Midterm Rock Identification - EES 1510L
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Rhyolite
- Igneous rock
- Felsic
- Fine-grained crystalline
- Fast cooling rate
- Came from an extrusive, explosive eruption
- Continental setting
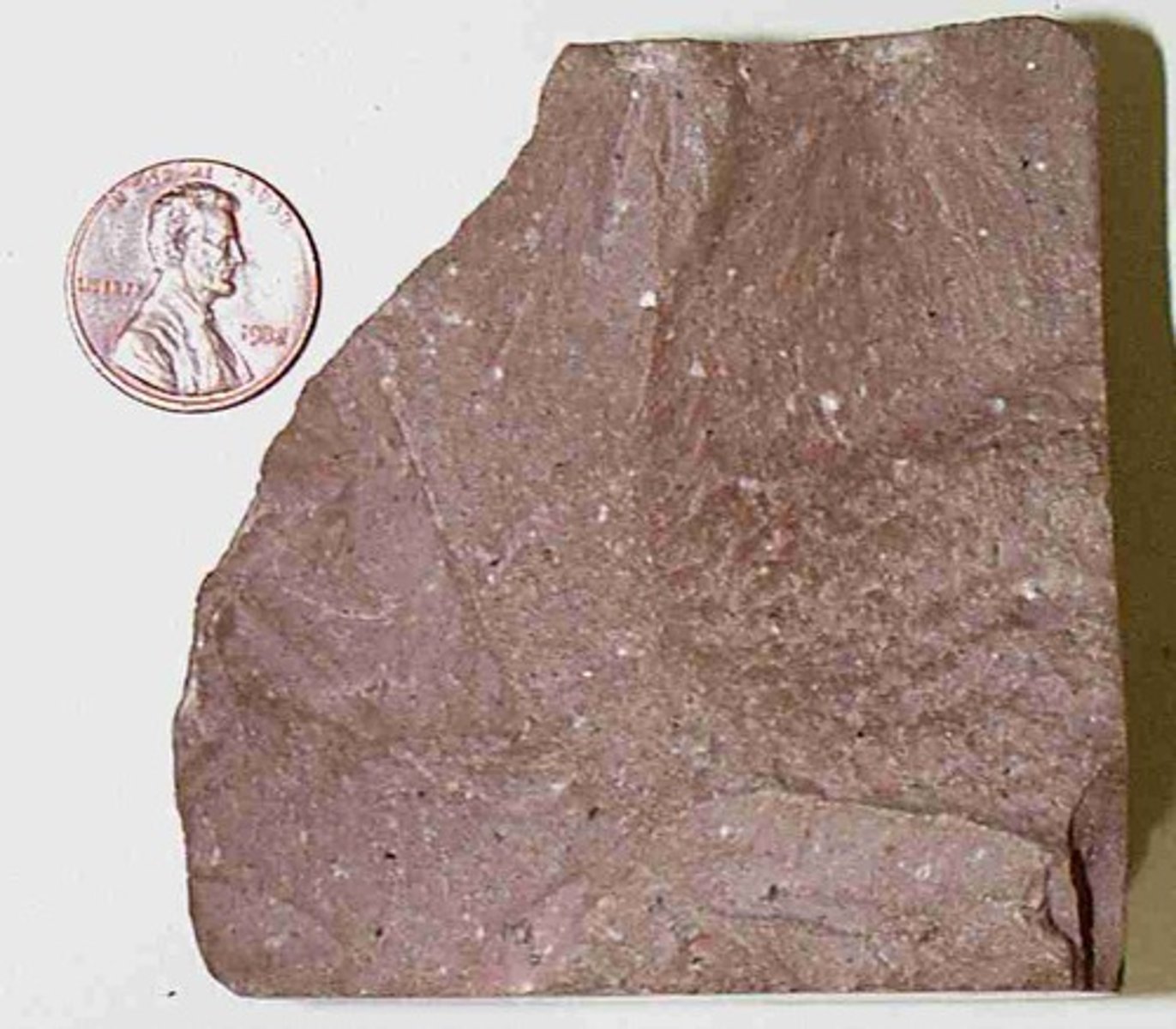

Andesite
- Igneous rock
- Intermediate
- Fine-grained crystalline
- Fast cooling, extrusive rock
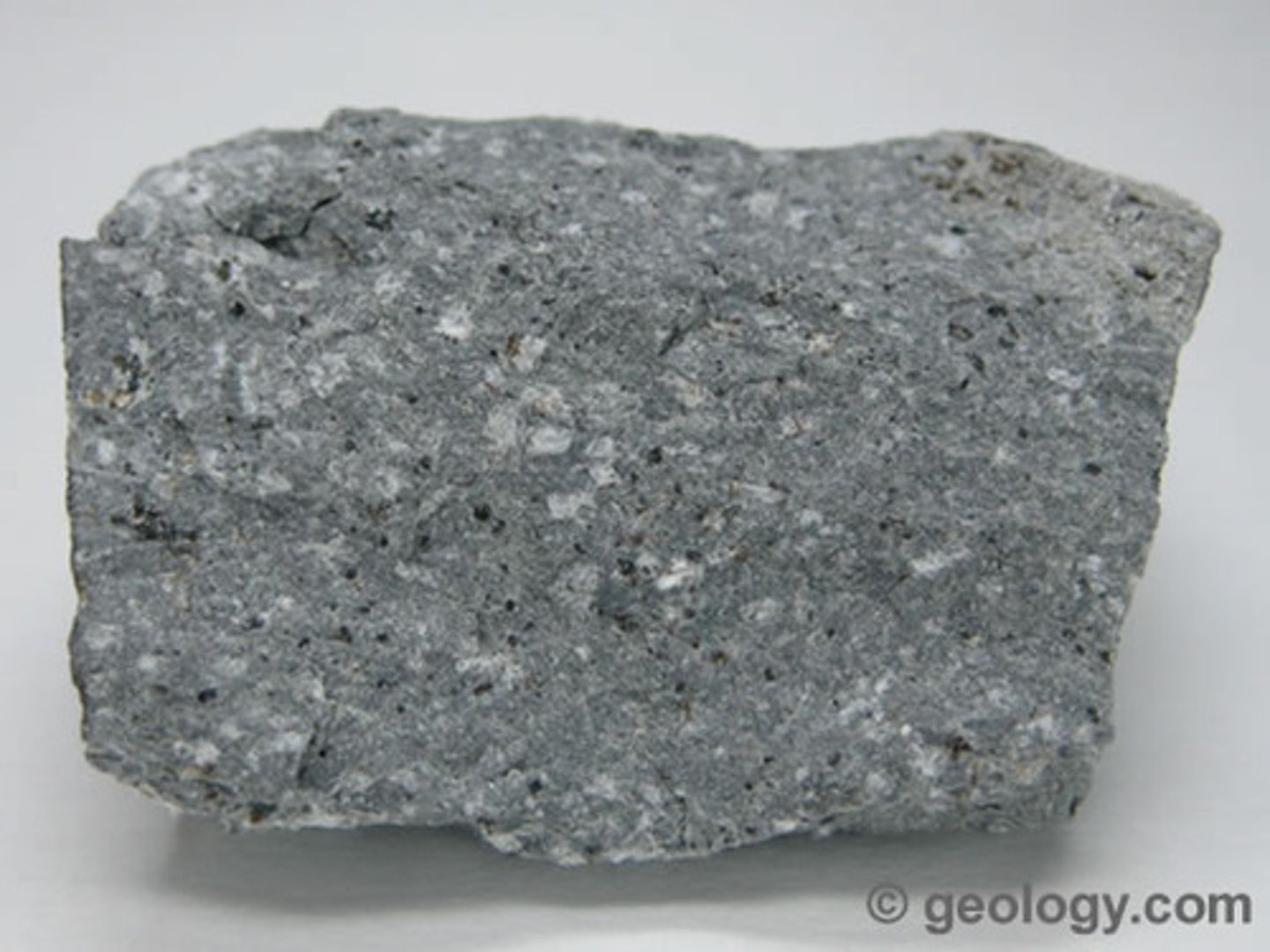

Basalt
- Igneous rock
- Mafic
- Fine-grained crystalline
- Cooled very quickly
- Effusive eruption
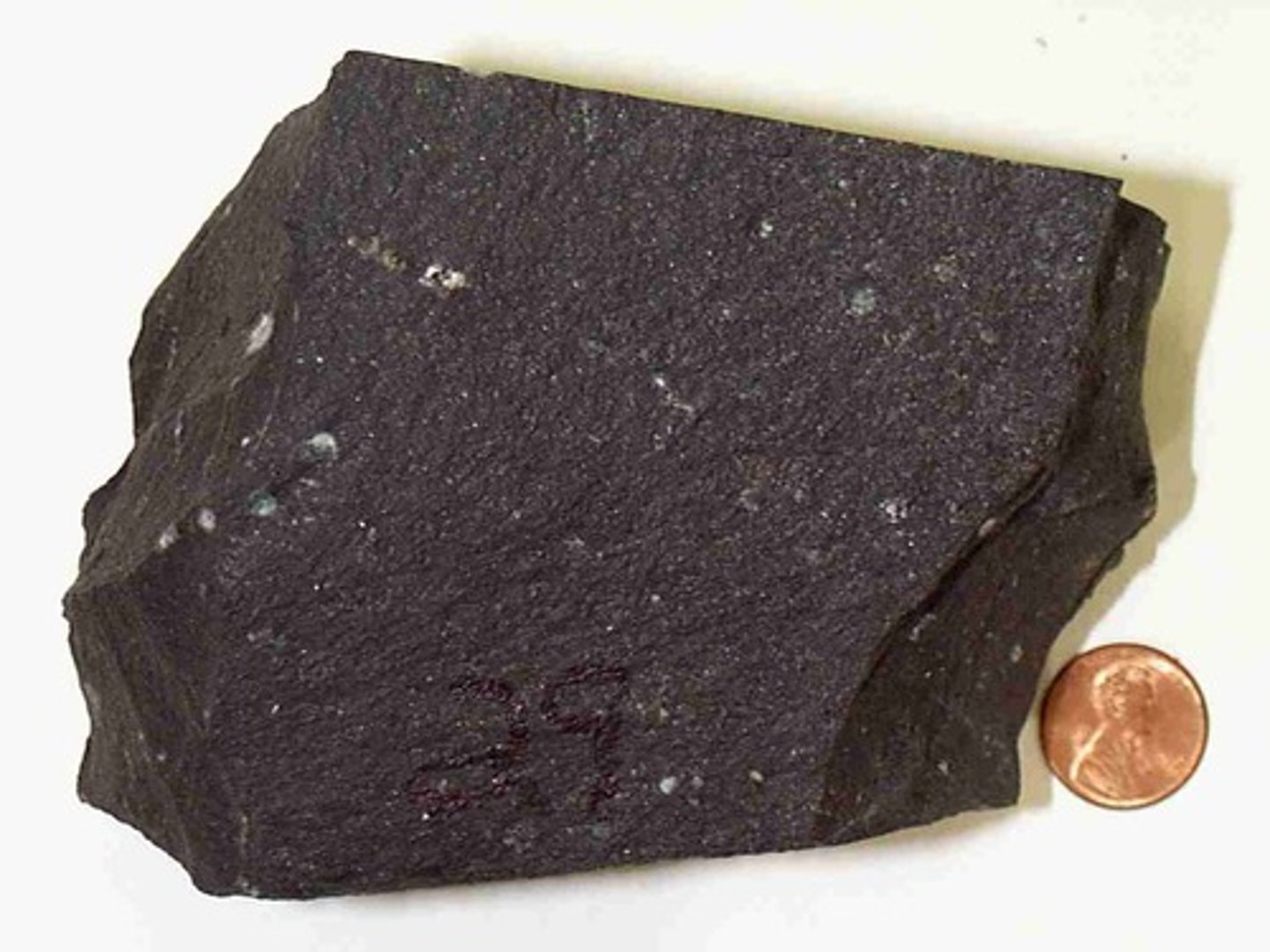

Granite
- Igneous rock
- Felsic
- Course-grained crystalline
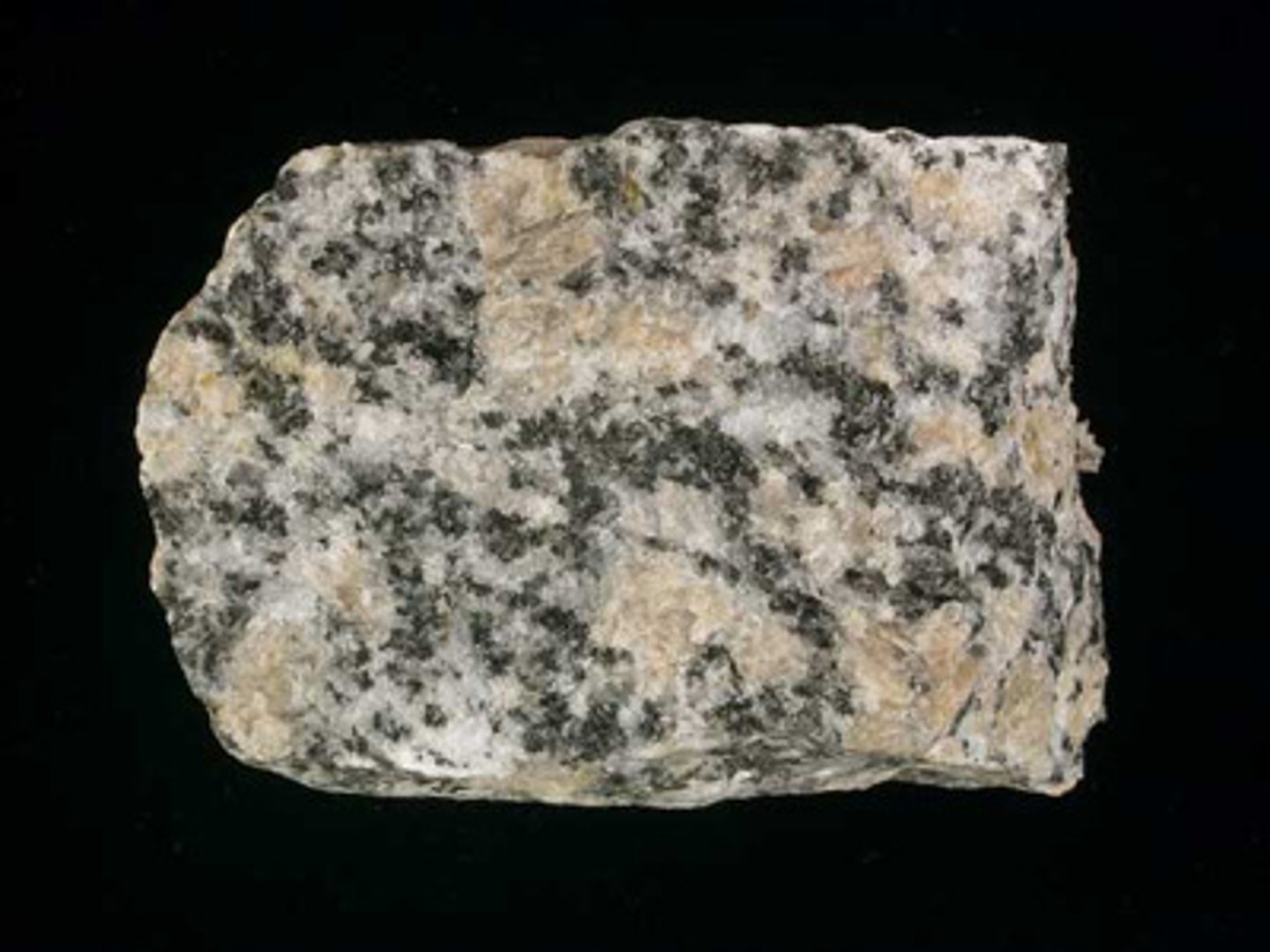

Diorite
- Igneous rock
- Intermediate
- Course-grained crystalline
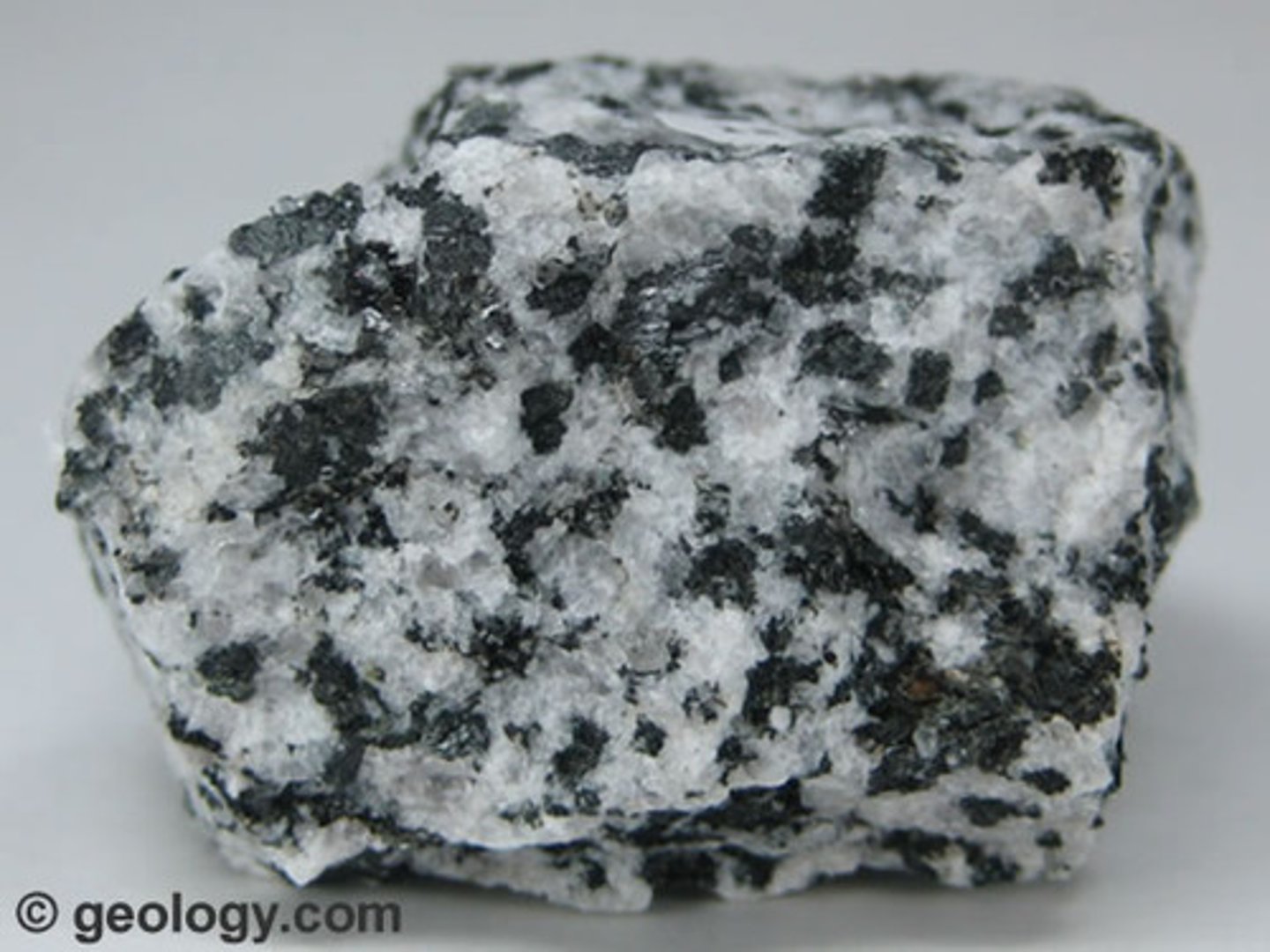

Gabbro
- Igneous rock
- Mafic
- Course-grained crystalline
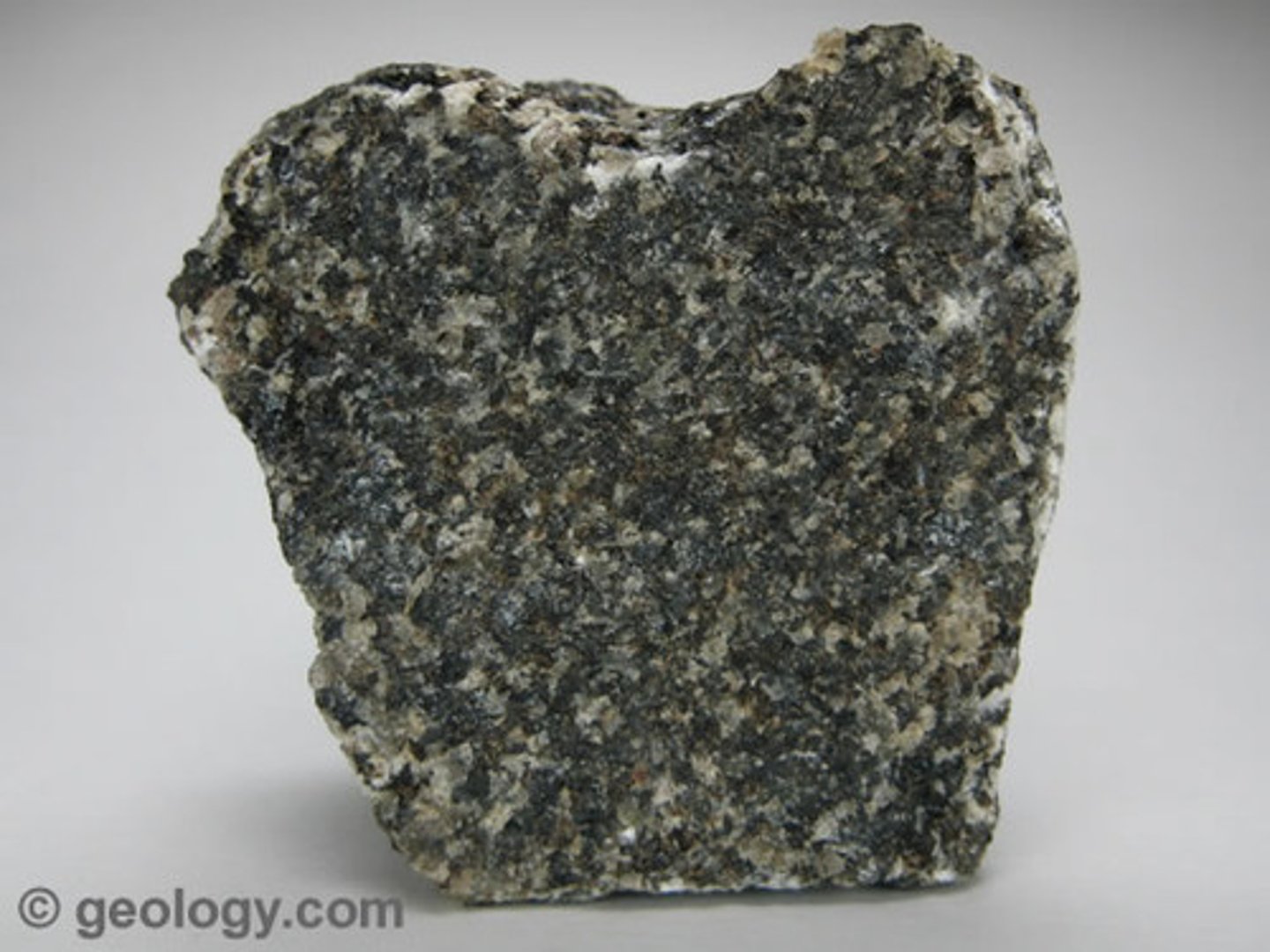

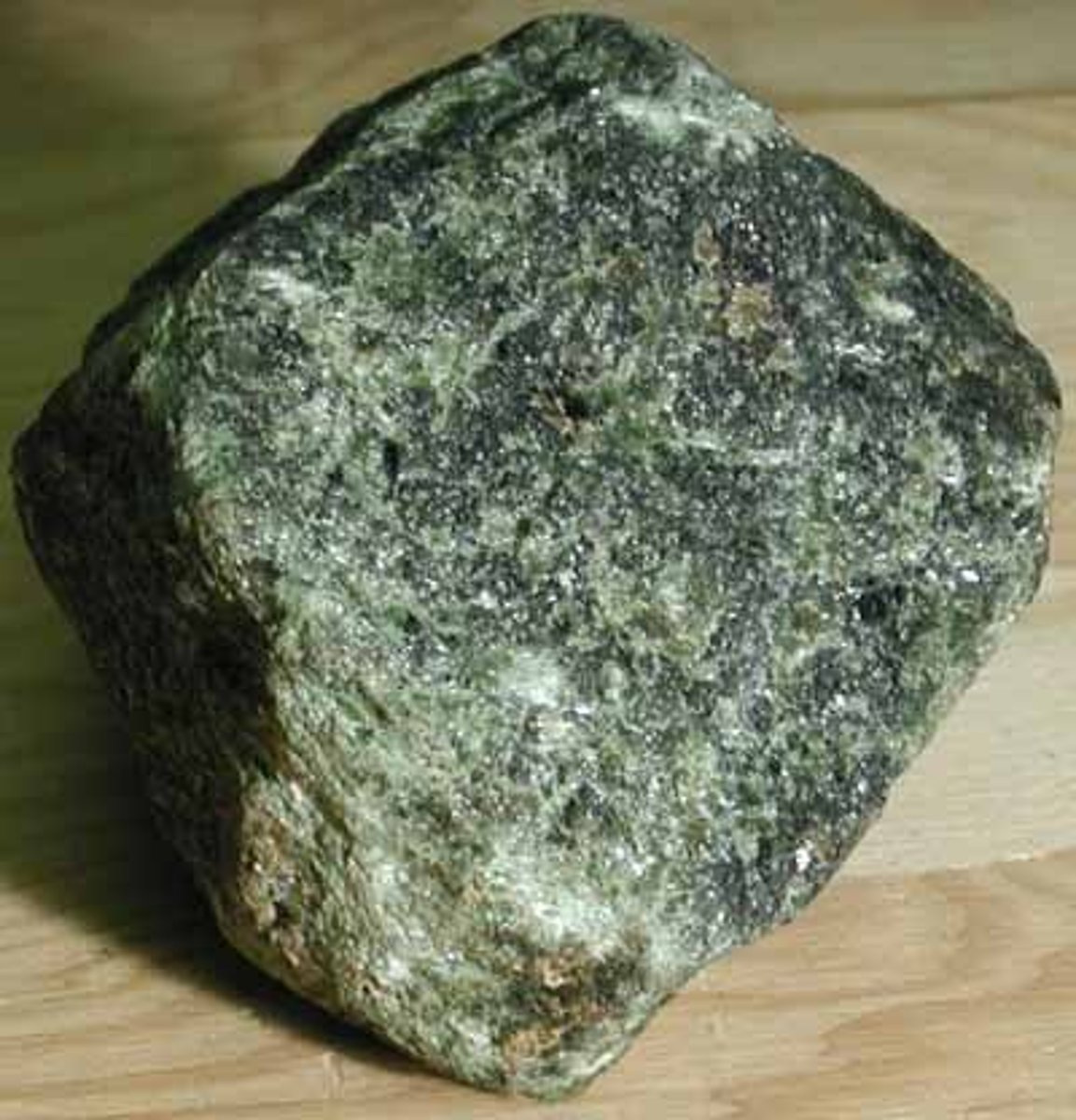
Peridotite
- Igneous rock
- Ultramafic
- Course-grained crystalline

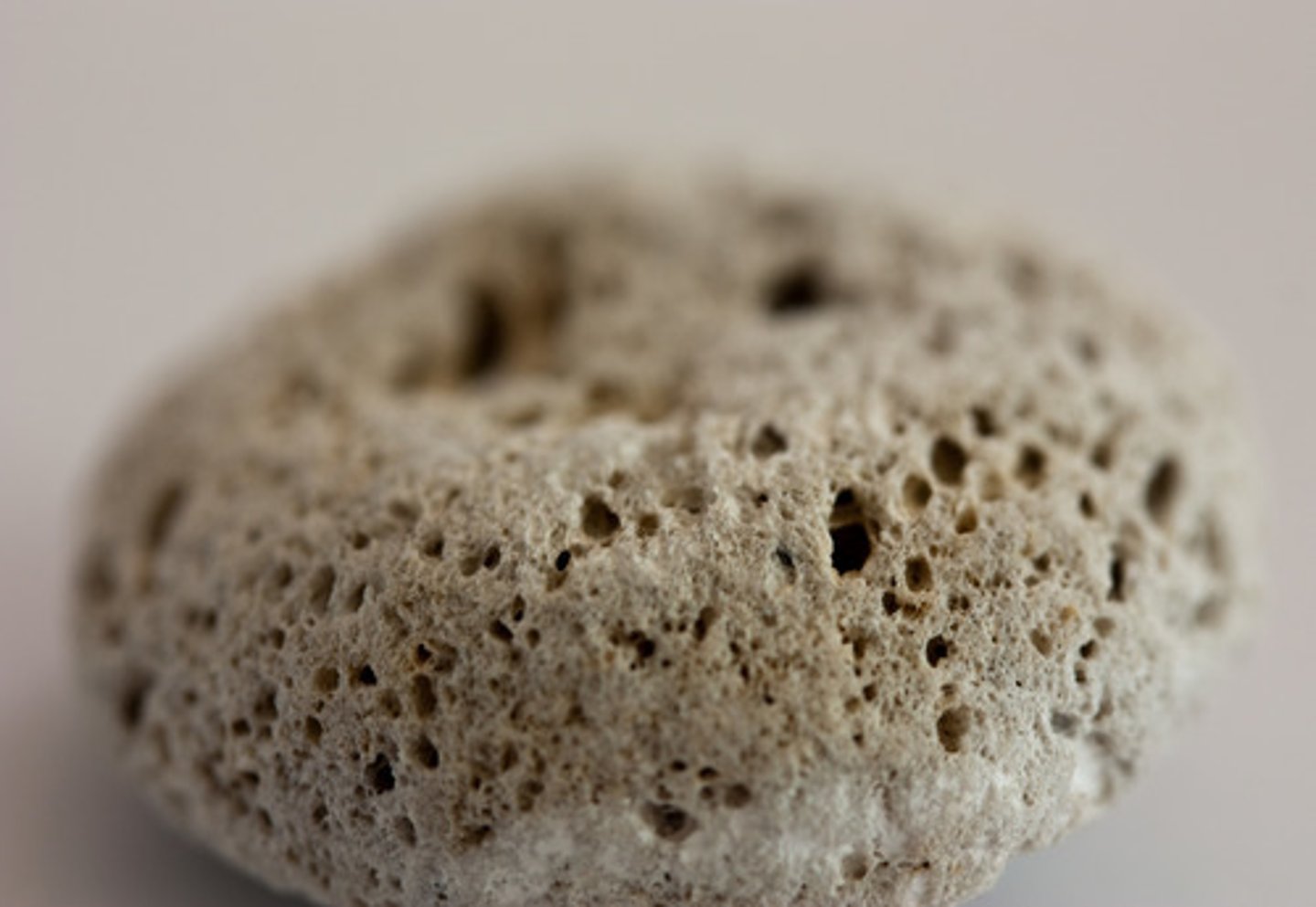
Pumice
- Igneous rock
- Glassy

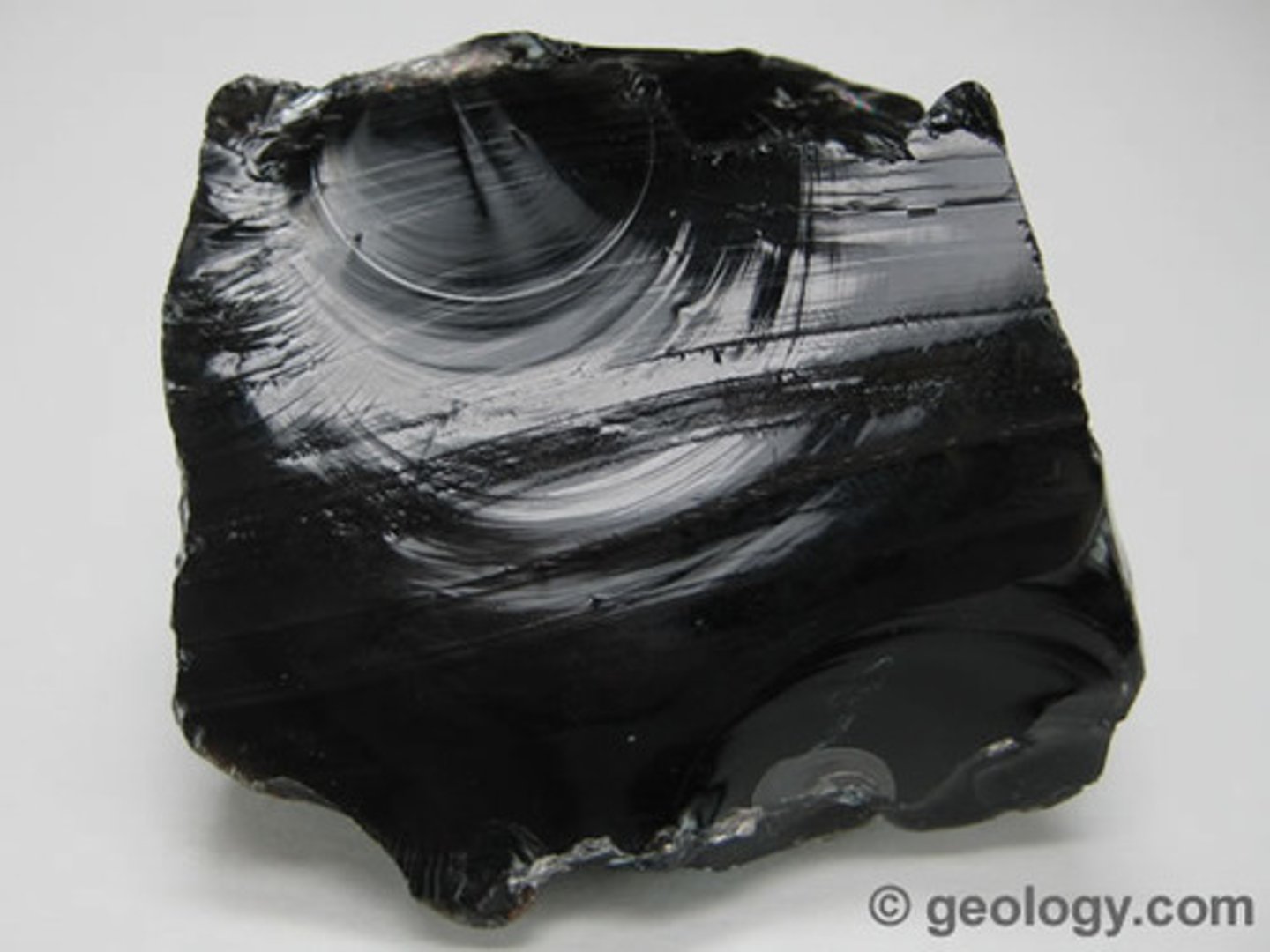
Obsidian
- Igneous rock
- Glassy

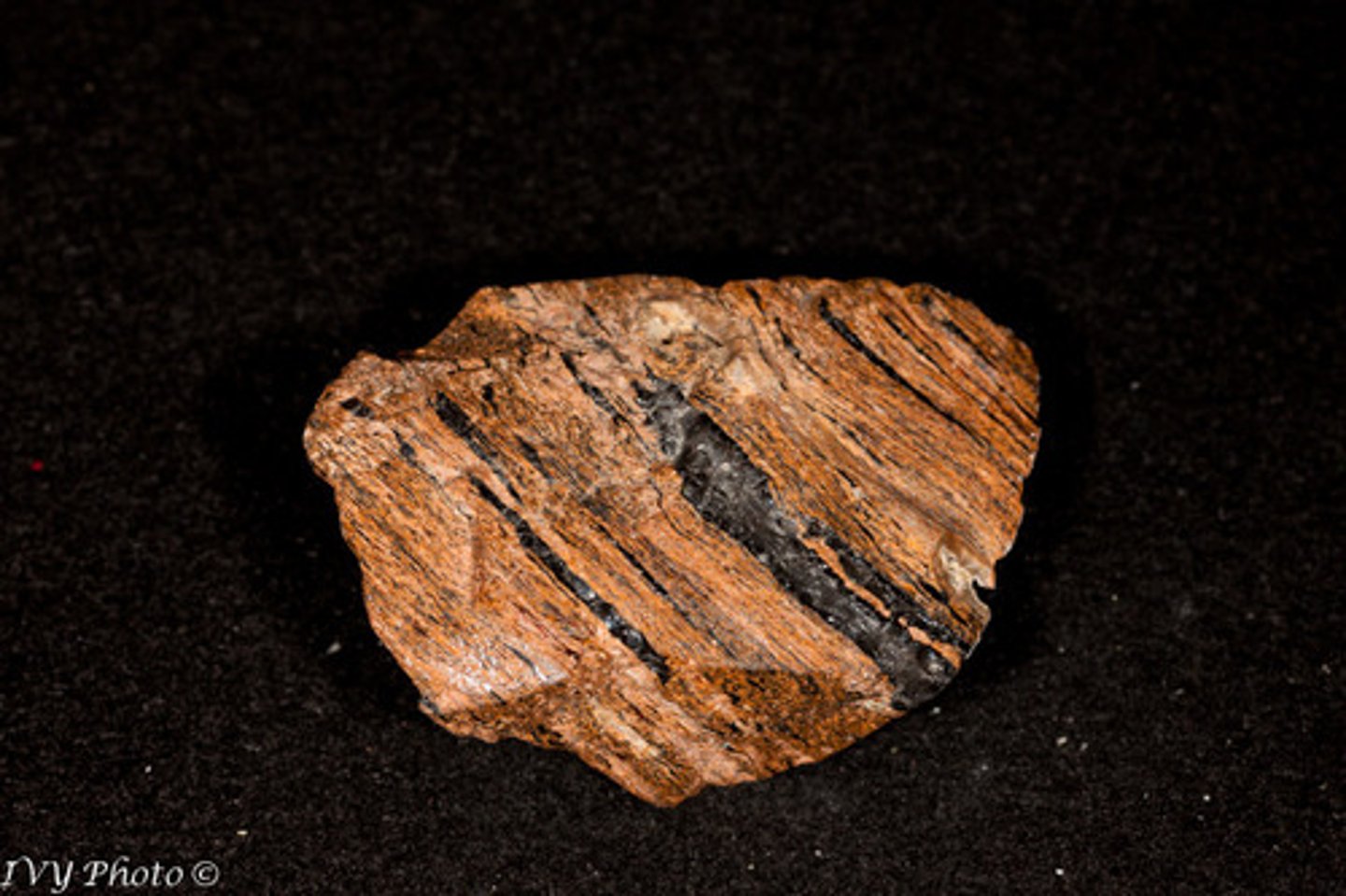
Welded Tuff
- Igneous rock
- Fragmental

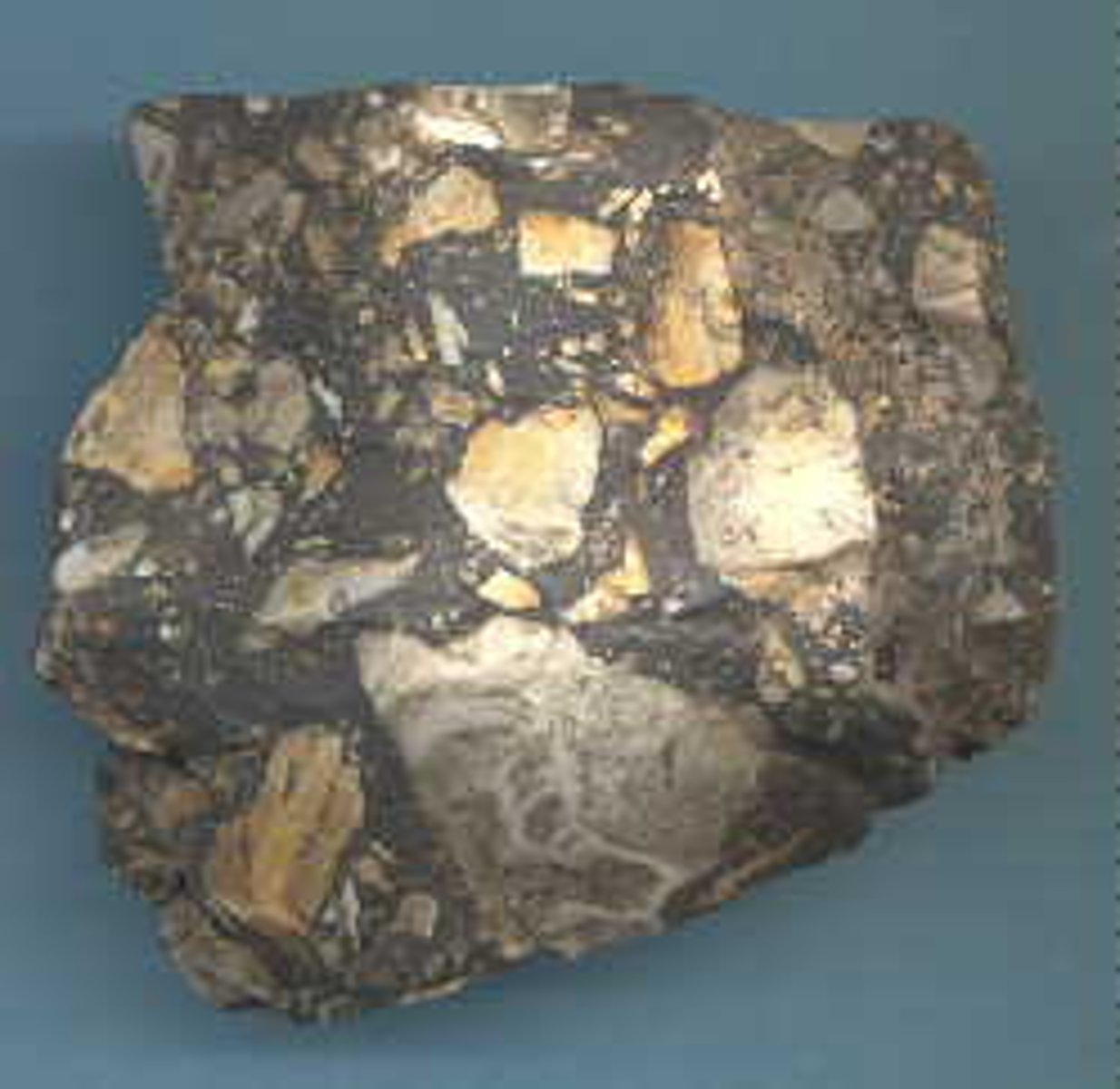
Breccia
- Sedimentary rock
- Clastic
- Gravel-sized particles
- Angular, poorly sorted
- Formed in an environment close to the source

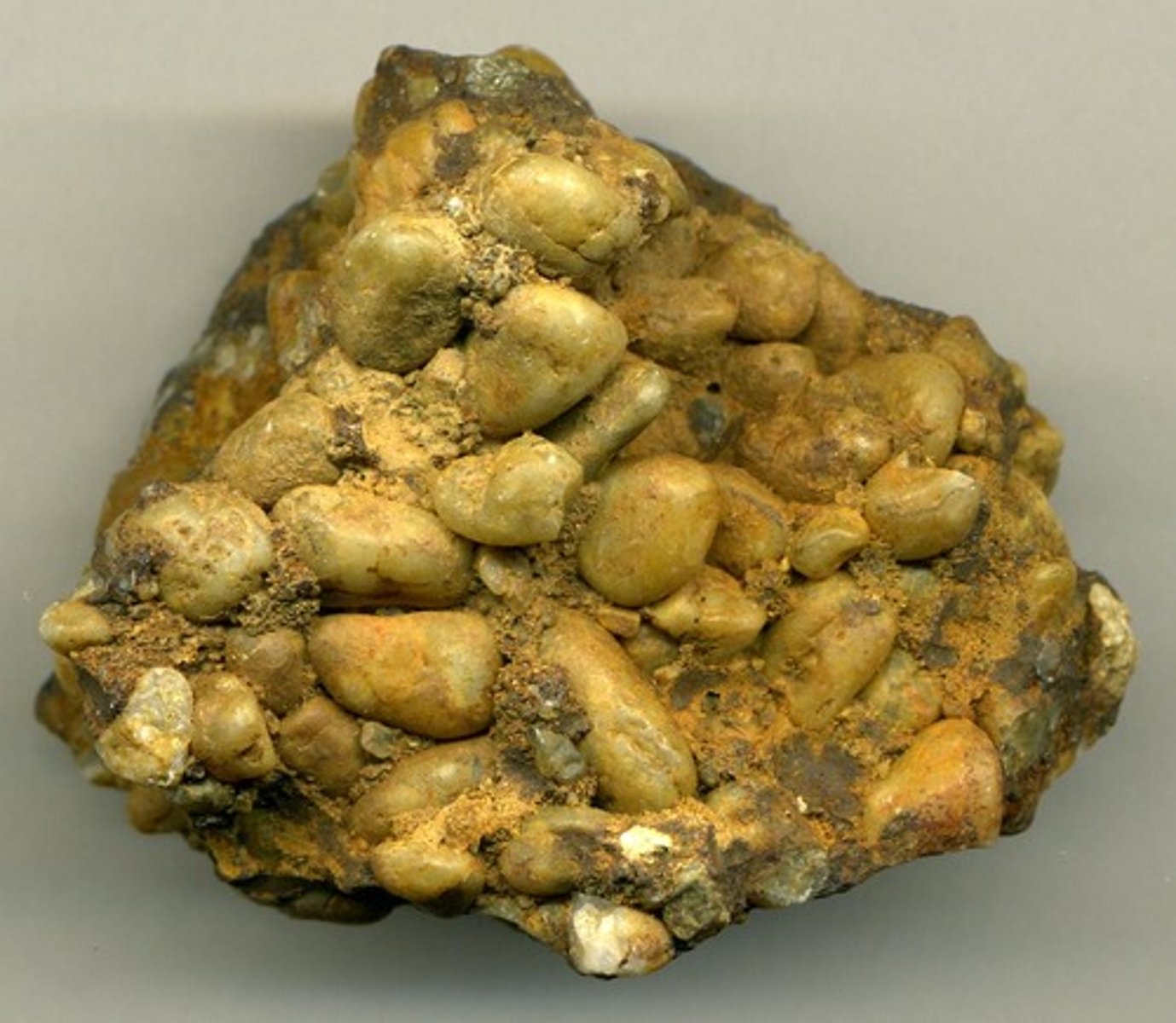
Conglomerate
- Sedimentary rock
- Clastic
- Gravel sized particles, with some silt and sand
- Poorly sorted
- Subrounded/subangular
- Formed in a high energy river

Quartz sandstone
- Sedimentary rock
- Clastic
- Particle size: sand
- Well-sorted
- Sub-rounded/rounded
- Formed in a river or beach
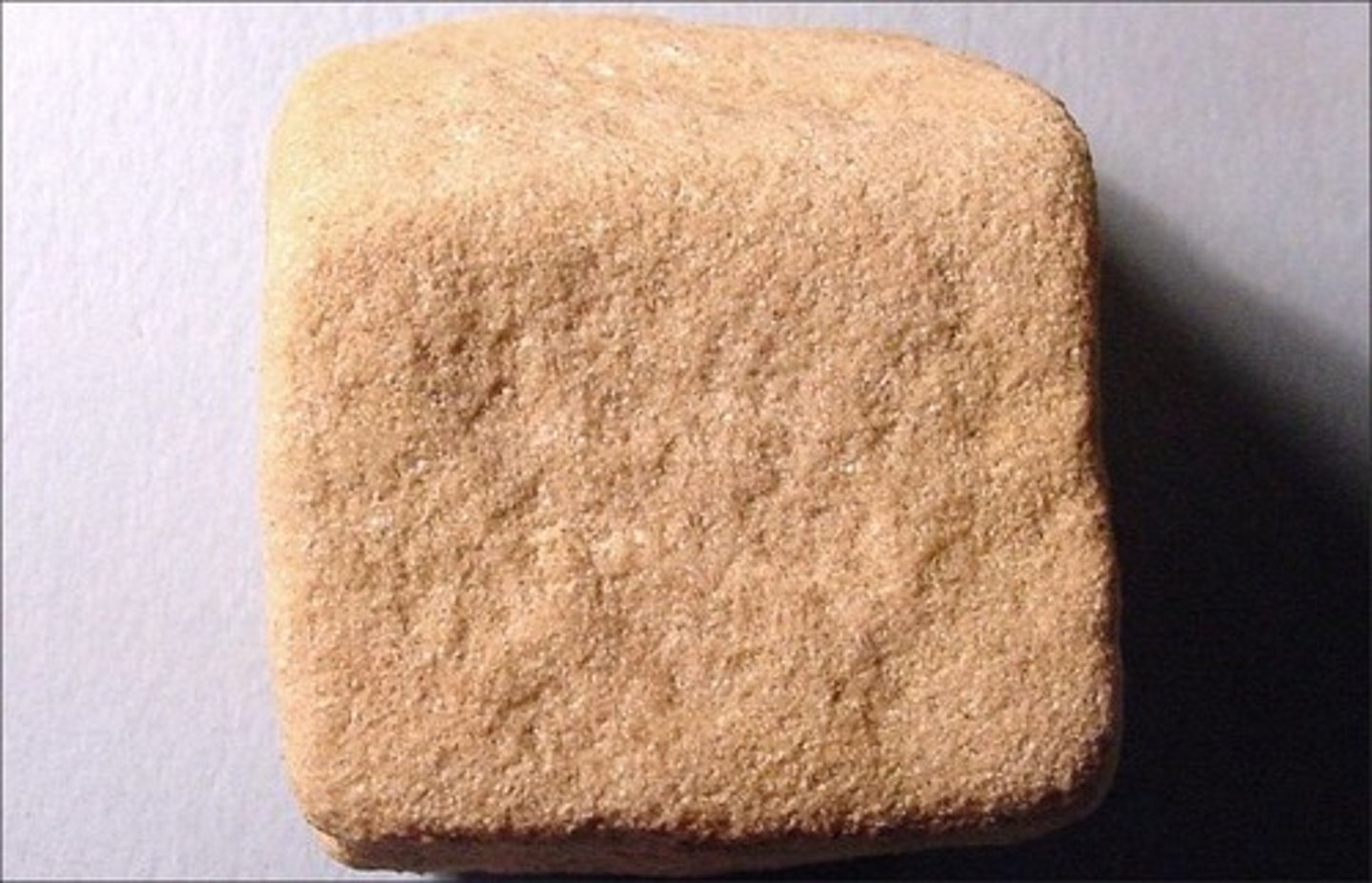

Siltstone
- Sedimentary rock
- Clastic
- Particle size: silt
- Formed in a low energy environment but higher than shale: probably small river or offshore marine
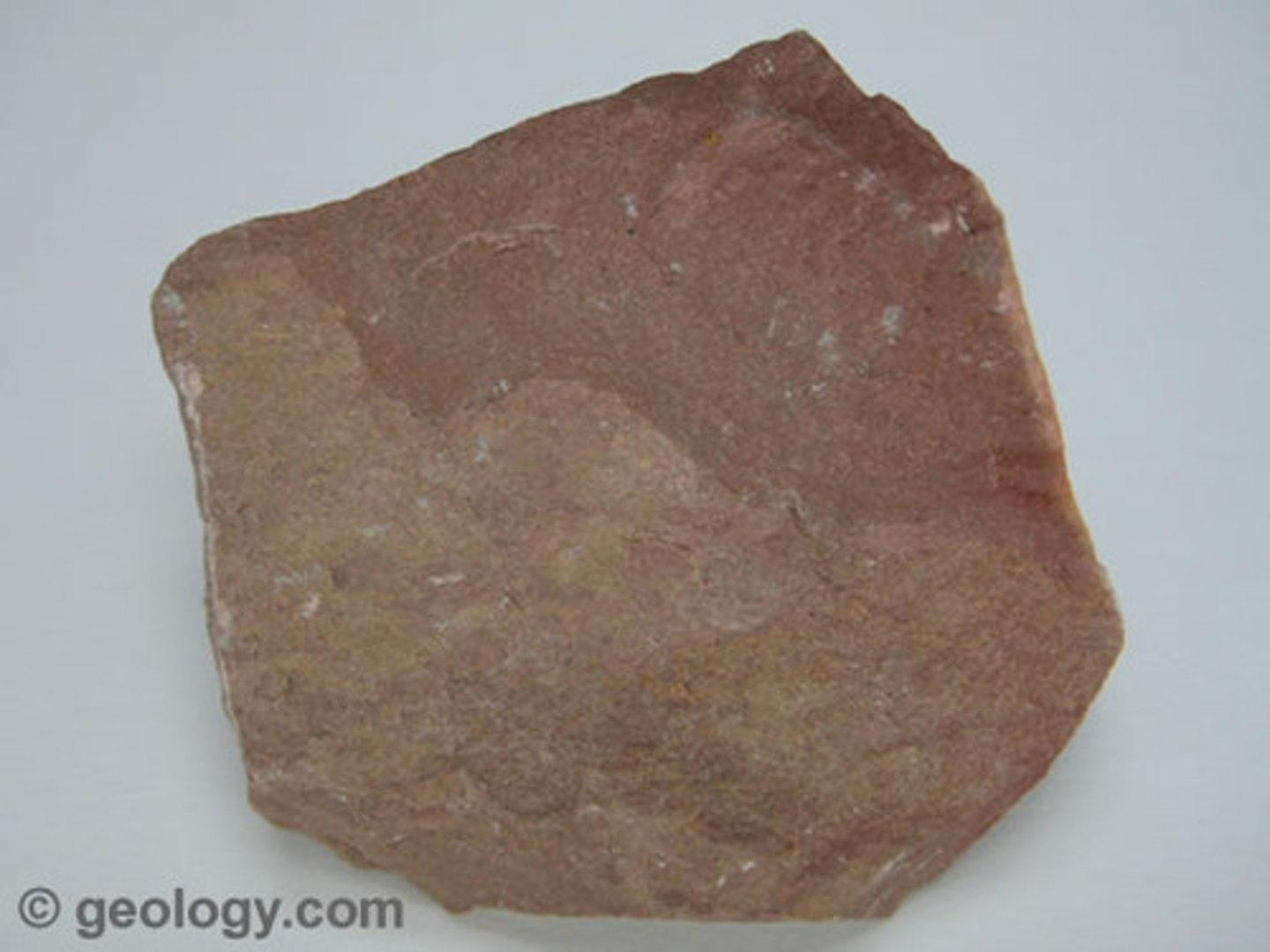

Shale
- Sedimentary rock
- Clastic
- Clay-sized particles
- Well-sorted
- Low energy environment

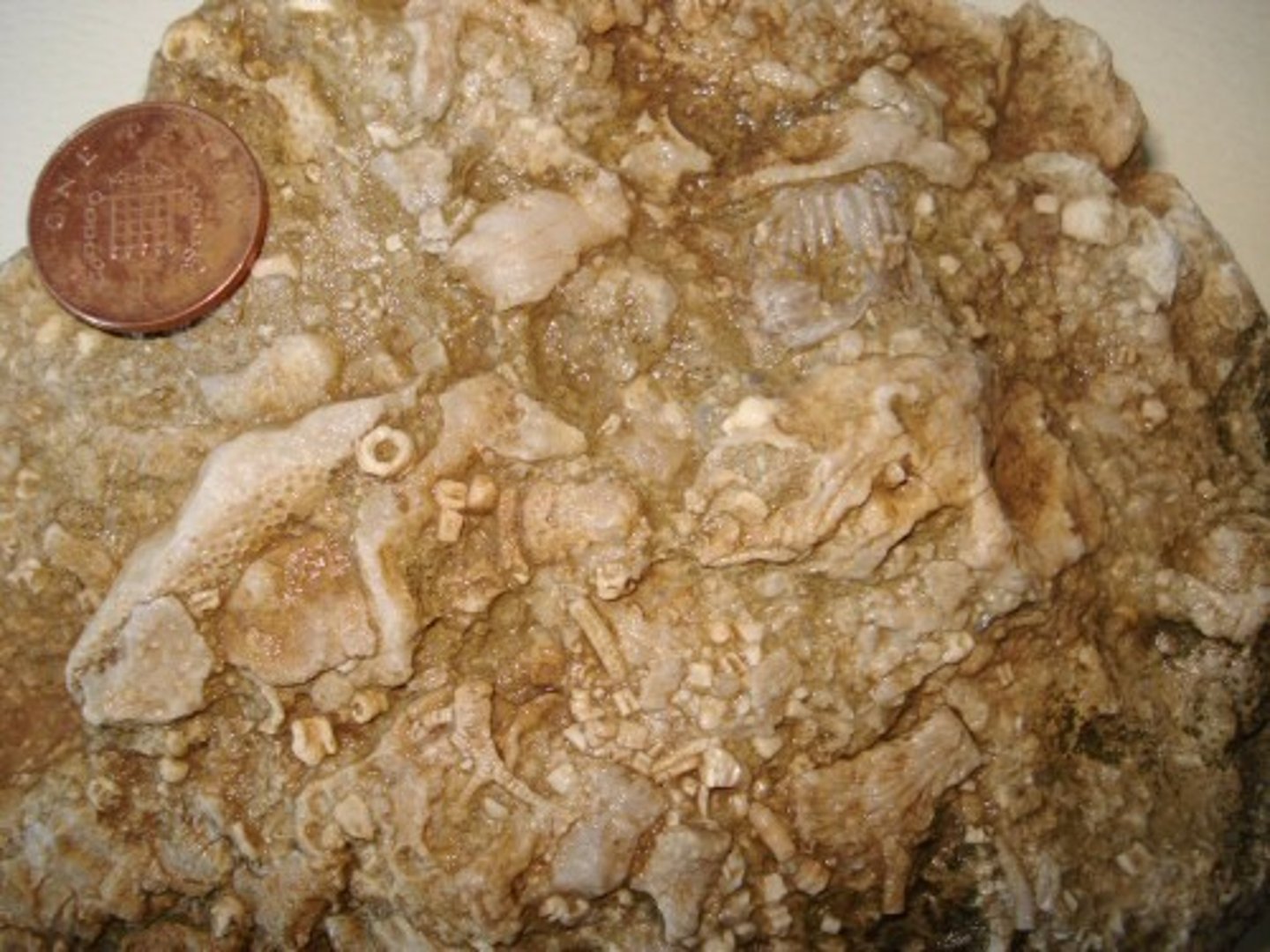
Fossiliferous limestone
- Sedimentary rock
- Biochemical
- Reacts with HCl
- Has fossils
- Formed in shallow warm marine water

Chalk
- Sedimentary rock
- Biochemical rock
- Reacts with HCl
- Formed in a deep marine, low energy environment

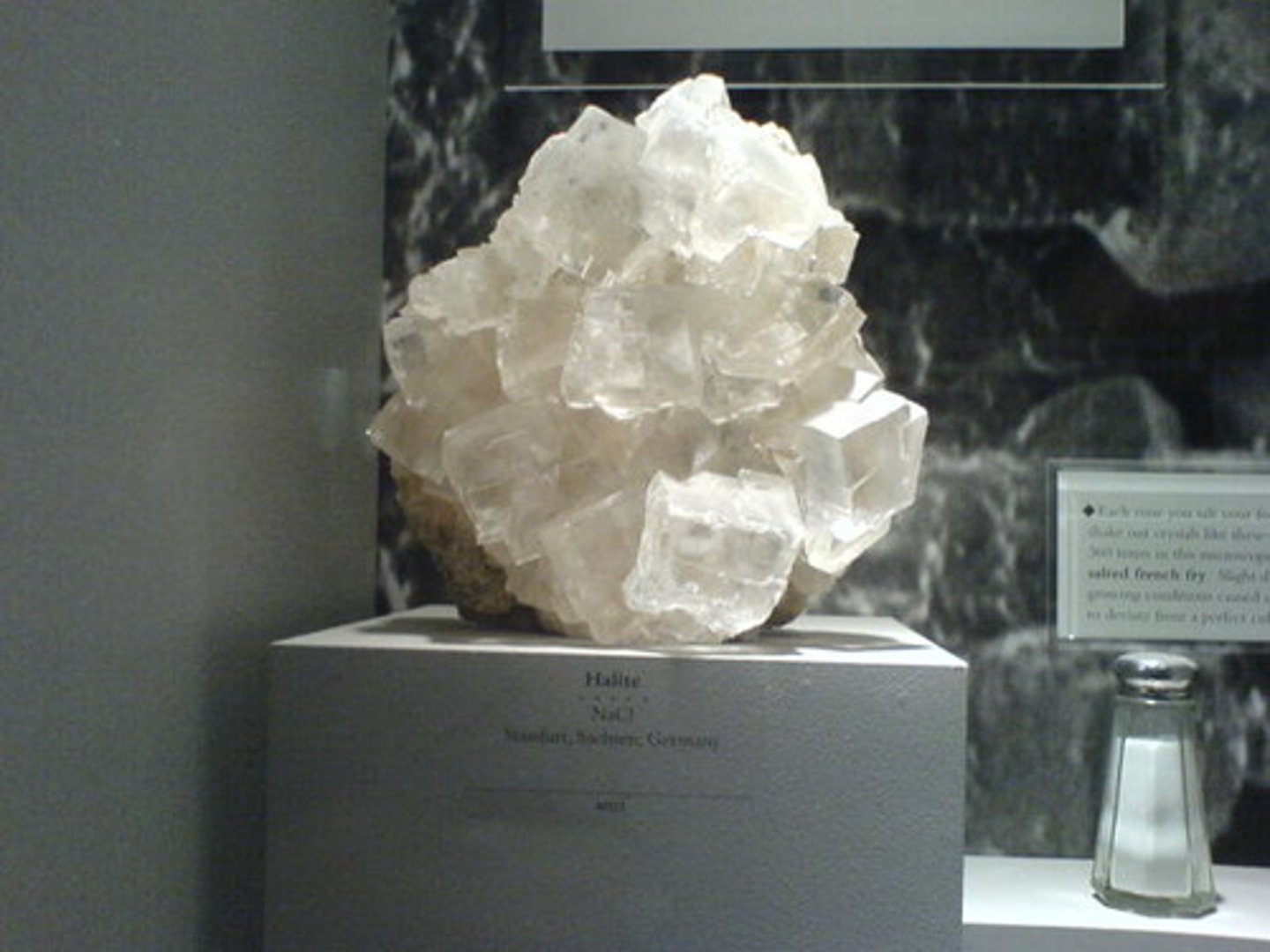
Halite
- Sedimentary rock
- Chemical
- Shallow water, pools evaporate

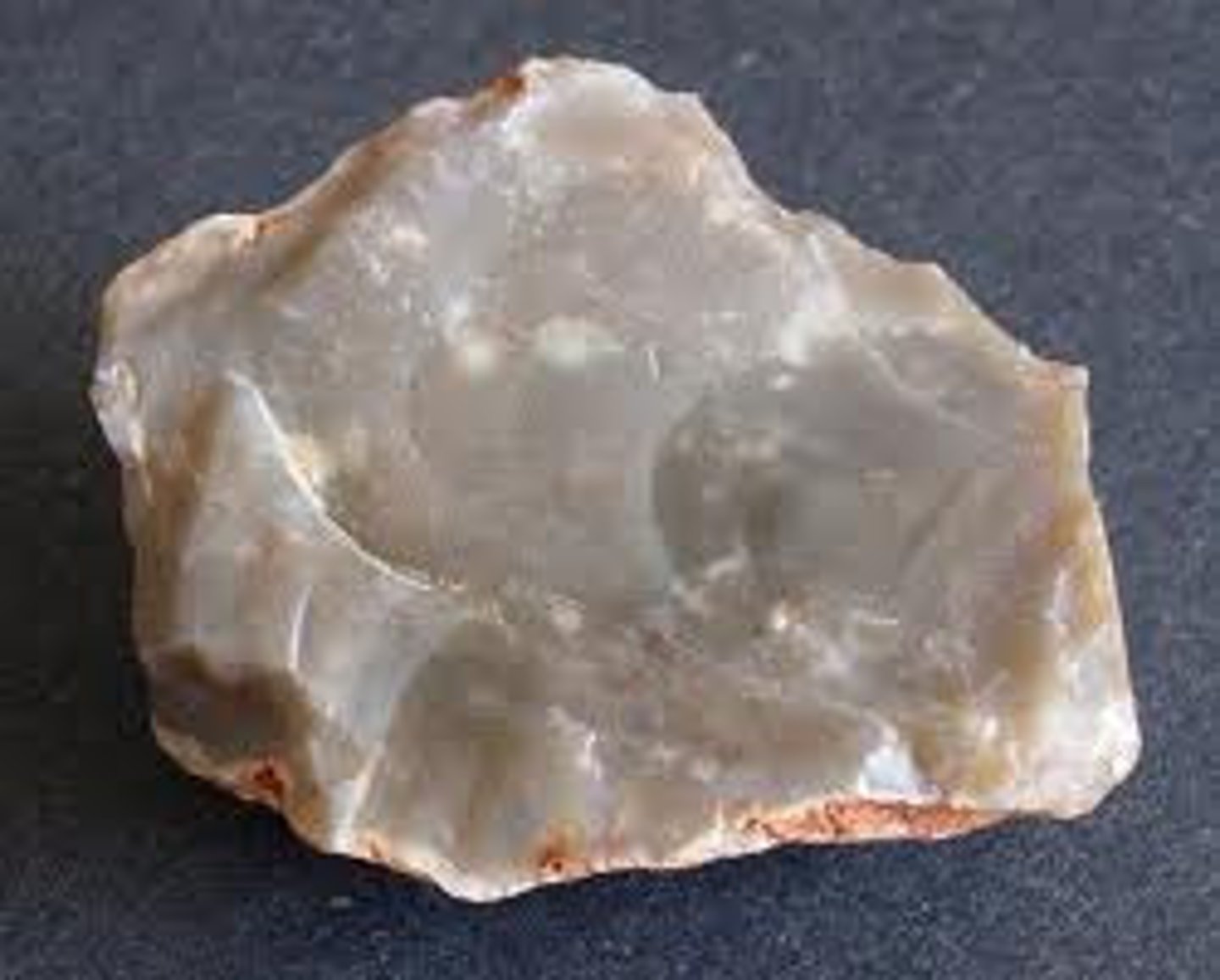
Chert
- Sedimentary rock
- Chemical
- Includes silica
- Well-sorted
- Formed in a shallow-marine area

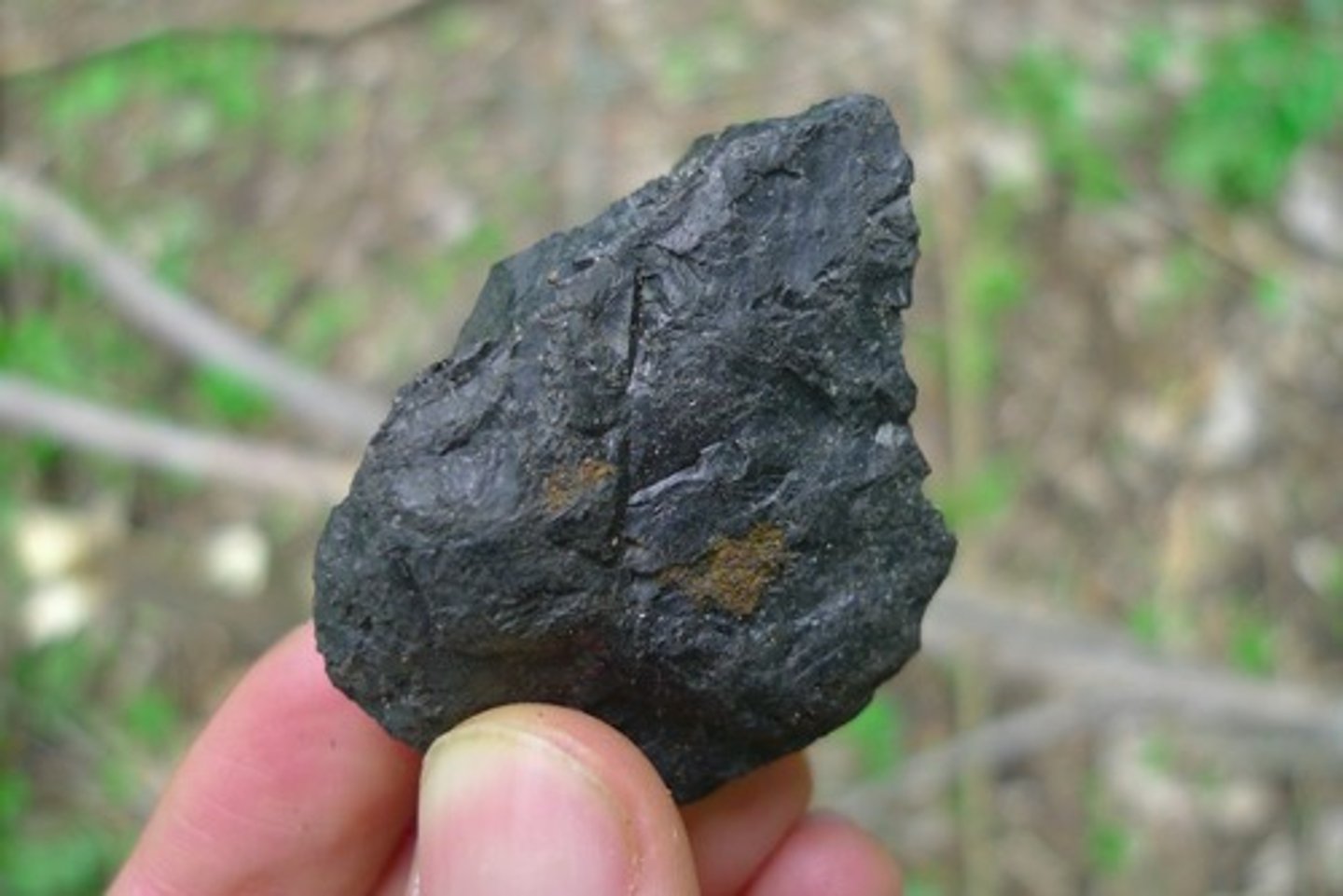
Coal
- Sedimentary rock
- Organic
- Formed in a swamp (low energy)

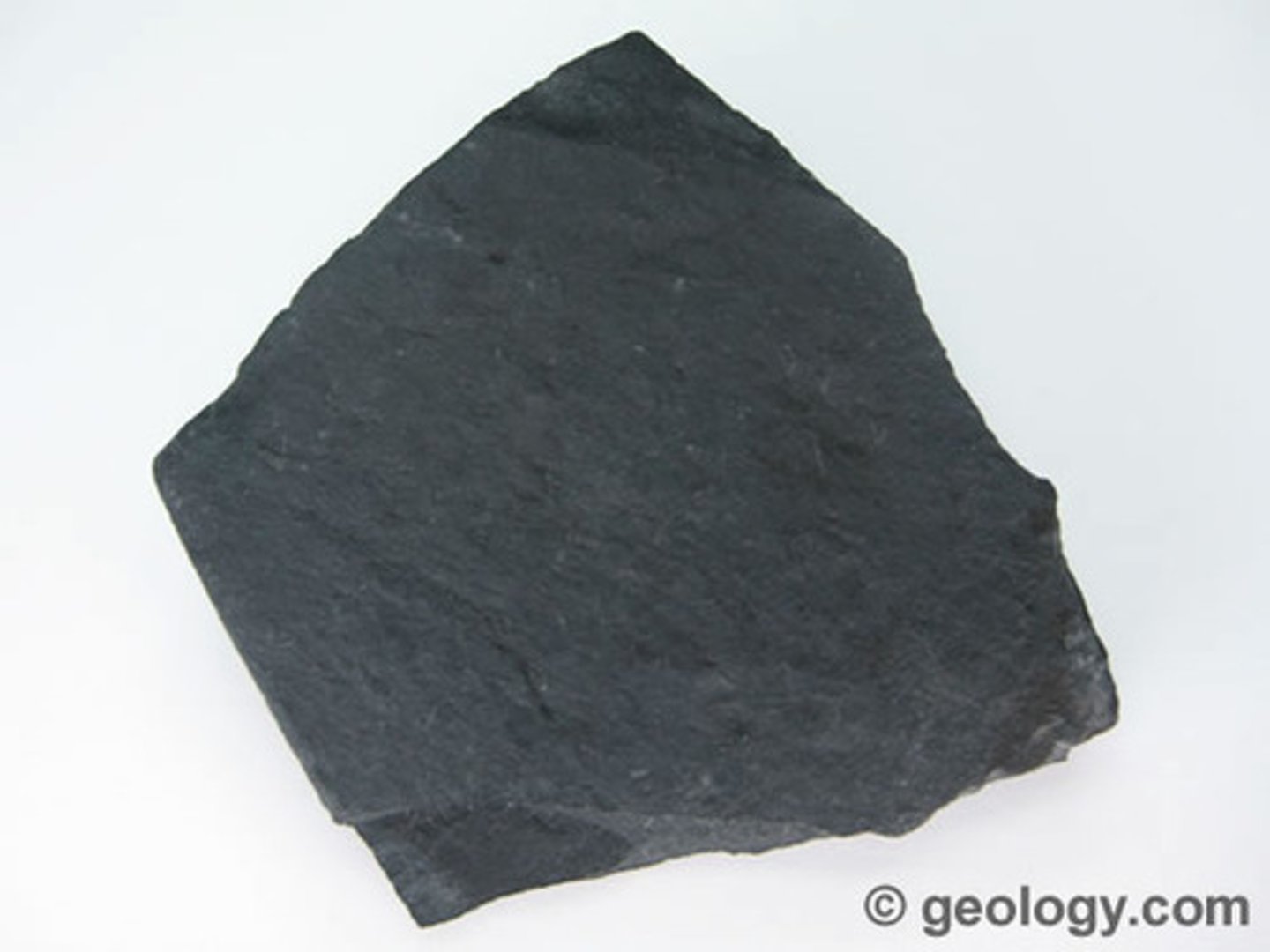
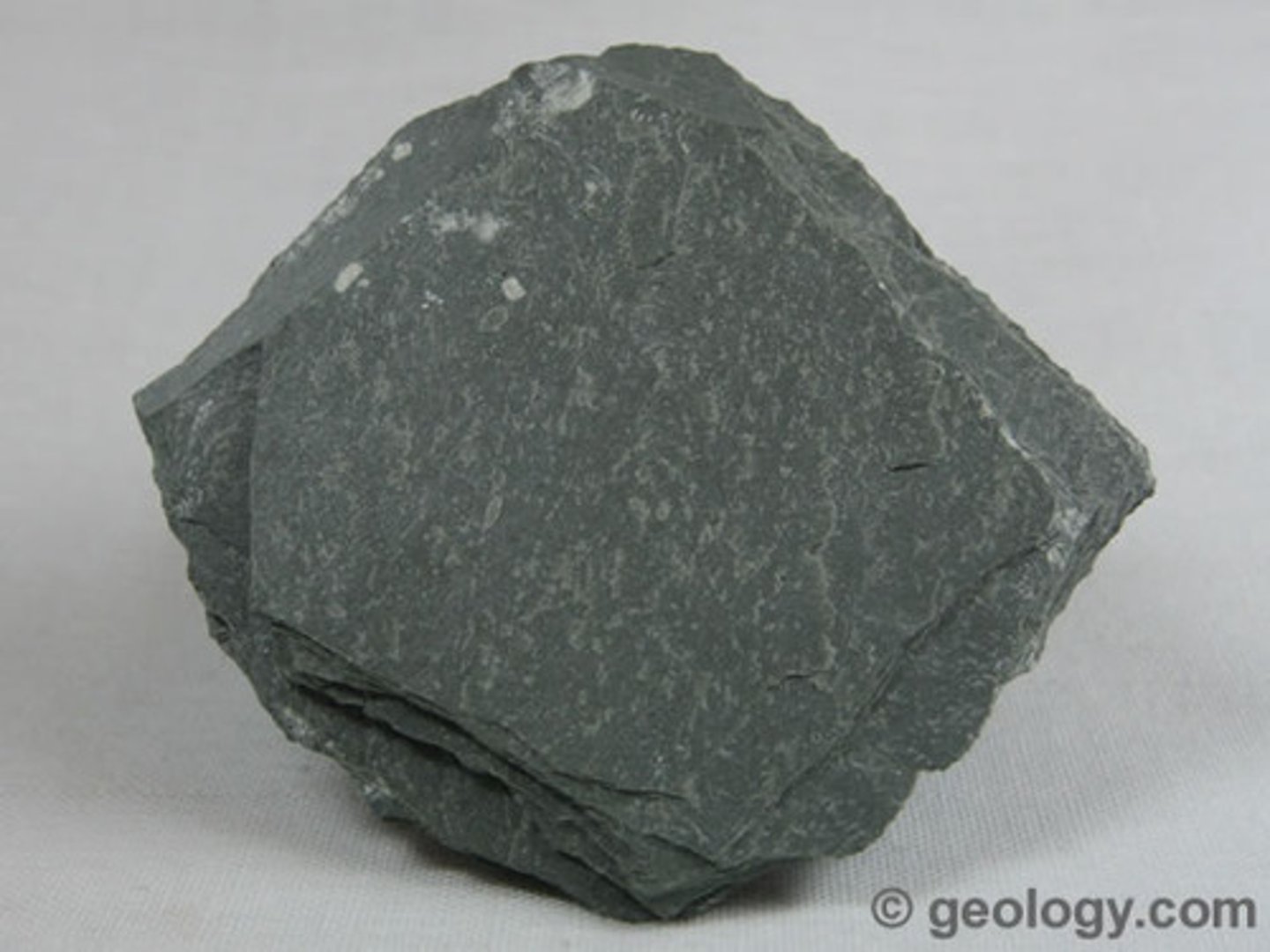
Slate
Foliated
Low-Grade Metamorphism
Protolith: Shale

Schist
Foliated
Intermediate-Grade Metamorphism
Protolith: Shale
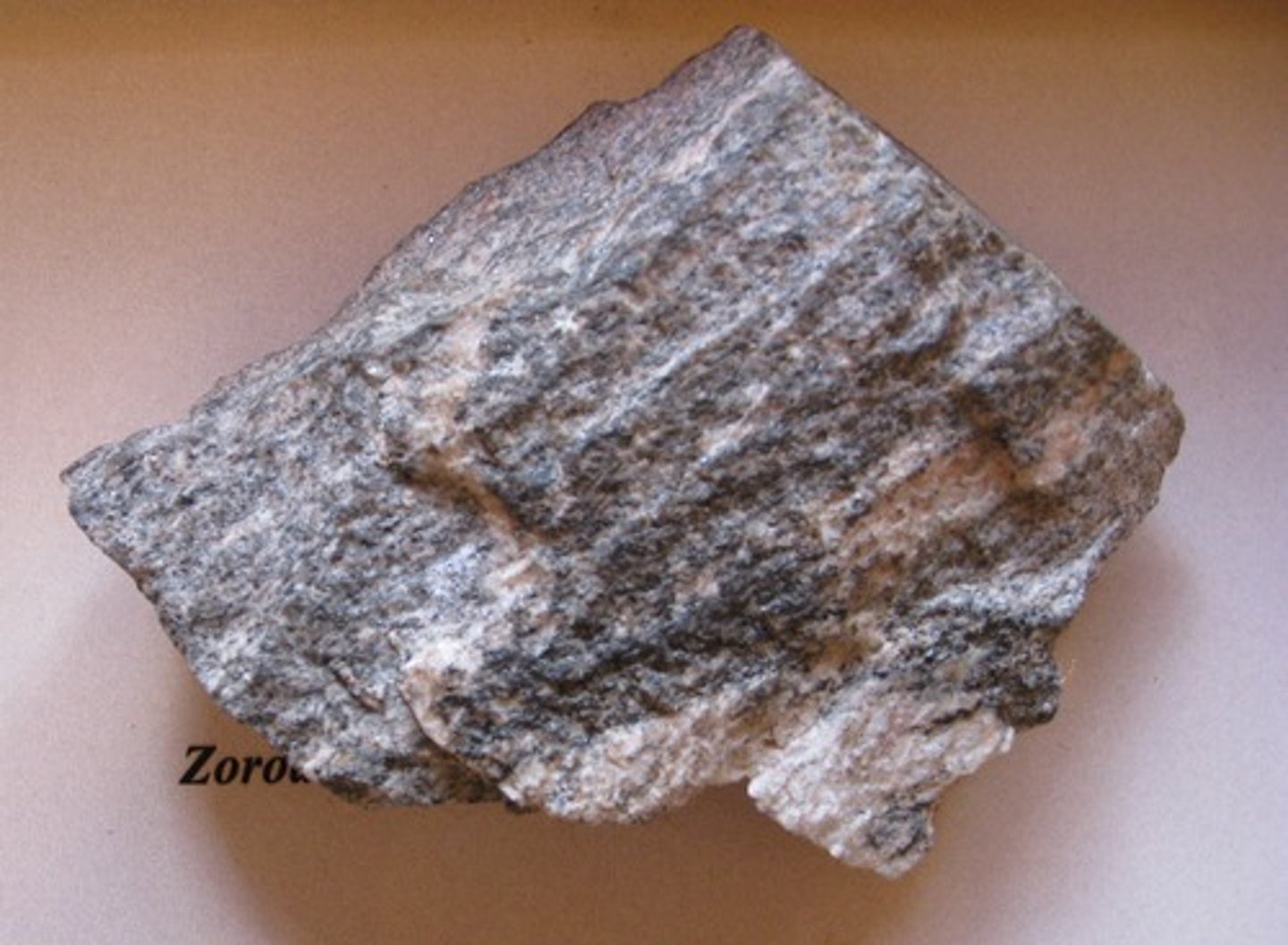

Phyllite
Foliated
Intermediate-Grade Metamorphism
Protolith: Shale

Gneiss
Foliated
High-Grade Metamorphism
Protolith: Shale/Granite/+more
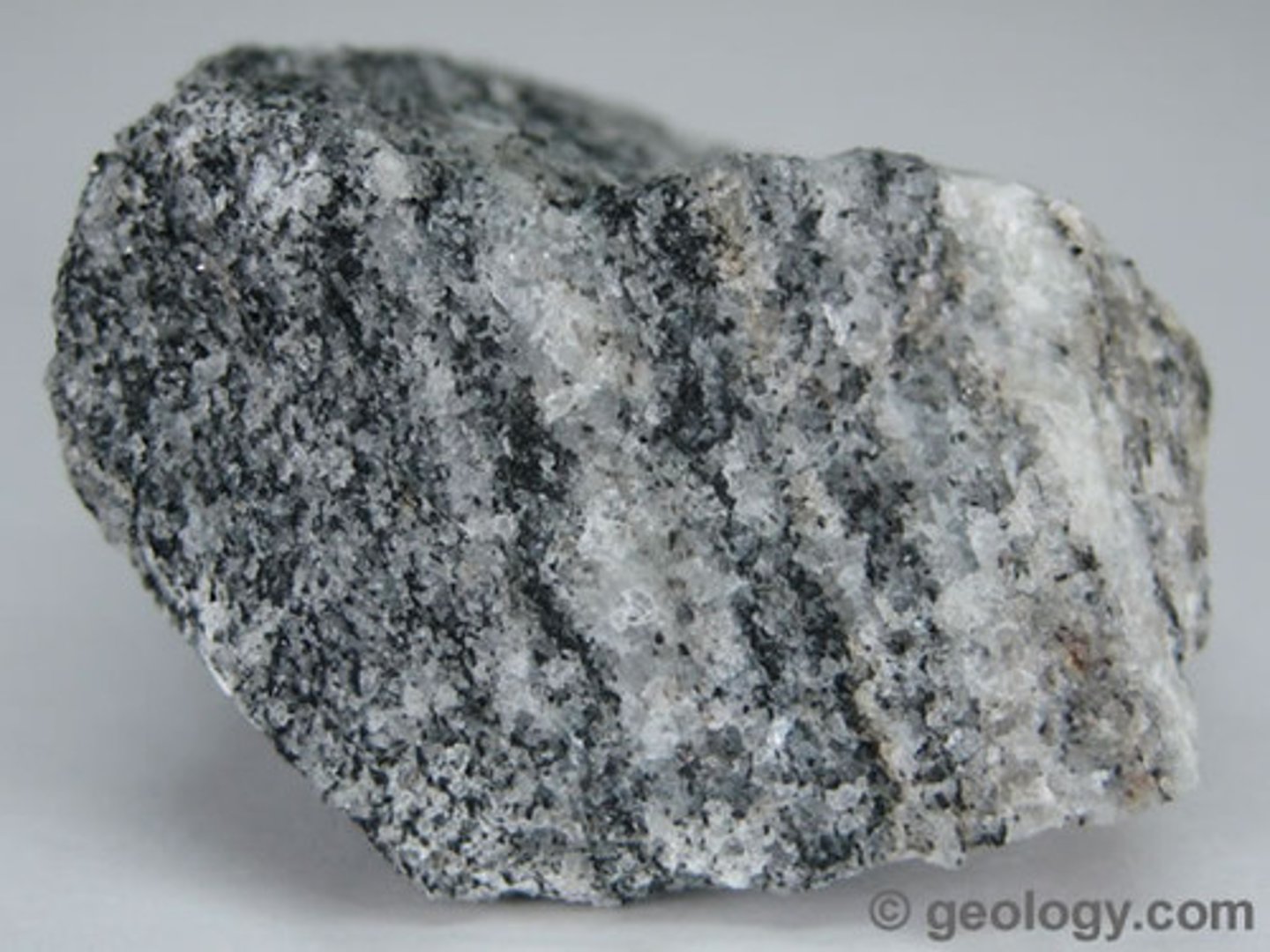

Quartzite
Non-foliated
Intermediate-Grade Metamorphism
Protolith: Quartz Sandstone
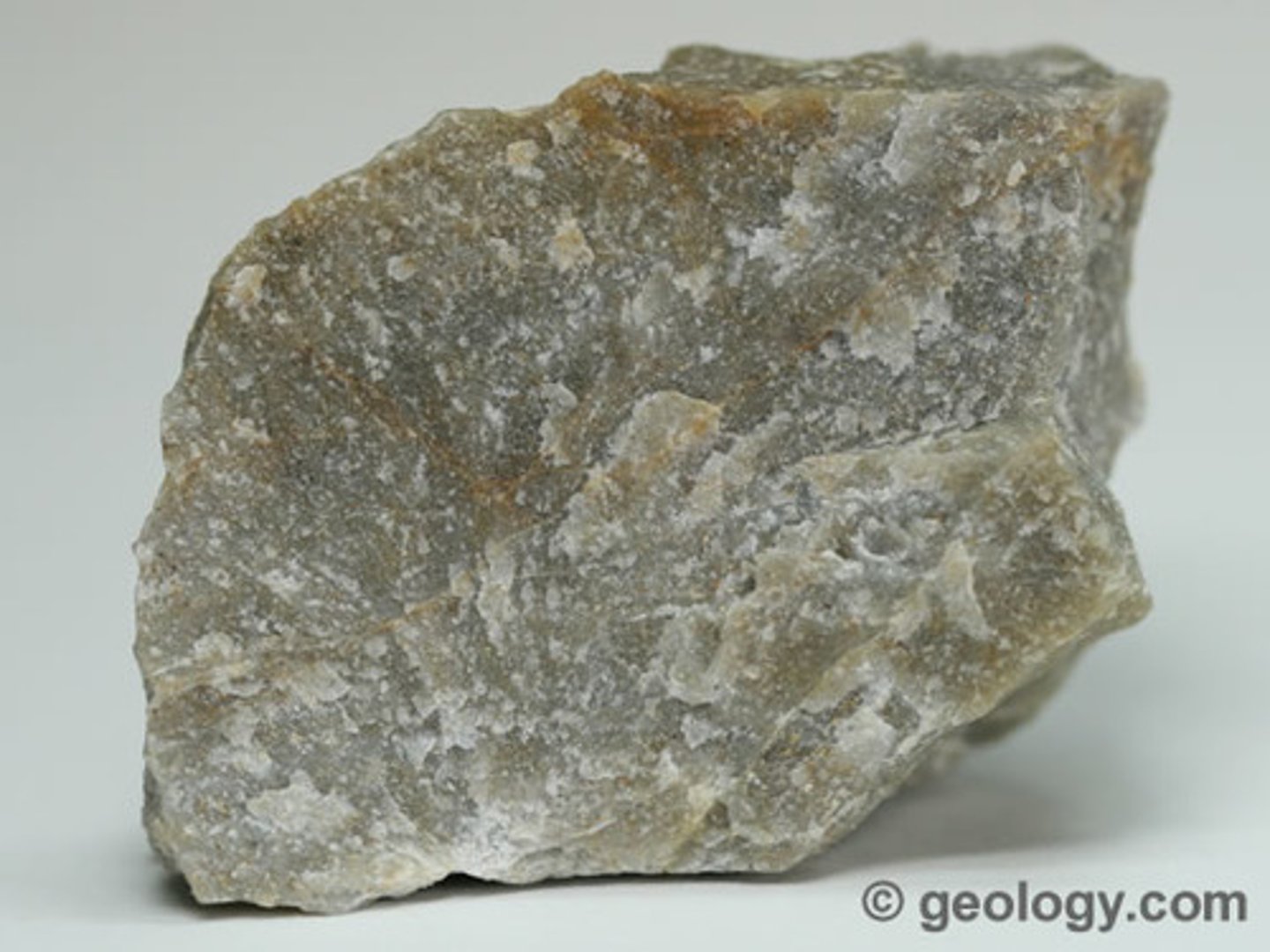

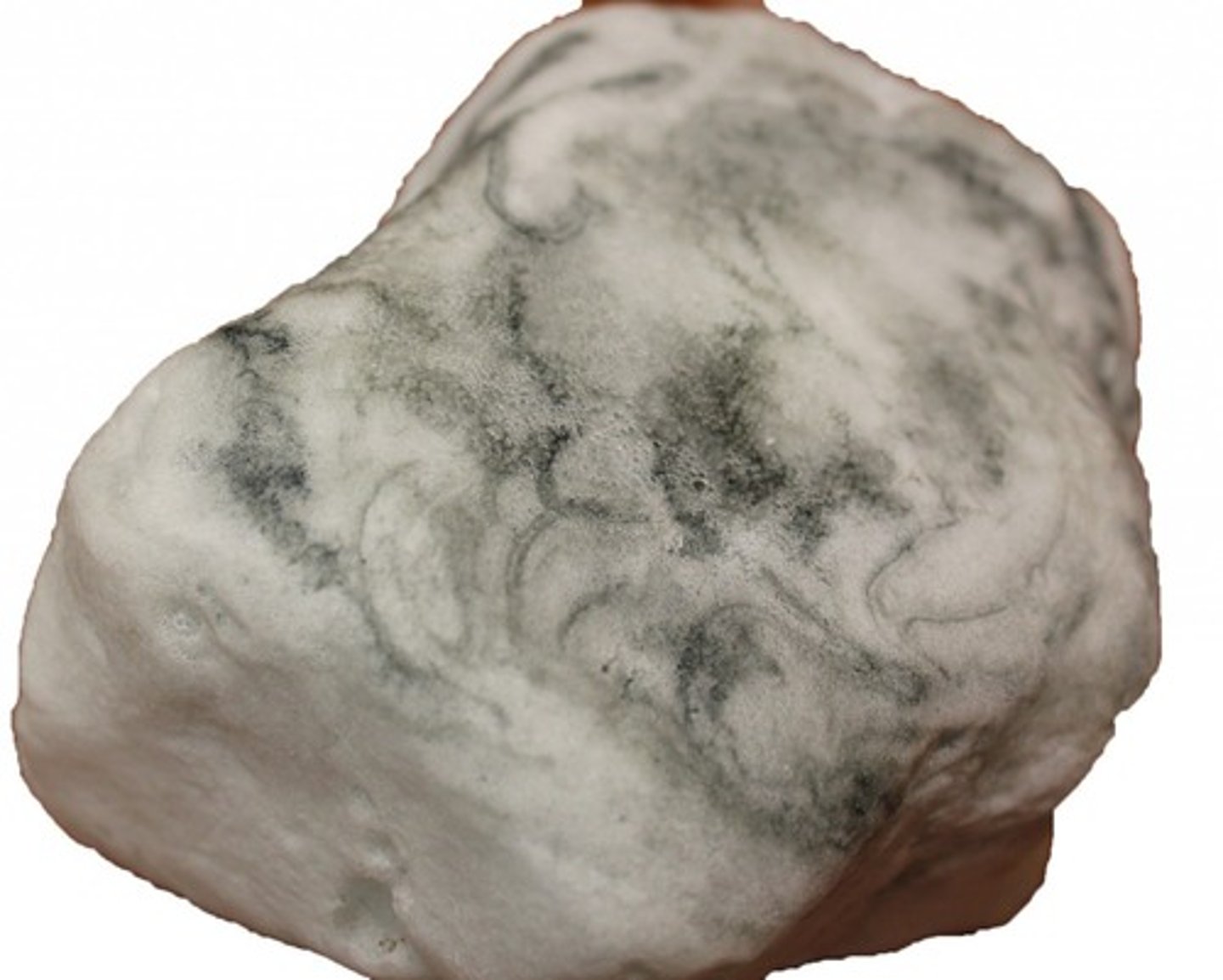
Marble
Non-foliated
Intermediate-Grade Metamorphism
Protolith: Fossiliferous Limestone

Shale Protolith Processes
Neocrystallization
Quartz Sandstone and Fossiliferous Limestone Protolith Processes
Recrystallization
Mineral
a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form
Rock
A naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic matter
Limestone rocks
more animals, and CaCO3 does not dissolve in warmer water; Form in calmer, warmer environments with more animals
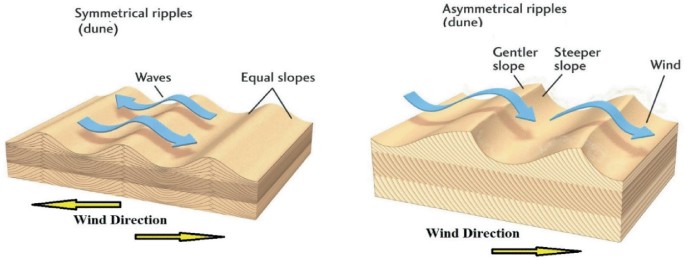
Symmetrical Ripples
Formed from bidirectional currents that oscillate
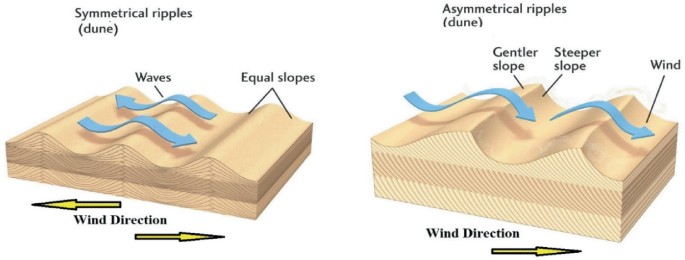
Asymmetrical Ripples
Form from asymmetrical ripples such as rivers/winds
Cross-bedding
produced when dunes or ripples are stacked on top of each other. Sediment is deposited at the angle of the flowing water or wind, which transports it.
Mudcracks
commonly seen due to the sediment being regularly exposed to air during low tides
Things each type of rock have in common:
Igneous
Interlocking minerals can vary in size due to the cooling rate
Sedimentary
Layered and visible fragments of other rocks and fossils
Metamorphic
Foliated or non-foliated
Elevation Map
Major lines are about 10 units apart and elevation increases as you go towards the center of the map
How to create an elevation profile
Draw a line and use that to create an elevation where:
X-axis is the distance from the origin
Y-axis is the elevation
What determines decay?
the decay rate
initial quantity of material
time passed in an isotopic system
Decay Equation
N = Noe-At
Note: the decay constant is always positive
The lost of initial daughter product does what (in terms of decay and age) ?
Underestimate of age
Additional daughter product does what (in terms of decay and age) ?
Artificially inflating the apparent age of the rock/mineral
Crystalline structure
Internal bonding/arrangement
Crystal habit
External shape of a crystal
Are crystalline structures and crystal habits always the same?
Crystalline structure does not equal crystal habit due to blockers (other rocks or minerals) that inhibit the minerals from growing into their crystal habit.
Cleavage
a mineral's property to break along specific planes when struck; break or split apart with smooth surfaces
Fracture
a mineral breaks with a rough or jagged surface
Conchoidal fracture
fracture with smooth, curved surfaces that resemble the interior of a seashell
Striations
parallel scratches or grooves in a rock surface that are created by geological processes
Felsic rocks tend to be more
light in color
Mafic rocks tend to be more
dark in color
Density
Mass over volume (mass must be in grams and volume must be cm³)
Continental Crust
Density (average) | Layer Thickness | Properties |
2.8 g/cm³ | 30-40 km | solid |
Oceanic Crust
Density (average) | Layer Thickness | Properties (highlight property) |
3.0 g/cm³ | 5-10 km | solid |
Mantle
Density (average) | Layer Thickness | Properties (highlight property) |
3.4-5.4 g/cm³ | 2850 km | solid/liquid |
Outer Core
Density (average) | Layer Thickness | Properties (highlight property) |
10-12.3g/cm³ | 2260 km | liquid |
Inner Core
Density (average) | Layer Thickness | Properties (highlight property) |
15g/cm³ | 1220 km | solid |
Pressure forces it to be solid
Which rock sample (basalt, granite, peridotite) represents the best match for:
Continental Crust: Granite
Oceanic Crust: Basalt
Mantle: Peridotite