Chapter 9, sexual reproduction and meiosis
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
in asexual reproduction one parent organism replicates its DNA and splits the contents of one cell into how many cells?
two identical daughter cells.
asexual reproduction is rare or common?
it is rare, single cell organisms like bacteria, archaea, and protists do it all the time, but among multicellular organisms like humans its not common
in sexual reproduction the DNA of the offspring comes from two parents ___ fuses with the ___ yielding the first cell of the next generation.
This results in:
sperm, egg
genetically diverse offspring
attracting a mate a nd producing sex cells requires a lot of energy which is costly to the organism… so why is sexual reproduction so common?
The benefits of sexual reproduction include increased genetic diversity, which enhances adaptability and survival of offspring in changing environments.
which two organisms are genetically the most similar?
a dog and its puppy or two ameobas
the ameobas
how many sets of chromosomes does a diploid cell have?
A diploid cell has two sets of chromosomes, one set inherited from each parent,
most cells in a sexually reproducing organism have two sets of chromosomes: one from mum and one from papa
cells with two sets of chromosomes are called?
diploid cells
human cells contain __ homologous sets of chromosomes?
23
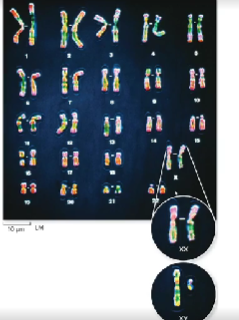
the image to the right is called a __ it shows all of the chromosomes from a diploid human cell
karyotype
22 out of the 23 chromosomes in humans are known as?
autosomes, which are the chromosomes that are the same in both males and females
each autosome pair consists of ___ equally sized chromosomes
two
human cells contain one set of?
sex chromosomes two XX is a female and a XY is a male
homologous sets of chromosomes carry the same sets of?
genes, although they may have different alleles.
the chromosomes of a ___ are similar in size and structer
homologous pair
the dna sequence is not exactly the same in a homologous set but?
each chromosome in a homologus pair has genes for the same traits
homologous sets of chromosomes are not identical true or false
True
alleles are alternative versions of the same?
gene
after replication, each chromosome consists of?
identical sister chromatids
when members of a homologous pair are replicated identical alleles are on?
sister chromatids
does DNA replication change chromosom e number or make cells diploid?
DNA replication does not change chromosome number; it simply duplicates the genetic material, resulting in two identical sister chromatids for each chromosome.

the image below shows two chromosomes from once cell which statement is true
a. both came from the persons mother?
b. 1-2 pair is identical to the 3-4 pair
c. 1 is identical to 2
d. the chromosomes have not been replicated yet
C 1 is identical to 2
what is shown in a karotype use these terms in your answer
sex chromosome
homologous
autosome
allele
diploid
gene
A karyotype is a visual representation of an individual's chromosomes, showcasing the number and structure of homologous pairs, including sex chromosomes and autosomes. It provides insights into the diploid number and allele variations for specific genes.
gametes like the sperm anf egg cell are?
haploid sex cells, meaning they only have one set of chromosomes
when gametes fuses it creates
a zygote, the first cell of an organism
it grows and devolops by mitosis
in adults specialized diploid cells called ___ divide by meiosis to form haploid gametes
germ cells
Meiosis halves the chromosome number and scrambles the allels how many gametes are produced?
Four unique gametes are produced.
compare the chromosomes you would find in a mans germ cells, sperm cells, and the rest of his body cells
Germ cells contain diploid chromosomes, sperm cells are haploid with half the number of chromosomes, while body cells are also diploid.
in meiosis dna replicates once but the nucleus divides?
nucleus divides twice
meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes by half, the germ cells start out with two pairs of homologous chromosomes then it turns into?
gametes that have two single unpaired chromosomes per cell
meiosis interphase
DNA replicates cell produces protiens needed for cell divison
meiosis prophase I early
chromosomes condense and become visible
prophase I late meiosis
crossing over occurs, spindles form, nuclear envelope breaks up
metaphase I
paired homologous chromosomes line up along equator of cell
anaphase I
homologous chromosomes seperate to opposite sides of the cell, sister chromatids remain joined
telophase and cytokensis
nuclear envelops form aroujnd chromosomes which may temprarily decondense, sindle diseapres then cells divide into two
Meiosis II prophase
spindles form nuclear envelope breaks up
metaphase II
chromosomes line up along equator of the cella
anaphase II
homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles.
telaphase II and cytokensis
the nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes, followed by the division of the cytoplasm into two distinct cells.
product of meiosis II
four genetically diverse haploid cells
a zygote contains 40 chromosomes how many chromosomes are in a ferrets sperm cell?
20 chromosomes
how does meiosis reduce the number of chromosomes by half
Meiosis involves two rounds of division, meiosis I and meiosis II, which separate homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids, respectively, resulting in cells with half the original chromosome number.
meiosis generates genetic variability how?
the chromosomes in the gamets produce meisosis are different because of prophase I which is crossing over and independent assortment in meta phase II
ccrossing over occurs in meiosis prophase I what is it?
during crossing over two homologous chromosomes pair up an exchange pieces scrambling the genetic material
ubdpendent assortment occurs in meiosis mentaphase I, what is it?
in indpenden assortment chromosome pairs align randomly scrambling the combination of chromosomes for each gamete
independent assortment produces many chromosome combinations a germ cell with three pairs of chromosomes has ____ possible arrangements during metaphase, yielding prossible gamets'
2³ =8
4
sometimes an embryo splits into two, then it develops independently which makes
two genetically identical siblings, known as identical twins.
dizygotic twins have uique DNA
fraternal tiwns are a testament to the varition amoung gametes two sperm cells fertilize two seperate egg cells and the offspring might look very different
many sets of triplets consists of a pair and a spare, that is two identical babies and one non identical baby producing this arrangements requires how many sperms anf eggs
2,2
each human germ cell contains 23 sets of homologous chromosomes
calculate the number of possible chromosome combinations for the gametes
These chromosomes are organized into 23 pairs, with one chromosome from each parent, making a total of 46 chromosomes per diploid somatic cell.
how are mitosis and meiosis different in division
Mitosis results in two identical diploid daughter cells, whereas meiosis produces four genetically diverse haploid gametes through two rounds of division.
compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis in terms of
which cells carry them out
the events that occur
number and type of new cells produced
chromosomes in the new cels haploid vs diploid
the processes of chromosome division and genetic variation. Mitosis results in identical diploid cells, while meiosis leads to genetically diverse haploid gametes.
if chromosomes fail to seperate properly abnormal gametes form this failure to seperate is called?
nondisjunction.
in what phase does nondisjunction occur?
Nondisjunction can occur during either anaphase I of meiosis or anaphase II of meiosis, leading to the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate.
down syndrome is caused by?
nondisjunction of chromosome 21, resulting in an extra copy of the chromosome. they have three rather than two
nondisjunction of sex chromosomes cause?
sex disorders
spermatogensis produces?
four sperm cells for each germ cell
oogenesis produces one egg for?
each germ cell, ensuring proper development and maturation.
compare gamete devlopment in males females and spore producing plants
In male and female animals, gamete development involves meiosis to produce sperm and eggs, respectively, while in spore-producing plants, sporophytes undergo meiosis to form spores, which develop into gametophytes.
how many sets of chromosomes do haploid cells vs diploid cells have?
Haploid cells have one set of chromosomes, while diploid cells have two sets.
sperm and egg have one chromosome each, they come together to create a zygote which has?
two sets of chromosomes, restoring the diploid state. then it goes through mitosis and its sets of chromosomes never changes
homologous chromosomes have similar?
size, shape, and GENE LOCATION
sister chromatids vs homologous chromosomes
Sister chromatids are identical copies of a chromosome that are connected by a centromere, while homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes, one inherited from each parent, that have the same genes but may have different alleles.
gern cells produce?
gametes, which are sperm and egg cells.
meiosis ___ the chromosomes and ___ alleles
halves, scrambles
produces 4 genetically unique daughter cells
dna replicates once but the nucleus divides twice
in meiosis, DNA replicates ___ but the nucleus divides___
once, twice
crossing over is specific to?
prophase I in meiosis, it does not happen in mitosis.
prophase I four main things happening:
spindles form from the centrosomes, nuclear envelope condence, nuclear envelope breaks up, DNA condenses.
when does crossing over happen?
It occurs during prophase I of meiosis, allowing for genetic recombination between homologous chromosomes.
what is the main difference between meiosis I and II
Meiosis I reduces chromosome number by half, while meiosis II separates sister chromatids without further reducing chromosome number.
Meiosis I involves homologous chromosomes, whereas Meiosis II involves sister chromatids.
homologous pair of chromosomes vs sister chromatids
A homologous pair of chromosomes consists of one chromosome from each parent that are similar in shape, size, and gene content, while sister chromatids are identical copies of a single chromosome connected at the centromere, formed during DNA replication.
why does crossing over not occur in prophase I
Crossing over does occur in prophase I; it is a crucial process for genetic diversity. However, it does not occur in prophase II of meiosis.
when does independent assortment occur?
Independent assortment occurs during meiosis I, specifically in metaphase I, when homologous chromosomes line up at the cell's equatorial plane.
name everything different about mitosis and meiosis
Mitosis produces two identical diploid cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse haploid cells. Mitosis involves one division, while meiosis has two divisions (meiosis I and meiosis II). Additionally, meiosis includes processes like crossing over and independent assortment that increase genetic variation.
non-disjunction happens in what phase that goes wrong
anaphase I or II