chem practice test
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1) To become incorporated into a liquid so as to form a solution
Dissolve
2) Able to be dissolved, especially in water.
Soluble
3) Incapable of dissolving, especially in water.
Insoluble
4) a measure of a materials ability to carry an electrical current.
conductivity
5) a force of attraction between atoms that holds them together to form molecules, crystals, or other structures, essentially allowing atoms to share or transfer electrons to reach a more stable state.
Chemical Bond
6) is the complete transfer of valence electron(s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions.
Ionic Bonding
7) linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms.
Molecular Covalent Bonding
8) a type of chemical bond that occurs between metal atoms where the valence electrons are delocalized and shared freely among a lattice of positively charged metal ions.
Metallic Bonding
9) a type of bond where atoms are connected in a continuous, three dimensional network, forming a large structure where every atom is covalently bonded to its neighbors.
Network Covalent Bonding
10) the smallest unit of a substance, composed of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds, which retains the composition and properties of that substance.
Molecule
11) a process where a thin layer of one metal is deposited onto the surface of another metal by using an electric current.
Electroplating
12) a picture representing ionic bonding
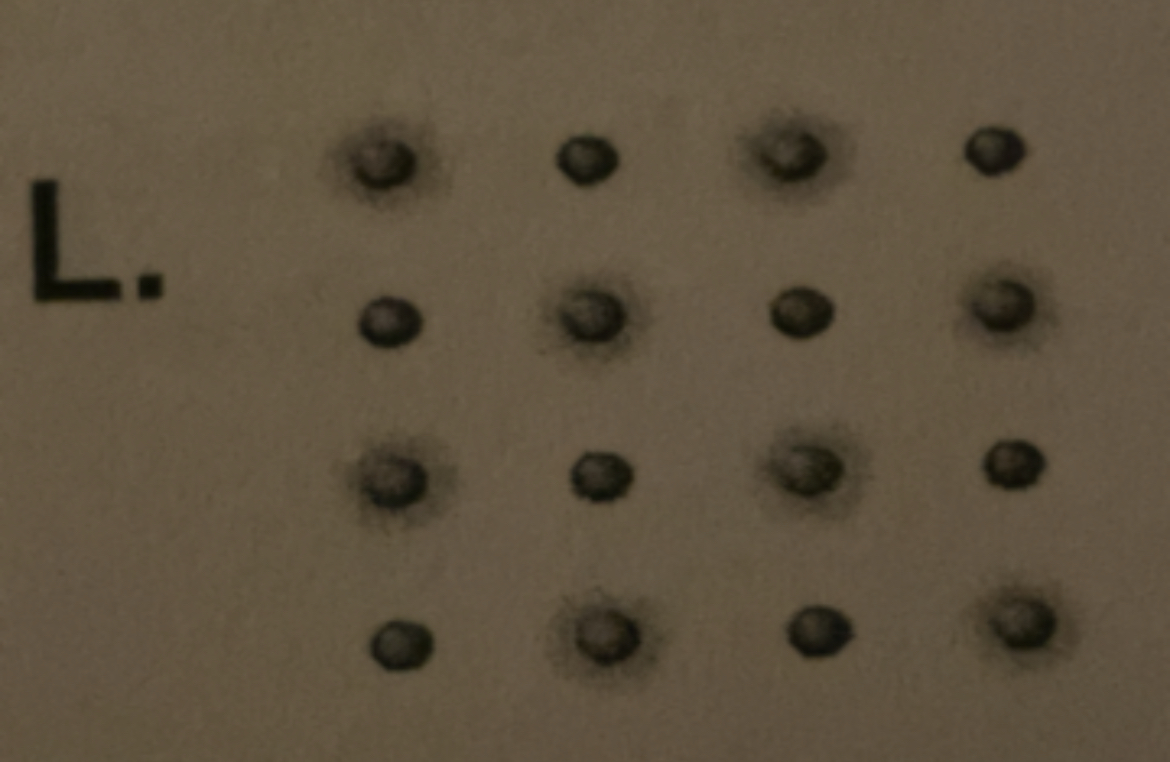

13) a picture representing molecular covalent bonding.

14) a picture representing network covalent bonding.
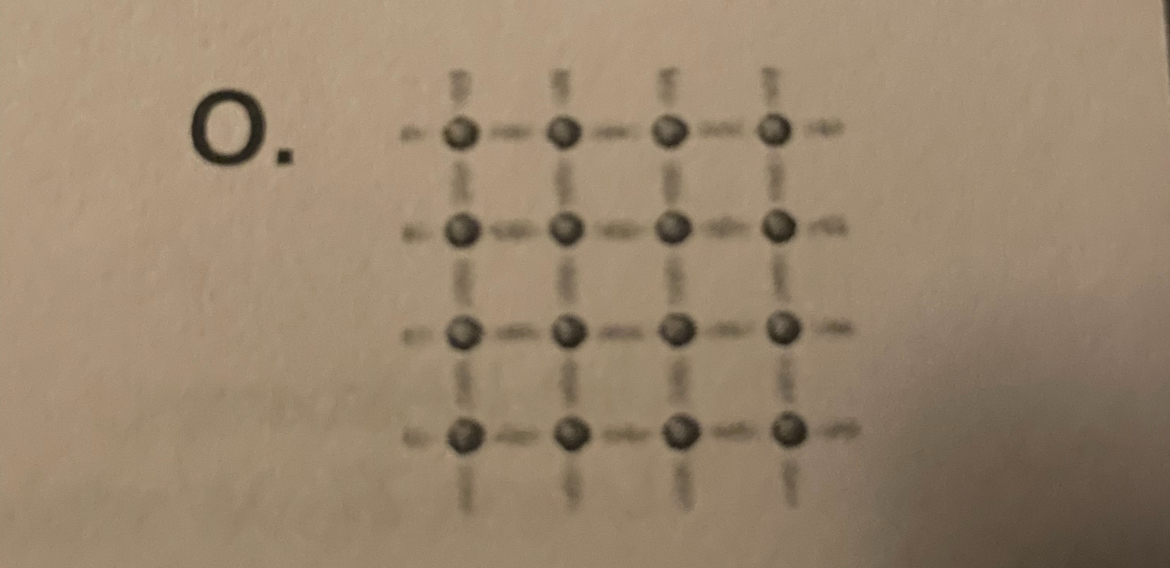
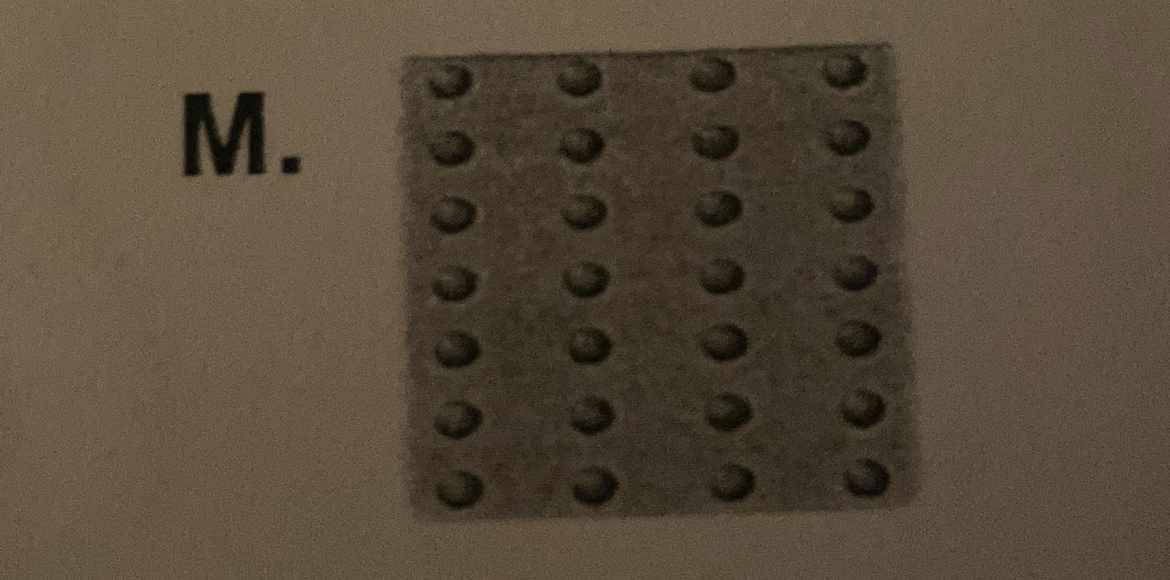
15) a picture representing metallic bonding.
16) Dissolves in water and does not conduct electricty.
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Molecular Covalent Bond
17) dissolves in water and DOES conduct electricity.
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Ionic bond
18) Does not dissolve in water and does not conduct electricity.
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Network Covalent Bond
19) Does NOT dissolve in water and does conduct electricity.
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Metallic Bond
20) formed between a Ca and O atoms.
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Ionic bond
21) formed between Ag atoms.
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Metallic Bond
22) formed between H, C, O atoms.
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Molecular Covalent Bond
23) formed between C atoms.
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Network Covalent Bond
24) formed between Ca atoms.
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Metallic Bond
25) formed between O2 atoms.
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Molecular Covalent Bond
26) made up of all metal atoms
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Metallic Bond
27) made up of both metal and nonmetal atoms
A) ionic bond
B) molecular covalent bond
C) network covalent bond
D) metallic bond
Ionic Bond
28) compounds made up entirely of ___ do not light up the bulb even when dissolved in water.
A) metals
B) nonmetals
C) transition metals
D) solids
Nonmetals
29) Compounds made up of a combination of ___ do not light up the bulb when they are in their solid form.
A) metals and nonmetals
B) metals
C) transition metals
Metals and Nonmetals
30) everything that lights up the bulb has ___ atoms in it.
A) nonmetal
B) metalloid
C) metal
Metal
31) What parts of the atom do you think are responsible for bonding atoms together?
A) nucleus
B) protons
C) neutrons
D) electrons
Electrons
32) Compound made up of entirely nonmental atoms will be a(n) ___ bond.
A) ionic
B) metallic
C) covalent (either molecular or network covelant)
covalent (either molecular or network covelant)
33) ___ are distributed differently depending on the type of bond.
A) protons
B) inner electron shells
C) valence electrons
D) neutrons
Valence Electrons
34) ___ are simply atoms or groups of atoms with charges on them because
they either are missing electrons or have extra electrons.
A) isotopes
B) compounds
C) molecules
D) ions
Ions
35)
36) Predict whether C12H220,1(aq), commonly known as sugar, will conduct electricity. Explain your reasoning.
Sugar will not conduct electricity because it is made up of all nonmetal atoms (C, H, & O) and therefore will form a molecular covalent bond Molecular covalently bonded substances do not conduct electricity.
37) Imagine that you have a mystery substance that does dissolve in water and does not conduct electricity.
i. What type of bonding will you probably find in your substance?
Explain.
Those properties. (does dissolve and does not conduct) indicate a molecular covalent bond
38) Define a chemical bond
a chemical bond is an attraction between atoms involving valence electrons
39)
40) How do you think we could get solid copper from a sample of copper (Il) sulfate, CuSO,?. Think about Activity 27. Explain
By using the process of electroplating and adding two electrons to the copper 2+ cations in solution causing them to become neutral copper atoms and be deposited on the negatively charged strip.
41)
42) Where does the copper come from that ends up on the nickel strip of the electroplating apparatus?
From the Copper (Il) sulfate (CuSO) solution. When dissolved, the solution contains aqueous Cu 2+ cations that can pick up electrons and come out of solution as copper atoms.
43) What is the main difference between copper atoms and copper ions?
Copper atoms are neutral, they have 29 positive protons and 29 negative electrons. Copper ions have lost 2 (negative) electrons and have a 2+ charge.
44) What is required to transform CuClaq) into Cu(s)?
This requires adding two electrons to the copper (2+) cations. This can be done with a battery and electroplating setup.