Exam 3 / Practice Test Questions
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Test Simulation—Offer
Carson Corp., a retail chain, asked Alto Construction to fix a broken window at one of Carson's stores. Alto offered to make the repairs within three days at a price to be agreed on after the work was completed. A contract based on Alto's offer would fail because of indefiniteness as to the:
a. Price involved.
b. Nature of the subject matter.
c. Parties to the contract.
d. Time for performance
A
Test Simulation—Offer
On September 10, Harris, Inc., a new car dealer, placed a newspaper advertisement stating that Harris would sell ten cars at its showroom for a special discount only on September 12,13, and 14. On September 12, King called Harris and expressed an interest in buying one of the advertised cars King was told that five of the cars had been sold and to come to the showroom as soon as possible. On September 13, Hams made a televised announcement that the sale would end at 10:00 PM that night. King went to Harris' showroom on September 14 and demanded the right to buy a car at the special discount Harris had sold the ten cars and refused King's demand King sued Harris for breach of contract. Harris' best defense to King's suit would be that Harris':
a. Offer was unenforceable.
b. Advertisement was not an offer.
c. Television announcement revoked the offer.
d. Offer had not been accepted.
B
Test Simulation—Offer
On June 15, Peters orally offered to sell a used lawn mower to Mason for $125. Peters specified that Mason had until June 20 to accept the offer. On June 16, Peters received an offer to purchase the lawn mower for $150 from Bronson, Mason's neighbor. Peters accepted Bronson's offer. On June 17, Mason saw Bronson using the lawn mower and was told the mower had been sold to Bronson. Mason immediately wrote to Peters to accept the June 15 offer. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. Mason's acceptance would be effective when received by Peters.
b. Mason's acceptance would be effective when mailed.
c. Peters' offer had been revoked and Mason's acceptance was ineffective.
d. Peters was obligated to keep the June 15 offer open until June 20.
C
Test Simulation—Offer
Calistoga offers to sell her home to Drake for $300,000. Drake asks her if she would accept $250,000. Which of the following is true?
a. Drake's response is mere inquiry; therefore, the $300,000 offer by Calistoga is still in force.
b. Drake's response is a counteroffer effectively terminating the $300,000 offer and instigating an offer for $250,000.
c. Drake's response is a rejection of the $300,000 offer and there is no offer for $250,000 because it is too indefinite to be an offer.
d. Because of ambiguity, both offers are terminated by operation of law.
A
Test Simulation—Offer
Opal offered, in writing, to sell Larkin a parcel of land for $300,000. If Opal dies, the offer will:
a. Terminate prior to Larkin's acceptance only if Larkin received notice of Opal's death.
b. Remain open for a reasonable period of time after Opal's death.
c. Automatically terminate despite Larkin's prior acceptance.
d. Automatically terminate prior to Larkin's acceptance.
D
Test Simulation—Acceptance
On April 1, Fine Corp. faxed Moss an offer to purchase Moss' warehouse for $500,000. The offer stated that it would remain open only until April 4 and that acceptance must be received to be effective. Moss sent an acceptance on April 4 by overnight mail and Fine received it on April 5. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. No contract was formed because Moss sent the acceptance by an unauthorized method.
b. No contract was formed because Fine received Moss' acceptance after April 4.
c. A contract was formed when Moss sent the acceptance.
d. A contract was formed when Fine received Moss' acceptance.
B
Test Simulation—Acceptance
On February 12, Harris sent Fresno a written offer to purchase Fresno's land. The offer included the following provision: "Acceptance of this offer must be by registered or certified mail, received by Harris no later than February 18 by 5:00 p.m. CST." On February 18, Fresno sent Harris a letter accepting the offer by private overnight delivery service Hams received the letter on February 19. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. A contract was formed on February 19.
b. Fresno's letter constituted a counteroffer.
c. Fresno's use of the overnight delivery service was an effective form of acceptance.
d. A contract was formed on February 18 regardless of when Harris actually received Fresno's letter.
B
Test Simulation—Acceptance
Kay, an art collector, promised Hammer, an art student that if Hammer could obtain certain rare artifacts within two weeks, Kay would pay for Hammer's postgraduate education At considerable effort and expense, Hammer obtained the specified artifacts within the two-w,eek period. When Hammer requested payment, Kay refused. Kay claimed that there was no consideration for the promise. Hammer would prevail against Kay based on:
a. Unilateral contract
b. Unjust enrichment
c. Public policy'
d. Quasi contract
A
Test Simulation—Acceptance
On September 27, Summers sent Fox a letter offering to sell Fox a vacation home for $150,000. On October 2, Fox replied by mail agreeing to buy the home for $145,000. Summers did not reply to Fox. Do Fox and Summers have a binding contract?
a. No, because Fox failed to sign and return Summers’ letter.
b. No, because Fox’s letter was a counteroffer.
c. Yes, because Summers’ offer was validly accepted.
d. Yes, because Summers’ silence is an implied acceptance of Fox’s letter.
B
Test Simulation—Formation Defenses
Wick Company made a contract in writing to hire Zake for five years for $150,000 per year. After two years, Zake asked Wick for a raise of $20,000 per year. Wick at first refused but agreed to pay Zake a $60,000 bonus after Zake completed the fifth year of work. Zake put some pressure on Wick to get Wick to agree to the terms. After the fifth year, Zake left and demanded Wick pay Zake the $60,000 bonus and Wick refused. Zake sued Wick for the $60,000 bonus. Who wins?
a. Zake, because Wick agreed to the bonus.
b. Zake, if the bonus was agreed to in writing.
c. Wick, even though Wick agreed to the bonus.
d. Wick, because Zake had applied pressure to get the bonus.
C
Test Simulation—Formation Defenses
Grove is seeking to avoid performing a promise to pay Brook $1,500. Grove is relying on lack of consideration on Brook’s part. Grove will prevail if he can establish that:
a. Prior to Grove’ promise, Brook had already performed the requested act.
b. Brooks’ only claim of consideration was the relinquishment of a legal right.
c. Brook’s asserted consideration is only worth $400.
d. The consideration to be performed by Brook will be performed by a third party.
A
Test Simulation—Formation Defenses
Dunne and Cook signed a contract requiring Cook to rebind 500 of Dunne’s books at $0.80 per book. Later, Dune requested, in good faith, that the price be reduced to $0.70 per book. Cook agreed orally to reduce the price to $0.70. Under the circumstances, the oral agreement is:
a. Enforceable, but proof of it is inadmissible into evidence.
b. Enforceable, and proof of it is admissible into evidence.
c. Unenforceable, because Dunne failed to give consideration, but proof of it is otherwise admissible into evidence.
d. Unenforceable, due to the statute of frauds, and proof of it is inadmissible into evidence.
C
Test Simulation—Formation Defenses
In which of the following situations does the first promise serve as valid consideration for the second promise?
a. A police officer’s promise to catch a thief for a victim’s promise to pay a reward.
b. A builder’s promise to complete a contract for a purchaser’s promise to extend the time for completion.
c. A debtor’s promise to pay $500 for a creditor’s promise to forgive the balance of $600 liquidated debt.
d. A debtor’s promise to pay $500 for a creditor’s promise to forgive the balance of a $600 disputed debt.
D
Test Simulation—Formation Defenses
Which of the following will be legally binding despite lack of consideration?
a. An employer’s promise to make a cash payment to a deceased employee’s family in recognition of the employee’s many years of service.
b. A promise to donate money to a charity on which the charity relied in incurring large expenditures.
c. A modification of a signed contract to purchase a parcel of land.
d. A merchant’s oral promise to keep an offer open for sixty days.
B
Test Simulation—Formation Defenses
Rail, who was sixteen years old, purchased an $800 computer from Elco Electronics. Rail and Elco are located in a state where the age of majority is eighteen. On several occasions Rail returned the computer to Elco for repairs. Rail was very unhappy with the computer. Two days after reaching the age of eighteen, Rail was still frustrated with the computer’s reliability, and returned it to Elco, demanding an $800 refund. Elco refused, claiming that Rail no longer had a right to disaffirm the contract. Elco’s refusal is:
a. Correct, because Rail’s multiple requests for service acted as a ratification of the contact.
b. Correct, because Rail could have transferred good title to a good-faith purchaser for value.
c. Incorrect, because Rail disaffirmed the contract within a reasonable period of time after reaching the age of eighteen.
d. Incorrect, because Rail could disaffirm the contract at any time.
C
Test Simulation—Formation Defenses
Green was adjudicated incompetent by a court having proper jurisdiction. Which of the following statements is correct regarding contracts subsequently entered into by Green?
a. All contracts are voidable.
b. All contracts are valid.
c. All contracts are void.
d. All contracts are enforceable.
C
Test Simulation—Formation Defenses
All of the following are effective methods of ratifying a contract entered into by a minor except
a. Expressly ratifying the contract after reaching the age of majority.
b. Failing to disaffirm the contract within a reasonable time after reaching the age of majority.
c. Ratifying the contract before reaching the age of majority.
d. Ratifying the contact by implication after reaching the age of majority.
C
Test Simulation—Formation Defenses
Under a personal services contract, which of the following circumstances will cause the discharge of a party’s duties?
a. Death of the party who is to receive the services.
b. Cost of performing the services has doubled.
c. Bankruptcy of the party who is to receive the services.
d. Illegality of the services to be performed.
D
Test Simulation—Formation Defenses
Which of the following would be unenforceable because the subject matter is illegal?
a. A contingent fee charged by an attorney to represent a plaintiff in a negligence action.
b. An arbitration clause in a supply contract.
c. A restrictive covenant in an employment contract prohibiting a former employee from using the employer’s trade secrets.
d. An employer’s promise not to press embezzlement charges against an employee who agrees to make restitution.
D
Which of the following, if intentionally misstated by a seller to a buyer, would be considered a fraudulent inducement to make a contract?
A) Nonexpert opinion
B) Appraised value
C) Prediction
D) Immaterial fact
B
If a buyer accepts an offer containing an immaterial unilateral mistake, the resulting contract will be…
A) Void as a matter of law
B) Void at the election of the buyer
C) Valid as to both parties
D) Voidable at the election of the seller
C
If a person is induced to enter into a contract by another person because of the close relationship between the parties, the contract may be voidable under which of the following defenses?
A) Fraud in the inducement
B) Unconscionability
C) Undue influence
D) Duress
C
Long purchased a life insurance policy with Tempo Life Insurance Co. The policy named Long’s daughter as beneficiary. Six months after the policy was issued, Long died of a heart attack. Long had failed to disclose on the insurance application a known preexisting heart condition that caused the heart attack. Tempo refused to pay the death benefit to Long’s daughter. If Long’s daughter sues, Tempo will…
A) Win, because Long’s daughter is an incidental beneficiary
B) Win, because of Long’s failure to disclose the preexisting heart condition
C) Lose, because Long’s death was from natural causes
D) Lose, because Long’s daughter is a third-party donee beneficiary
B
Petersen went to Jackson's home to buy a used car advertised in the newspaper. Jackson told Petersen that "it is a great car" and that "the engine had been overhauled a year ago." Shortly after he bought the car, Petersen began experiencing problems with the engine. When Jackson refused to refund his money, Petersen sued for fraud based on it was not a "great car" and also based on the fact, as learned later, the overhaul was done thirteen months ago, not a year. Will Petersen win his case?
A) Yes, Jackson’s statement that “it is a great car” is actionable fraud
B) Yes, Jackson’s statement about the overhaul is actionable fraud
C) Yes, both the statement that “it is a great car” and the statement about the overhaul are actionable fraud
D) No
D
A building subcontractor submitted a bid for construction of a portion of a high-rise office building. The bid contained material computational errors. The general contractor accepted the bid with knowledge of errors. Which of the following statements best represents the subcontractor's liability?
A) Not liable because the contractor knew of the errors
B) Not liable because the errors were a result of gross negligence
C) Liable because the errors were unilateral
D) Liable because the errors were material
A
Maco, Inc. and Kent contracted for Kent to provide Maco certain consulting services at an hourly rate of $20. Kent's normal hourly rate was $90 per hour, the fair market value of the services. Kent agreed to the $20 rate because Kent was having serious financial problems. At the time the agreement was negotiated, Maco was aware of Kent's financial conditions and refused to pay more then $20 per hour for Kent's services. Kent has now sued to rescind the contract with Maco, claiming duress by Maco during the negotiations. Under the circumstances, Kent will...
A) Win, because Maco refused to pay the fair market value of Kent’s services
B) Win, because Maco was aware of Kent’s serious financial problems
C) Lose, because Maco’s actions did NOT constitute duress
D) Lose, because Maco cannot prove that Kent, at the time, had no other offers to provide consulting services
C
To prevail in common law action for fraud in the inducement, a plaintiff must prove that the...
A) Defendant was an expert with regard to the misrepresentations
B) Defendant made the misrepresentations with knowledge of their falsity and with an intention to deceive
C) Misrepresentations were in writing
D) Plaintiff was in a fiduciary relationship with defendant
B

D

B

A

D

D

C

C

B

C

D

B

C) Not materially increase the other party’s risk or duty
D) Not be revocable by the assignor
C

C

D

D

Baxter, Inc. and Globe entered into a contract. After receiving valuable consideration from Clay, Baxter assigned…
A

A

C

B

Which of the following types of conditions affecting performance may validly be present in contracts?
A

A
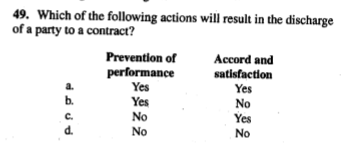
A

C

B

D

Ames Construction Co. contracted to build a warehouse for White Corp. The construction specifications required Ames to use Ace lighting fixtures. Inadvertently, Ames installed Perfection lighting fixtures which are of slightly lesser quality…
A

A

C

A

B
A
A
C
B
B
A
A
A
B
A
C

F
F
F
F
F
T
T

F
T
T
T
F

F
T
T