MICROBIO1 EXAM 2 Actinomyces, Dermatophilus, Nocardia, and Corynebacterium; Trueperella, Rhodococcus, Listeria & Erysipelothrix
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
- highly diverse group of G+ bacteria
- cell morphology is coccoid to filamentous
- rods or filament morophology, often branching
- facultative or obligate anaerobes
- enriched media needed for culture
- opportunistic pathogens
actinomyces
polymicrobal infection
actinomycosis is what type of infection
- oral mucosa
- tooth surfaces (dental plaque)
- mucous membranes of nasopharynx
- urogenital tract
- intestinal tract
most Actinomyces species are commensals of mammals and primarily habitat
pyogranulomatous reactions
What type of reactions are typical in actinomycosis
endogenous
Actinomyces are opportunistic pathogens, so most infections are _______, or come from the host's own microbiota
increased
Pathogenicity of actinomyces in mixed infections is increased or decreased?
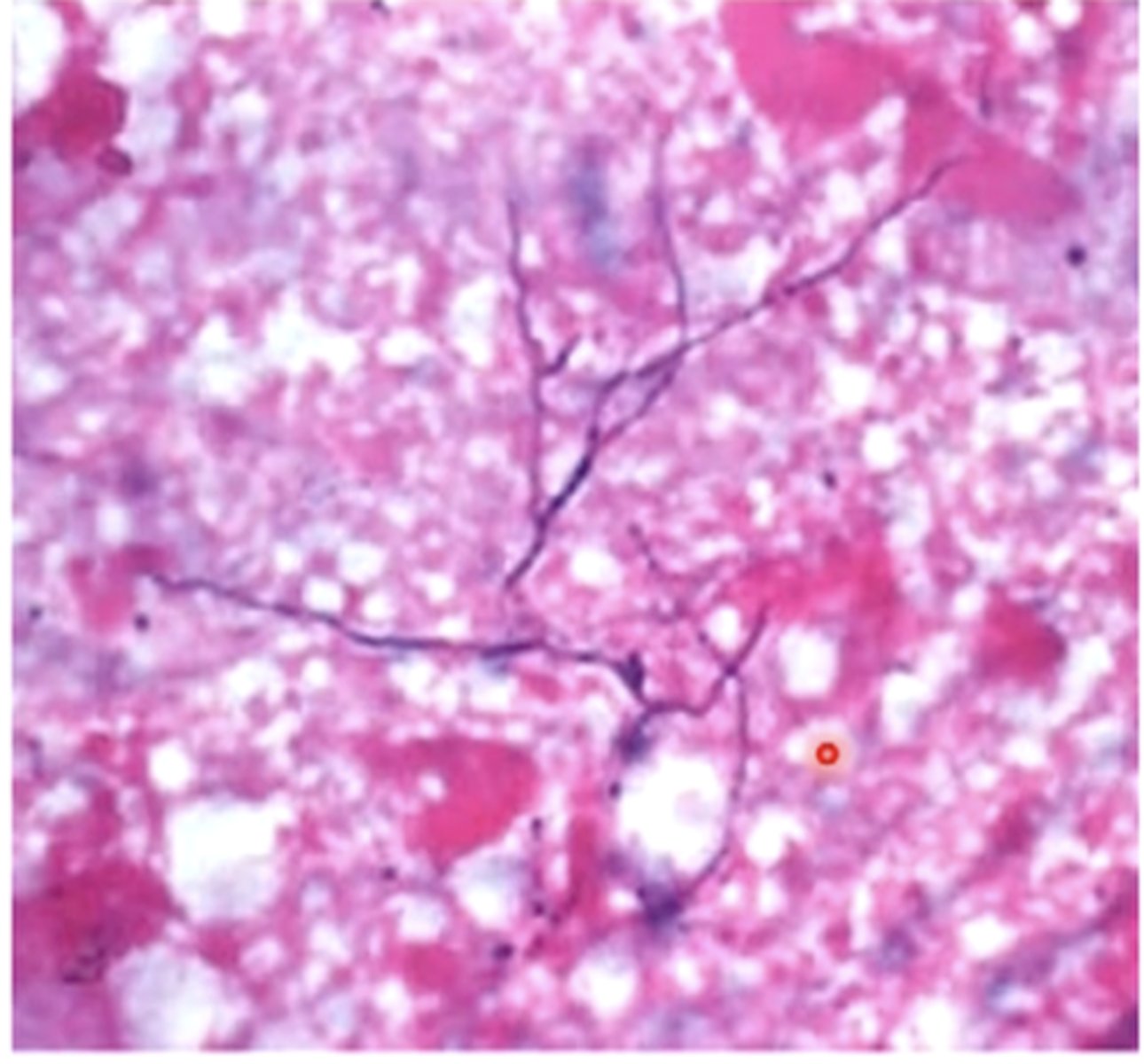
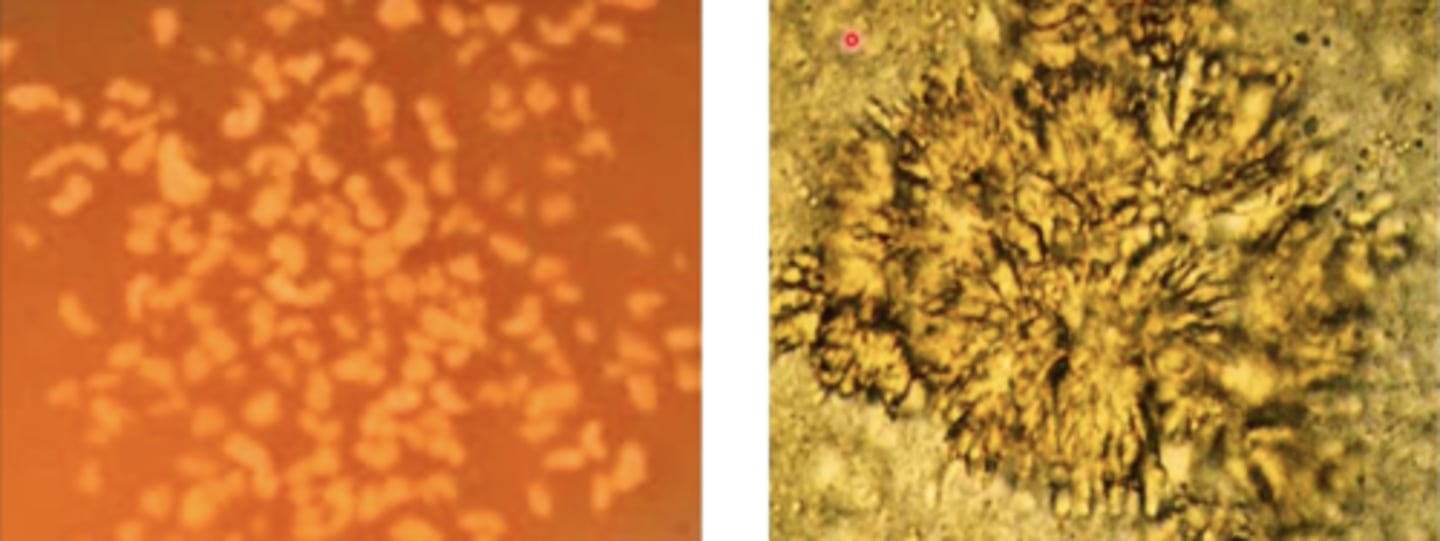
sulfur granules
fibrinous tracts of pyogranulomatous lesions from Actinomyces secrete purulent exudate that contains
bacterial filaments surrounded by club-shaped, mineralized calcium phosphate crystals
sulfur granules are made up of what
Actinomyces bovis
- causes lumpy jaw in ruminants, particularly cattle
- indurated, suppurative lesions in soft tissue and bone (mainly mandible)
- abscess may forms and discharge through fistulas
- can cause pulmonary infection but less common
- tooth dislodgement
- inability to chew
- mandibular fractures
osteomylelitis from Actinomyces bovis can cause
- bite wound, course hay or sticks puncturing mouth while eating, erupting teeth
how can cattle get Actinmyces bovis
Actinomyces suis
- causes mastitis and ventral subcutaneous lesions in sows
- occasional infection in lungs, splene, kidneys, and other organs
traumatic inoculation during suckling and weaning
how can sows get Actinomyces suis
Actinomyces viscosus
- Actinomyces species that primarily causes subcutaneous masses in dogs and cats
- can also cause thoracic infections or abdominal and retroperitoneal infections
pyothorax and bite wound abscesses
most common disorders in cats that Actinomyces species is isolated
- clinical presentation
- lumpy jaw
- exudates/aspirates may contain sulfur granules
sulfure granules from Actinoymces
- club shaped colonies with bacterial-sized filaments
- surgery
- prolonged administration of abx
treatment of Actinomyces
- sodium iodide IV with antibiotics
- debridement of bone lesions
- lavage with iodine solution
treatment of Actinomyces bovis (lumpy jaw)
- ensure good oral care
- limit amount of rough forage fed
- protect pets from grass awns
prevention of Actinomycosis
- branching filaments
- produces flagellated (motile) spores
- obligate parasite
- zoonotic
- facultative anaerobe
- capnophilic, grows well on blood agar
Dermatophilus congolensis
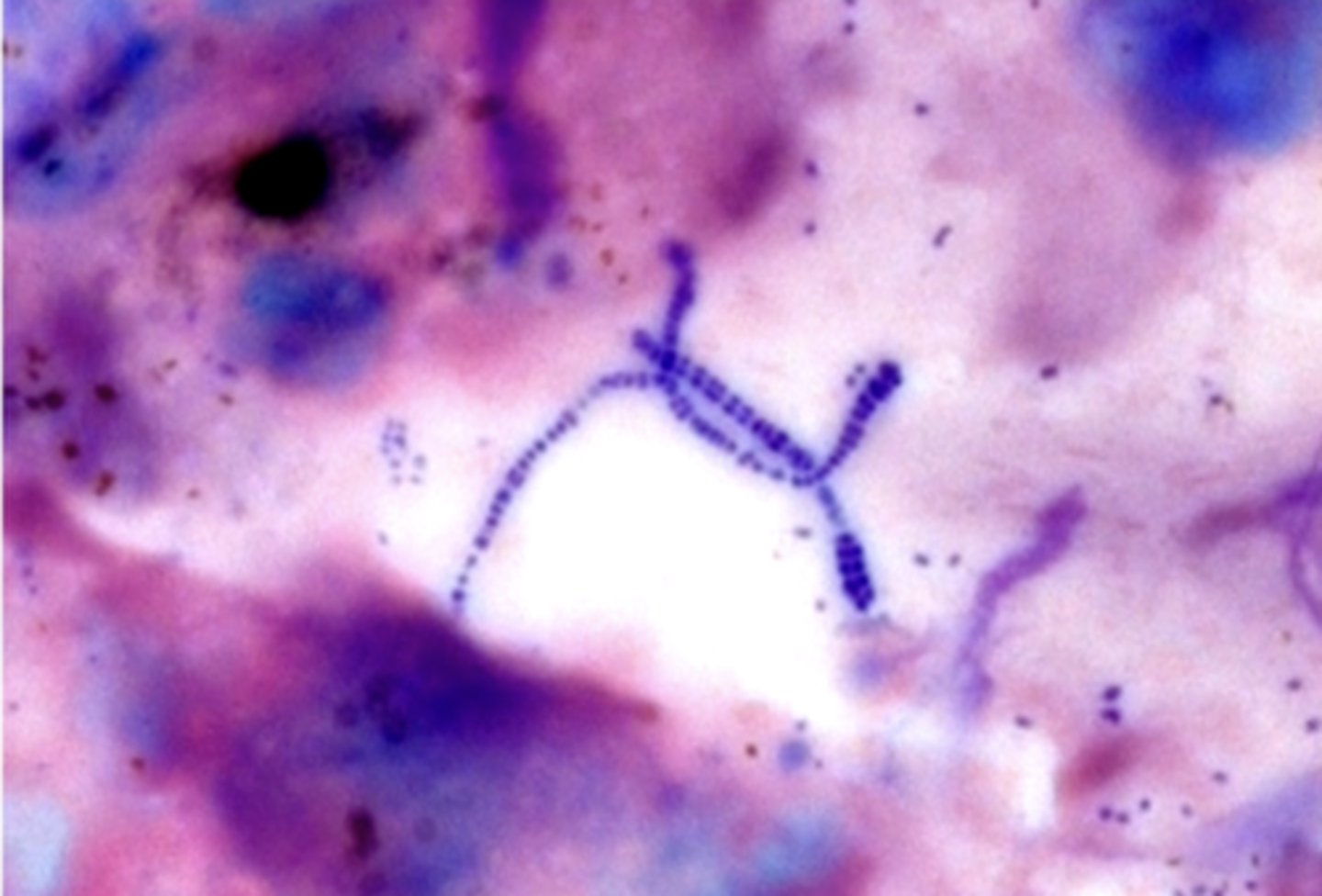
direct contact, fomites, and biting arthropods
how is Dermatophilus congolensis transmitted
cattle, sheep, horses
common hosts of Dermatophilus congolensis
asymptomatic chronically infected hosts
main reservoir or Dermatophilus congolensis
- dermatophilosis
- trauma/persistent wetting facilitate invasion of epidermis and hair follicles
- virulence factors (enzymes)
pathogenesis of Dermatophilus congolensis
exudative dermatitis with formation of scabs/crusts
dermatophilosis
- paintbrush lesions of matted hair
clinical manifestations of Dermatophilosis congolensins
- clinical findings plus demonstration of organisms in stained preps from scabs
- isolation/ID via culture or PCR
diagnosis of Dermtophilosis
- grooming and isolation in dry quarters for mild cases
- parenteral antibiotics for severe cases
- topical treatment following grooming for horses
treatment for Dermatophilosis
- isolate/cull clinically affected animals
- minimize skin trauma and exposure to rain and ectoparasites
control/prevention of dermatophilosis
Nocardia
- branching filaments that fragment into rods and cocci
- partially acid fast
- obligate aerobes, grow well on blood agar
- saprophytes
- cause opportunistic infections
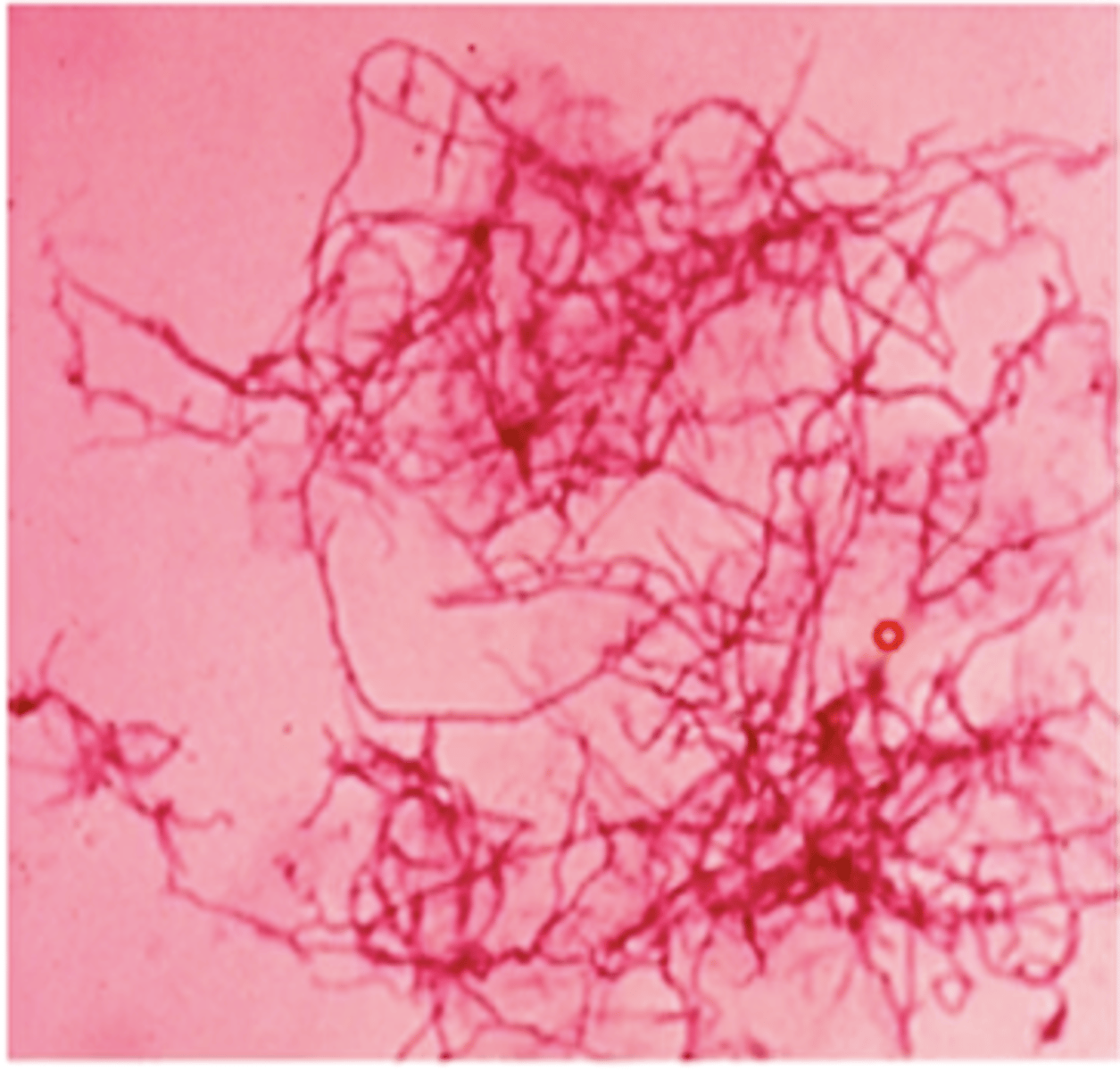
soil
reservoir of infection of Nocardiosis
widspread in soil and water
saprophytes
- trauma to skin
- inoculation of teat canal
- inhalation
- ingestion
routes of infection of Nocardia
true
T/F: Nocardia is typically not contagious
- suppurating lesions with variable granulomatous features
- sanguinopurulent exudates that can sometimes contain soft granules
- lymph nodes often involved
- hematogenous dissemination may occur
Nocardiosis
- facultative intracellular organisms
- survive and grow inside of phagocytes
- virulence factors prevent phagocytosis
pathogenesis of nocardia
- mastitis
- pneumonia
- abortion
- abscesses
disease patterns of Nocardia
- gram positive
- partially acid fast bacilli
nocardiosis presumative diagnosis
- culture
- antimicrobial susceptibility testing
nocardiosis definitive diagnosis
cats
which species is reported/identified cases of Nocardiosis more commonly seen in
immunosuppressive disorders
Nocardiosis in dogs and cats is associated with
Corynebacterium
- pleomorphic bacilli, non spore forming
- facultative anaerobes and aerobes, need enriched media
- commensals
- tissue trauma precedes infection/disease and lesions tend to suppurate
- Corynbacterium pseudotuberculosis
- the species of Corynbacterium most often seen in animal infections (small ruminants)
- facultative intracellular pathogen
skin trauma
how does Corynbacterium pseudotuberculosis colonization happen
- phospholipase D
- call wall lipids
virulence factors of Corynbacterium
acts as vasodilator, enhances spread via lymphatic vessels. also causes dermonecrosis, phagocyte toxicity, and other damage
how does phospholipase D act as a virulence factor for Corynbacterium?
protect against lysosomal enzymes of phagocytes, also induce tissue necrosis and abscess formation
how do cell wall lipids act as virulence factors for Corynbacterium
survives, grows in phagocytes
- transported from site of infection to superficial lymph nodes and then to internal lymph nodes and other reticuloendothelial tissues
pathogenesis of Corynbacterium pseudotuberculosis
- caseous lymphadenitis in sheep/goats (onion ring appearance when sectioned)
- chronic infection, may persist for host's life
disease patterns of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
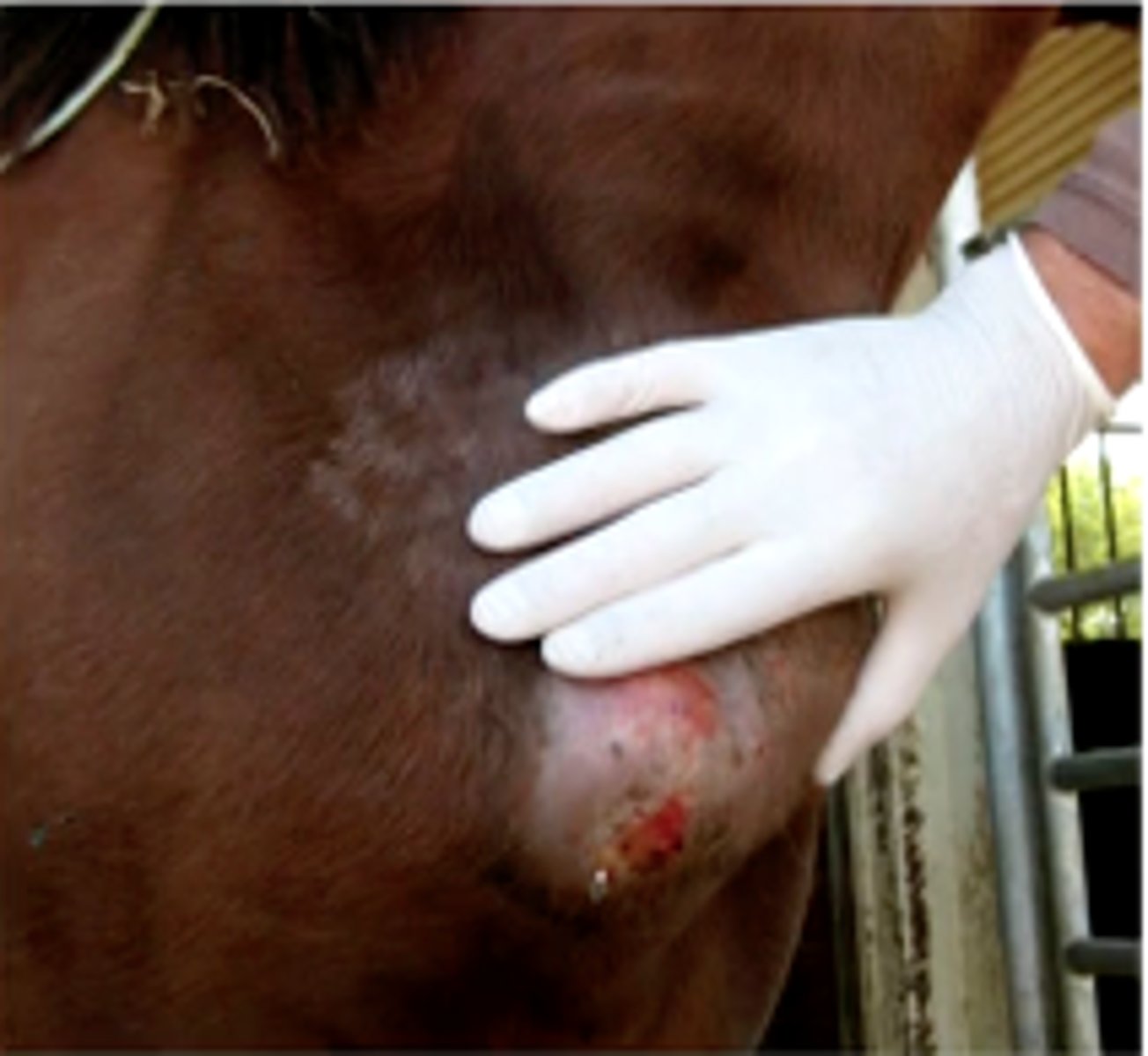
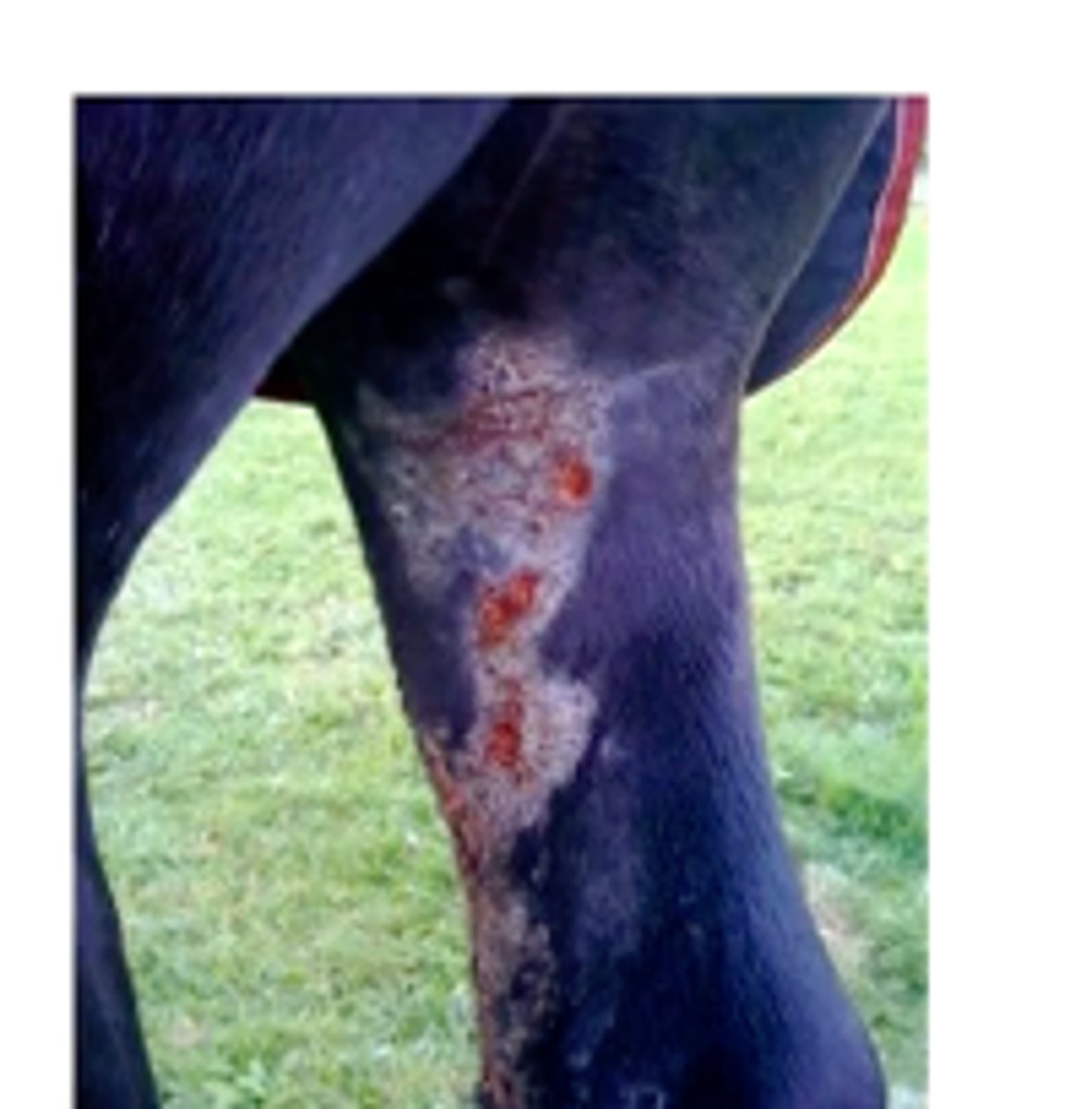
- abscesses in pectoral region (Pigeon fever), ventral abdomen, preputial or mammary regions
- ulcerative lymphangitis
In equids, where does the external form typically shop up in?
pigeon fever from C. pseudotuberculosis
ulcerative lymphangitis from C. pseudotuberculosis
- radiography and ultrasonography to detect abscesses
- serological test to detect antibodies
diagnosis of internal C. psuedotuberculosis
- lance, drain, and lavage external abscesses with antiseptic solution
- may need long term antibiotics
treatment of C. pseudotuberculosis
recurrence is common even with effective antibiotics treatment
what is one thing to keep in mind with treatment of C. pseudotuberculosis
Actinobacteria
Which phylum are Trueperella pyogenes and Rhodococcus equi in
FIrmicutes
Which phylum are Listeria spp. and Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in?
- pleomorphic
- gram positive bacilli
- non spore forming
- facultative anaerobes and aerobes, cultured on enriched media
- capnophiles
morphology of Trueperella spp
mucous membranes of mammals
which part of the body are Trueperella spp commensals in?
T. pyogenes
Trueperella species that is of primary importance in veterinary medicine
- coccobacillary to short rods
- club shaped in young cultures
- facultative anaerobe, capnophilic
- grows well on blood agar
T. pyogenes
- upper respiratory
- urogenital
- GI tracts
T. pyogenes is normal inhabitant of which tracts in mammals
endogenous
T. pyogenes are opportunistic pathogens, most infections are
- causes suppurative lesions in many organs/tissues
- abscesses that are often encapsulated, empyema, pyogranulomas
what types of lesions does T. pyogenes cause
hematogenous
how is T. pyogenes spread
- pyolysin O
- Neuraminidase
virulence factors of T. pyogenes
cytotoxic to macrophages, neutrophils, and RBCs
how does T. pyogenes use Pyolysin O as a virulence factor
bind to host cells and extracellular matrix
how does T. pyogenes use Neuraminidase and other adhesins as virulence factors
synergistic pathogen
T. pyogenes acts as a ________ in bovine liver abscesses caused by Fusobacterium necrophorum
septic arthritis
what does T. pyogenes cause in swine
severe mastitis
what does T. pyogenes cause in cattle
- flies
- teat contact with contaminated environment
- contaminated milking equipment
how is T pyogenes transmitted in cattle
- control flies
- disinfect and chemically dry living quarters and calving areas
- treat heifers and dry cows with prophylactic long-acting penicillin
- isolate/cull affected animals
control/prevention of mastitis
- pleomorphic
- gram positive to gram variable
- non spore forming
- aerobes
- saprophytes
Rhodococcus spp
Rhodococcus equi
- cocci, coccobacilli, rods
- readily cultured on blood agar
- opportunisitc pathogen of young foals
soil and intestinal tracts and feces of healthy animals
reservoir of Rhodococcus equi
inhalation or ingestion of virulent strains found in contaminated soil
main routes of infection of Rhodococcus equi
- granulomas, pyogranulomas, and abscesses
- hematogenous dissemination can occur
- survive and grow inside of macrophages (facultative intracellular pathogens)
pathogenesis of Rhodococcus equi
- Vap proteins
- capsule
- mycolic acid
- cholesterol oxidase
what are some virulence factors does Rhodococcus equi have that allows them to survive and grow inside macrophages
pyogranulomatous bronchopneumonia
what does Rhodococcus equi cause in foals, mostl cases happening between 1 and 4 months of age
protective type I immune response
Rhodococcus equi can occur in foals that are lacking
immunodeficient
Rhodococcus equi can infect adult horses that are
submandibular and cervical lymphadenitis
Rhodococcus equi is a common cause of what in swine
gram positive pleomorphic cells within macrophages in smears from tracheal wash, pus from lesions, etc
presumptive diagnosis of Rhodococcus equi
- long term combination therapy
- supportive care
treatment of Rhodococcus equi
- gram positive
- non spore forming coccobacilli
- facultative anaerobes, grow well on blood agar
- saprophytes
Listeria spp
Listeria monocytogenes
spp of Listeria that infects imammals, primarily causes septicemia, abortion, and CNS infections
blood agar with reduced O2 and increased CO2
how is Listeria monocytogenes typically grown
soil, silage, sewer effluent, freshwater habitats, and Gi tracts/feces of many animals
where is Listeria monocytogenes found
ingestion of contaminated food
how is Listeria monocytogenes spread
CNS
where does Listeria monocytogenes have predilection for in the body
vertical transmission
how can Listeria monocytogenes be spread
penetrates intestinal epithelium via transcellular/paracellular routes, spread via lymph nodes and blood to tissue, alternative route to CNS via breaks in oral/nasal mucosae, infects cranial nerves and brain
pathogenesis of Listeria monocytogenes
listeriolysin O
what is an important virulence factor of Listeria monocytogenes
allows bacteria cell to escape phagosome and spread
what does listeriolysin O allow L. monocytogenous to do?
- encephalitis
- abortion (3rd trimester)
- septicemia in neonates
what does listeriosis cause in ruminants
- rare but more likely in young birds
- septicemic form most common with lesions in heart, liver and other abdominal viscera
Listeriosis in poultry
- gram positive rods in smears from infected tissue
diagnosis of listeriosis