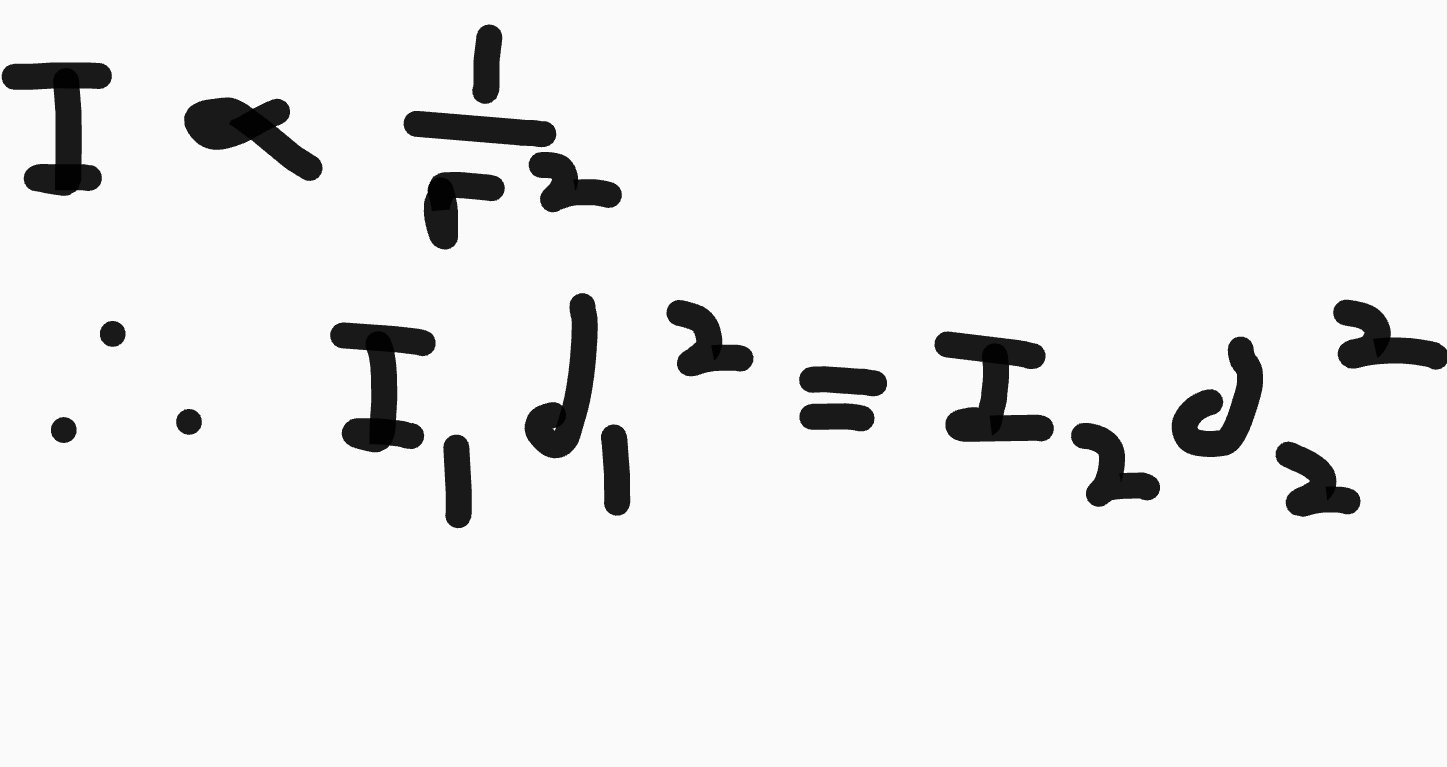Progressive waves (7.1)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What does a wave transfer?
A wave transfers energy and information between points without transferring mass
What is meant by wave motion in transverse and longitudinal waves? And how can ripple tanks be used to demonstrate this?
Waves move in oscillations or vibrations, which can be visualised using ropes and springs:
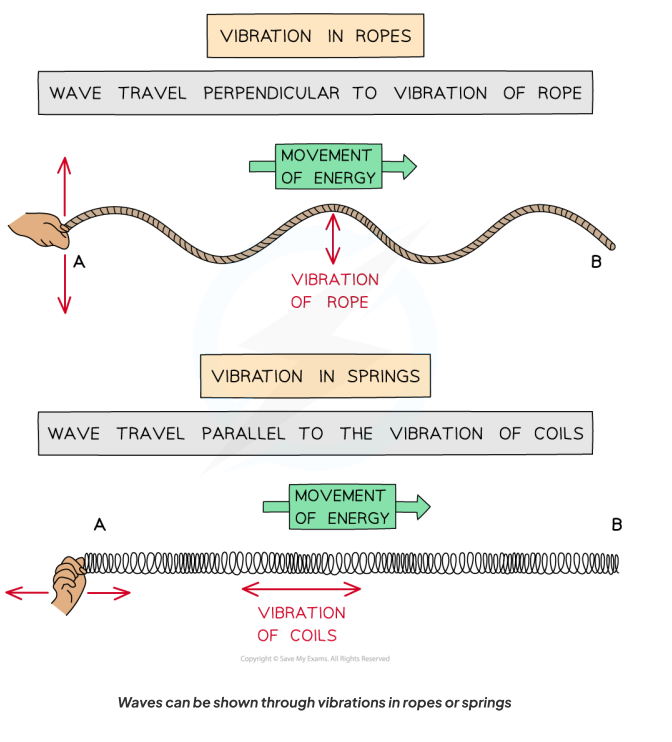
A transverse wave oscillates perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
A longitudinal wave oscillates parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
Ripple tanks
Ripple tanks produce a combination of transverse and longitudinal waves:
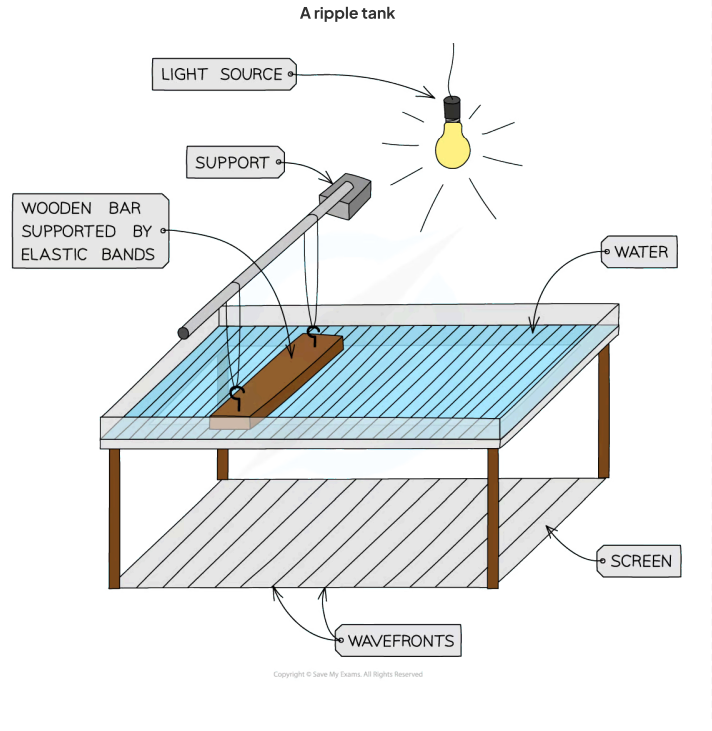
The taller regions of water block more light allowing the wavefronts to be seen using shadows
What are the definitions of these terms:
Displacement
Amplitude
Wavelength
(Time) Period
Frequency
Speed
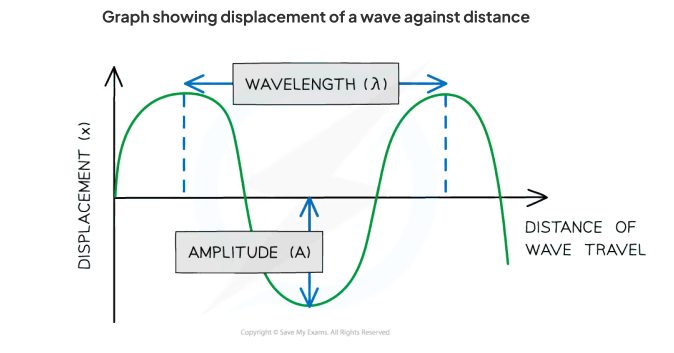
Displacement (x) - the distance from its equilibrium position
Amplitude (A) - The maximum displacement of a particle in a wave from its equilibrium position
Wavelength (λ) - the distance between adjacent peaks on a wave
Period (T) - The time taken for one complete oscillation of the wave
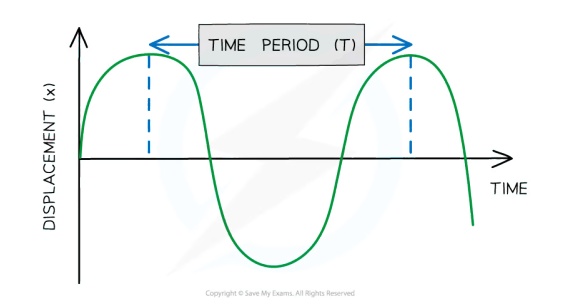
Frequency (f) - the number of complete oscillations per unit time. Measured in hertz (Hz)
Speed (s) - the distance travelled by the wave per unit time
What is the equation that relates time period and frequency?
Equation
T = 1/f
Where T is time period in s
Where f is frequency in Hz
What is the equation that relates speed, frequency and wavelength?
Equation
v=fλ
Where v is speed in m/s
Where f is frequency in Hz
Where λ is wavelength in m
For a wave of constant speed:
As the wavelength increases, the frequency decreases
As the wavelength decreases, the frequency increases
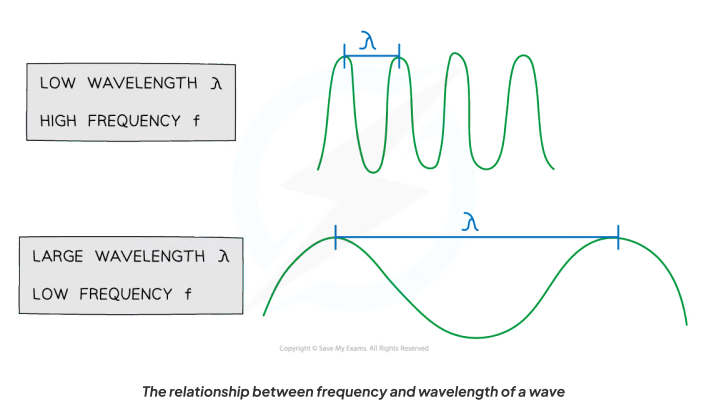
How can v=fλ be derived?
1) The speed of a particle is given by s=d/t
2) For a wave the wave speed = distance travelled by the wave / time
3) In one time period, the wave travels one full time period so wave speed = wavelength/ time period
4) Time period = 1 / frequency
5) Therefore wave speed = wavelength x frequency
What is phase (difference)?
Phase
Phase difference tells us how much a point or a wave is in front or behind another
The waves must have the same frequency, wavelength and speed
When the crests and troughs are aligned the waves are in phase
When the crest of one wave aligns with the trough of another, the waves are in anti-phase
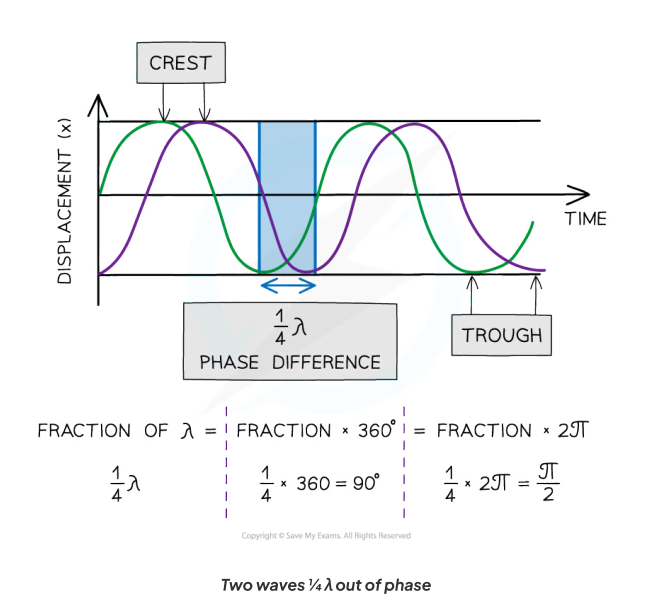
The phase difference between two points is:
2nπ when in phase. e.g. 2π, 4π
2n±1π when in antiphase. e.g. π, 3π, 5π
Calculating phase difference
Phase difference = distance between same points on each wave (path difference) / wavelength x 2π

What are progressive and stationary waves?
Progressive waves - waves that transfer energy
Stationary waves - waves that don’t transfer energy
How do you use a cathode-ray oscilloscope (CRO)?
CRO
An A.C. on an oscilloscope can be used to represent a transverse wave.
An oscilloscope can be used to determine a waves frequency and amplitude
The x-axis is the time and the y-axis is the voltage
To zoom in you decrease the time-base of the oscilloscope and to zoom out you increase it
Determining frequency and amplitude
To determine frequency, count the boxes between adjacent peaks and multiply them by the time-base setting to get the wave’s time period. Then use f=1/T
To determine amplitude, count the boxes between the peak and trough and half it, multiply by the size of the boxes
What is intensity?
Intensity is the power received/incident per unit area
Thus:
I = P/A
Where I is intensity in W/m2
Where P is power in W
Where A in area in m2
How is intensity related to frequency and amplitude?
Intensity is directly proportional to both A2 and f2
This means that if either frequency or amplitude is doubled, intensity is quadrupled (22)
This means that:
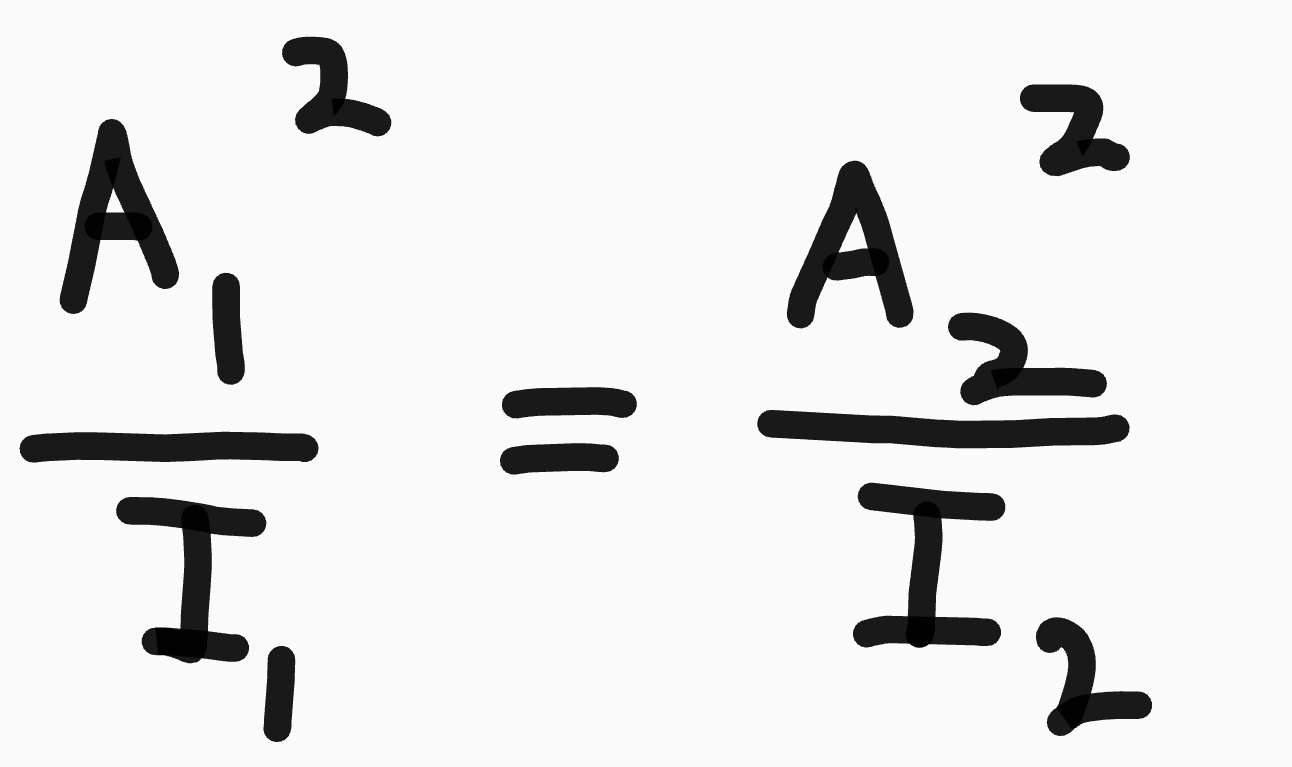
What is the inverse square law?
If a source emits a wave equally in all directions (a light bulb), the intensity follows an inverse square law.
The intensity at the surface of the sphere is:
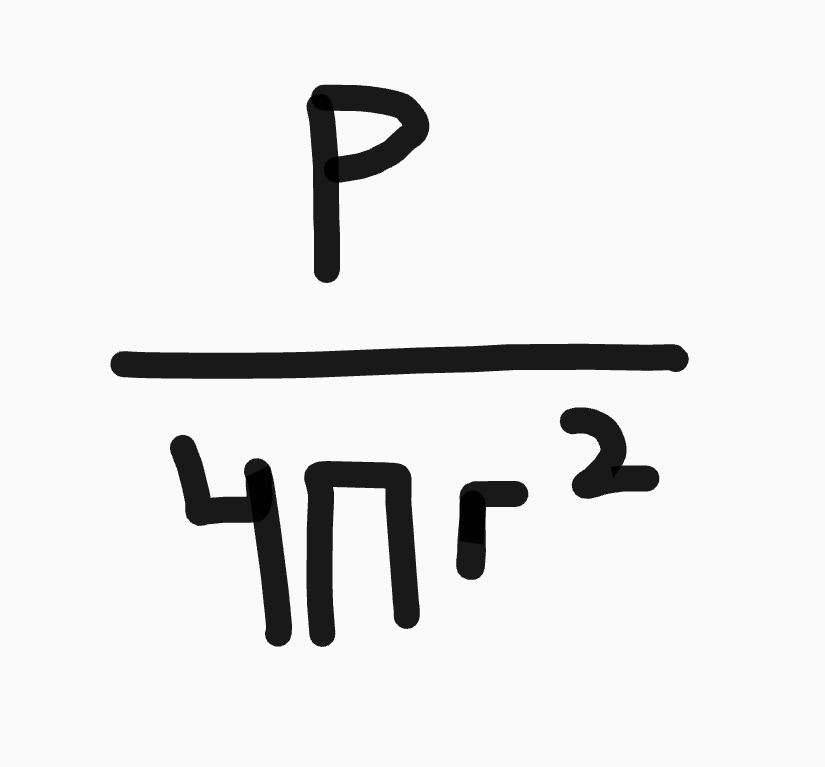
and:
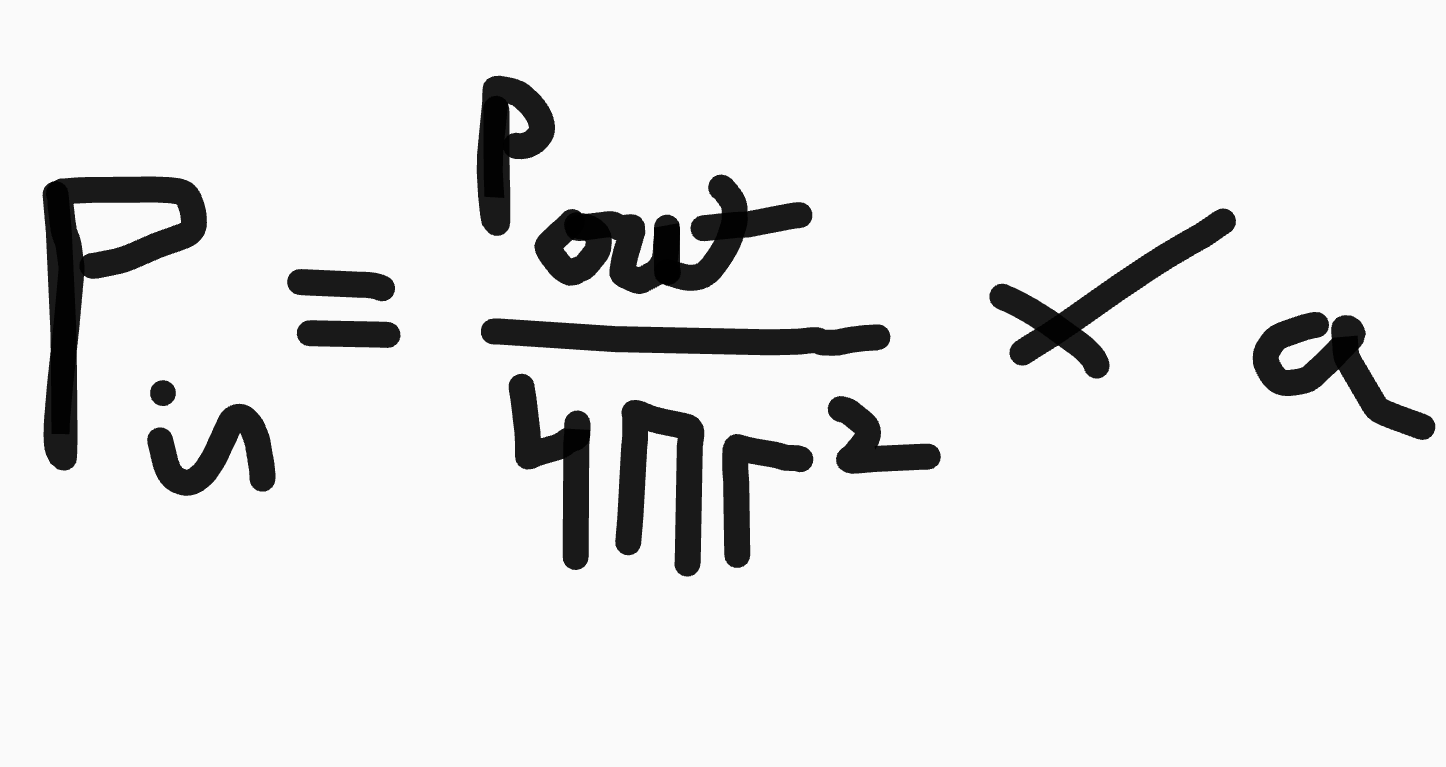
The inverse square law: