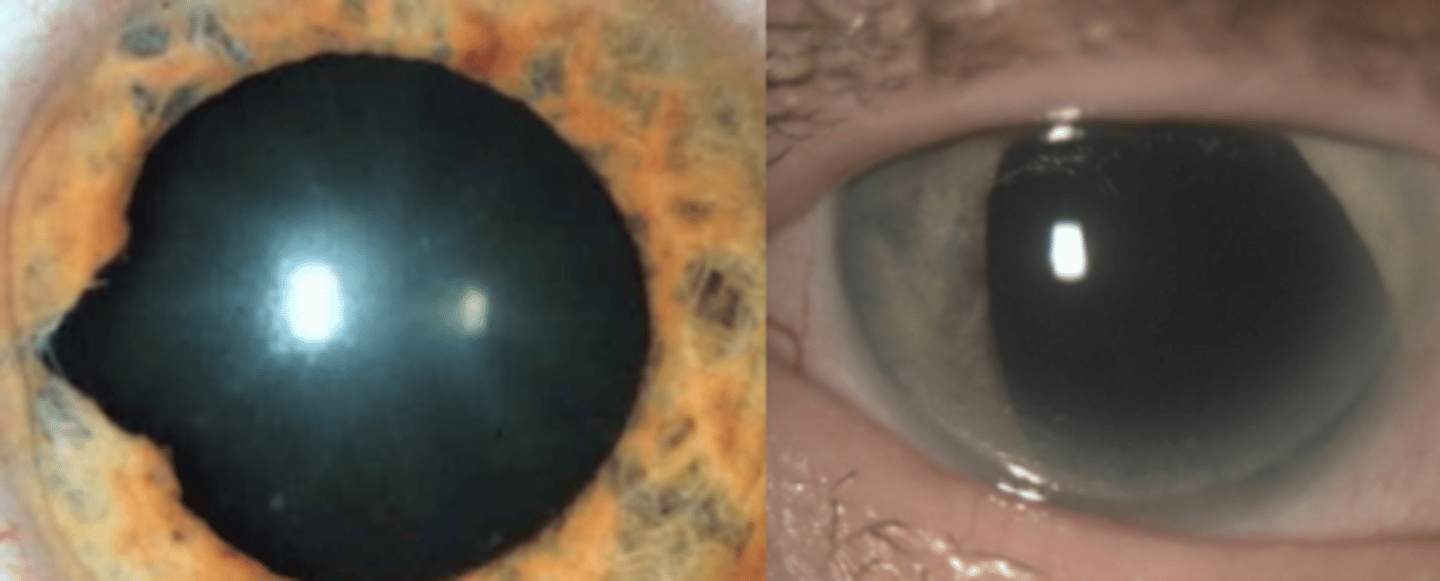
Iris Tumors, Iris Nodules, Iris Trauma
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Iris nevi
very common hyperpigmentation of the iris that varies in size, shape, color. Has mild to no vascularization or pupil distortion and is less than 3 mm.
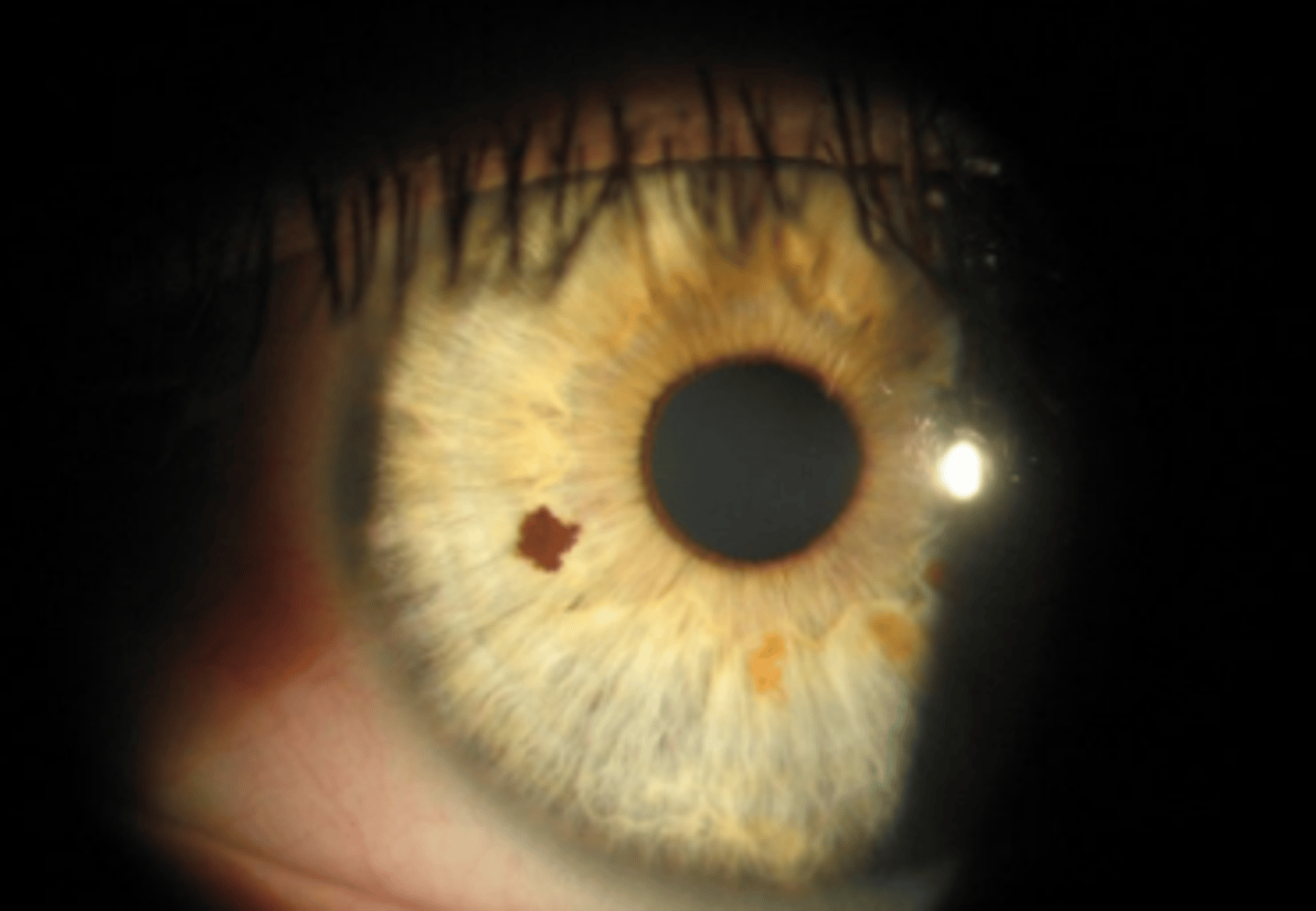
Iris cysts
uncommon unilateral fluid filled tumors of the iris. Are classified as primary (asymptomatic, stationary, rarely cause complications) or secondary (symptomatic, required therapy, more commonly cause complications).
Primary iris cysts
iris cysts arising from the iris pigment epithelium or stroma. Most frequently presents with no symptoms, or mild cosmesis. Less common there will be visual axis obstruction, blurred VA, uveitis, and angle closure glaucoma.
Pigment epithelial cyst
primary iris cyst appearance as a globular, dark brown, lesion.
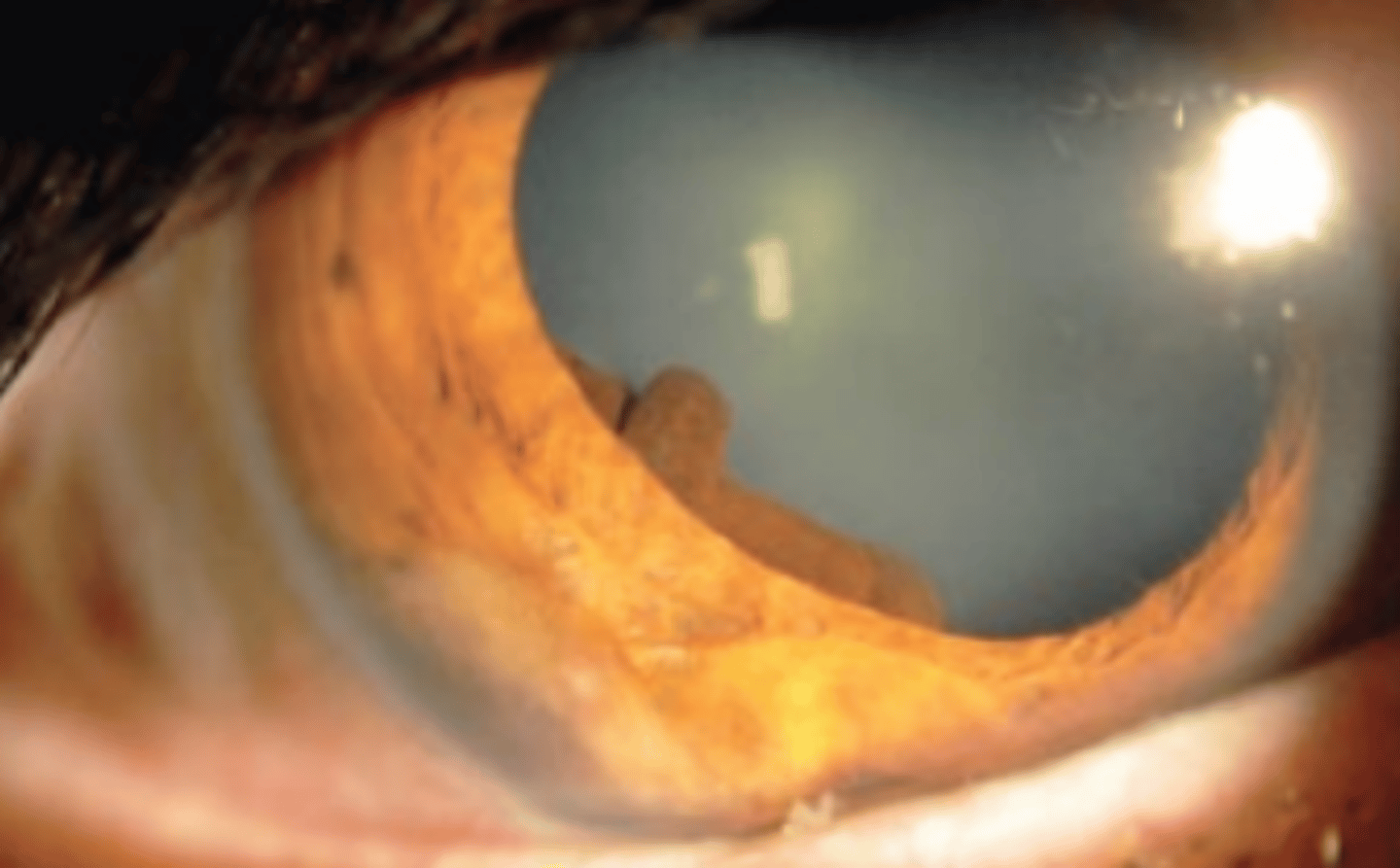
Central
pigment epithelial cyst located from the pupillary margin to the iris root.
Midzonal
pigment epithelial cyst located from the iris root to the ciliary body. Will change in shape upon dilation, differentiating them from iris melanomas.
Peripheral
pigment epithelial cyst located at the iridociliary border
Stromal cyst
primary iris cyst having a clear anterior wall with a fluid filled lumen. Will transilluminate and usually causes iris deformation. Can be congenital, or acquired. Are not likely to obstruct the angle.
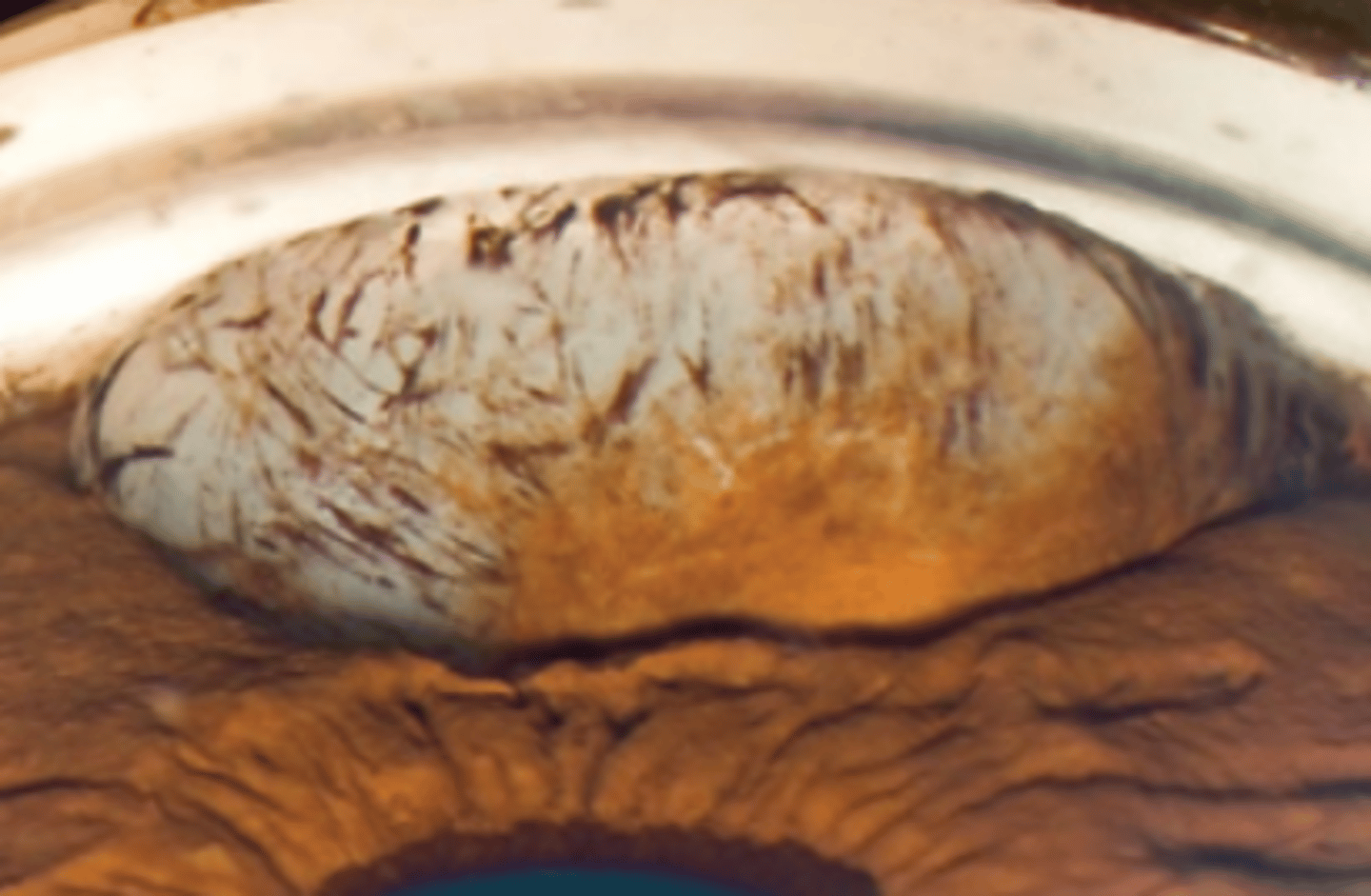
Free floating cyst
primary iris cyst which is a dislodged pigment epithelial cyst. Do not transilluminate. Can dislodge anteriorly (asymptomatic) or posteriorly (mimic intraocular foreign bodies).
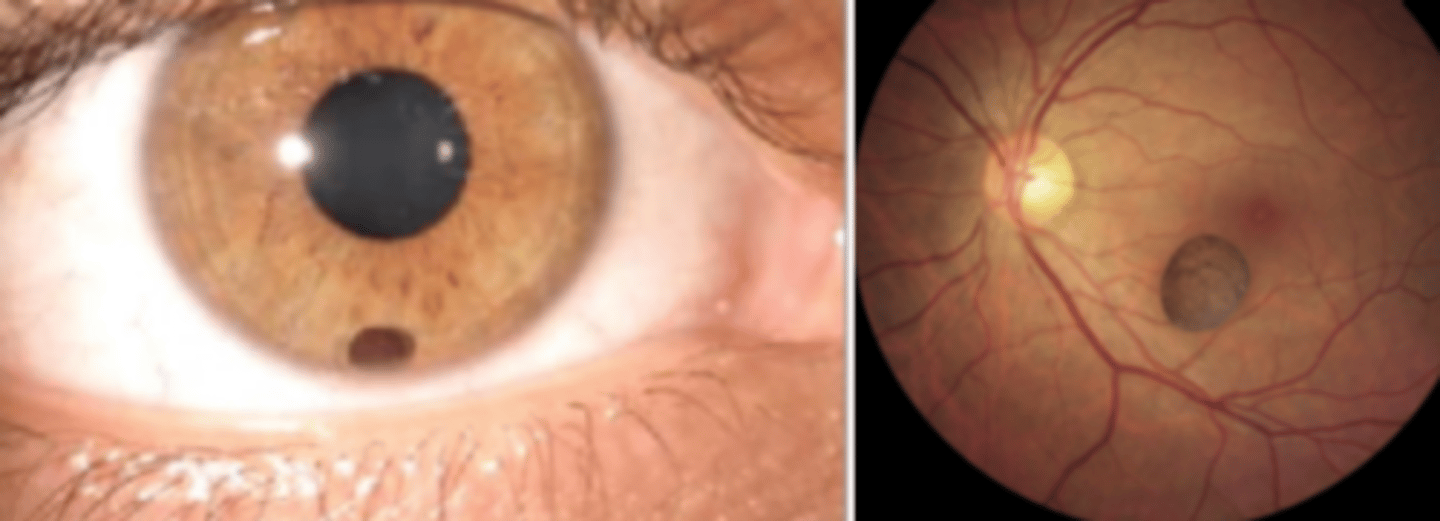
Secondary iris cyst
iris cyst having an identifiable cause and is classified on pathogenic mechanism. Are more likely to cause complications such as uveitis, decrease in VA, glaucoma, lens subluxation, iris, bombe, and surgical complications. I.e.) implantation cysts**, drug induced (miotics, latanoprost), tumor induced, parasitic, systemic disease
Iris melanoma
growth of the iris that is more common in light irises and in the inferior aspect. Vary in presentation (pigmented or not, smooth or regular, etc). Are slow growing with low mortality rate. Most commonly appear in the 5th to 6th decade.
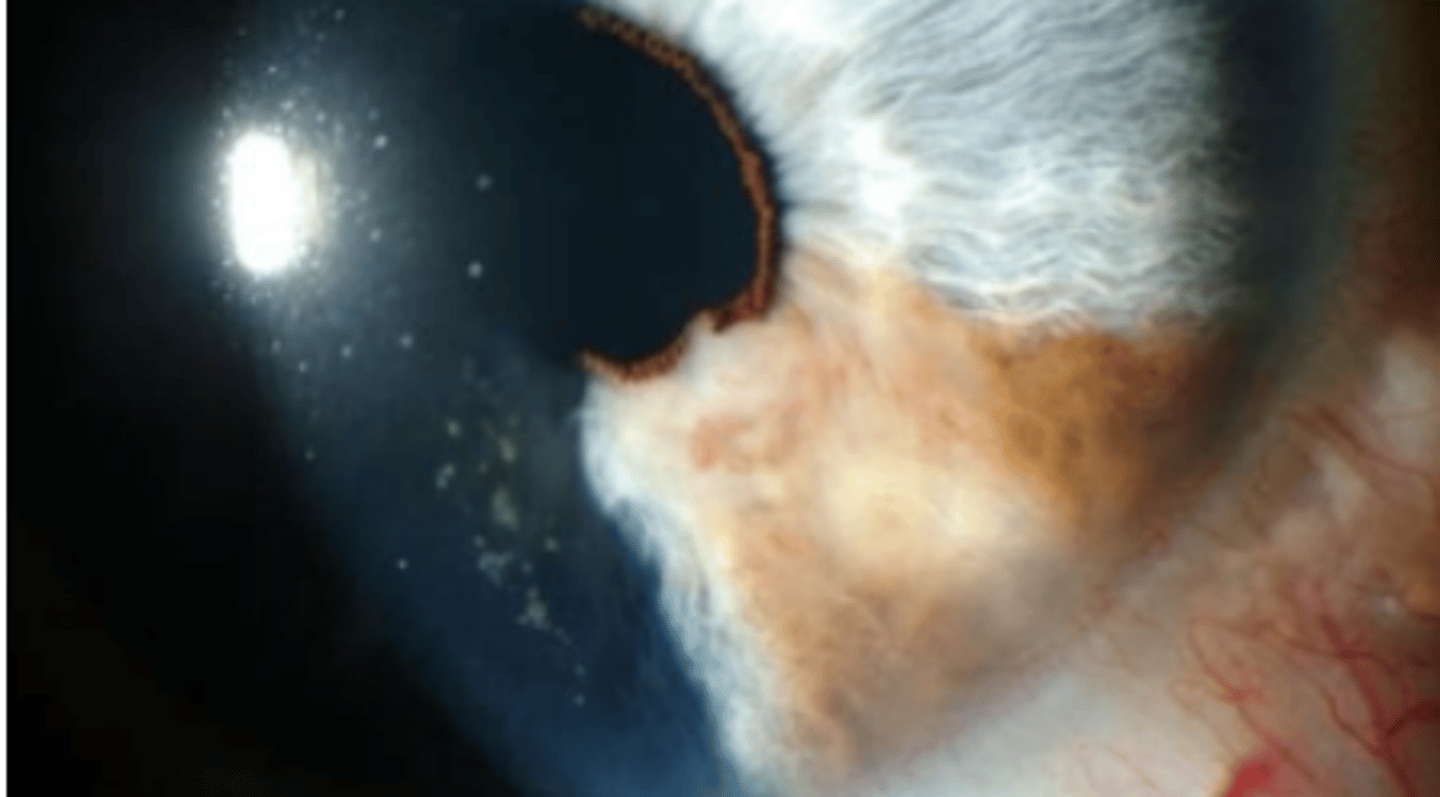
Greater than 3 mm
how is a iris melanoma distinguished from iris nevi?
Documentation of growth
Neovascularization
Ectropion uveae
Secondary glaucoma
Secondary cataract
Iris melanoma presents with 3 of 5 of these indications
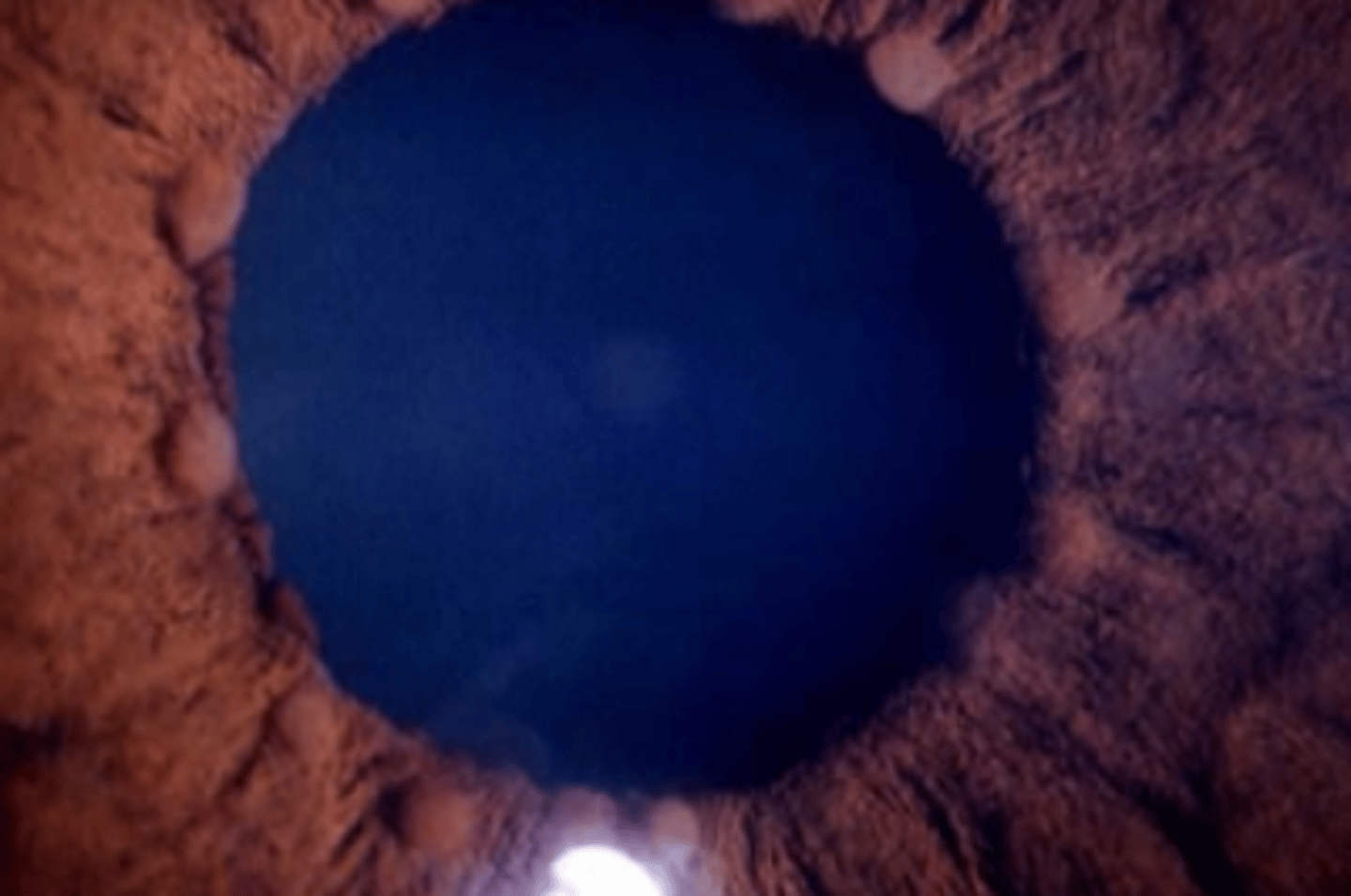
Koeppe nodules
inflammatory nodules of the iris stroma located at the pupil border. Can occur with any form of ocular inflammation, granulomatous or non-granulomatous.

Busacca nodules
inflammatory nodules of the iris stroma slightly displaced from the pupil border. Is indicative of granulomatous inflammation.
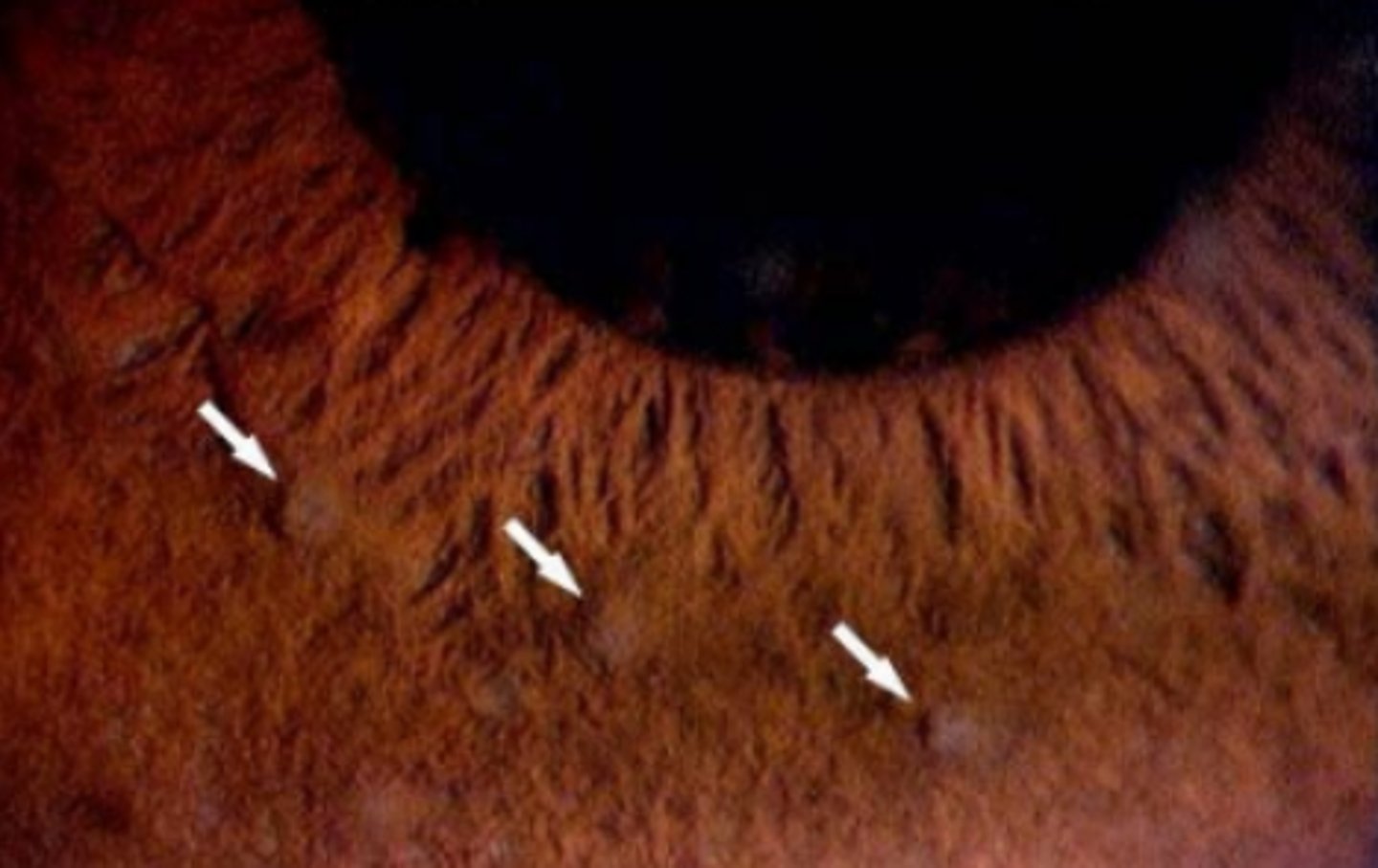
Lisch nodules
tan (varying depending on eye color) melanocytic progressive growths on the iris associated with neurofibromatosis 1.
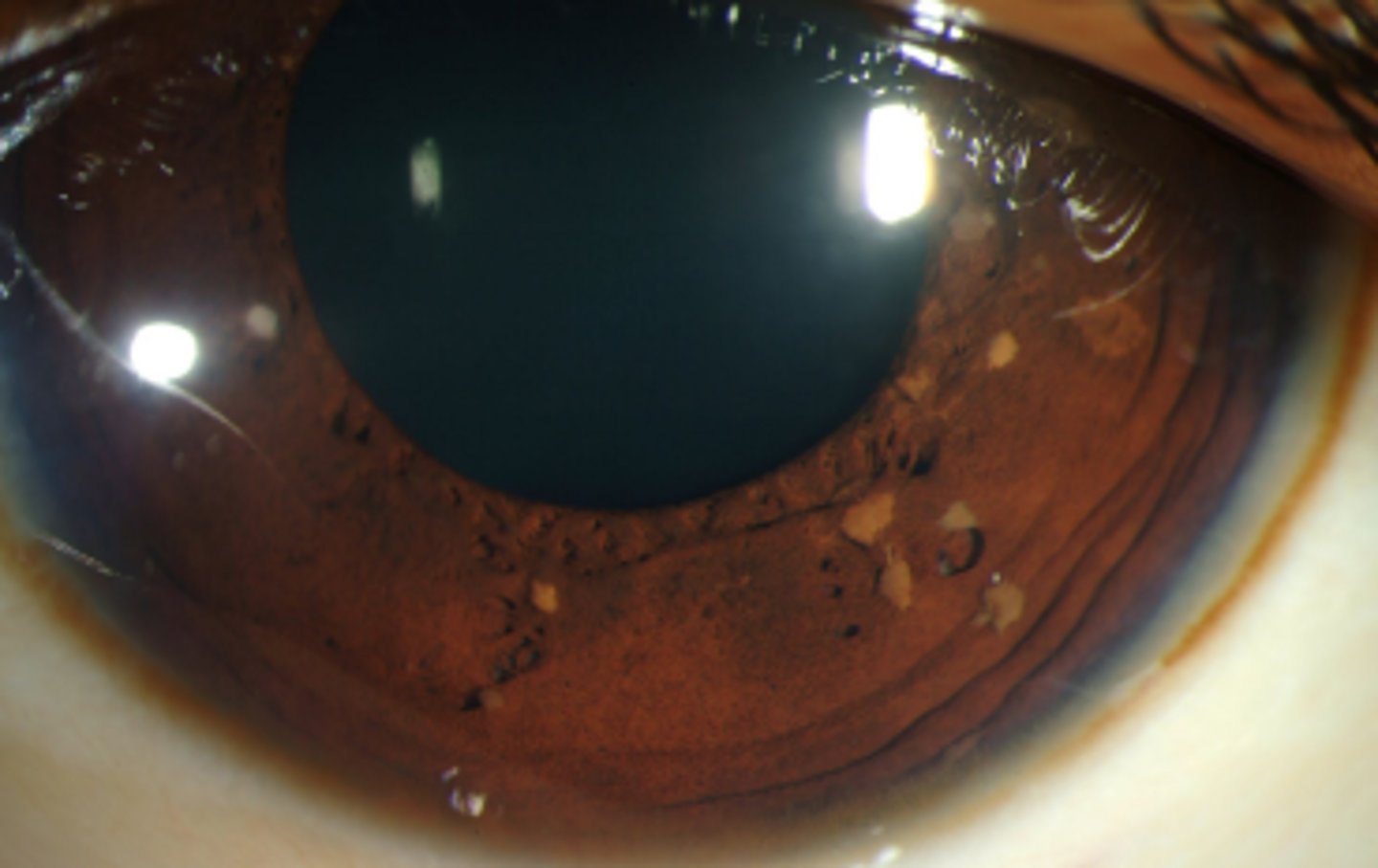
Iris mammillations
diffuse, tiny villiform lesions of the iris which can be sporadic or autosomal dominant. Are uniform differentiating it from Cogan Reese syndrome
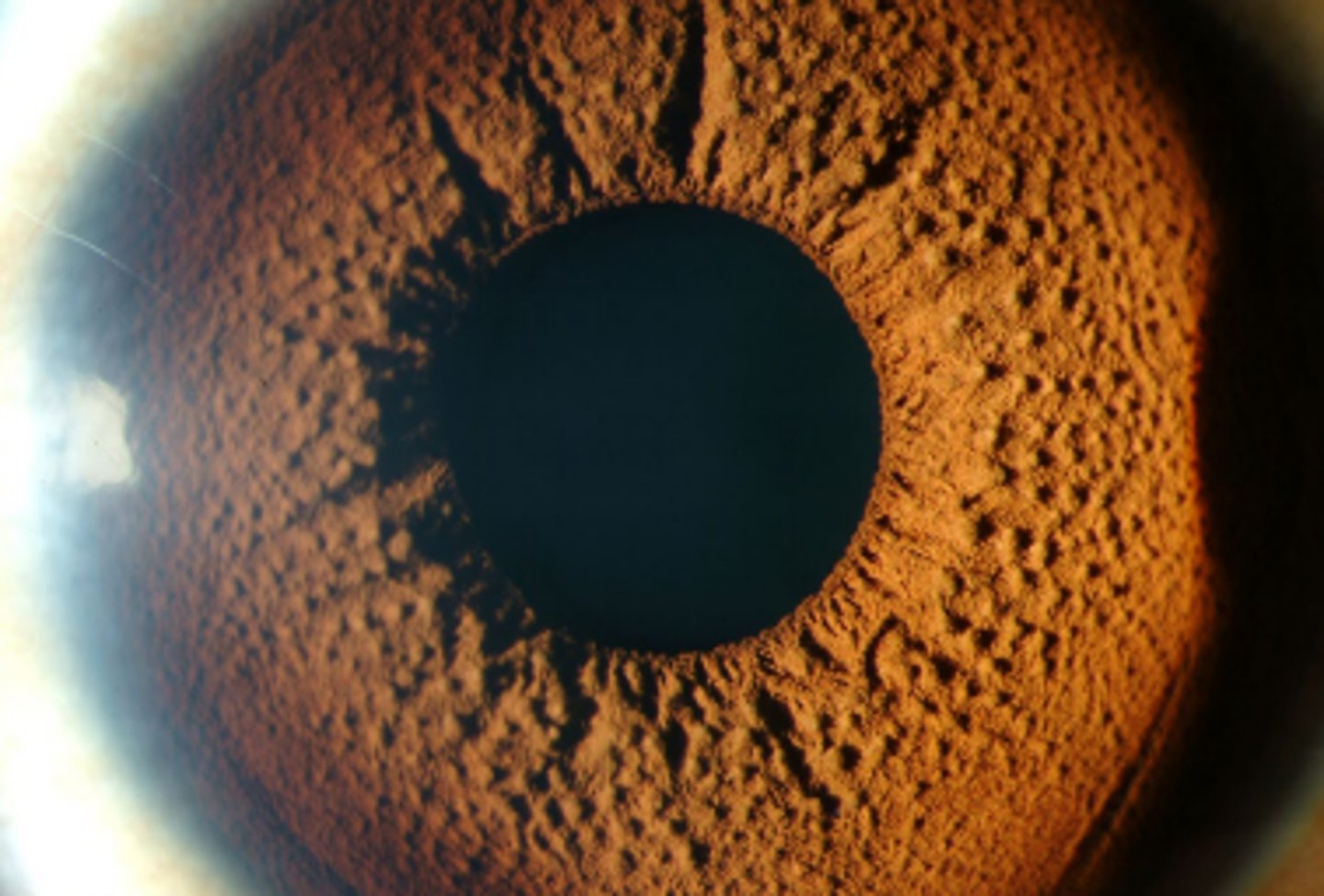
Brushfield spots
grey brown spots on the iris which are focal areas of stromal hyperplasia. Are more common in light irises and have an association with Down's syndrome.
are uniform
how do iris mammillations differ from elevations seen in cogan reese syndrome?
Rubeosis irides
neovascularization of the iris due to retinal ischemia most often occurring at the pupil border, but may also migrate into the angle. Is associated with diabetes mellitus and should be documented if it is or isn't present. Can also be seen in patients having central retinal vein occlusion. Can cause ectropion uvea due to contraction of blood vessels.
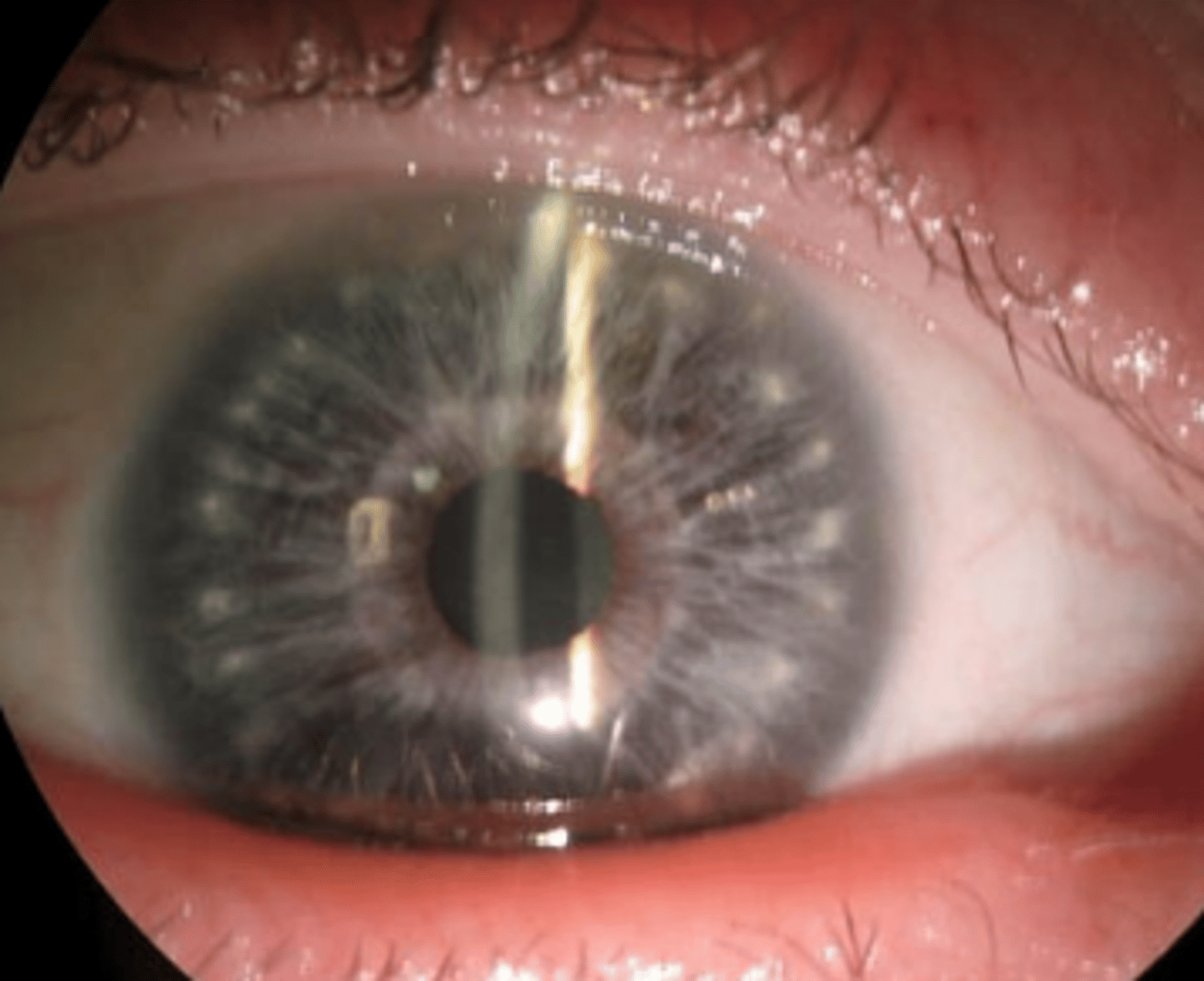
Intraoperative Floppy iris syndrome
a triad of complications occurring during cataract surgery involving flaccid iris stroma, prolapsed iris stroma towards incision site, and progressive pupil constriction despite pharmacologic dilation. Is associated with the use of various oral medication, advanced age, male gender, and decreased pupil diameter.
Tamulosin
a selective alpha 1 receptor adrenergic agonist used to stimulate urination BPH. Also blocks alpha 1 receptors of the iris dilator and can result in floppy iris syndrome. Explains why men are more likely to develop this condition.
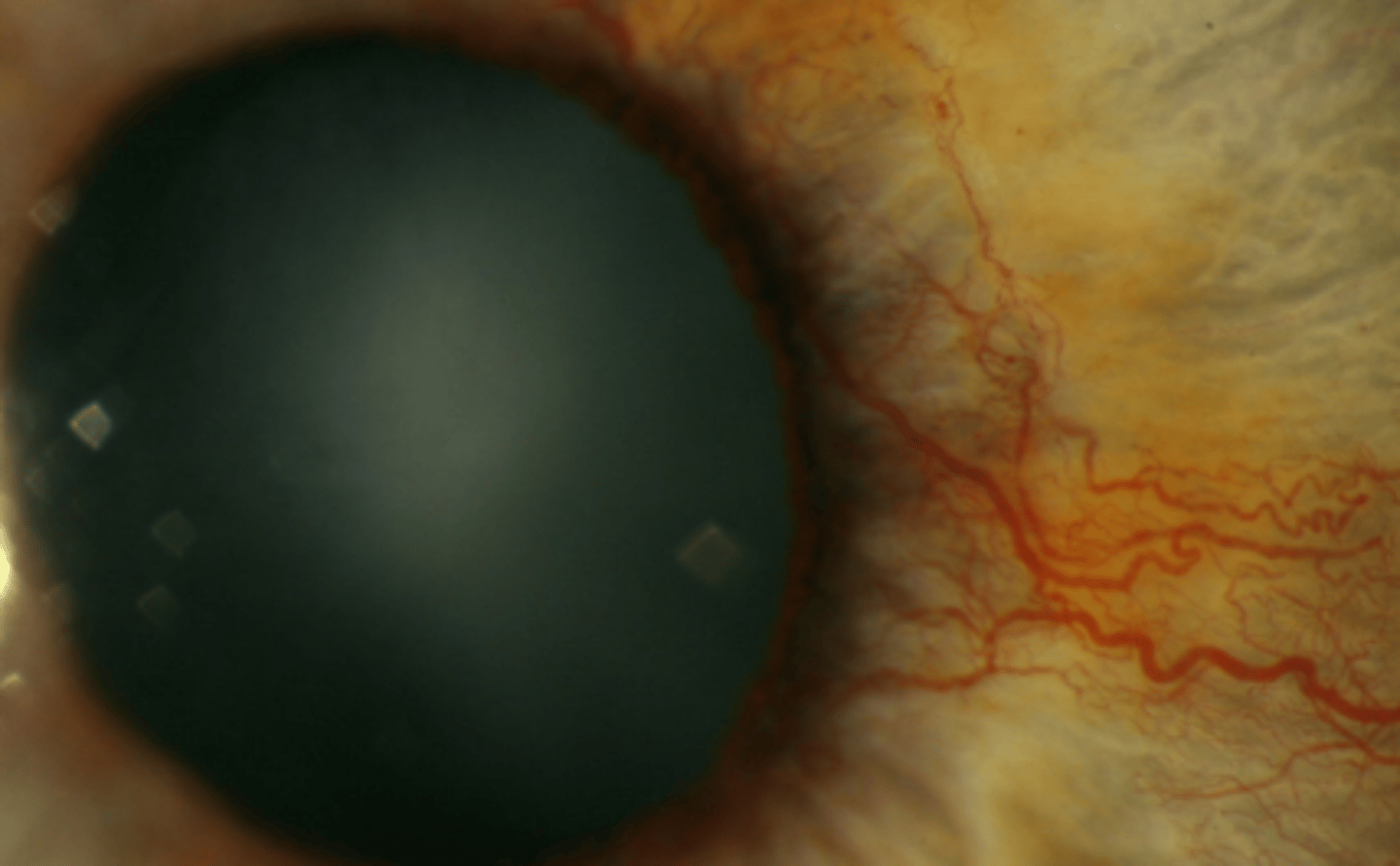
Iridodonesis
shaking or fluttering of the iris with eye movement. Is associated with Marfan syndrome, ectopia lentis, post cataract surgery, and trauma. Is usually asymptomatic, but may result in vertigo.
Iridodialysis
tear of the iris at the iris root. Blunt force trauma or penetrating injuries pose a risk. Can result in misshapen pupil, hyphema, damage to the angle, and traumatic iritis. Symptoms include glare, photophobia, diplopia, and cosmesis. Complications include lens dislocation, cataract, and secondary glaucoma.
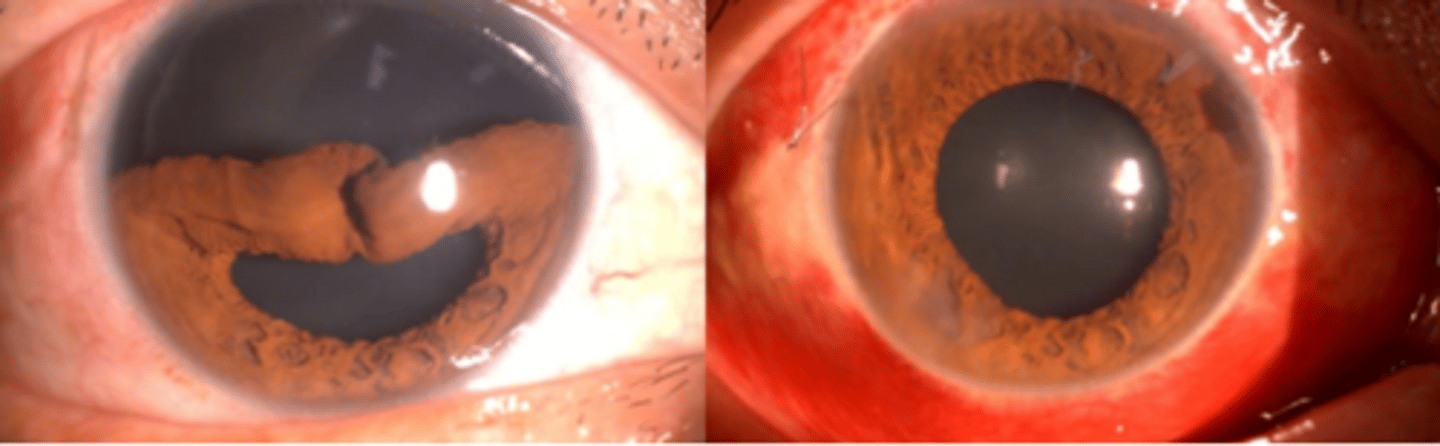
Iris sphincter tears
a tear in the iris sphincter muscle which can be focal (triangular defect) or sectoral (large mischapen pupil). Blunt force trauma, penetrating injuries, and surgery post a risk. Can result in hyphema, misshapen pupil, poorly reactive pupil, and traumatic iritis. Symptoms include photophobia and cosmesis