Physical Properties of Solutions: Concentration, Colligative Properties, and Pharmacological Applications
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a solution?
A chemically and physically homogeneous mixture of two or more substances.
What is a binary solution?
A mixture of only two components, called solute and solvent.
What are the advantages of solutions in pharmaceutical practice?
Faster onset of activity, good for children and elderly patients, homogeneous, flexible dosing, and can be given by any route of administration.
What are the disadvantages of solutions?
Bulkiness, leakage from containers, less stability than solids, and more pronounced taste.
What is molarity?
A common unit for concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
What is normality?
A concentration term based on chemical activity, defined as gram equivalents of solute per liter of solution.
What is the formula for calculating molarity?
Molarity = # moles of solute / 1 Liter of solution.
What is the formula for calculating normality?
Normality = # gram equivalents of solute / Volume of solvent in liters.
What are colligative properties?
Properties that depend only on the number of solute particles in a solution, not on their identity.
What are the four colligative properties?
Vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure.
What is Raoult's law?
The vapor pressure of a liquid in a solution is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure liquid multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution.
What distinguishes ideal solutions from real solutions?
Ideal solutions show no change in physical properties other than dilution, while real solutions exhibit changes when mixed.
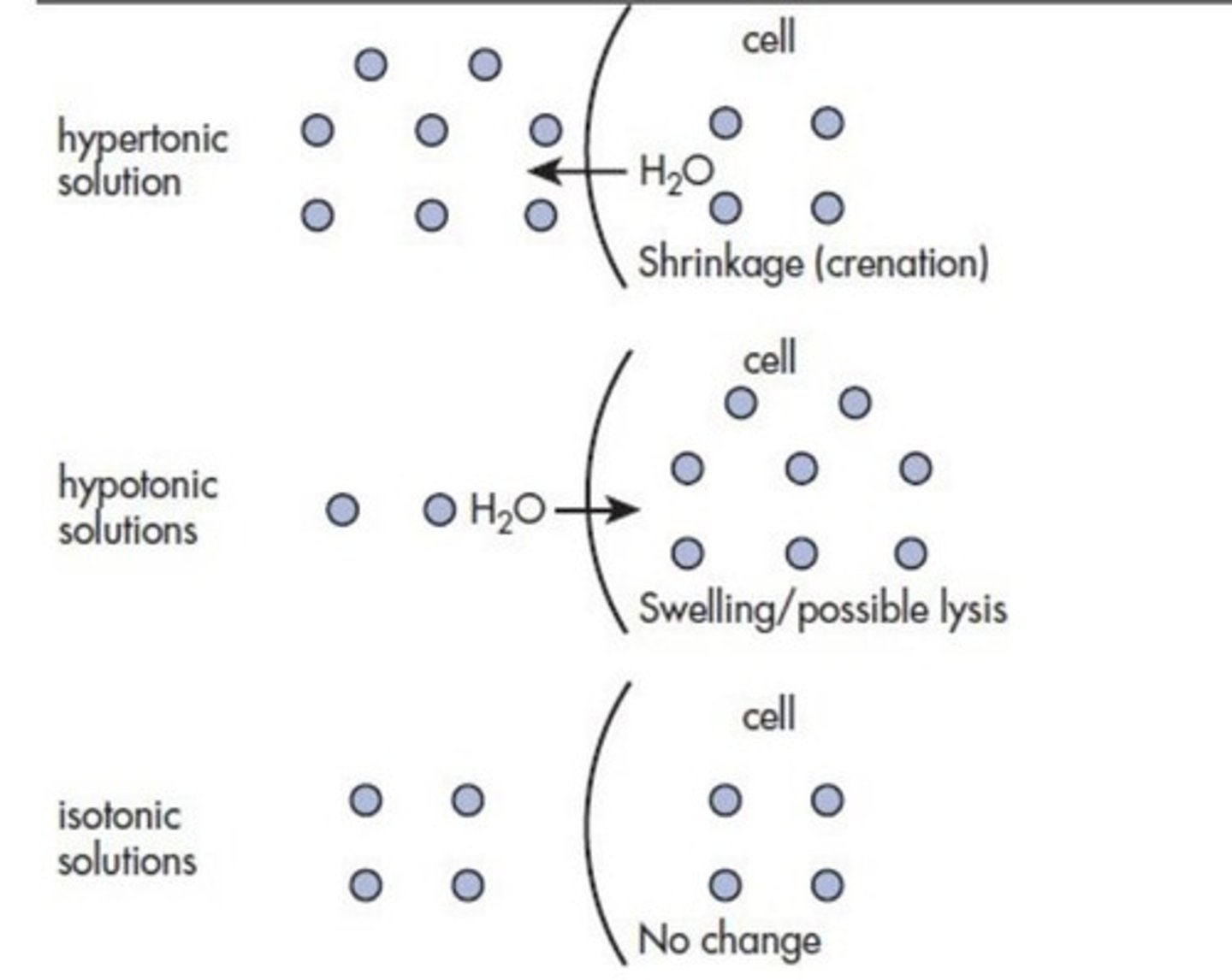
What is an isotonic solution?
A solution that has the same osmotic pressure as another solution, typically physiological saline (0.9% w/v NaCl).
How is freezing point depression related to isotonic solutions?
An isotonic solution has a freezing point depression of 0.52 °C for sodium chloride.
What assumptions are made when applying colligative properties to pharmaceutical systems?
The solute is nonvolatile, the solvent is water, solutions are dilute, and properties depend on ionization for electrolytes.
What is the significance of osmolarity in pharmaceutical formulations?
It helps avoid cell and tissue damage and patient discomfort when administering drugs to sensitive areas.
What types of solutes are classified in aqueous solution systems?
Non-electrolytes, strong electrolytes, and weak electrolytes.
What is the relationship between colligative properties and the number of ions in strong electrolytes?
The values of colligative properties depend on the number of ions produced by the strong electrolytes.
What is the importance of understanding concentration expressions in pharmacy?
Pharmacists must convert between different expressions of solution concentrations, such as percentages, molarity, normality, and osmolarity.
What is the impact of temperature on molarity?
Molarity can vary slightly with changes in temperature due to its dependence on the volume of the solution.
What are the physiologic implications of colligative properties?
They affect the behavior of solutions in biological systems, influencing drug efficacy and safety.
What is the E-value method for calculating isotonic solutions?
It uses the equivalent of a 0.9% w/v NaCl solution.
What is the D-value method for isotonic solutions?
It refers to the solution having a freezing point depression of 0.52 °C.
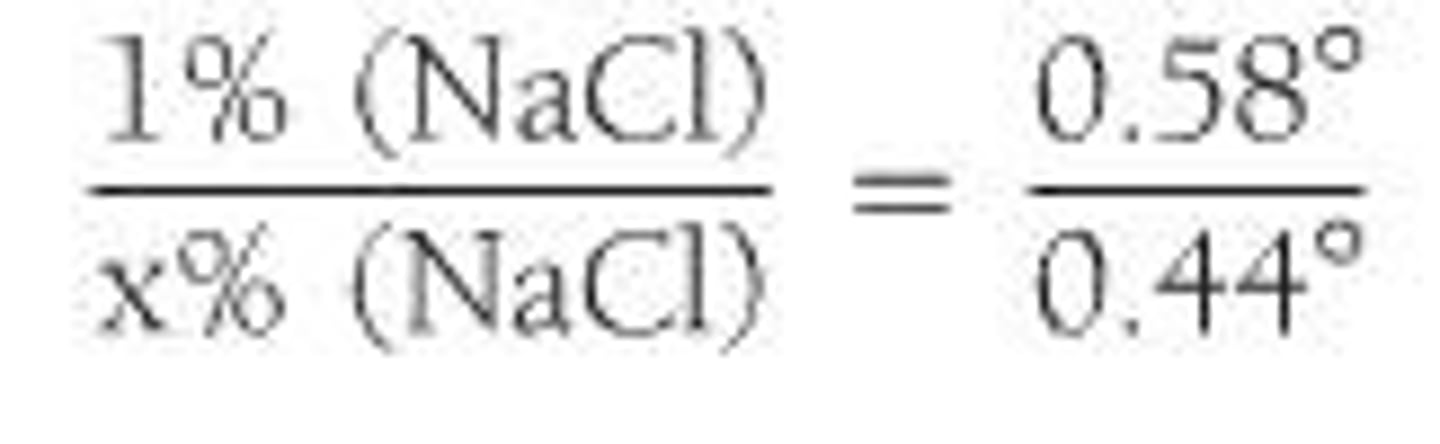
What is the significance of the term 'homogeneous' in the context of solutions?
It indicates that the components of the solution are uniformly distributed at the molecular level.
What is the role of freezing point depression in isotonicity calculations?
It helps determine the concentration of solute needed to achieve isotonicity with physiological fluids.
What is the relationship between vapor pressure and mole fraction in solutions?
According to Raoult's law, the vapor pressure of a component is proportional to its mole fraction in the solution.