Physical Diagnosis III MSK
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
joints are held together by...
ligaments
joints are attached to muscles by...
tendons
joints are cushioned by...
cartilage
most joints are...
synovial joints (freely moving articulations)
What lines the joints and secretes the serous lubricating synovial fluid?
synovial membrane
What develops in the spaces of connective tissue between tendons, ligaments, and bones to promote ease of motion at points where friction would occur?
bursae
What type of joint is the wrist?
radiocarpal joint
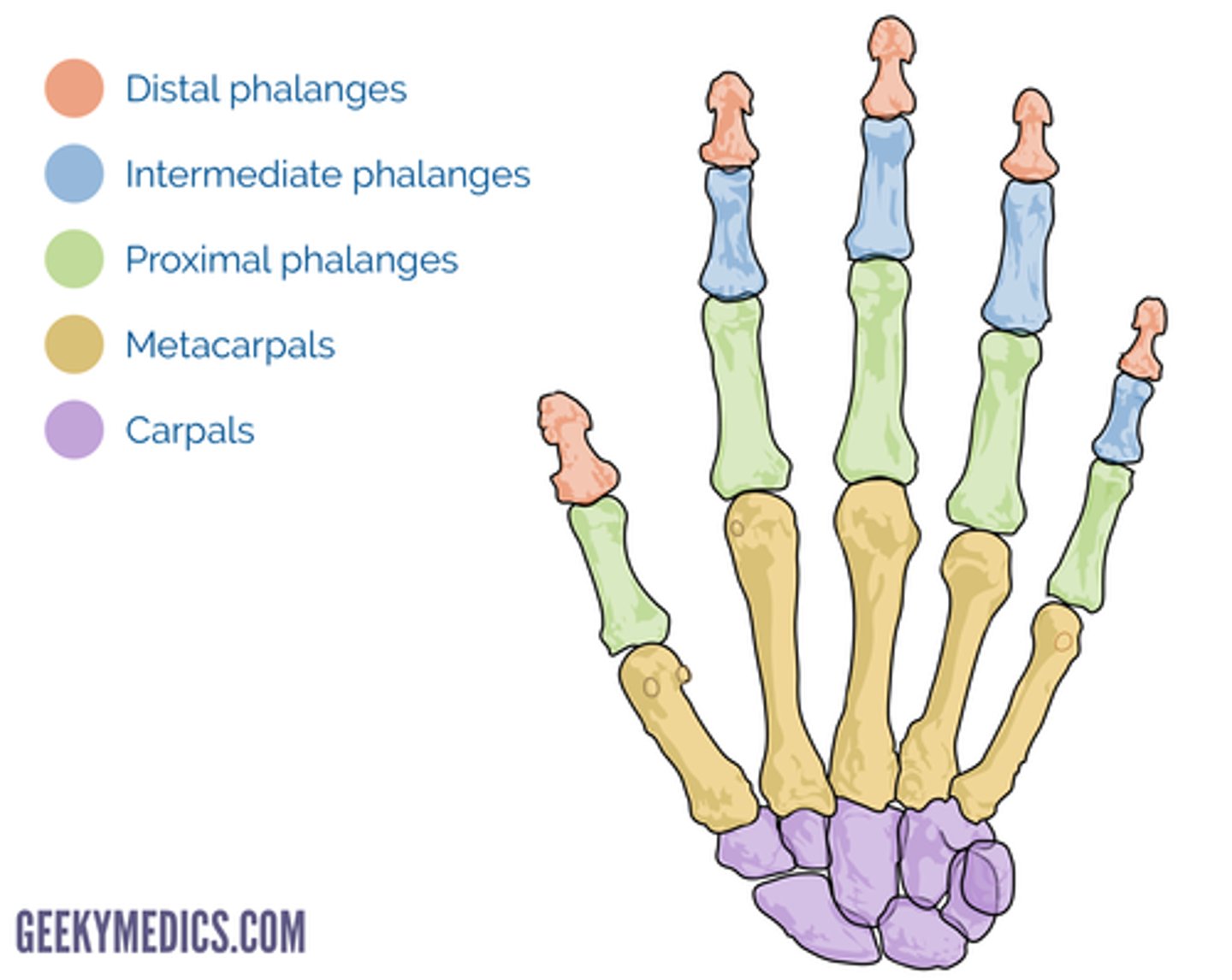
Which joints are in the hand?
PIP, DIP, MCP
The elbow is which type of joint?
hinge joint (movement in one plane; flexion and extension)
What is the shoulder joint? the most unstable joint in the body because it can do every range of motion
glenohumoral joint (ball and socket)
Which muscles comprise the rotator cuff, the term for the muscles that stabilize the shoulder and position of the humoral head?
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres major
Subscapularis
(SITS muscles)
Which joints make up the shoulder girdle?
sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, glenohumeral
Which joints is the strongest? The acromioclavicular joint, the articulation between the acromion process and the clavicle, OR the sternoclavicular joint, the articulation between the manubrium of sternum and clavicle.
Sternoclavicular joint
1 multiple choice option
All but the ______ vertebrae are separate from each other by fibrocartilaginous disks.
sacral
Which part of the spine has the most movement in different axes?
cervical
Which cervical vertebrae is the atlas, providing flexion and extension?
C1
Which cervical vertebrae is the axis, providing rotation?
C2
This joint is a ball-and-socket joint, an articulation between the acetabulum and the femur, that has three strong ligaments and three bursae.
hip joint
The articulation of the femur, tibia, and patella. A hinge joint, permitting flexion and extension in one plane. Also has a meniscus.
knee joint
These are medial and lateral fibrocartilaginous disks that cushion the tibia and femur and are attached to the tibia and the joint capsule.
menisci
The ankle is an articulation of the tibia, fibula, and talus that permits flexion and extension in one plane, a hinge joint. It is called a.....
tibiotalar joint
Which joints provide pronation and supination of the ankle?
talocalcaneal (subtalar) and transverse tarsal joints
______ are stronger than bones until adolescence.
ligaments
At what age is bone growth completed?
20
At what age is peak bone mass achieved?
35
Which medications effect the joints?
NSAIDs (diclofenac, tramadol, ibuprofen), Acetaminophen, immunosuppressants, corticosteroids, topical analgesics, glucosamine, chondroitin, and hyaluronic acid.
In the assessment of a MSK injury, always check which thing?
neurovascular status before and after treatment
You find this patient has lordosis of the spine. She is most likely....
pregnant
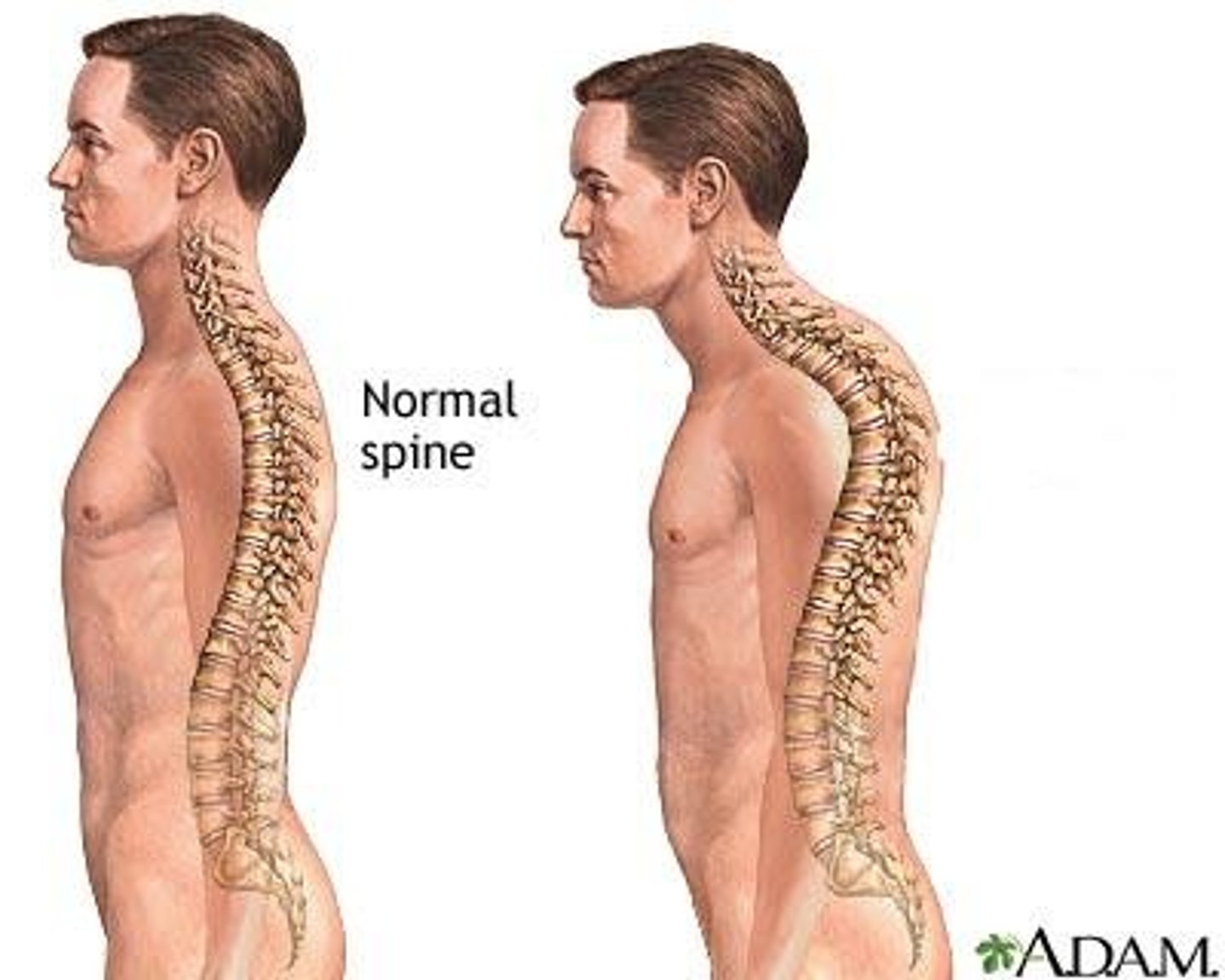
Over-curvature of the thoracic vertebrae, commonly seen in the elderly. Looks like humpback
Kyphosis
Spine is curved from side to side
scoliosis
In a specific joint complaint, always evaluate what other thing(s)?
the joints above and below
______ ROM may exceed ______ ROM by 5 degrees.
passive, active
What do you use to measure joint range of motion?
goniometer

Graded 0-5
0: no movement
1: trace of movement
2: full rom, but not against gravity
3: full rom against gravity, but not resistance
4: full rom against gravity and some resistance, but weak
5: full rom against gravity, full resistance
Muscle strength assessment
What is swan neck deformities?
hyperextension of PIP joint with fixed flexion of DIP joint

What is boutonniere deformity?
flexion of PIP and hyperextension of DIP

You find Heberden nodes on physical exam of the patients hands. You know this is associated with....
osteoarthritis

You find Bouchard nodes on physical exam of the patients hands. What are Bouchard nodes associated with?
rheumatoid arthritis

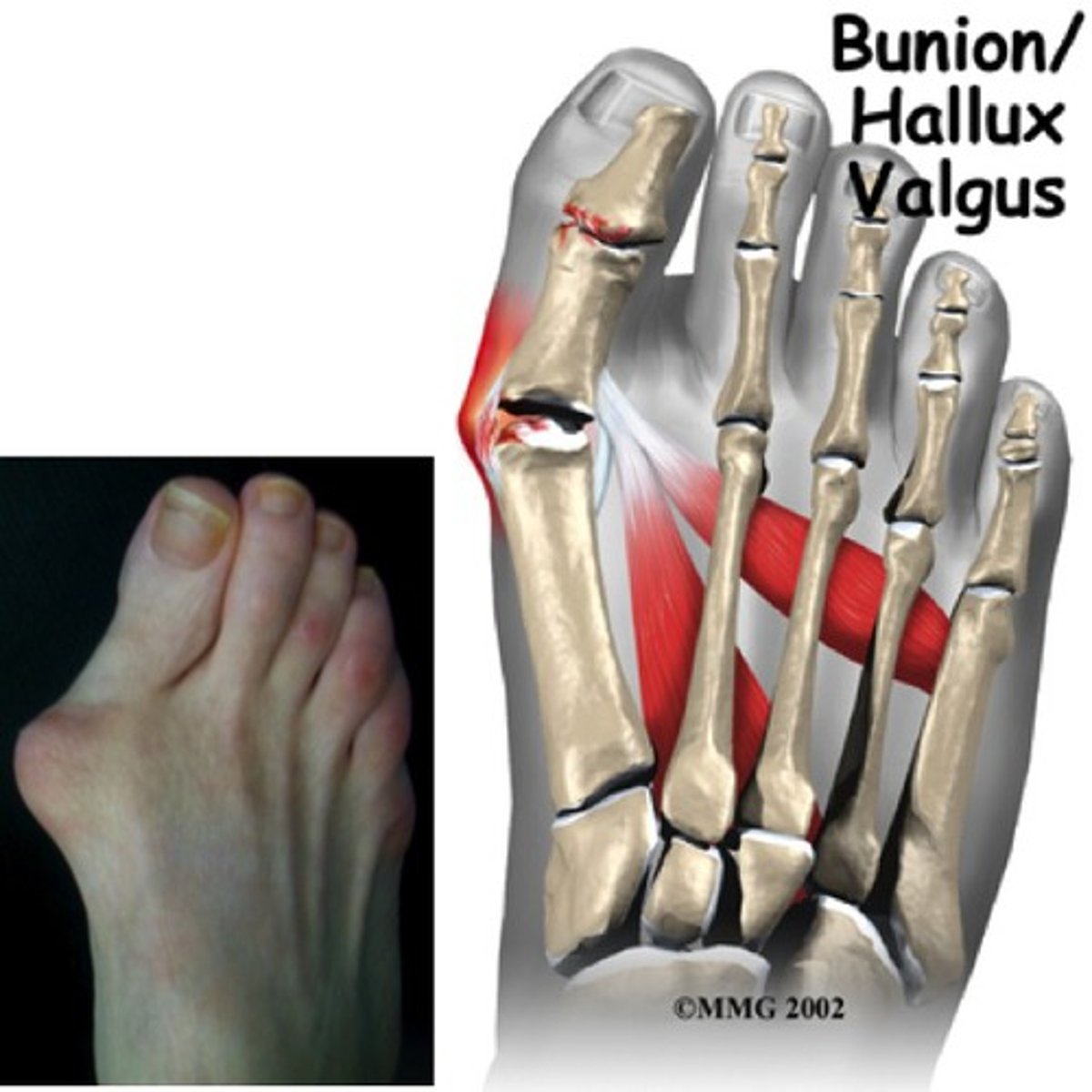
Valgus means what
- knock knees, bunion
the most distal part is lateral
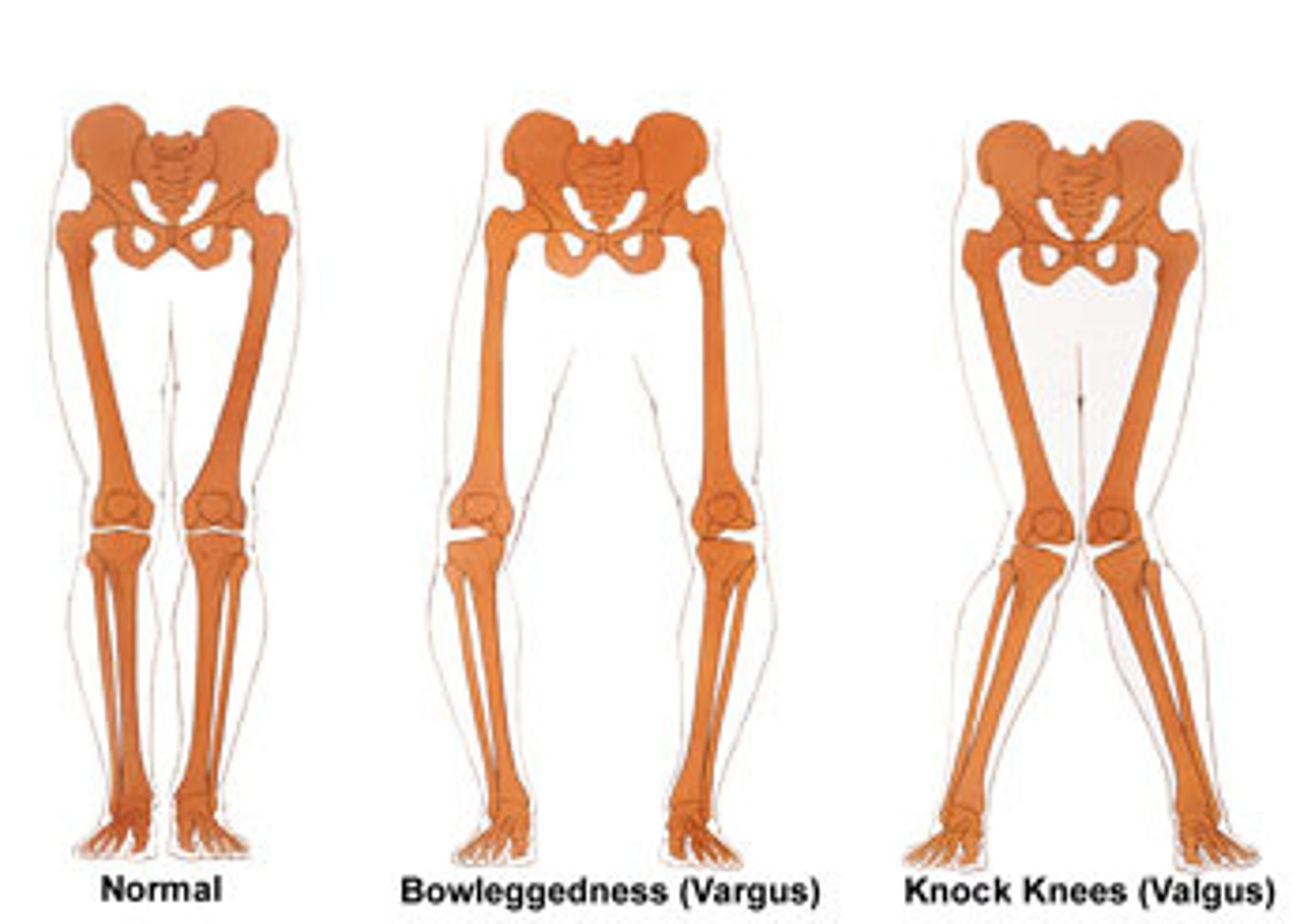
Varus means what?
- bowlegged
the most distal part is medial
When you abduct arms 90 degrees and flex shoulders forward 30 degrees; then apply downward pressure on distal humerus when arms are rotated, so that the thumbs point down or up, what muscle of the rotator cuff are you testing?
supraspinatus
When the pt has their arms at the side, and flex their elbow 90 degrees, then you ask them to rotate their forearm medially against resistance, what muscle of the rotator cuff are you testing?
subscapularis
With the arms at side, and elbow flexed 90 degrees, the patient rotates their arm laterally against resistance. This tests which rotator cuff muscles?
infraspinatus and teres minor
What is gibbus of the spine, which is associated with osteoporosis?
Where the thoracic spine points outward like a camels back
To assess hip alignment, it is easy to look at the....
gluteal folds
The most common joint to find crepitus is the...
knee
What is hallux valgus with bunion?
Lateral abduction of the great toe w/ medial deviation (adduction) of the 1st metatarsal
- the first metatarsophalangeal joint
Which joints are extended and flexed for protruding metatarsal heads with callosities?
extension at the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints
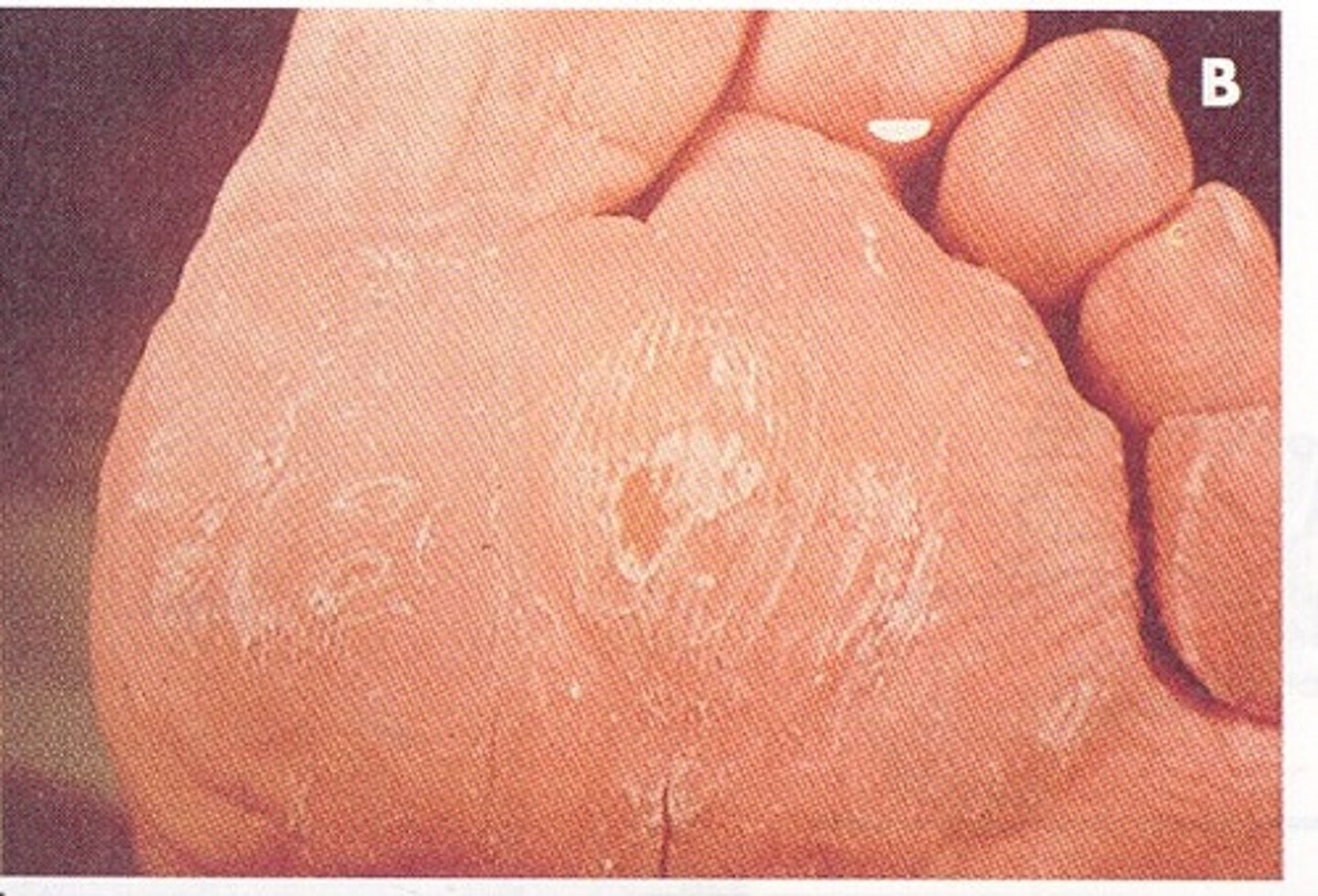
Explain the joints involved in hammertoes.
the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint is flexed, the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint is extended, and the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint is also extended
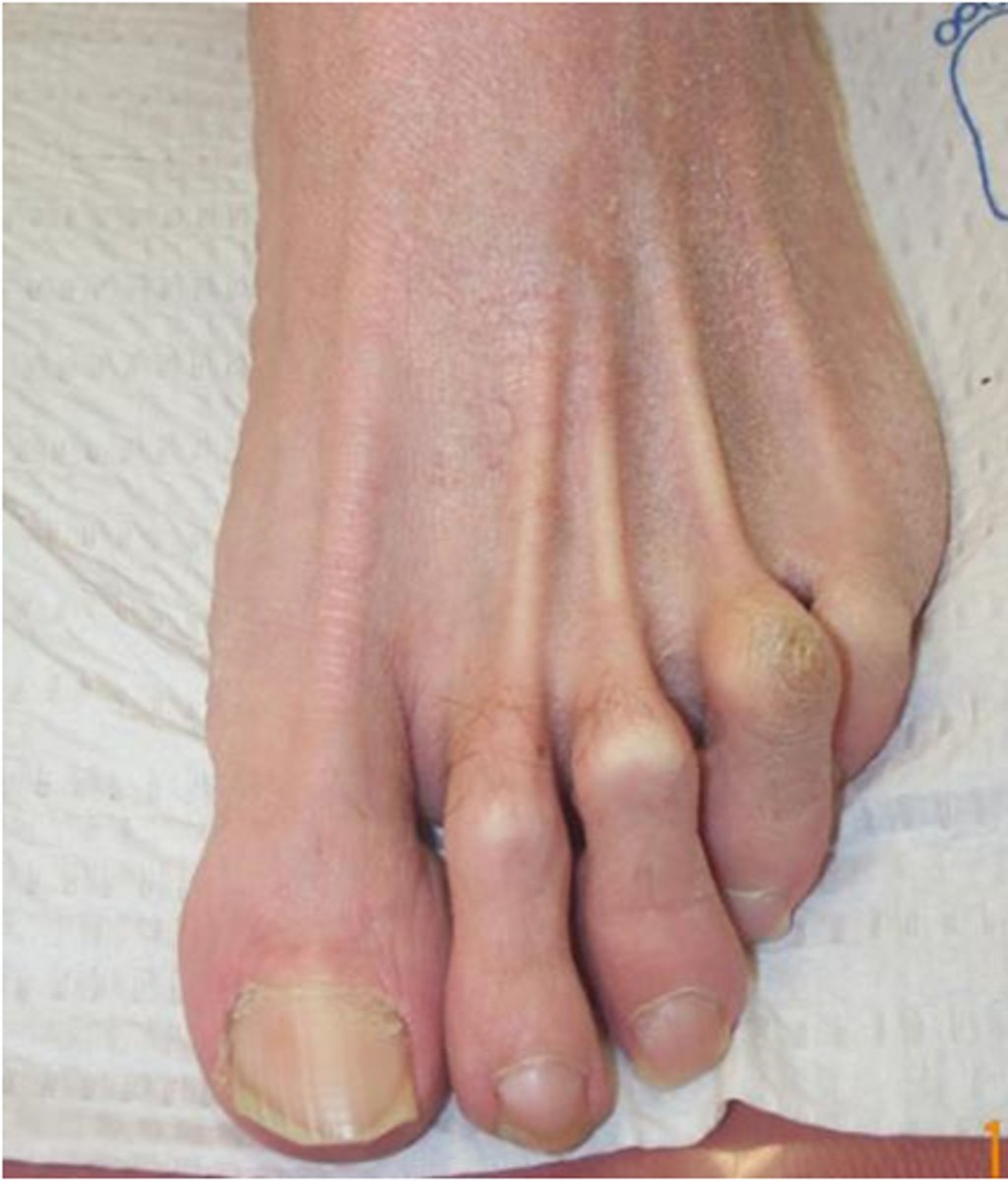
Explain the joints involved in Mallet toe.
the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint is flexed (bent downward), while the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) and metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints are in a neutral or extended position
Explain the joints involved in Claw toes.
the Metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint is extended, while the proximal and distal interphalangeal (PIP and DIP) joints are flexed

the test for a torn medial or lateral meniscus
McMurray test
the test for anterior cruciate ligament integrity
Lachman test
test for instability of lateral and medial collateral ligaments
Varus and Valgus stress test
Which maneuver is used to detect hip dislocation or subluxation and should be performed each time you examine the infant for the first year of life?
Barlow-Ortolani
Bowlegs are described as...
genu varum
Knock-knees are described as....
genu valgum
The supraspinatus muscle of the rotator cuff is the...
most commonly torn muscle
What is the most common congenital foot deformity
metatarsus adductus
Dislocation injury, called nursemaid's elbow
radial head subluxation
Inquiry about nocturnal muscle spasms would be most significant when taking the musculoskeletal history of
older adults
The most common cardiovascular condition of athletes. Temporary participation restriction for Stage 2
hypertension
What is the female athlete triad? Also known as Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S)
low energy with/without disordered eating, amenorrhea, osteoporosis (low bone mineral density)
What are the two conditions that are ABSOLUTE contraindications to sports participation?
Carditis, Fever
1. No activity; physical and cognitive rest (until asymptomatic)
2. Light aerobic exercise; walking, swimming, no resistance training
3. Sport-specific exercise w/o head impact: running drills
4. Noncontact training drills: passing drills in football
5. Full contact practice after medical clearance
6. Return to play
Return to Play Protocol
Which individual would be at higher risk for atlantoaxial instability?
Person with Down Syndrome