8: The Moon
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
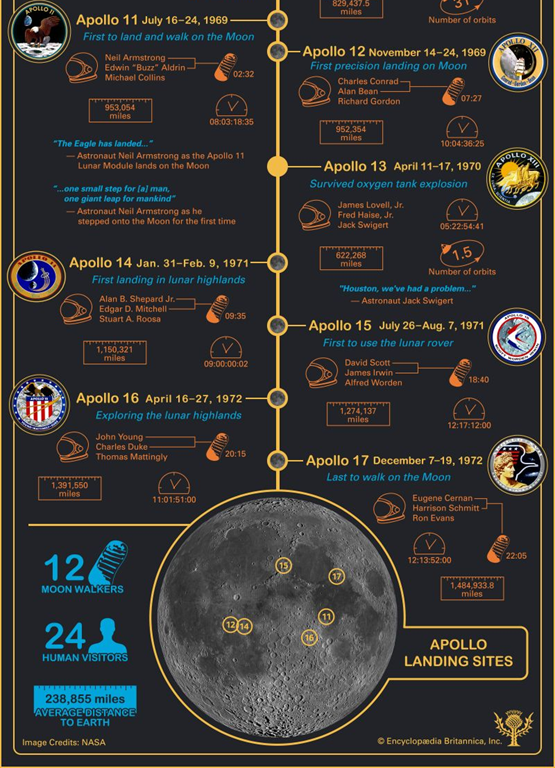
Apollo 11
1969 H-class mission
neil armstrong, buzz aldrin and mike collins
sea of tranquility
21.6kg rocks and soils
FIRST LUNAR SAMPLES
basalts, pyroxenes and plagioclase
Apollo 12
1969
Pete Conrad, alan bean, richard gordon
ocean of storms
34.3kg rock
mostly basalt
KREEP rich in K, REE and Phosphorus
COPERNICUS IMPACT 800Mya
Apollo 14
1971 H-class mission
alan sheppard, edgar mitchell and stuart roosa
Fra Mauro
42.3kg rocks
date imbrium basin
impact ~3.85Ga
Apollo 15
1971 J-class mission
david scott, jim irwin, al wordon
Hadley Rille
77.3kg rocks
Edge of Mare Imbrium
lava channel
vesicles - gas rich, explosive volcanism, anorthosite

apollo 16
1972 J-class mission
John young, charlie duke, ken mattingly
Descartes Highlands
impact melt 3.92ga
anorthosites 4.5ga
apollo 17
1972 j-class mission
gene cernan, harrison schmidt, ron evans
110.5kg rocks
ORANGE SOIL - melt glass
NORITES and TROCTOLITES
what are norites
plagioclase and pyroxene
what are troctolites
plagioclase and olivine
Who was the only geologists to walk on the Moon?
Jack Schmidtt: others were given a crash course in geology
Lunar rover capabilities
some issues: dust covers equiptment
up to 30km covered each mission
Summarise the apollo missions
What si the farside vs darkside of the moon
Farside: faces away from us - less is known
Darkside: faces us, more mare (darker)
how did moon exploration begin?
soviet us spacerace - politically motivated
90s it picked up in momentum
NASA Artemis would like to return people to the moon
Change 5 & 6 both important

USSR and moon missions
first soviet mission 1959 - flyby - first pictures of darkside (17)
Lunokhod Rovers
first robotic sampling of planetary surface
funny shapes
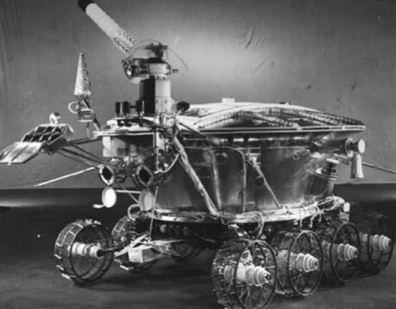
what are Lunokhod Rovers
ussr spacecrafts on moon
sited surveys for possible crewed landings
onboard experiments: cameras, soil, x-ray
Luna 17: Mare Imbrium 1970, 10.5km
Luna 21: Mare Serenitatis 1973, 37-42km
America and moon missions
ranger programmes 1961-1965: hard landers (1-6 failed, 7-9 gave images till impact)
Apollo: 2.4-3.5bil per launch, 6 successful landings 1969-1973 - 382kg rocks

Where did the apollo missions land?
All equitorial
o Apollo 11 – Mare Tranquility mare basalt
o Apollo 12 – Oceanus Procellarum mare basalt
o Apollo 13 – did not land
o Apollo 14 – Fra Mauro highlands (Imbrium ejecta)
o Apollo 15 – Hadley Rille and Imbrium mare basalt
o Apollo 16 – Cayley Plains and Descartes Highland
o Apollo 17 – Taurus Littrow valley mare basalt and highlands

Lunar rocks
All shapes and sizes
middle shows cesicular basalt
bottom left shows apollo 15 white highland genesis rock
top right shows orange glass beads (volcanic, fire fountain events)
Lunar minerals
Silicates: plag, pyroxene, olivine, quartz
oxides: ilmenite, spinel
FeNi metal
troilites (iron sulphide)
glass
ferroan anorthosites
magnesian suite
high alkali suite
observations and missions to see the moon from orbit
earth based observations
moon satellites
1950s-1960s: Luna, lunar orbiter, ranger, surveyor, apollo
1990s-now: galileo, clementine, lunar prospector, SMART1, kaguya, change 1&2, LRO, LCROSS, LADEE
photography: illumination angle, oblique vs perppendicular sun

Clementine mission
CCD camera mapping of lunar surface in 5 UV/VIS wavelength
created topographic map
apparent nearside/farside crustal asymmetry
farside/nearside crustal asymmetry
big basin southpole - aitken
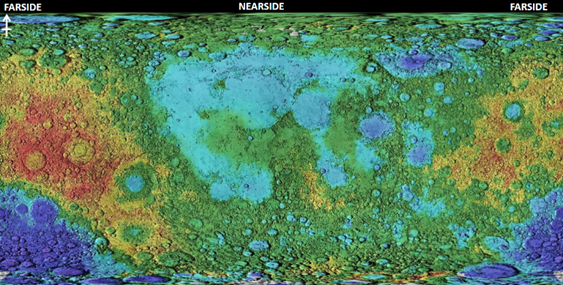
chemical diversity
farside highlands - Al2o3, CaO rich, FeO poor (anorthosites)
nearside mare regions - FeO, TiO2-rich (basalts-lavas)
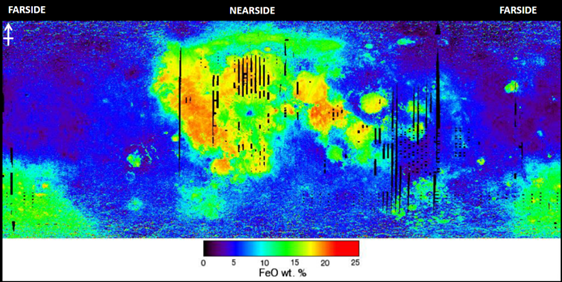
Makeup of the lunar crust
Primary: anorthosites (highlands)
secondary crust: volcanic/magmatic - intrusive volcanic processes or extrusive (mare)
tertiary crust: impact soil, sediments
Lunar geological ages
Pre-Nectarian
Imbrian
Eratosthenian
Copernican

Timing of Lunar origin
~4.5Ga
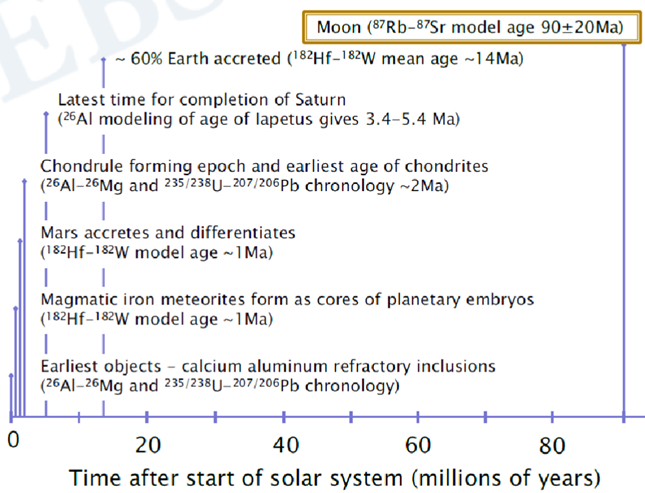
What is the Giant Impact theory?
moon likely formed in giant impact event 4.456ga
~62Mya after formation of Solar System
significantly later than formation of asteroids and Mars
Theia (potential impactor, mars-sized)
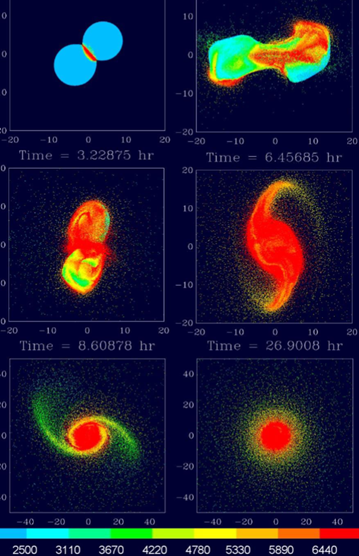
Lunar differentiation
small core, mantle and crust
core ~330km (1-3% total moon mass)
core formation event dated using lunar rocks by Hf-W system
material remaining after core formation likely forms overlying magma ocean

lunar ingterior differentiation and crust formation
magma ocean cooled
minerals crystallised
time of crystallisation unknown
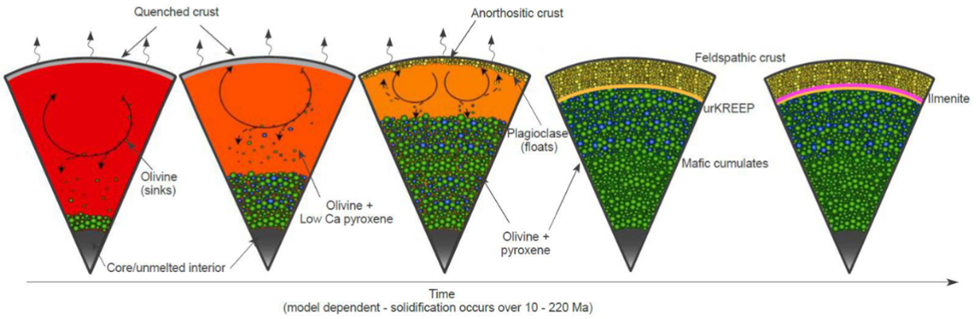
how does lunar ocean crystallisation occur?
dense minerals rich in Mg sink to form lunar mantle
after ~80% magma ocean crystallisation plag formed as it is less dense and floats
late stage KREEP plase and Fe-rich minerals (ilmenite) form and trapped between mantle and crust
What is Ferroan Anorthosite
pre-nectarian >3.92ga
primary crust
white rock
rich in Al, Ca and Si (plag)
farside dominated by FAN rocks

When was the formation of lunar crust?
4.5-4.3Ga
When did early lunar magmatism occur?
4.5-4.0Ga
secondary crust
generated suites of intrusive events and erupted lavas
High Mg, Alkali, Al and KREEP basalts
when did impact bombardment occur
4.5-3.8Ga to present
asteroids, comets and dust impacts
large impact craters and basins form on moon
Impact craters
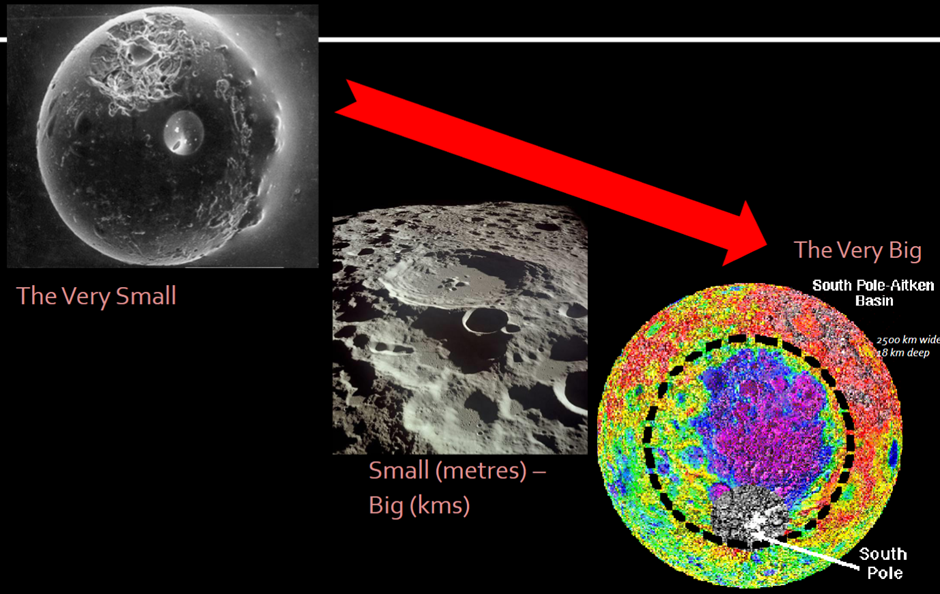
What is the Aitken Basin?
Largest basin in SS
2500km diameter, ~13km deep
excavated through crust into underlying mantle
formed ~4.33Ga
What is Lunar Cataclysm?
Late Heavy Bombardment
Violent Early Solar System
cluster of ages, 3.85Ga
all basins formed in 20Ma or 200Ma
what is the Nice Model?
scattering of small objects in SS due to migration of giant planets (3.9Ga) - more impactors in inner solar system
What are the Lunar Maria?
topographic lows, fe rich, low albedo
impact basins with dark basaltic flows
3.8-3Ga
effect of lunar volcanism
basalt eruption and emplacement
pyroclastic glass
What is the Hadley Rille?
Apollo 15
sinuous lava channel that ranges in depth (180-270m)
370m deep at apollo landing site
