Chemistry Final
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
don't fail. positivity. grace. harmony. vision. joy. embracement. lock in. don't fail.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
CHP 1.1 Matter
Matter: is the physical material of the universe; it is anything that has mass and occupies space.
CHP 1.1 Property
Property: is any characteristic that allows us to recognize a particular type of matter and to distinguish it from other types.
CHP 1.1 Molecules
two or more atoms are joined in specific shapes
minor differences in the composition or structure of molecules can caused profound differences in property
CHP 1.2 Gas
vapor) has no fixed volume or shape; rather, it uniformly fills its container. A gas can be compressed to occupy a smaller volume, or it can expand to occupy a larger one.
CHP 1.2 Liquid
a distinct volume independent of its container, assumes the shape of the portion of the container it occupies, and is not compressible to any appreciable extent.
CHP 1.2 Solid
both a definite shape and a definite volume and is not compressible to any appreciable extent.
CHP 1.2 pure substance
has a constant properties and composition. Ex; ice only contains H20.
usually referred to simply as a substance) Matter that has distinct properties and a composition that does not vary from sample to sample.
CHP 1.2 Mixture
does not have a constant property and composition. Ex; dirty snowball has twigs, dirt, ice
combination of two or more substances in which each substance retains its chemical identity.
CHP 1.2 Element
can’t be chemically simplified. Elements are combinations of matter and have only 100 substances. Each element is composed of only one kind of atom.
CHP 1.2 Compound
can be chemically simplified.
are substances composed of two or more elements; they contain two or more kinds of atoms. Water, for example, is a compound composed of two elements hydrogen and oxygen.
CHP 1.2 Homogenous
it is uniform throughout.
CHP 1.2 Heterogenous
Not uniform throughout.
CHP 1.3 Physical change
do not change composition
a substance changes its physical appearance but not its composition. Same substance before and after the change.
dissolving is a physical change
CHP 1.3 Chemical changes
change composition
a substance is transformed into a chemically different substance. Ex; hydrogen burning in air combines with oxygen to form water.
CHP 1.3 Physical properties
Properties a substance shows by itself without interacting with another substance.
can be observed without changing the identity and composition of the substance. These properties include color, odor, density, melting point, boiling point, and hardness.
CHP 1.3 Chemical properties
properties a substance shows as it interacts with, or transforms into another substance. Always involve a chemical change.
CHP 1.3 example problem: salt dissolving in water
physical change
CHP 1.5 Kilogram
kg
CHP 1.5 Meter
m
CHP 1.5 second
s
CHP 1.5 kelvin
K
CHP 1.5 mole
mol
CHP 1.5 c x 10n
C= any number 1 to 9
n= integer
CHP 1.5 density formula
density= mass/volume
CHP 1.5 giga
G
109
CHP 1.5 mega
M
106
CHP 1.5 kilo
k
103
CHP 1.5 deci
d
10-1
CHP 1.5 centi
c
10-2
CHP 1.5 milli
m
10-3
CHP 1.5 micro
μ
10-6
CHP 1.5 nano
n
10-9
CHP 1.5 pico
p
10-12
CHP 1.6 Precision
precise measurements are tightly clustered around the same value.
number of digits on a scale represents precision
CHP 1.6 Accuracy
measurements that are near to the true value.
CHP 1.6 significant figures
if a decimal point is present, all zeros to the right of the last nondigit are significant. ex: 6.700
zeros to the left of a non zero numbers are not signficiant ex: 00067
if a decimal point is present, cross out all zeros between the PACIFIC and the first non zero. Atlantic demical point isn’t present
CHP 1.7 Dimensional analysis
converting fractions and different units
CHP 2.1 Atomic theory of matter
4 main ideas:
each element is composed of indivisible atoms
atoms of the same element are identical and atoms of different elements are different
atoms can’t change their element
compounds form when different atoms combine
CHP 2.3 Atomic Structure
structure of atom
CHP 2.3 Three Subatomic Particles
Electrons Protons Neutrons
Charge -1 +1 0
Mass 0 amu 1 amu 1 amu
Home Electron cloud Nucleus Nucleus
CHP 2.3 Role of Subatomic Particles
Electrons: the number of electrons determine an atom’s charge and reactivity
Protons: the number of protons determine an atom’s element
Neutrons: weigh the atom down
CHP 2.3 𝐴z𝑋 𝑛
z = atomic number (number of protons)
X= atomic symbol of the element
n= charge (protons minus electrons)
A= mass number; A = Z + n0
n0= number of neutrons in nucleus
CHP 2.3 Ionization
when the number of electrons changes the charge and it causes an ion
CHP 2.3 Ions
atoms or molecules with a net charge
Cation (+) Charge
Anion (-) Charge
CHP 2.3 Isotopes
the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons
Isotopes have the same atomic number, but a different mass number
all Isotopes have identical chemical properties
CHP 2.4 Atomic weights (mass)
average mass of an atom of that element. Atomic mass is on periodic table
CHP 2.5 Periodic table
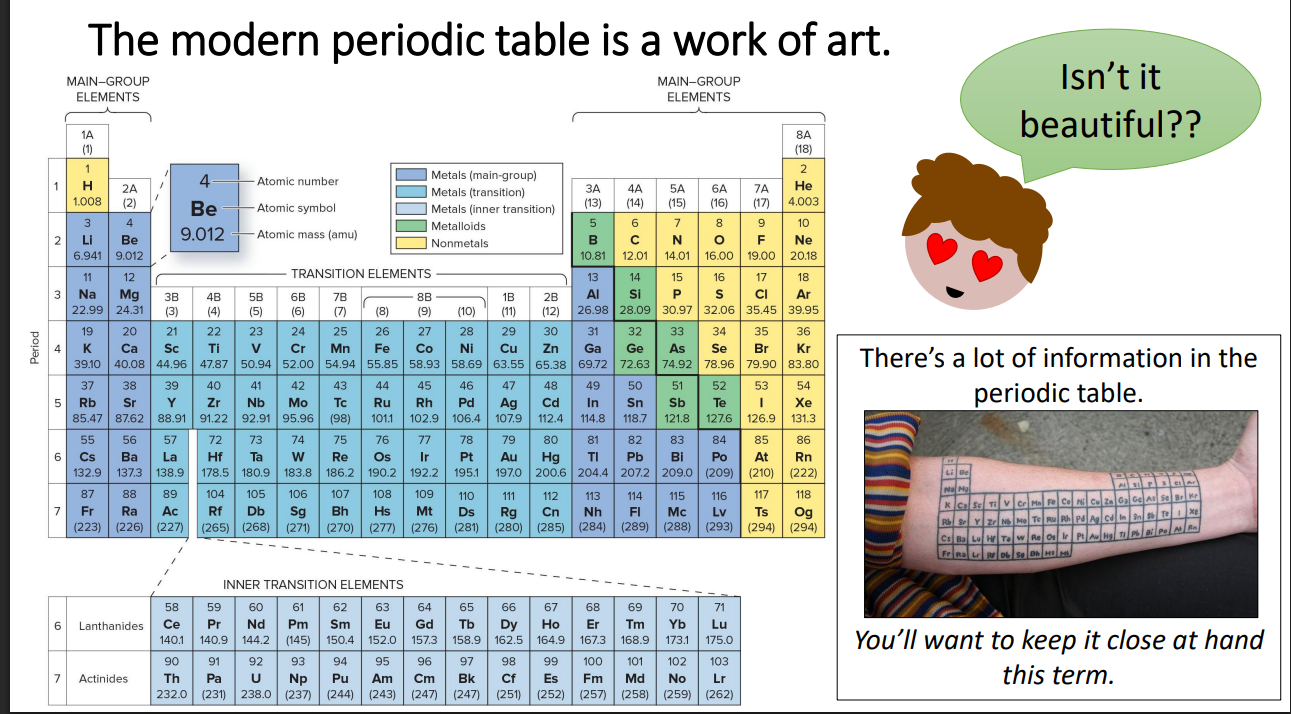

CHP 2.5 Rows v Columns
Columns go down think of a column of a house
Rows go across think of rowing across a river
CHP 2.5 Metals
tend to lose electrons
CHP 2.5 Non metals
tend to gain electrons
CHP 2.5 Group names
Group 1 Alkali metals
Group 2 Alkaline earth metals
Group 17 Halogens
Group 18 Noble Gases
CHP 2.7 Ionic bond
Ions of opposite charges attracting to bond together.
CHP 2.7 Ionic compounds
Repeating pattern of opposite charges Ions
have a neutral charge
form salts
for binary ionic compounds cation goes first and anion is second
usually contain a metal and a non metal
CHP 2.8 Covalent compounds
form discrete molecules
only contains non metals
CHP 2.8 Exceptions
Ag is always Ag+
Zn is always Zn2+
CHP 2.8 Monatomic ions 1+
H+ hydrogen
Li+ lithium
Na+ sodium
K+ potassium
Cs+ cesium
Ag+ silver
CHP 2.8 Monatomic ions 1-
H- hydride
F- flouride
Cl- chloride
Br- bromide
I- iodide
CHP 2.8 Monatomic ions 2+
Mg2+ Magnesium
Ca2+ calcium
Sr2+ strontium
Ba2+ barium
Zn2+ zinc
CHP 2.8 Monatomic ions 2-
O2- oxide
S2- sulfide
CHP 2.8 Monatomic ions 3+
Al3+ aluminum
CHP 2.8 Monatomic ions 3-
N3- nitride
CHP 2.8 Polyatomic ions
contain multiple atoms held together covalently and has an overall charge
CHP 2.8 Polyatomic cation
NH4+ ammonium
CHP 2.8 Polyatomic anions
CH3COO- acetate
CN- cyanide
OH- hydroxide
CLO- hypochlorite
CLO2- chlorite
CLO3- chlorate
CLO4- perchlorate
NO2- nitrite
NO3- nitrate
MnO4- permanganate
CO32- carbonate
HCO3- bicarbonate
O22- peroxide
PO43- phosphate
SO32- sulfite
SO42- sulfate
CHP 2.6 Diatomic elements
BrINClHOF
Br2
I2
N2
Cl2
H2
O2
F2