microscope that uses light
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
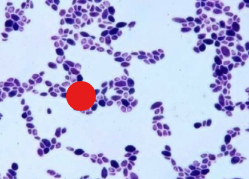
compound illumination
Dark objects are visible to a bright background
compound illumination for specimen
Light reflected off the specimen does not enter objective lens
what does compound use to keep light from refracting
Immersion oil

what kind of cells does compound not see
unstained cells
Darkfield how does light enter the objective lenses
Only reflect light off the specimen enters the objective lens
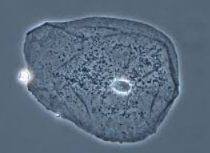
Phase-Contrast is used to see …
Living organisms and internal cell structures
Phase-Contrast uses how many light rays
two sets of light rays, direct rays, and diffracted rays to form an image
Phase-Contrast illumination
light passing through an annular (ring-shaped) diaphragm; Direct light rays(unaltered by the specimen) travel a different path from light rays that are reflected or diffracted as they pass through the specimen
microscope with dead cell for viewing
Compound

Darkfield illumination
light objects are visible against a dark background
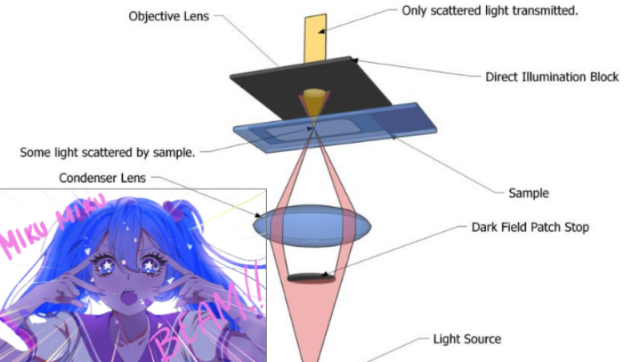
Darkfield illumination for specimen
opaque disk placed in condenser that eliminates light in the center of the beam
darkfield uses what two colors for Reflected or diffracted light rays
Blue: Reflected or diffracted light rays; Re: direct rays
phase contrast is used for
greater differentiation of internal structures and clearly shows the pellicle
Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) is similar to phase contrast except
different refractive indexes

Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) uses how may light beams
2 light beams and prisms to split light beams; giving more contrast and color to the specimen

Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) is used for
Images are brightly colored and appear 3-D

Fluorescence uses what light waves
Fluorescent substance absorb UV light and emit longer wavelength (visible) light
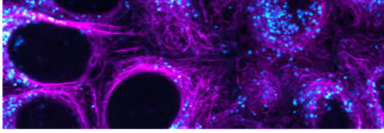
Fluorescence is stained with what substance
Cells may be stained with fluorescent dyes (fluorochrome) if they do not naturally fluoresce
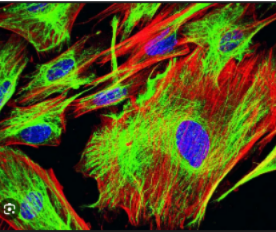
Fluorescence what colors do they stain
May stain bright yellow, green, orange against dark field of view
what is the application for : fluorescence antibody
Immofluorescence
Antibodies specific for a type of microbial pathogen are prepared and tagged with fluorochrome
FA are applied to a microscope slide bearing the specimen that may contain pathogenic microbe
what is fluorescence mainly used to see
Rapid and specific detection of pathogens
Confocal uses what to stain
fluorochrome

what wavelength is used to in confocal
Shortwavelength (blue) light is used to excite a single plane of a specimen
what is used to scan one plane on a confocal
Uses pinhole aperture to scan one plane at a time
what dimension are used in the confocal
Clear 2-D images at a time
what dimension are used in the confocal that appear on the computer
3-D image
two photon is stained with what dye
fluorochrome
what wavelength is used on the two-photon
Two photons of long wavelength (red) light are used to excite the dyes
what is the two-photon used for
Study living cells and track cell activity in real time
Super-Resolution Light Microscopy uses how many light beams
Uses two laser beams
what does the first wavelength in the super-resolution
stimulates fluorescent molecules to glow
what does the second wavelength in the super-resolution
cancels out all fluorescence except for that in 1nm
what does super-resolution used for
Computer scans the specimen by nm by nm then puts the images together
what microscope uses dead microbes
compound
what microscope uses alive microbes
darkfield, phase-contrast, Differential Interference Contrast (DIC), Fluorescence, Confocal, two-photon, and super-resolution
what microscope uses no staining
phase-contrast