Module 4- Worksheets Surface Anatomy and General Questions about bony, soft tissue, and muscular anatomy of knee region
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Which motion do both of the collateral ligaments resist at the knee?
A) extension
B) medial rotation
C) lateral rotation
D) flexion
B) medial rotation
Which of the following palpation techniques allows you to palpate the edges of the medial condyle of the femur when the knee is extended?
A) Move the patella superiorly
B) Move patella inferiorly
C) Move the patella laterally
D) Move the patella medially
C) Move the patella laterally
In what area does the peroneal nerve become accessible (and vulnerable)?
A) near the adductor tubercle
B) lateral to the gastrocnemius belly
C) medial to the biceps femoris tendon
D) posterior surface of the head of the fibula
D) posterior surface of the head of the fibula
Which of the following is an action of the plantaris?
A) weak dorsiflexion of the ankle
B) inversion the foot
C) weak plantar flexion of the ankle
D) eversion the foot
C) weak plantar flexion of the ankle
What is the bony landmark distal to the patella?
A) femoral condyle
B) tibial tuberosity
C) head of the fibula
D) adductor tubercle
B) tibial tuberosity
What shape is the plantaris and where does it insert?
A) Oblique muscle about 1-inch thick; Calcaneal tendon
B) Long thin muscle about 6-inchs in length; Calcaneal tendon
C) Oblique muscle about 1-inch thick; Lateral supracondylar line of femur
D) Long thin muscle about 6-inchs in length; Lateral supracondylar line of femur
A) Oblique muscle about 1-inch thick; Calcaneal tendon
The medial collateral ligament originates on the medial aspect of the upper medial femoral condyle and inserts on the medial tibial surface.
A) True
B) False
A) True
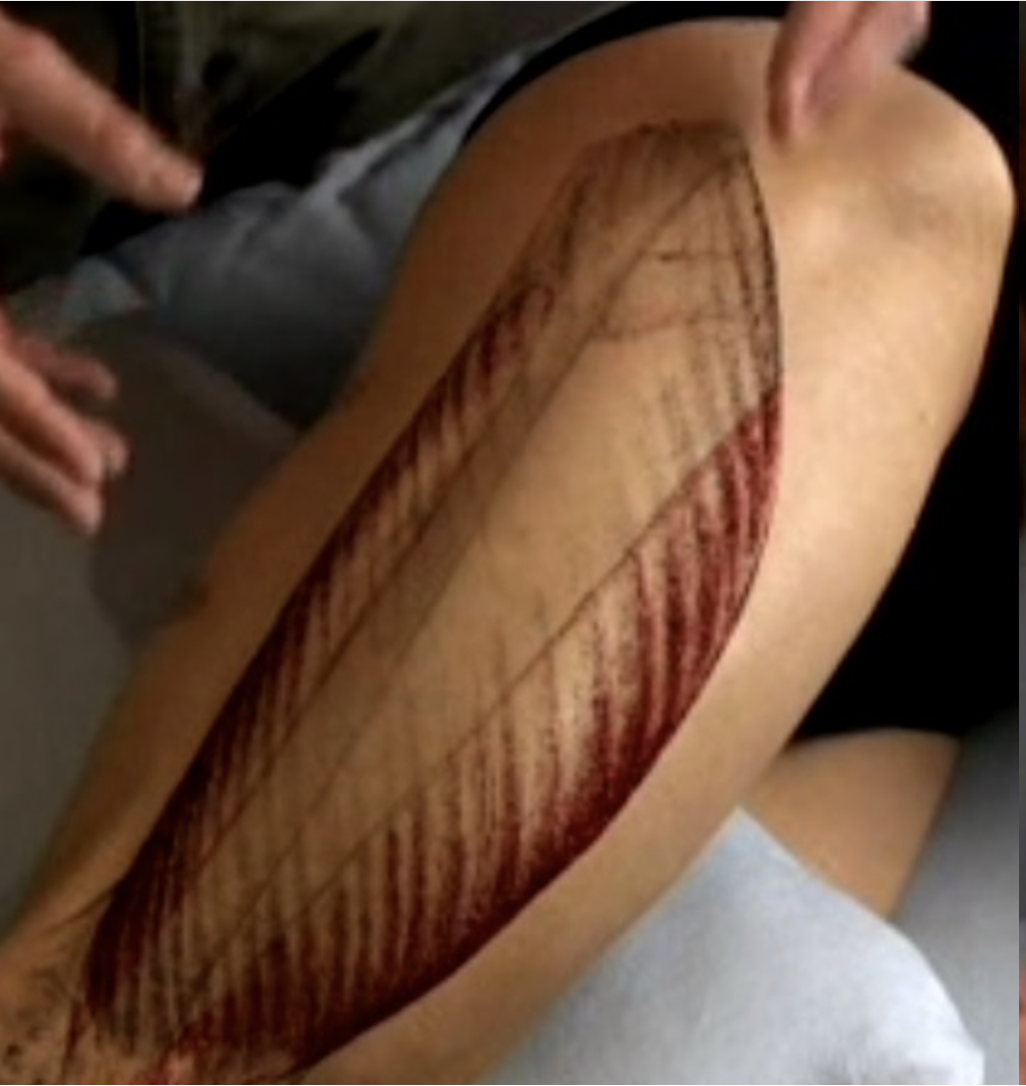
Identify the vastus lateralis muscle.
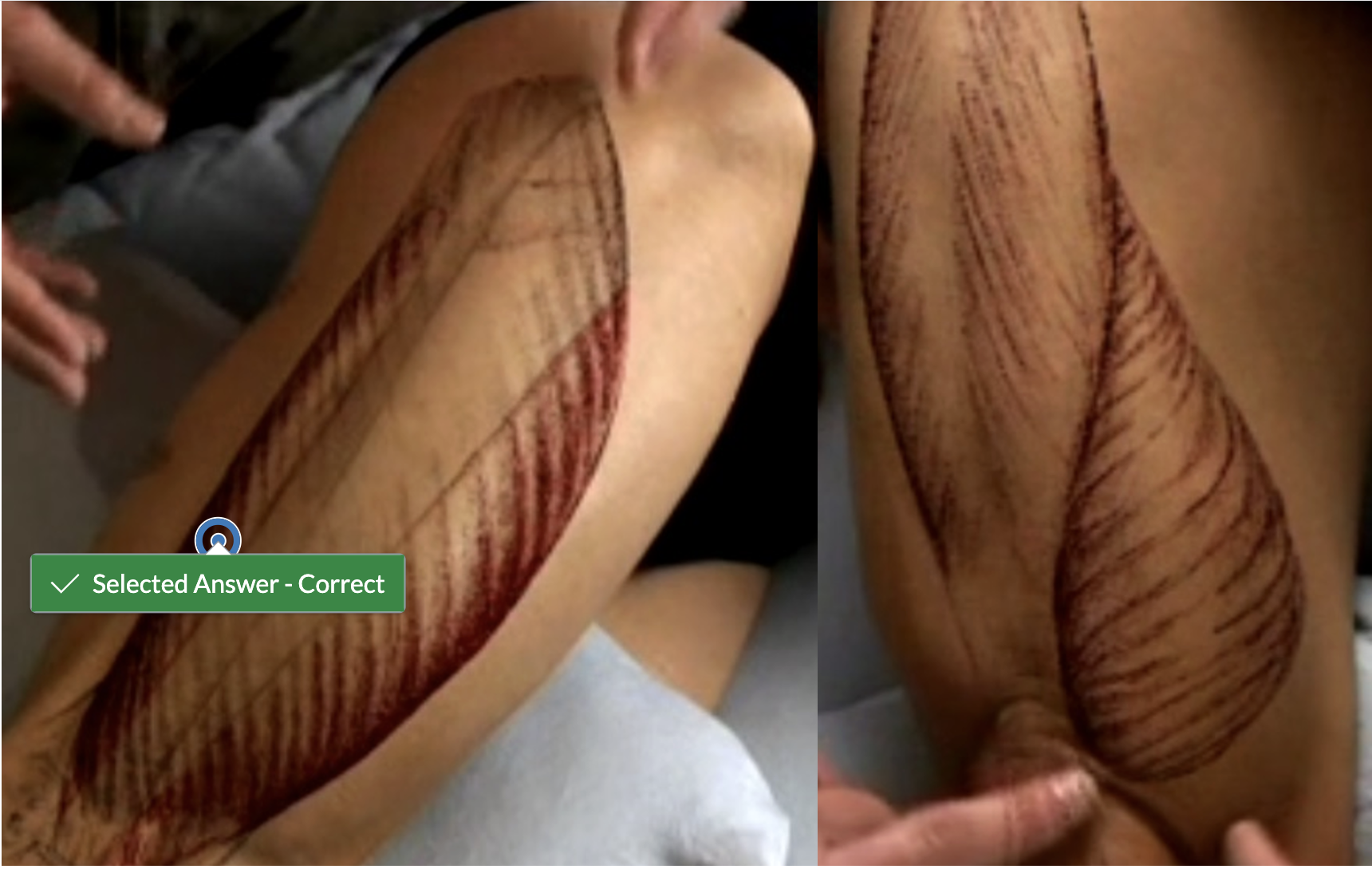
Identify the most medial portion of the semimembranosus tendon.
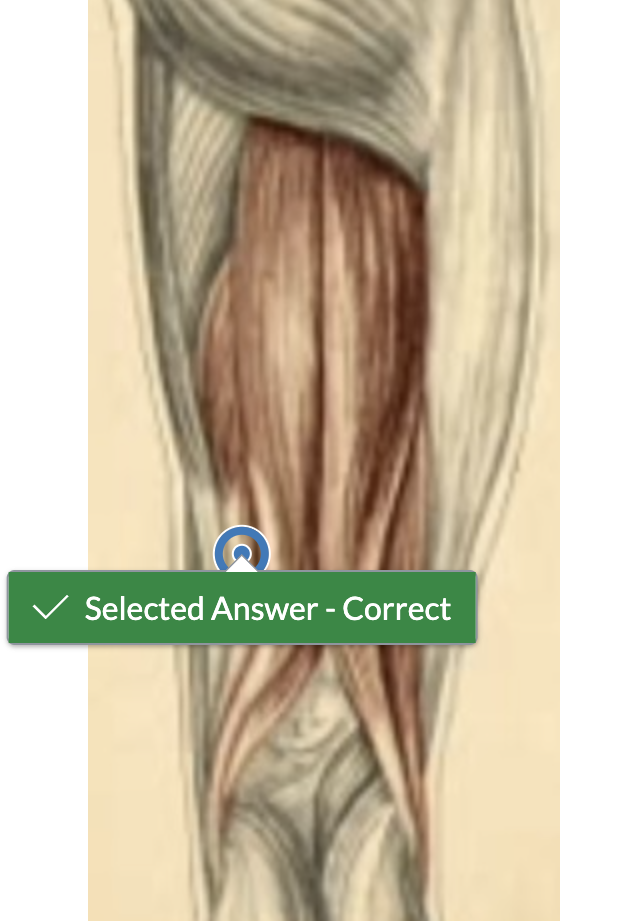
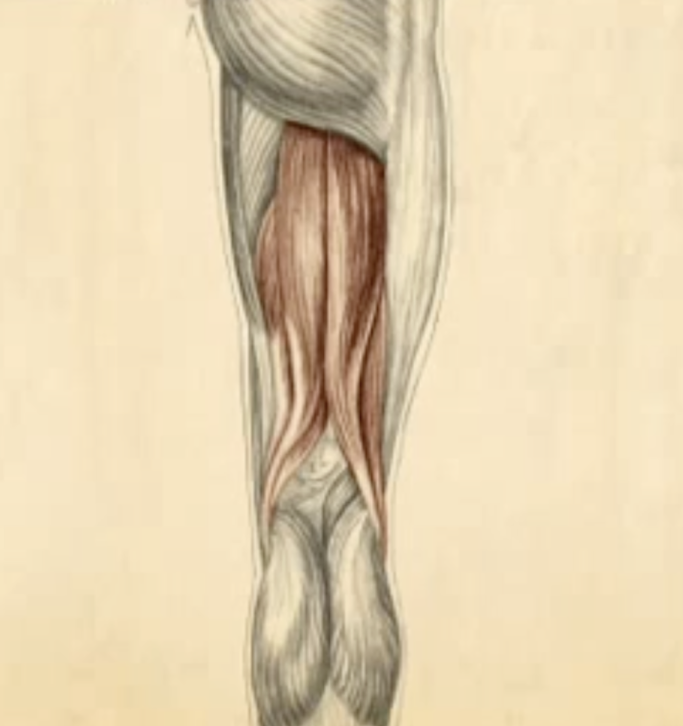
Which muscles have their origin or insertion on the head of the fibula? (More than one answer)
A) Fibularis brevis
B) Rectus femoris
C) Biceps femoris
D) Soleus
E) Fibularis longus
F) Vastus lateralis
G) Flexor hallicus longus
bicep femoris soleus fibularis longus
The anterior surface of the patella is concave.
A) True
B) False
B) False
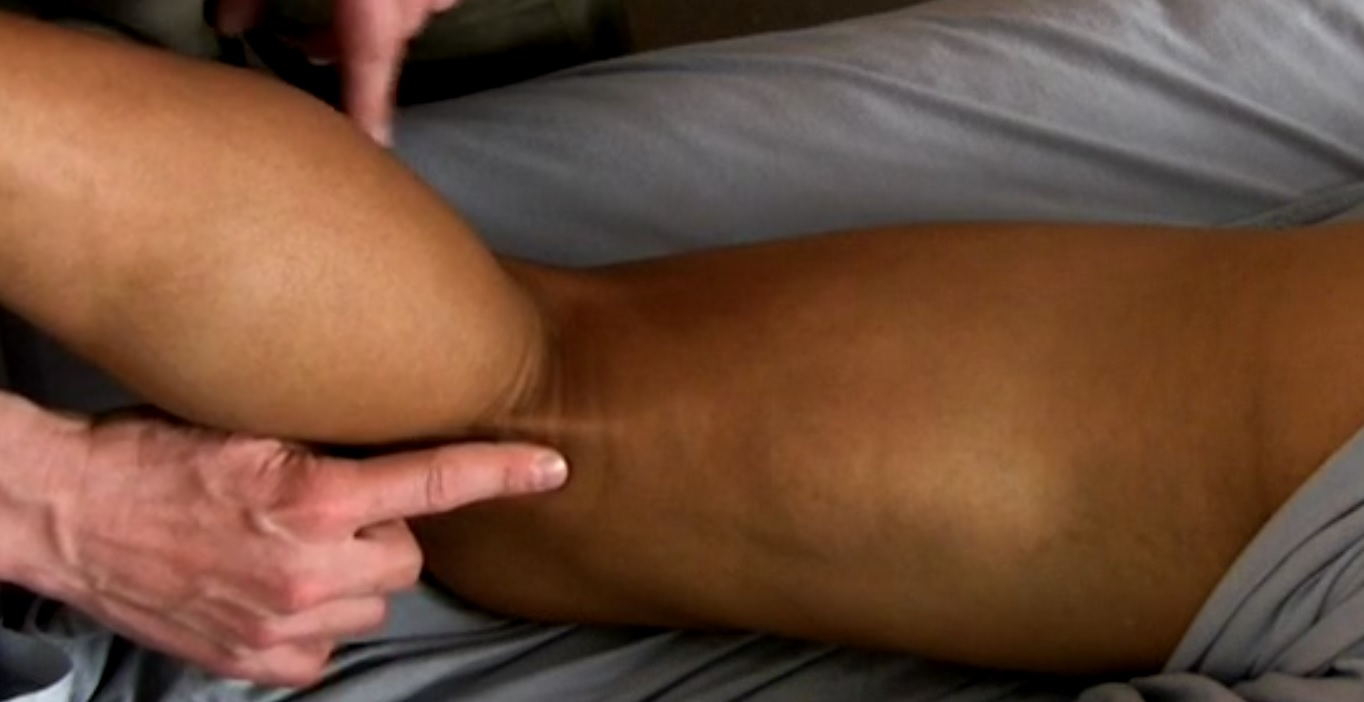

Identify the biceps femoris tendon.
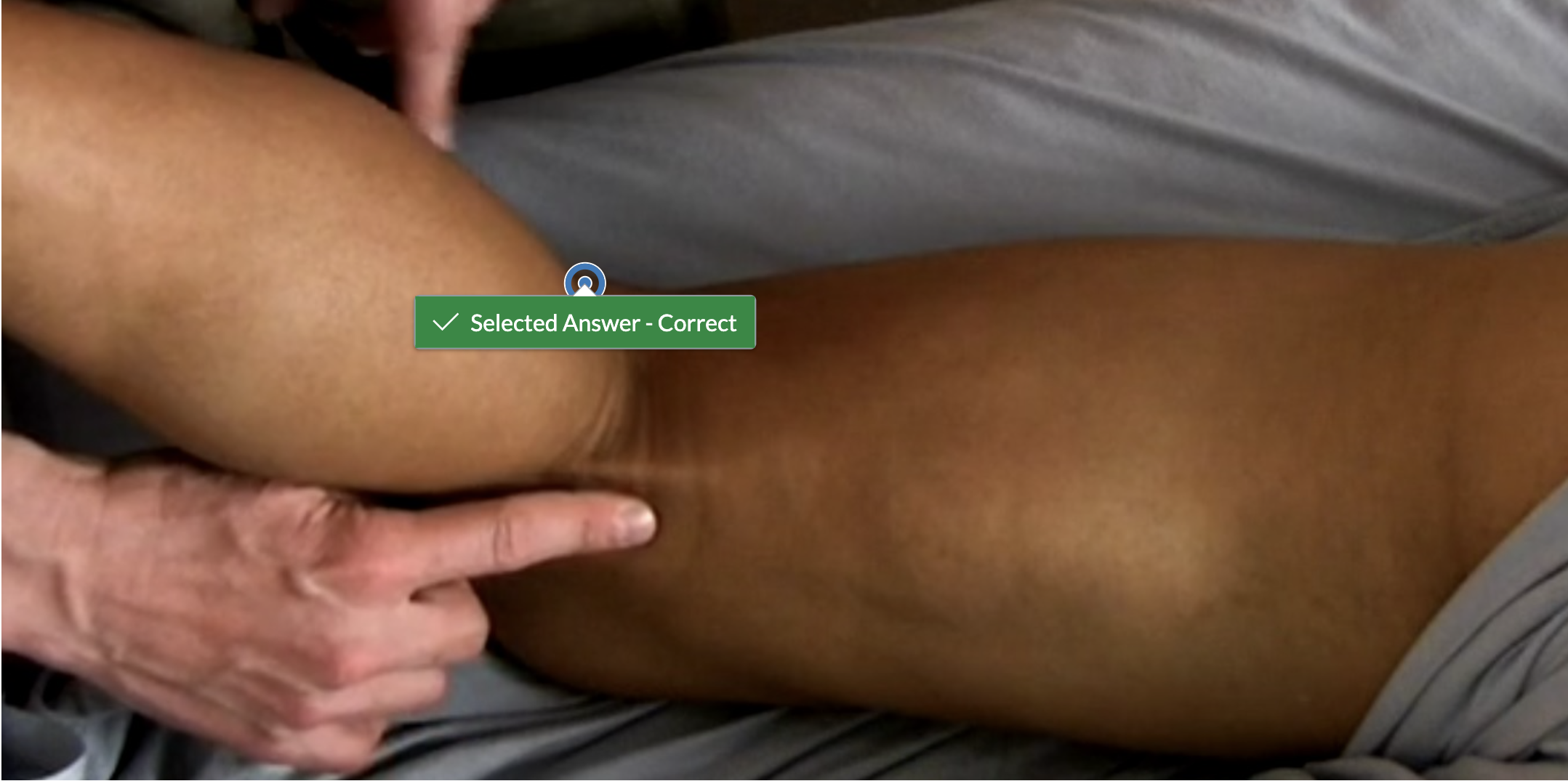
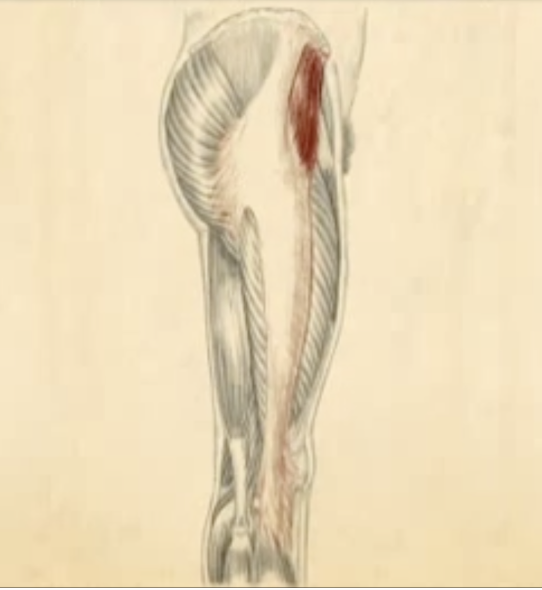
Identify the distal end of the iliotibial band.
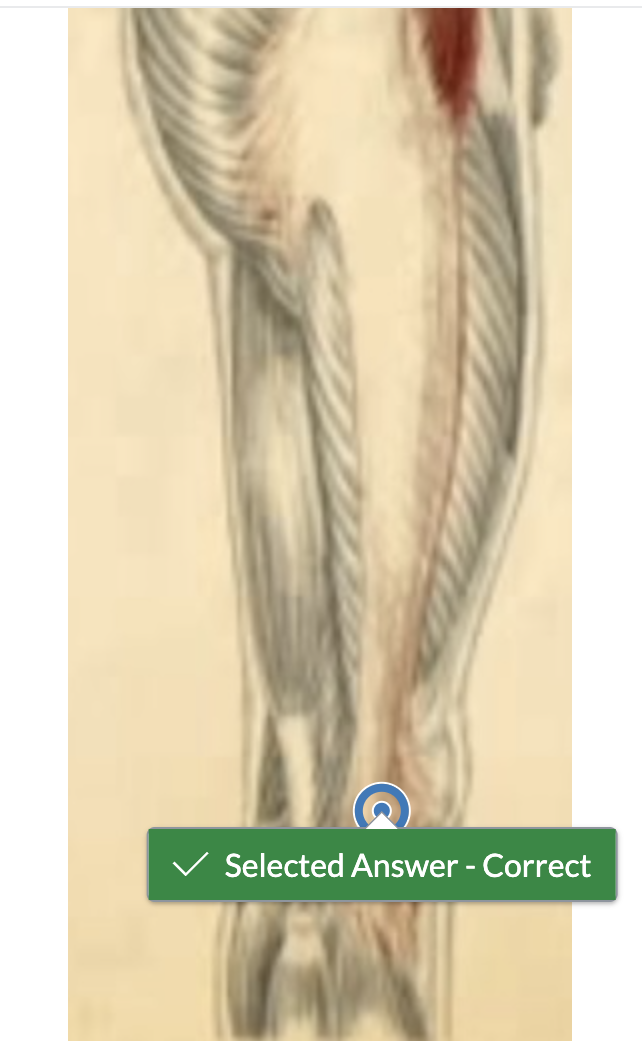
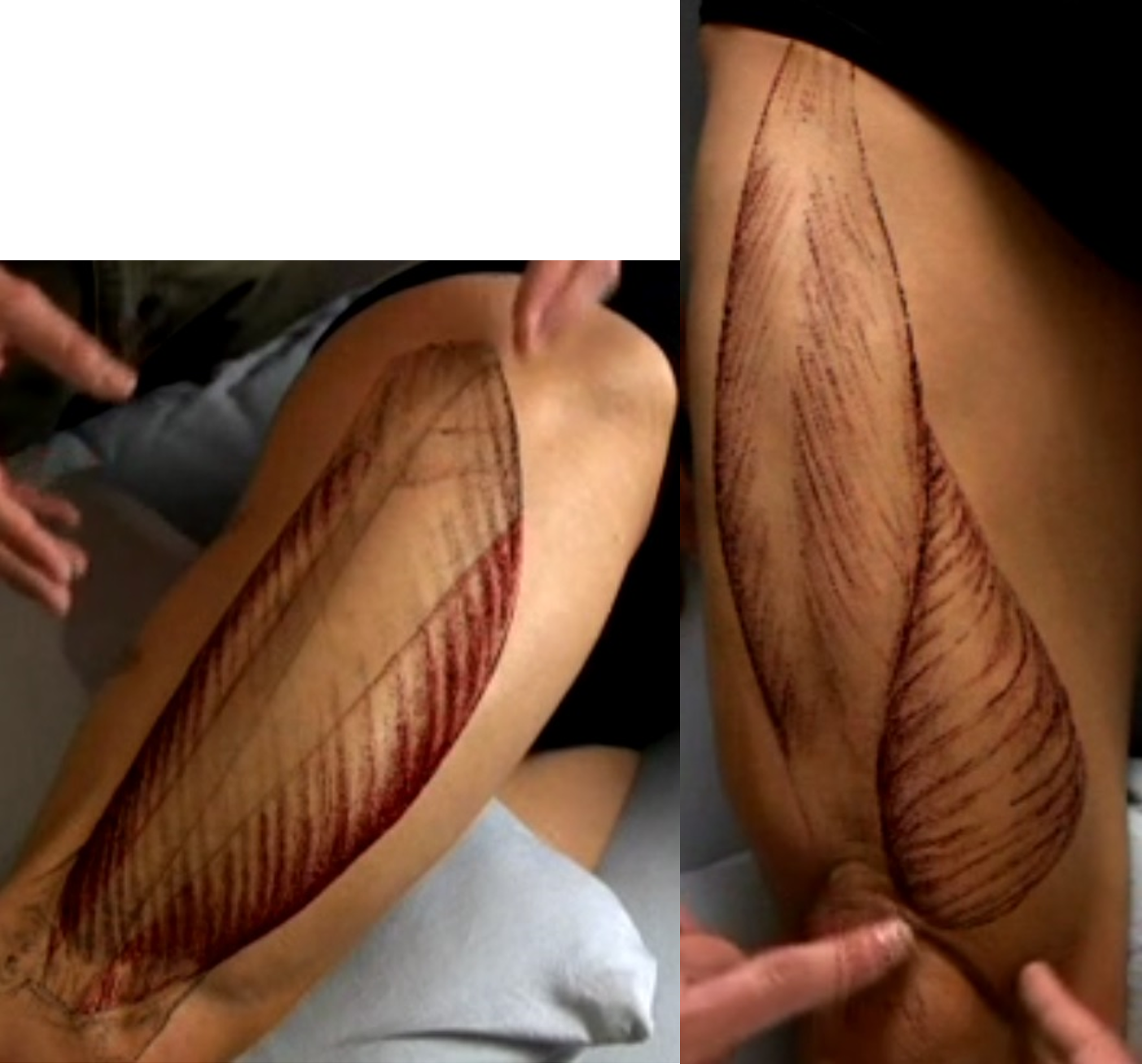
Identify the vastus medialis muscle
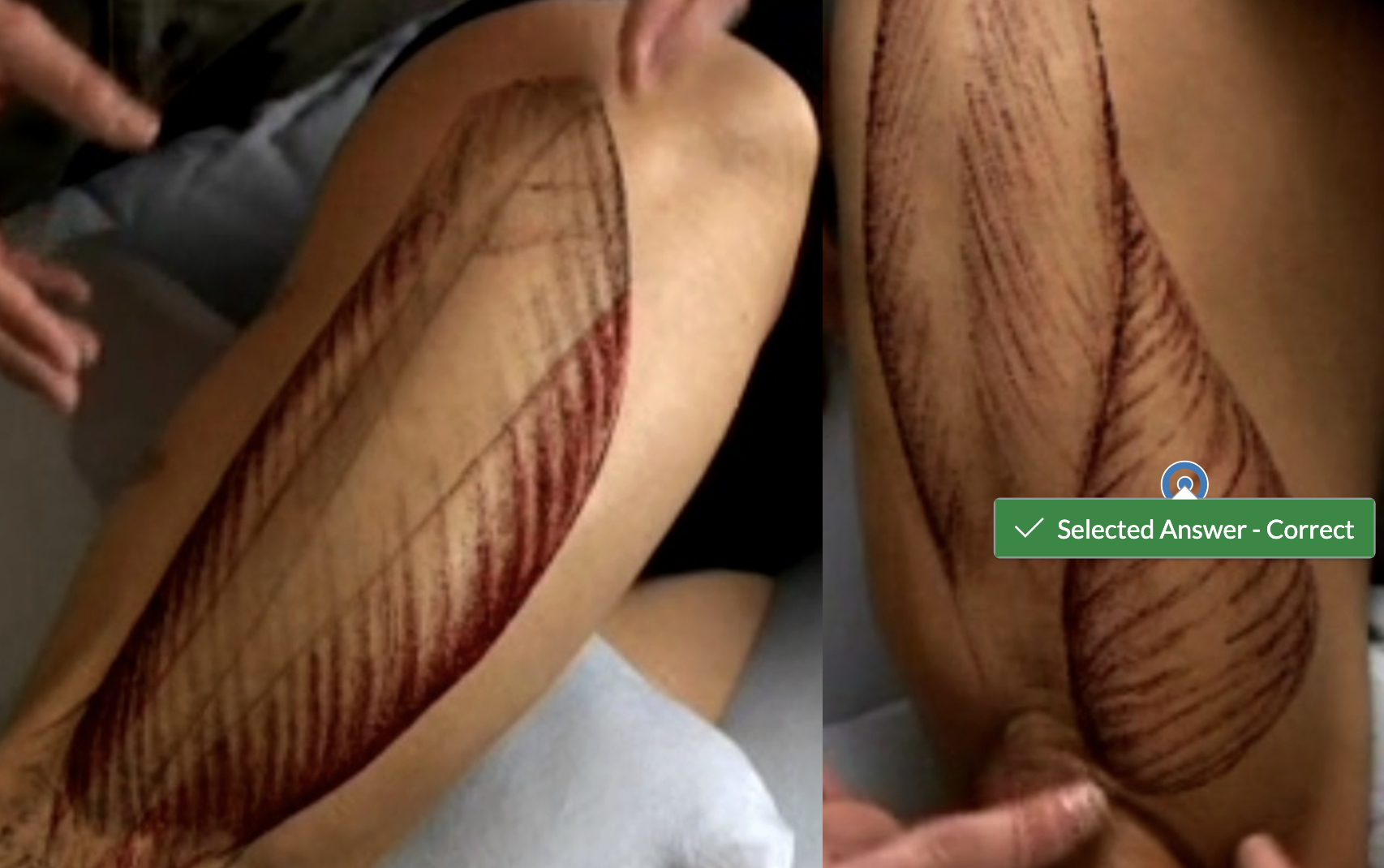
When the knee is extended, what role does the popliteus muscle play?
A) It unlocks the knee by laterally rotating the tibia
B) It provides stability by locking the knee into extension
C) It provides stability by locking the knee into flexion
D) It unlocks the knee by medially rotating the tibia
D) It unlocks the knee by medially rotating the tibia
What are the agonists to knee flexion? (6 of them)
Rectus Femoris
Vastus Lateralis
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Plantaris
Vastus Medialis
Biceps Femoris
Gastrocnemius
Popliteus
Soleus
Tensor Fascia Lata
Vastus Intermedius
Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Plantaris Biceps Femoris Gastrocnemius Popliteus
What is the small, fluid-filled sac directly superficial to the patella?
A) subcutaneous infrapatellar bursa
B) deep infrapatellar bursa
C) pes anserinus bursa
D) prepatellar bursa
D) prepatellar bursa
Which two bony landmarks does the patella seem to sink into when the knee is flexed? (More than one answer)
A) Lateral femoral condyle
B) Abductor tubercle
C) Lateral tibial tubercle
D) Adductor tubercle
E) Medial femoral condyle
F) Medial tibial tubercle
lateral femoral condyle medial femoral condyle
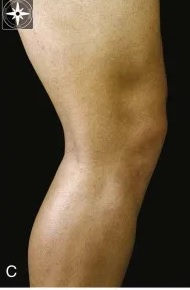
Identify the fibular head.
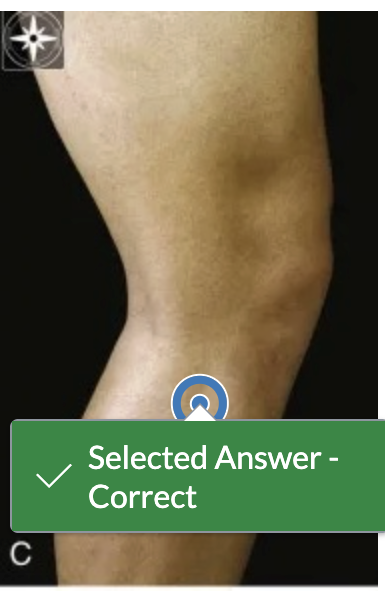
To access the tendinous attachment of the popliteus, you have to push the overlying edges of which muscle(s) aside?
A) tibialis anterior
B) extensor digitorum longus
C) peroneus longus and brevis
D) gastrocnemius and soleus
D) gastrocnemius and soleus
Which ligament has its distal attachment on the head of the fibula?
A) Lateral collateral
B) Anterior cruciate
C) Medial collateral
D) Posterior cruciate
A) Lateral collateral
Which movement will lengthen the fibers of the plantaris?
A) dorsiflexion
B) knee extension
C) plantar flexion
D) inversion
A) dorsiflexion
What motion can you have your partner perform to visualize the quadriceps muscles?
A) Hip adduction
B) Knee flexion
C) Knee extension
D) Hip flexion
C) Knee extension
Which of the following is not correct regarding menisci in the knee joint?
A) Deepens tibial fossa
B) Decreases stability
C) Attached to the tibia
D) Forms cushions between bones
B) Decreases stability
In order to palpate the lateral femoral epicondyle, you will need to palpate through the ________ _______
iliotibial band
What motion can you have your partner perform to visualize the hamstring muscles?
A) Knee flexion
B) Hip flexion
C) Hip adduction
D) Knee extension
A) Knee flexion
The connective tissue structure that connects the patella to the tibial tuberosity is the ________ ligament/tendon
patellar
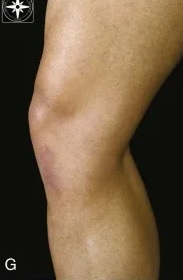
Identify the pes anserine tendon attachment.
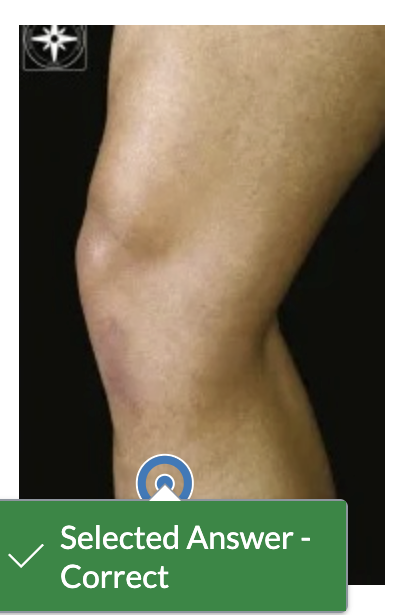
The lateral collateral ligament originates on the lateral femoral condyle distally to the popliteus muscle origin and inserts on the fibular head.
A) True
B) False
B) False
Medial and lateral rotation of the knee can occur when the knee is in a ______ position.
flexed
Which muscle has the longest tendon in the human body?
A) Extensor digitorum longus
B) Plantaris
C) Popliteus
D) Flexor hallicus longus
B) Plantaris
What bony landmark is located proximal to the medial epicondyle and has the tendon of a large muscle attach to it?
A) Greater tubercle
B) Abductor tubercle
C) Adductor tubercle
D) Tibia tubercle
C) Adductor tubercle
What is the anatomical name for the main knee joint?
A) talofemoral
B) patellotalar
C) patellafemoral
D) tibiofemoral
D) tibiofemoral
Which tendons join to form the pes anserine tendon on the medial knee? (More than one answer)
A) Semitendinosus
B) Sartorius
C) Biceps femoris
D) Semimembranosus
E) Gracilis
F) Vastus medialis
semitendinosus sartorius gracilis
What are the antagonists to knee flexion? (4 of them)
Rectus Femoris
Vastus Lateralis
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Plantaris
Vastus Medialis
Biceps Femoris
Gastrocnemius
Popliteus
Soleus
Tensor Fascia Lata
Vastus Intermedius
rectus femoris vastus lateralis vastus medialis vastus intermedius