IB Bio D.1.2
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
In transcription, which enzyme has a role similar to that of helicase in replication?
A. DNA polymerase III
B. Ligase
C. RNA polymerase
D. DNA polymerase I
C. RNA polymerase
A. mRNA splicing
B. Removal of introns
C. Codon-anticodon binding
D. Synthesis of RNA in a 5′ to 3′ direction
D. Synthesis of RNA in a 5′ to 3′ direction
The gene that codes for a particular polypeptide includes the base sequence shown.
GAGTACCCT
What is the base sequence of the mRNA molecule which is complementary to this sequence?
A. GAGTACCCT
B. CTCATGGGA
C. GUGTUCCCT
D. CUCAUGGGA
D. CUCAUGGGA

Which base sequence of an mRNA molecule would code for an arginine–leucine–valine tripeptide?
A. GCA AAU CAG
B. GCA AAT CAG
C. CGT TTA GTC
D. CGU UUA GUC
D. CGU UUA GUC
Which statement applies to tRNA?
A. There is at least one type of tRNA that combines with each known amino acid.
B. One type of tRNA can combine with all of the known amino acids.
C. tRNA carries out its main role within the nucleus.
D. tRNA is produced by the process of translation.
A. There is at least one type of tRNA that combines with each known amino acid.
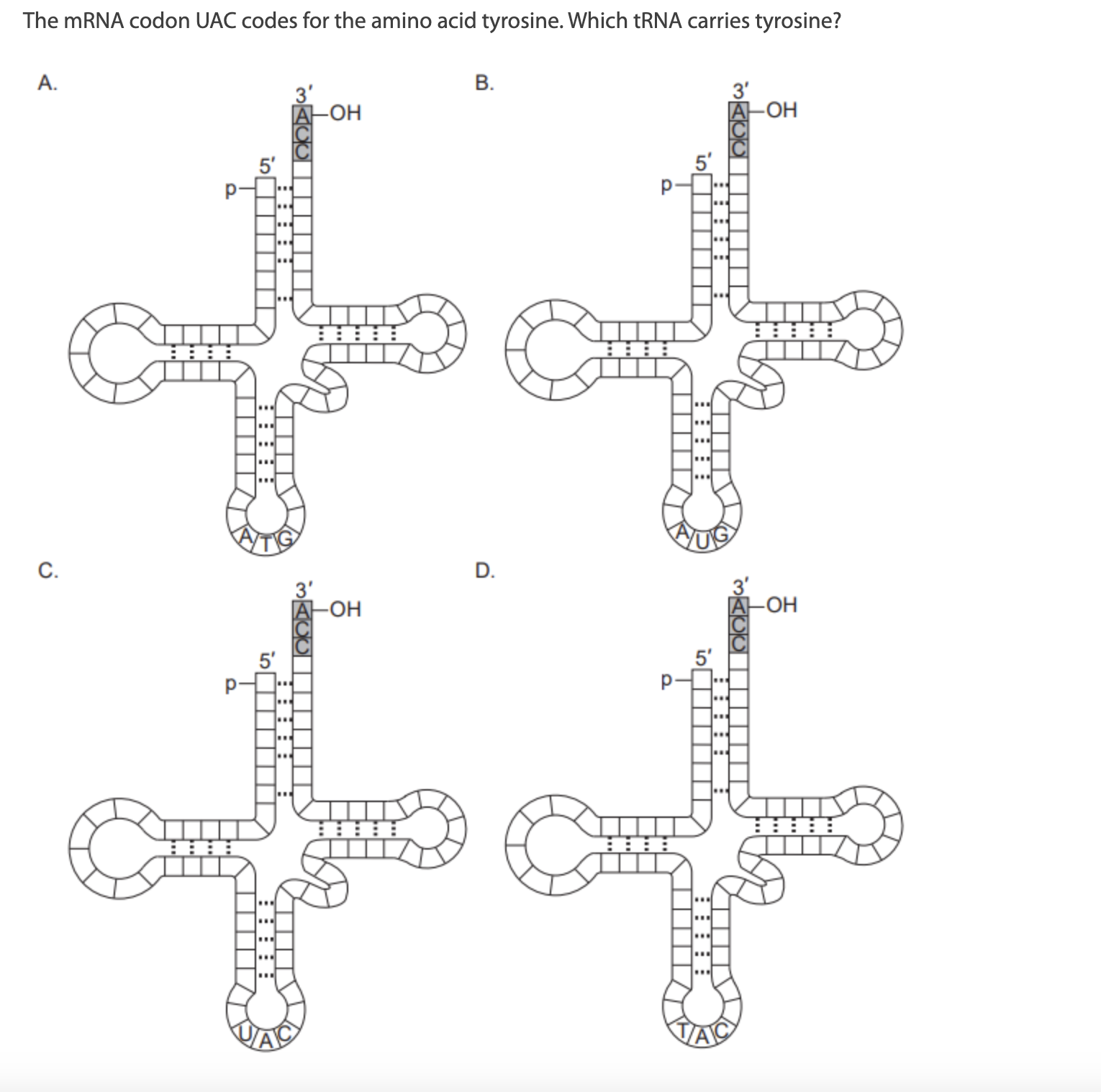
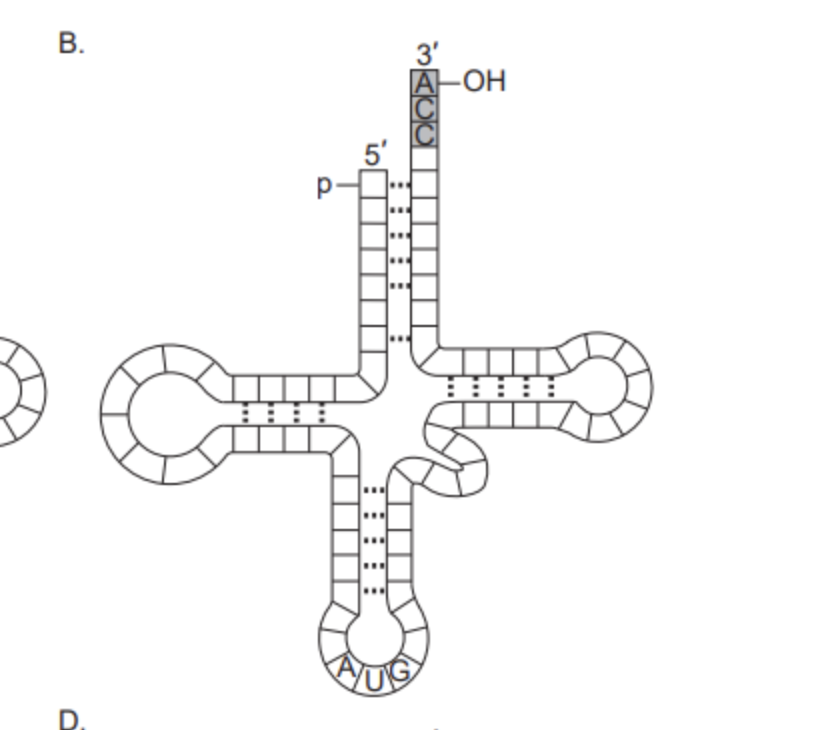
A DNA triplet on the strand that is transcribed has the bases TAG. Which anticodon on tRNA is used in translation?
A. AUC
B. UAG
C. TAG
D. ATC
B. UAG
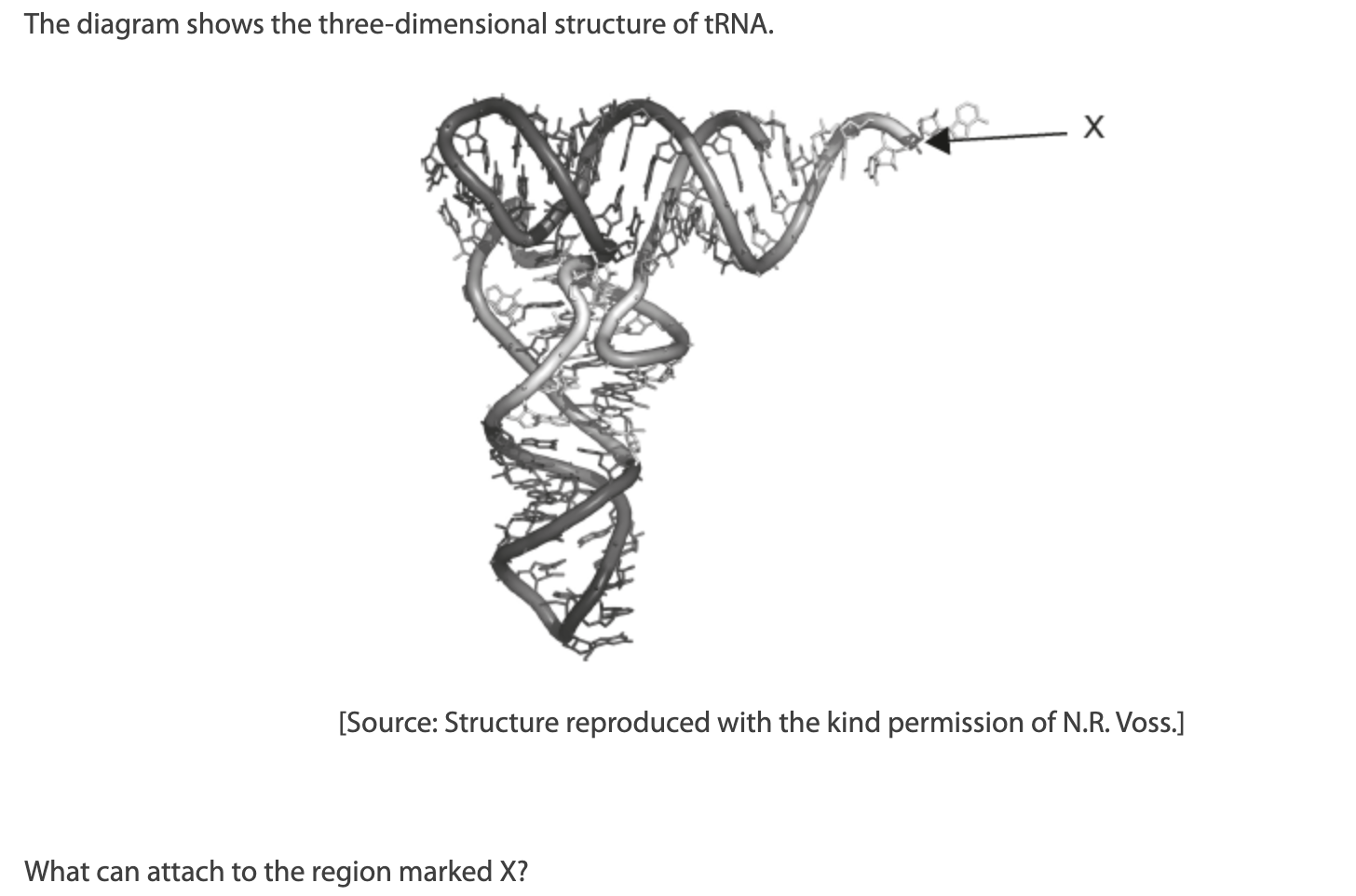
What can attach to the region marked X?
A. mRNA
B. An amino acid
C. An anticodon
D. The P site of the ribosome
B. An amino acid
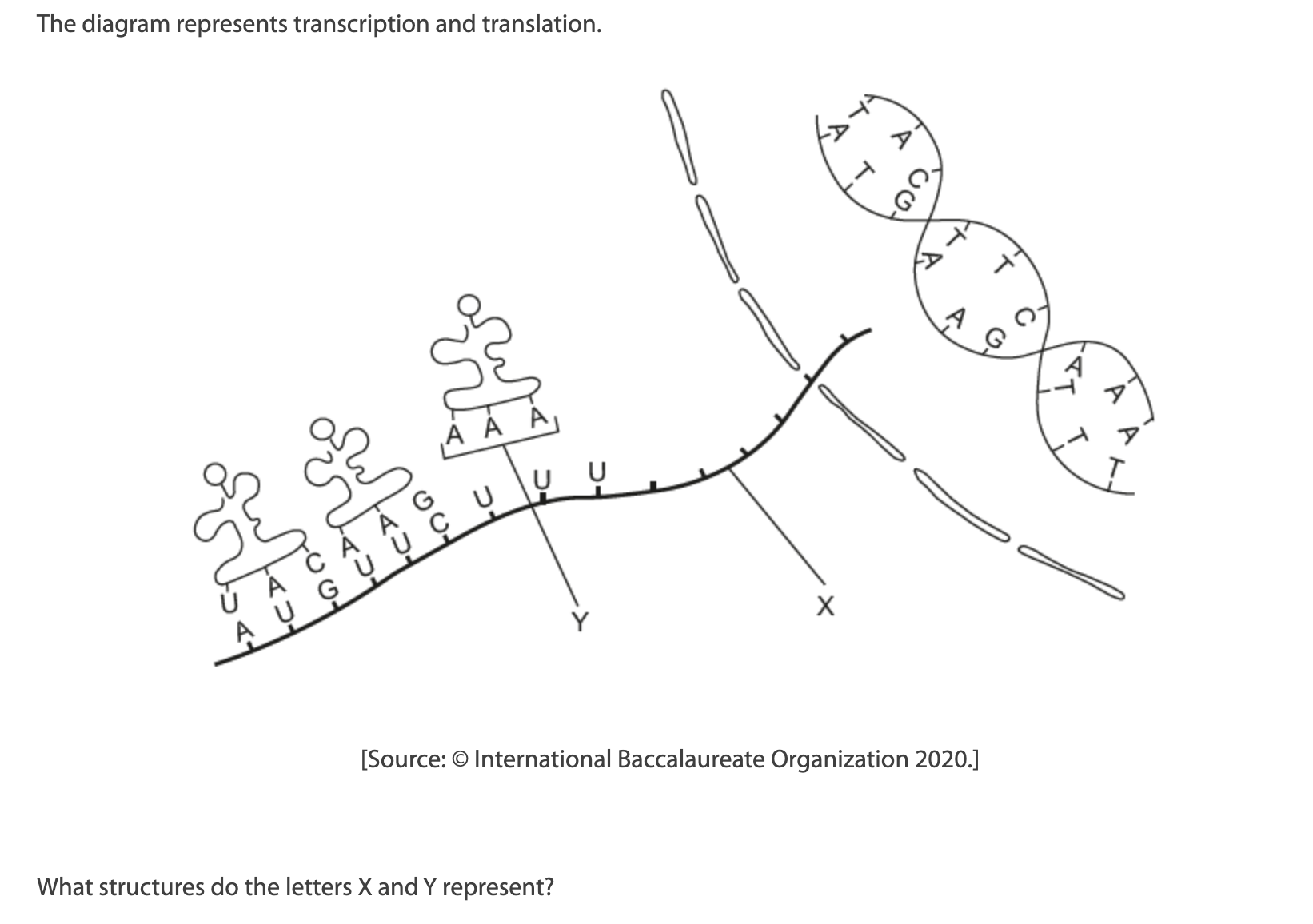
B

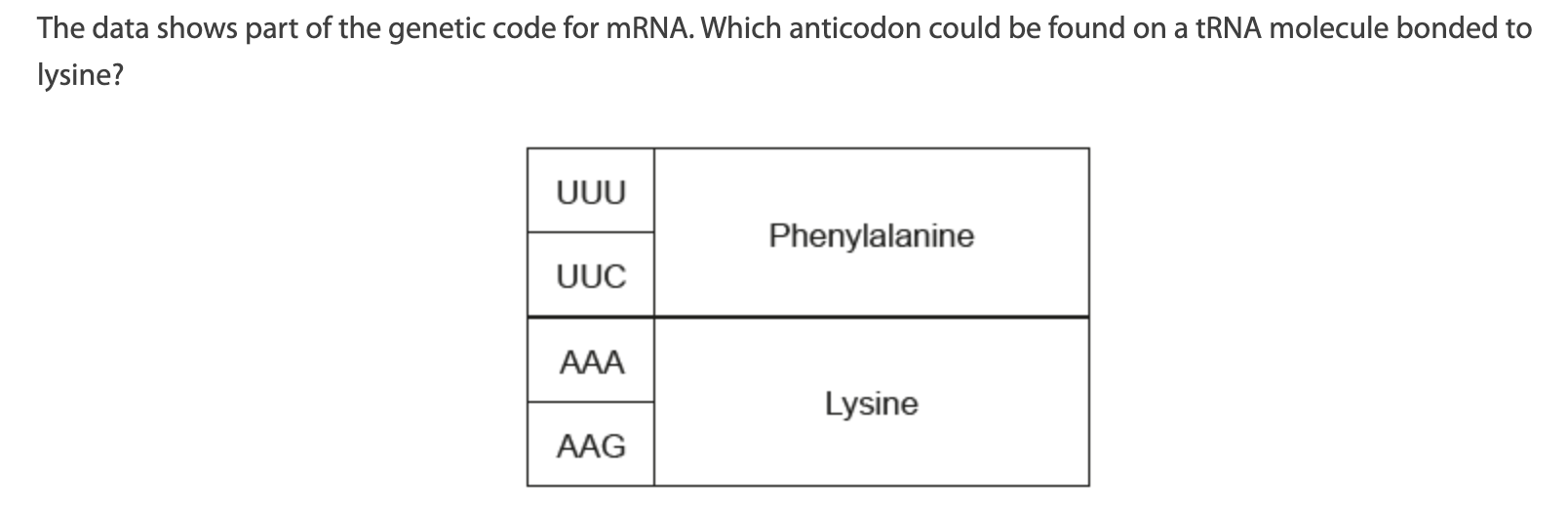
A. AAG
B. UUC
C. TTT
D. GAA
B. UUC
Why is leucyl-tRNA synthetase not used to join the amino acid valine to tRNA?
A. Phosphorylation of valine occurs at a later stage.
B. Valine does not need to be activated to attach to tRNA.
C. Leucyl-tRNA synthetase is substrate-specific.
D. Valine has a different anticodon from leucine.
C. Leucyl-tRNA synthetase is substrate-specific.
What is a universal characteristic of the genetic code?
A. There are more than 64 different anticodons.
B. There are more nucleotides than codons.
C. There are more codons than amino acids.
D. There are two or more amino acids for each codon.
C. There are more codons than amino acids.
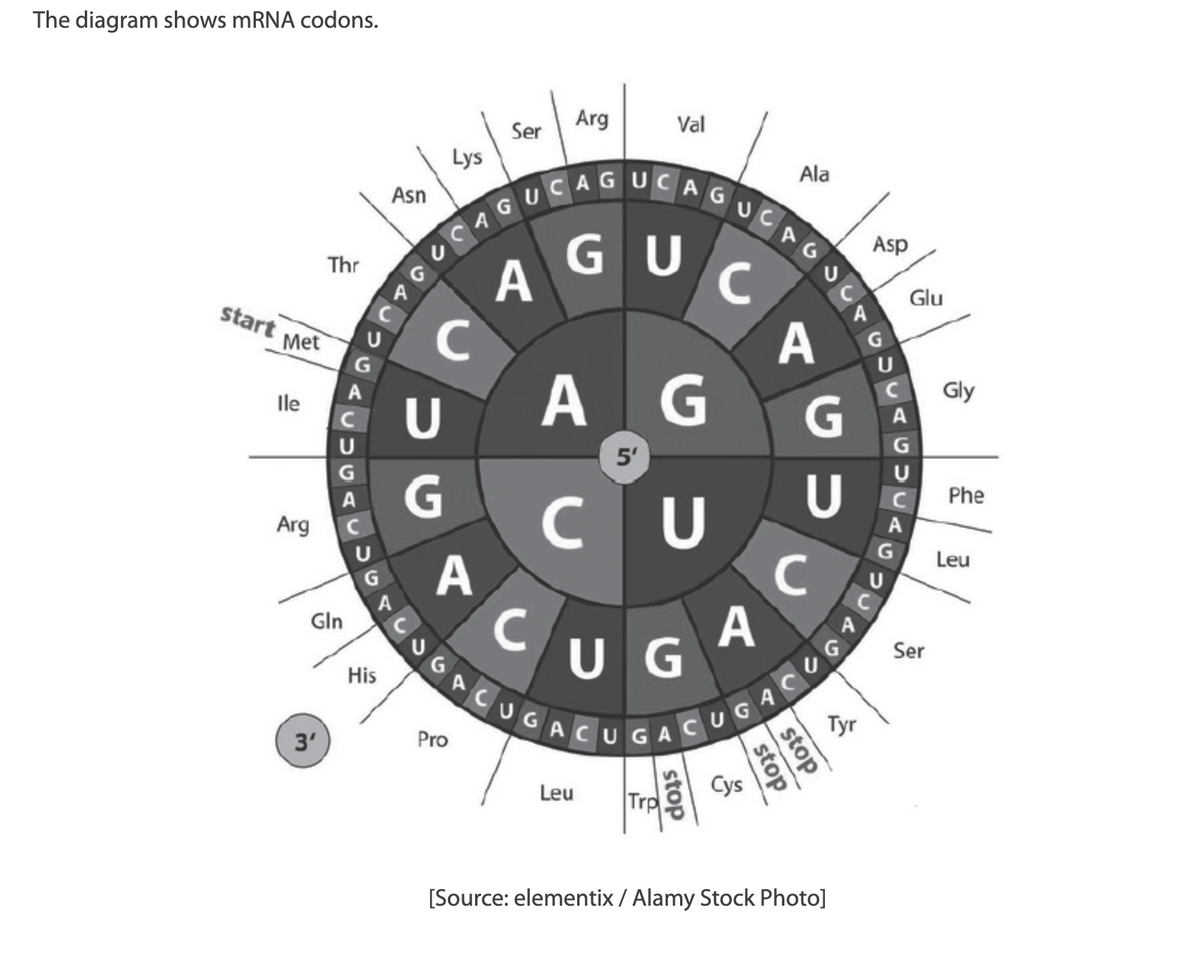
The mRNA sequence UGGAACGUA codes for what amino acid sequence?
A. Glycine-Glutamine-Methionine
B. Methionine-Glutamine-Glycine
C. Threonine-Valine-Histidine
D. Tryptophan-Asparagine-Valine
D. Tryptophan-Asparagine-Valine
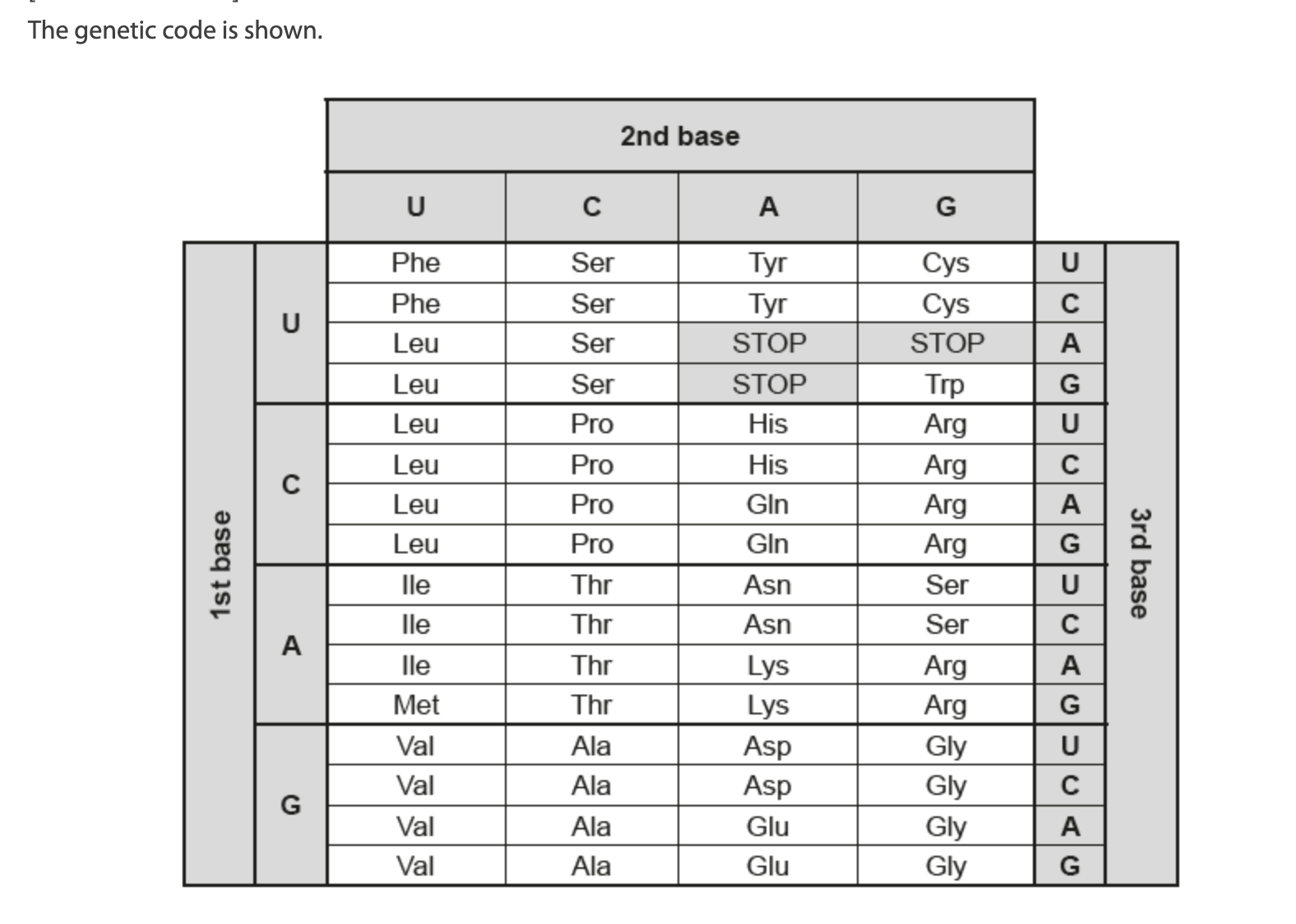
In a coding gene, the DNA triplet in the transcribed strand is changed from AGG to TCG.
What would be the result of this change in the genome?
A. A non-functional protein
B. A different but functional protein
C. No change in the protein
D. Termination of the polypeptide
C. No change in the protein
What is the minimum number of nucleotides needed to code for a polypeptide composed of 210 amino acids?
A. 70
B. 210
C. 420
D. 630
D. 630

C
What applies to DNA base sequences?
I. Some genes do not code for proteins.
II. Promoters are transcribed along with the gene.
III. Introns are only found within genes coding for proteins.
A. I only
B. II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
B. II only
Promoters are non-coding regions in DNA. What is the role of a promoter?
A. It starts translation.
B. It starts mRNA splicing.
C. It is a binding site for DNA polymerase during DNA replication.
D. It is a binding site for RNA polymerase during transcription.
D. It is a binding site for RNA polymerase during transcription.
Which regions of DNA code for the production of specific proteins?
A. Telomeres
B. Genes for ribosomal RNA
C. Exons
D. Regulators of gene expression
C. Exons
During modification in eukaryotes, mRNA is spliced. What is splicing of mRNA?
A. Separation of mRNA from DNA during transcription
B. The removal of non-coding RNA sections in prokaryotic cells
C. Linking together exons
D. Replacement of primers with RNA bases
C. Linking together exons
What happens to an RNA molecule in eukaryotes after transcription in order to process it into mRNA?
A. Introns are added.
B. Exons are removed.
C. Adenine nucleotides are added at the 3’ end.
D. Adenine nucleotides are removed from the 5’ end.
C. Adenine nucleotides are added at the 3’ end.
Which are examples of non-coding DNA?
A. Dominant and recessive alleles
B. Promoters and telomeres
C. Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes
D. Introns and exons
B. Promoters and telomeres
What happens to an RNA molecule in eukaryotes after transcription in order to process it into mRNA?
A. Introns are added.
B. Exons are removed.
C. Adenine nucleotides are added at the 3’ end.
D. Adenine nucleotides are removed from the 5’ end.
C. Adenine nucleotides are added at the 3’ end.
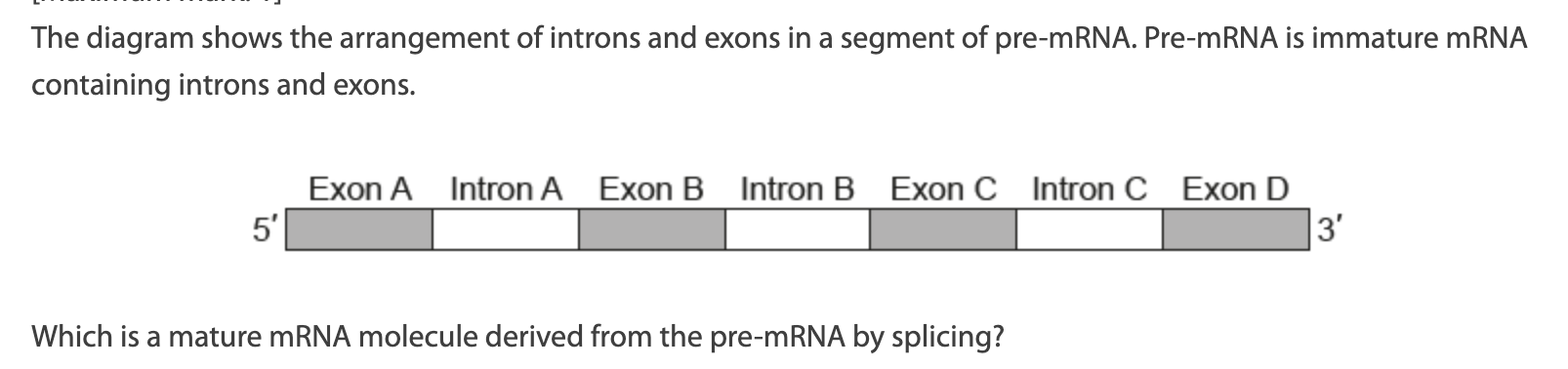
A
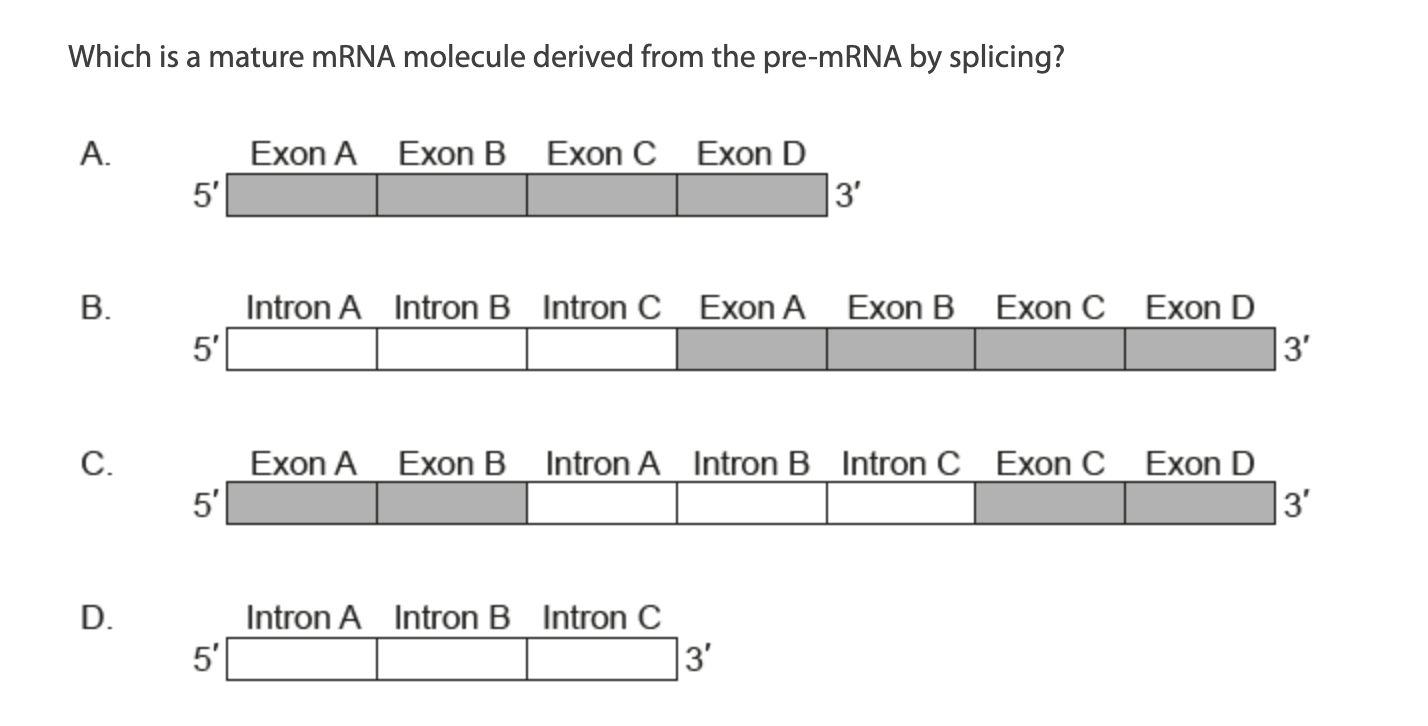
B

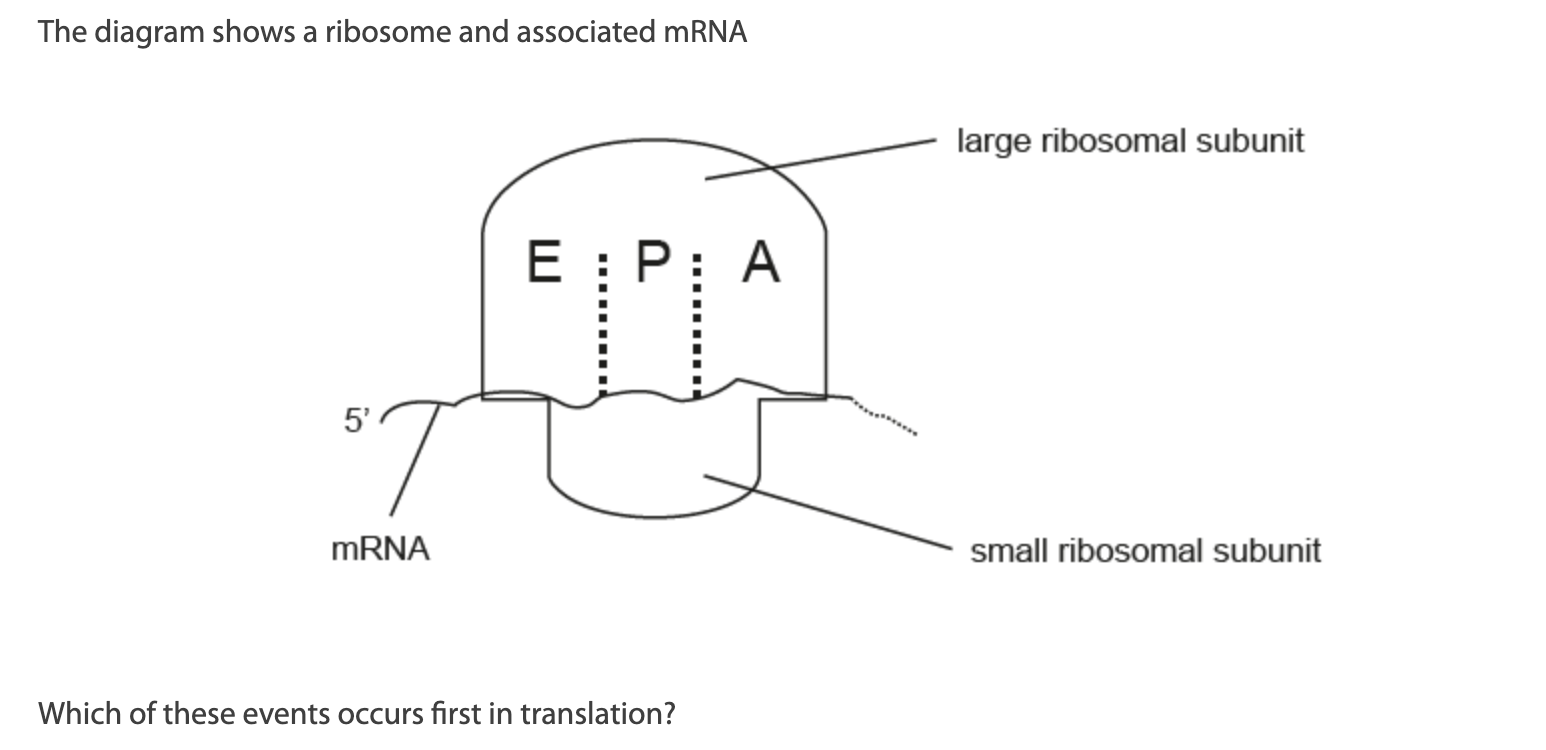
Which of these events occurs first in translation?
A. Small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA.
B. Large ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA.
C. Initiator tRNA enters E site.
D. Initiator tRNA enters A site.
A. Small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA.
B
What is the proteome of an individual?
A. The amino acids unique to an individual making up the proteins in cells
B. The way in which an individual’s polypeptides are folded into a three-dimensional structure
C. The proteins synthesized as an expression of an individual’s genes
D. All possible combinations of amino acids an individual contains
C. The proteins synthesized as an expression of an individual’s genes