Chapter 4 - Nervous systems
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CNS and PNS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
CNS is made from
Brain - memory, reasoning, conscious movements
Spinal cord - reflexes, transmit signal to and from brain
PNS consists of
Nerve + Ganglia
Afferent division (Sensory)
Efferent division (Motor Efferent) ME
Afferent division
Carry nerve impulse into the CNS
Visceral sensory (Signals from internal organs)
Somatic sensory (Signals from skin, muscle and external stimuli)
Efferent division
Carry nerve impulse away from the CNS to
Somatic NS - skeletal muscles and regulates conscious response, complete control (always excitation)
Autonomic NS - smooth muscles, cardiac muscles and glands
regulates involuntary response
excitation and inhibition
Autonomic nervous system
Carries NI away from the CNS to smooth muscles, cardiac muscles and glands (involuntary)
Sympathetic division - fight or flight
Parasympathetic - rest and digest
Protection of the CNS
Bones
Meninges
Cerebrospinal fluid
Bones
Cranium - part of the skull that protects the brain
Vertebrae - protects the spinal cord
STRONG, RIGID structure to protect
against DIRECT, HARD, IMPACT
Meninges consists of
Dura mater (Outer)
Arachnoid mater (Middle)
Pia mater (Inner)
Meninges is found inside the
bones
covering surface of brain
Spinal cord
Dura mater (Brain)
Tough and fibrous layer
Laid flush against the cranium
Holds the brain in place
Dura mater (Spinal cord)
On the inside of the vertebral canal there is a space containing, fat, connective tissue and blood vessels - serve as padding and allow the spinal cord to bend
Arachnoid mater
loose mesh of fibres (connect the DM and PM)
Pia mater
inner meningeal layer: sticks closely to the surface of the brain and spinal cord
Delicate layer
laid flush against the cerebral cortex
prevents the entry of pathogens
Cerebrospinal fluid
Clear, watery fluid containing protein, urea, glucose and salts (PUGS)
Between middle and inner layer of meninges
Cavities in the brain and through a canal in the centre of the spinal cord
Brain suspended in clear, watery fluid
absorbs shock
and dissipates the energy from the impact
Cerebrospinal fluid functions: (SPT)
Support - Brain is suspended inside the cranium and floats in the fluid that surrounds it
Protection - shock absorber and dissipates energy
Transport - takes nutrients to the cells of the brain and SC and carries away their waste
CNS consists of
Outer grey matter - Dendrites, unmyelinated fibres, Nerve cell bodies (DUN)
Inner white matter - myelinated fibres
tract is
bundle of nerves (white matter)
Parts of the brain
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Medulla oblongata
Hypothalamus
Corpus callosum
Cerebrum
Biggest part of the brain that consists of
Outer surface of grey matter - cerebral cortex
Grey matter deep inside the cerebrum - basal ganglia
Inner white matter
Cerebral cortex - outer grey matter
Greatly folded to increase SA for a large number of neurons - convolutions
Folding produces rounded ridges called convolutions = gyrus
Shallow downfolds - sulcus
Deep downfolds - fissures
Longitudinal fissure
deepest fissure
splits the cerebrum into 2 halves, the left and right cerebral hemisphere
Lobes of the cerebrum (FITOP)
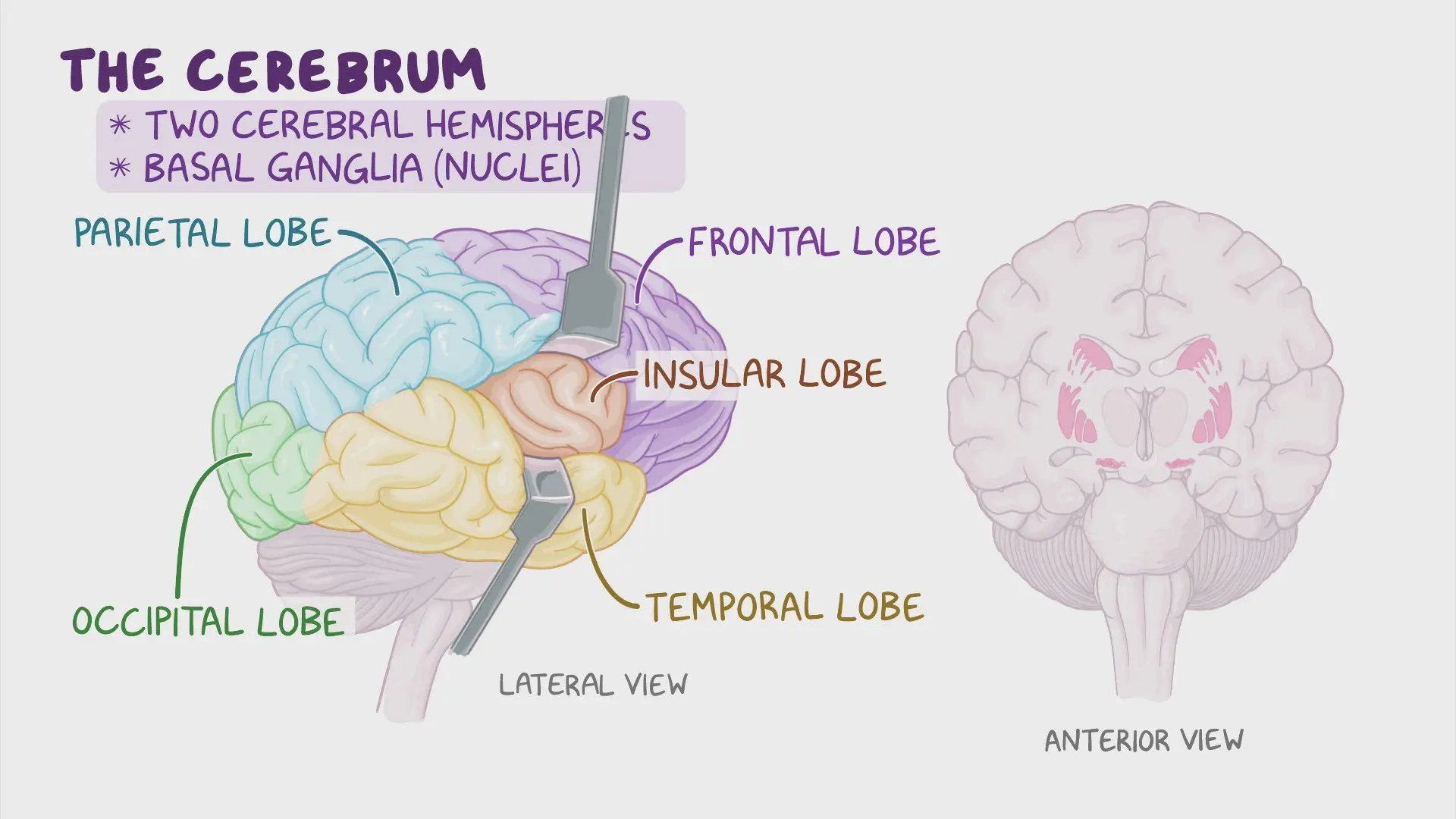

Frontal lobe MUST GIVE EXAMPLE
Higher-order function - problem solving skills
Complex decision making
Initiate skeletal muscle movement
Broca’s area speech production
Parietal lobe
Process temperature, touch, taste, pain and movement - sensory information
Temporal lobe
Process memories and link with senses
receives auditory information
Wernicke’s area speech comprehension
Occipital lobe
Vision, interpretation of signals from eyes
Insula
Recognition of different senses and emotions, addiction and psychiatric disorders
Cerebral cortex function
Involved in mental activities such as thinking, reasoning, learning, memory intelligence and sense of responsibility
perception of senses
initiation and control of voluntary muscle contraction
Functional areas in cerebral cortex
Sensory area - interpret impulses from receptors
Motor area - control muscular movement
Association area - concerned with intellectual and emotional processes
Association area of cerebral cortex is involved with
Memory
memories are not stored in indivdual memory cells instead they are a pathway of neurons
when a memory is stored, new links are made between neurons or existing links are modified
Basal ganglia - inner grey matter deep inside each hemisphere
Consists of
a group of nerve cell bodies associated with the control of skeletal muscles
Inner white matter
Consists of myelinated fibres has 3 tracts
connect various areas of the cortex within the SAME hemisphere
carry impulse BETWEEN the left and right hemisphere
connect cortex to other parts of the brain and spinal cord
Corpus callosum
Bundle of nerve fibres (tract) that lie underneath the cerebrum at the base of the longitudinal fissure
composed of myelinated fibres
Function: allow the right and left hemisphere to communicate
Cerebellum
Lies under rear part of the cerebrum
surface folded into a series of parallel ridges
Outer folded part - grey matter
Inside is white matter branches to all parts of the cerebellum
Function: control posture, balance and fine coordination of voluntary muscles
Smoothen out skeletal muscle movement
What happens if the cerebellum is damaged/removed
functions take place below the conscious level
Jerky
Spasmodic
Uncontrolled
Hypothalamus
Lies in the middle of the brain, controls many body activites but mainly HOMEOSTASIS
The hypothalamus regulates
Core body temperature
Patterns of waking and sleeping
Secretion of hormones
Medulla Oblongata
Contains
Cardiac centre - regulates rate and force of heartbeat
Respiratory centre - control rate and depth of breathing
Vasomotor centre - regulates diameter of arteries/arterioles
also regulates reflexes of swallowing, sneezing, coughing and vomitting
All the centres are controlled by the hypothalamus
Spinal cord
Ascending tract - sensory axons that carry impulse towards the brain
Descending tract - motor axons that carry impulse downwards away from the brain
Function:
Carry sensory impulse up to the brain and motor impulse down the brain
integrate certain reflexes
Ganglia
group of nerve cell bodies outside the CNS
Cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves arise from the brain
most are mixed nerves (contains sensory and motor fibres)
a few only carry sensory impulse or motor impulse
Spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves arise from the spinal cord
ALL are mixed nerves joined to the spinal cord by the dorsal and ventral root
Ventral root
contains the axons of motor neurons that have their cell body in the grey matter of the spinal cord
Dorsal root
Contains sensory axons that have their cell bodies in a small swelling on the dorsal root —> dorsal root ganglion
Autonomic pathway
2 motor neurons from CNS to effector (involuntary muscles, cardiac muscles and glands)
Synapse in ganglion
NT: acetylcholine / noradrenaline
Somatic pathway
one motor neuron
carry NI to effector (skeletal muscles)
NT: acetylcholine
Autonomic nervous system receive two sets of nerve fibres
Sympathetic fibres: prepare for strenuous activity - fight or flight
noradrenaline
Parasympathetic fibres: maintain body during rest and digest
acetylcholine