AP Chem Compound Structure and Properties Unit 2
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Ionic compounds
metal + nonmetal
ionic compounds are usually
Brittle, have high melting points
ionic compounds conduct electricity when
dissolved into solution
covalent compounds
non-metals + non-metals
covalent compounds conduct electricity
never
Polar Covalent Bonds
nonmetals are “hogging” the electrons
Non-polar covalent bonds
both non-metals are sharing electrons equally (or almost)
The farther away electrons are
the higher potential energy there is
The closer electrons are
the lower potential energy there is
Single bonds are the
weakest and the longest
triple bonds are the
strongest and the shortest
In a crystal lattice
positive ions are smaller and negative ions are larger
Metallic bonding exhibit
delocalized valance electrons that basically float around
Metals conduct electricity so well because they have
free floating electrons
Substiutional Alloys
formed when atoms of the added element substitute some of the metal atoms in the structure
Substiutional Alloys must be
about the same size
Interstitial Alloy
Formed when small atoms fit into the spaces (interstices) between the larger metal atoms
a single bond is composed of
1 sigma
a double bond is composed of
1 sigma & 1 pi
a triple bond is composed of
1 sigma & 2 pi
The hybridization is sp if
2 atoms are surrounded around the central atom
The hybridization is sp2
3 atoms are surrounded around the central atom
The hybridization is sp3 if
4 atoms are surrounded around the central atom
Linear molecular geometry has a bond angle of
180 degrees
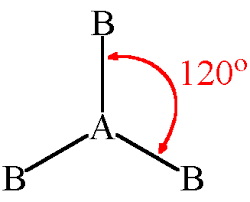
Trigonal Planar has a bond angle of
120 degrees
Tetrahedral has a bond angle of
109.5
Trigonal Bipyramidal has a bond angle of
90 degrees & 120 degrees
Octahedral has a bond angle of
90 degrees
Trigonal Planar
tetrahedral

trigonal Bipyramidal

Octahedral

The best representation for a structure to have is to have a
formal charge of zero
geometries that cancel out (non polar)
linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, Octahedral
geometries that don't cancel out ( polar)
Bent, Trigonal Pyramidal, Seesaw, T-Shaped
brittleness is due to
internal repulsion of ion layers within the crystal lattice, moving adjacent layers
interstitial Alloys are smaller or bigger than the spaces they occupy
smaller
Malleability shows what
how adjacent layers of positive ions can move relative to one another while remaining in full contact with the electron sea
Formal charge equals
Valence electrons - non-bonding valance electrons - bonding electrons
4 electron domains has what molecular geometry?
tetrahedral
3 electron domains has what molecular geometry?
trigonal planar
2 electron domains has what molecular geometry?
linear