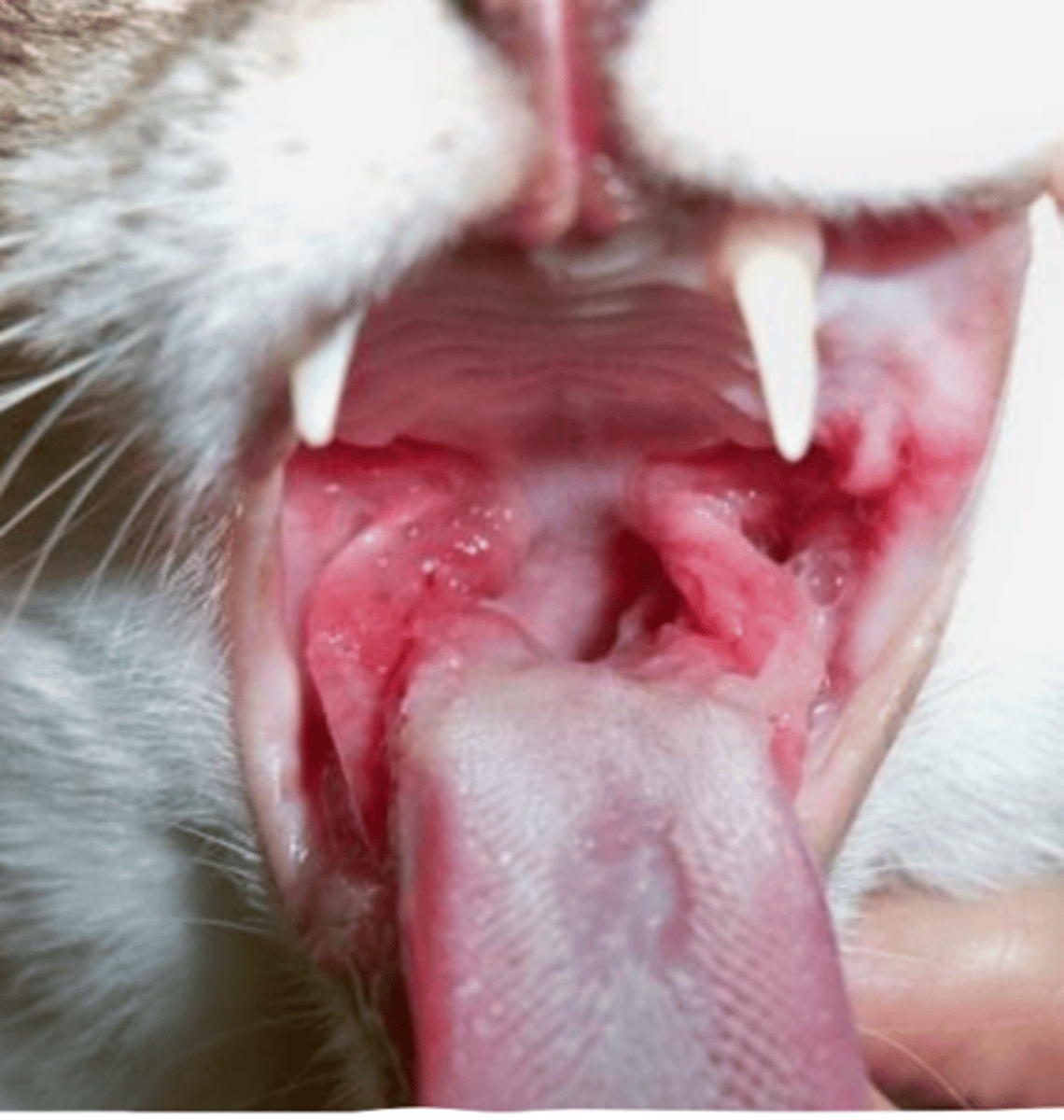
pharyngitis (inflammation of the pharynx)
what is the problem with this cat?
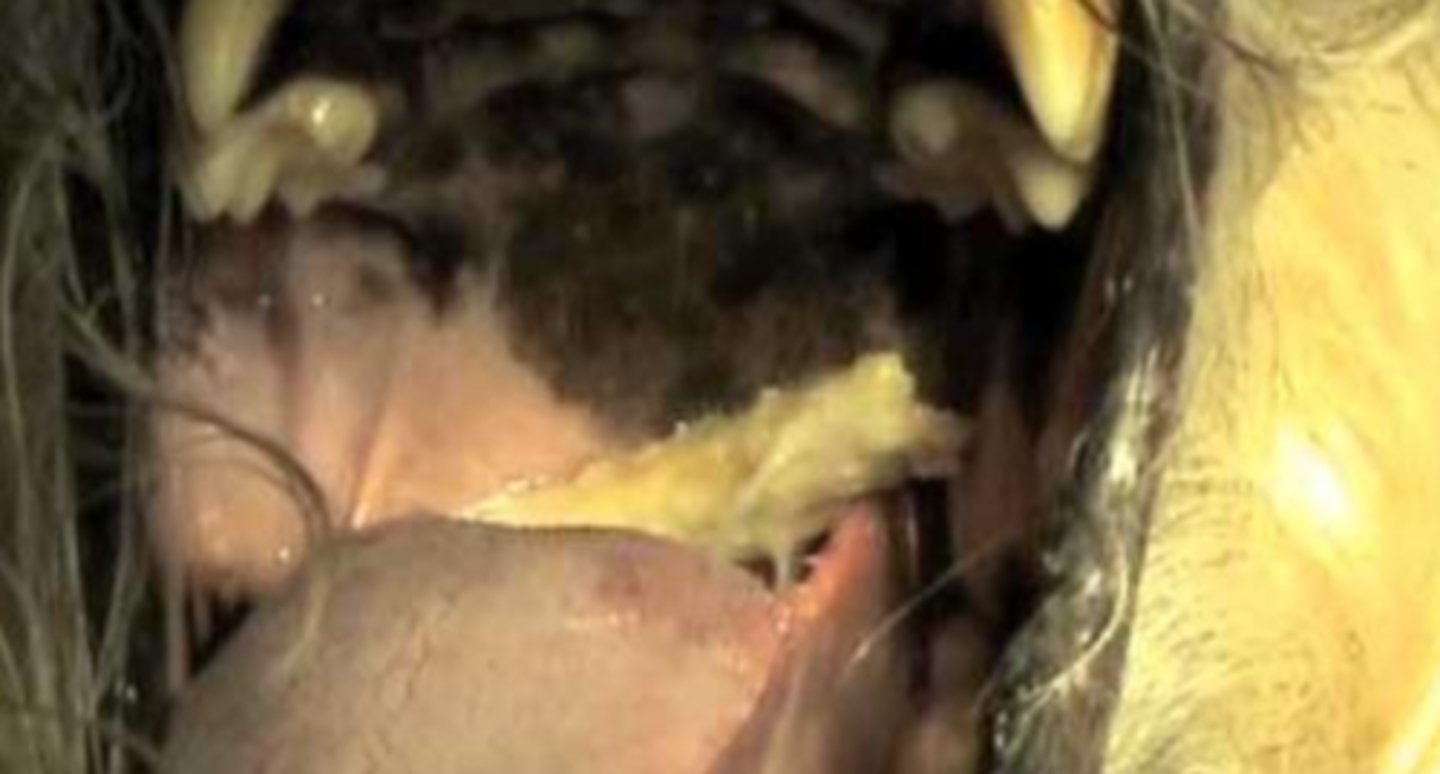
foreign body stuck in the pharynx
what is the problem here?
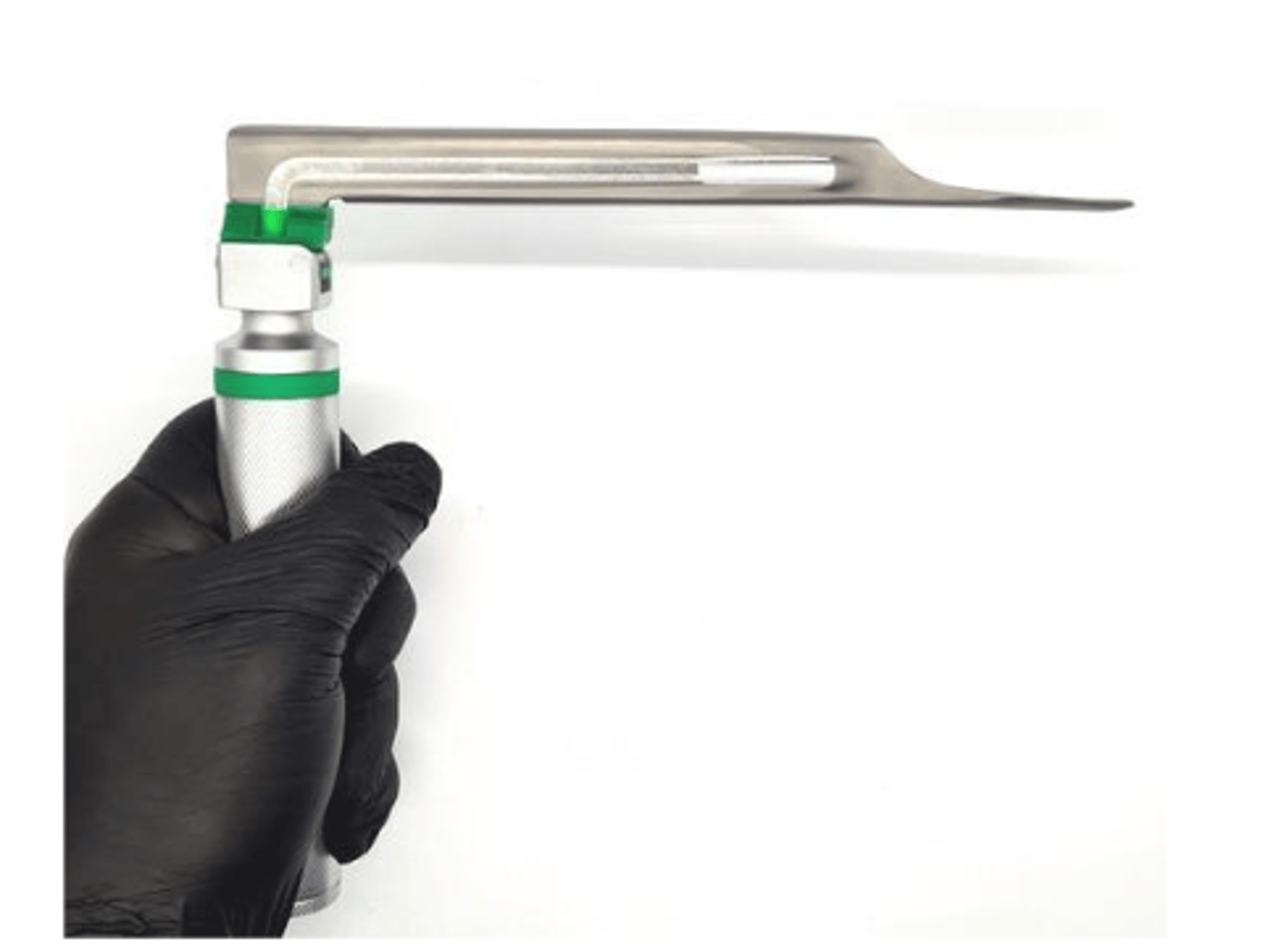
we must sedate the animal and use a laryngoscope
how can we explore the larynx internally?
internal inspection of the larynx
what is a laryngoscope used for?
lidocaine
in cats, what must we use if we must intubate?
cats
which species require lidocaine when intubating?
asphyxia
edema in the larynx might put the animal at risk for ......
laryngitis
what is the medical term for inflammation of the larynx?
a laryngoscope
what is this?
it cannot eat/breathe
what problems might the animal have if it has laryngeal paralysis?
endoscope
what do we use to internally inspect the trachea?
the dorsal part of the trachea falls inside
what is tracheal collapse?
the trachea has collapsed
trachea- what is the problem?
-volume/shape
-deviation
-ring integrity
-sensibility (pain)
-cough reflex
what do we check when palpating the trachea?
if we gently press the trachea and the animal coughs, there is tracheitis
what is the cough reflex, and what can we diagnose when performing this?
tracheal palpation
what is being performed?
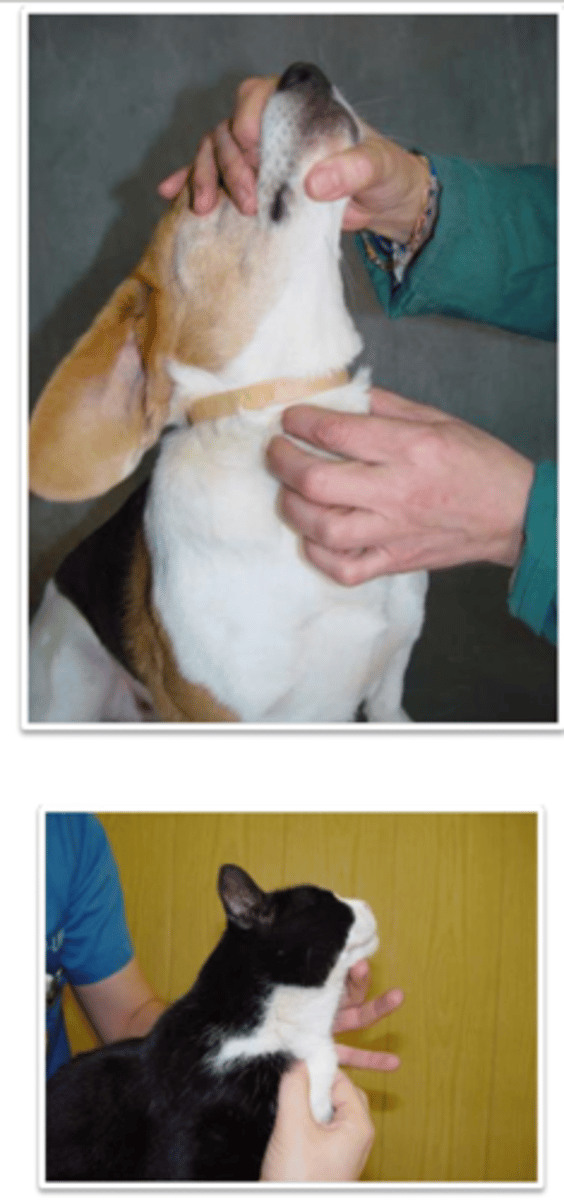

cough reflex
what reflex is tested when palpating the trachea?
tracheitis
if the animal coughs when we gently press its trachea, this indicates what issue?
irritation or inflammation of the airways (larynx, trachea, bronchi)
stimulus: chemicals, physical, viral, bacterial, mucus
what is coughing caused by?
vagus
sensitive information is transferred by the _____ nerve to the cough center
cigarettes, carpet with mites, aerosols
what are some environmental causes of cough?
small breeds
what breeds easily have tracheal collapse?
asthma, infectious bronchitis
cats are more prone than dogs to what respiratory issues?
tracheal collapse, cardiopathy
excitation and exercise puts the animal more at risk for what respiratory issues?
1. productive
2. dry/ non-productive
what are the 2 types of coughs?
non-productive
what type of cough- productive or non-productive requires treatment?
we must treat the cause, not the cough itself
how do we treat a productive cough?
the expulsion of mucus or sputum with the cough through the nose or mouth
what is expectoration?
a thick type of mucus made in your lungs
what is sputum?
irritations and emphysema
what are the consequences caused by a dry/non-productive cough?
the gradual damage of lung tissue, specifically the destruction of the alveoli
what is emphysema?
legs spread, neck extended
what is a dyspnoeic posture?
-dyspnoeic posture
-slow, fast, or noisy breathing
-cyanotic mucosa
-cough
-sneezing
-runny nose
-chest deformations
what symptoms are specific of a respiratory problem?
-lethargy
-anorexia
-depression
-weakness
-exercise intolerance
what are the symptoms may be caused by a respiratory problem but do not necessarily indicate a respiratory problem (unspecific signs)?
cyanotic mucosa
what is this called?
bilateral- because there are 2 lungs
do we perform a unilateral or bilateral inspection of the thorax?
constant- inspiration, expiration, and pauses must be regular in duration
how must the respiration rhythm be?
difficulty in air entry (airway stenosis)
if there is inspiration prolongation, what could be the cause?
upper
if there is inspiration prolongation (breathing in takes too long), is this an upper or lower respiratory tract issue?
inspiratory dyspnea
what is the medical word for inspiratory prolongation?
expiratory dyspnea
what is the medical term for expiratory prolongation?
lungs
expiratory dyspnea indicates that the animal has a problem in what part of the body?
emphysema, loss of lung elasticity, pneumonia
what might the problem be that causes expiratory dyspnea?
the animal has pain in the thorax or abdomen
if there are prolonged pauses in respiration, what is the problem?
inspiration
which should be shorter- inspiration or expiration?
-the amplitude of respiratory movements
-the difference on displacement of the ribs at the end of inspiration and at the end of expiration
what is respiratory depth?
not very noticeable
should the respiratory depth be noticeable?
hyperpneas
what is the word for pathological deep breaths?