Cell Structure and Function- Lecture 11-13(Unit 3)
1/357
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
358 Terms
Cellular respiration
harvests the energy remaining in pyruvate and NADH from glycolysis
external
Cellular respiration uses an _________ electron acceptor to
oxidize substrates completely to CO2
aerobic respiration
the terminal electron acceptor is oxygen, and the reduced form is water
CO2
With O2 as the terminal electron acceptor, pyruvate can be
oxidized completely to ____
More ATP
Having oxygen as the terminal electron acceptor allows for the
generation of _____ than glycolysis alone
Oxygen
provides a means of continuous reoxidation of NADH
and other reduced coenzymes
Mitochondria
___________ are found in virtually all aerobic cells of eukaryotes
chemotrophic and phototrophic
Mitochondria They are present in both ___________ and ____________ cells
need for ATP
Mitochondria are frequently clustered in regions of cells with the greatest __________, such as muscle cells
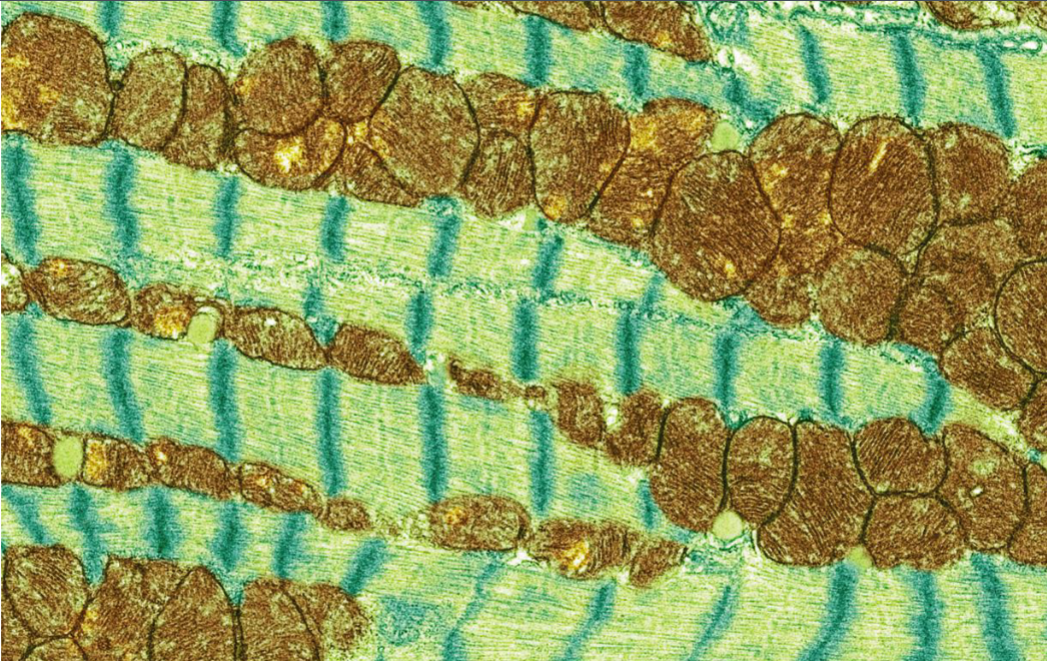
mitochondria
What is the brown stuff in this muscle cell
porins
outer membrane(mitochondria) contains ________ that allow passage of solutes with molecular weights up to 5000
intermembrane space
The _______________ between the inner and outer membranes(mitochondria)
intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix
The inner membrane is impermeable to most solutes, partitioning the mitochondrion into two separate compartments that _________ and __________
cristae
The inner membrane of most mitochondria has many infoldings called _________
They increase surface area of the inner membrane and
provide more space for electron transport to take place
Benefits of having cristae in the mitochondria
cytosol
95% of proteins in mito are encoded by nuclear genes
and are synthesized in ________
Transit sequences
__________ are targeting signals located on the N-
terminal of a polypeptide
Transit peptidase
____________ are enzymes that remove the transit
sequence once the polypeptide has arrived
Special transport complexes
______________ on the outer and inner membrane of the mitochondria allow for uptake of polypeptide chains
TOM and TIM
Two pores for transport into and out of the mito are
TOM
translocase of the outer membrane
TIM
translocase of the inner membrane
Transit sequence receptors
component of transport complex that recognizes
transit sequences
Chaperone proteins
bind polypeptides targeted to the mitochondria to help maintain
the unfolded state
1st step for transporting polypeptides into the mitochondrial matrix
Hsp70 chaperone proteins bind to the polypeptide. Help unfold
2nd step for transporting polypeptides into the mitochondrial matrix
TOM transit sequence receptor binds the N-terminus of the polypeptide
3rd step for transporting polypeptides into the mitochondrial matrix
Chaperone proteins are released, and ATP is hydrolyzed as polypeptide moves through the TOM and TIM pores
4th step for transporting polypeptides into the mitochondrial matrix
Transit sequence is removed by transit peptidase in the matrix as
soon as the transit sequence enters the matrix
5th step for transporting polypeptides into the mitochondrial matrix
Mitochondrial Hsp70 chaperone proteins bind polypeptide as it
enters the matrix
6th step for transporting polypeptides into the mitochondrial matrix
Often, mitochondrial Hsp60 chaperone proteins bind the
polypeptide and assist in proper folding
drive ATP synthesis
In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate is oxidized fully to
carbon dioxide with the released energy used to ___________
tricarboxylic acid cycle, TCA cycle
The citric acid cycle is also known as ______ and ________
citrate
in the citric acid cycle, _______ is an important intermediate
Krebs cycle
The citric acid cycle is also called the _______ after Hans Krebs, whose lab played a key role in elucidating the cycle
carbons, CO2, oxaloacetate
Each round of the citric acid cycle involves the entry of two ______, the release of two _____, and the regeneration of _________
electrons
The overall TCA cycle, in each case the _______ are accepted by coenzymes
pyruvate
The glycolytic pathway ends with _________, which can enter the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion
transports pyruvate into the matrix
At the inner mitochondrial membrane, a specific symporter ________________ , along with a proton
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH).
After being transported into the matrix pyruvate is converted
to acetyl CoA by _________________
3 carbon compound, 4 C compound, decarboxylations, NADH, FADH2, GTP
Summary of TCA cycle:
• Start with ___________
– Cleave off one CO2 in bridging reaction
– Add the other two to __________ to make their cleavage easier
• Two ___________
• 3 ______ produced, 1 ______, and 1 ___
CoA
_____ is co-enzyme co-substrate in bridging reaction and in cycle
they would have two protons added and it would be FADH2
What would be added to the Nitrogen’s on FAD after it it reduced
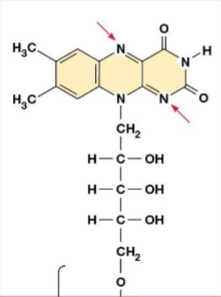
3, CO, COA - SH
The citric acid cycle can be summarized as follows:
acetyl COA + _NAD + FAD + ADP + Pi=
2___ + _NADH + FADH + _______ + ATP
10NAD, 2FAD, 6CO2
Including glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation, and the
citric acid cycle, the overall reaction is as follows:
glucose + __NAD + _FAD + 4ADP + 4Pi =
_CO + __NADH + _FADH + 4ATP
allosteric regulation
Most of the control of the TCA cycle involves ____________ of four key enzymes by specific effector molecules
Substrates of TCA
CoA, NAD+, FAD, and ADP
Products of TCA
3NADH, FADH2, 2CO2, and ATP
NAD H, ATP, and acetyl CoA
are allosteric inhibitors of enzymes in this cycle
NAD+, ADP, and AMP
each activate at least one regulator enzyme in this cycle
four, two, two, ATP, NADH and FADH2
Chemotrophic energy metabolism through the citric acid
cycle accounts for synthesis of ____ ATP per glucose
– ___ from glycolysis
– ___ from the citric acid cycle
▪ GTP gets converted to ____
• The remainder is stored in _____ and ______
electron transport
Transfer of electrons from reduced cofactors (NADH,
FADH2) to oxygen is called ___________
functionally linked
Electron transport and ATP generation are not independent processes; they are_____________ to each other.
electron transport chain (ETC).
Electron transfer is carried out as a multistep process
involving an ordered series of reversibly oxidized electron carriers functioning together.
• This is called the ________________
inner mitochondrial membrane, plasma membrane
The ETC contains a number of integral membrane proteins that are found in the ____________________ (or ___________ of bacteria)
I, III, and IV
Complexes _________ are found in the inner
mitochondrial membrane
II
Complex __ is involved in succinate oxidation
10 protons are pumped from the matrix into
the intermembrane space
For each pair of electrons transported through complexes
I, III, and IV, _______________________________
Complex I, NADH dehydrogenase
__________ transfers electrons from NADH to CoQ and is called the NADH–coenzyme Q oxidation complex (or____________ )
FMN cofactor
Complex I receives electrons from NADH and transfers them to a bound ________. The electrons are transferred to an Fe-S center, which passes them to a mobile pool of CoQ
Fe-S center, CoQ
Complex I transfers the electrons to an Fe-S center, which
passes them to a mobile pool of ___
4 protons
From complex 1 when 2 electrons are transferred, _____ are pumped across the membrane
Complex II
transfers electrons from succinate to FAD (generating FADH2; this is reaction CAC-6). The electrons in FADH2 are transferred through three Fe-S centers to CoQ
0
In complex II _ protons are pumped during this reaction
succinate–coenzyme Q oxidoreductase complex, or succinate dehydrogenase
This complex(II) is called the ____________________
cytochrome complex
Complex III is called the _____________ because two
cytochromes are prominent components
coenzyme Q–cytochrome c oxidoreductase complex
Complex III is also called ____________________________ because it accepts electrons from CoQ and transfers them to cytochrome c
4
In complex III when 2 electrons are transferred, _ protons are pumped across the membrane
cytochrome c oxidase
Complex IV is called ____________
Fe atom in the heme, cytochrome a3, copper atoms
In complex IV electrons transfer from cytochrome c to an __________, A cofactor of cytochrome a then to _________. There are two ________ which each receive one electron
four electrons
In complex IV, _____________ are needed to reduce O2 to H2O
two
In complex IV, ___ protons are pumped across the membrane for each electron pair
Cytochrome c oxidase (complex IV)
is the terminal oxidase, transferring electrons directly to oxygen
Cyanide and azide ions, Fe-Cu
_____________ are poisons
– bind the ____ center of cytochrome c oxidase, blocking final electron transport
DNA and protein synthesizing
Mitochondria contain their own ________________
machinery
cytosol
more than 95% of proteins residing in the mitochondria
are encoded by nuclear DNA and synthesized in the _______
– Complex I, II, III, IV proteins
– tRNAs
– Mitochondrial rRNA
Genes encoded by mito DNA include
Complexes I and III, incomplete reduction
______________ can also transfer electrons to oxygen,
resulting in its ___________
O2, H2O2
Complex I and III transfering electrons to oxygen can generate toxic superoxide anion ____ or hydrogen peroxide ______, both of which contribute to cellular aging
antioxidants
Role of _________ in cells is to soak up these highly
reactive oxidants(O2, H2O2) and prevent cellular damage
mitochondrial inner membrane
The electron transport chain generates a proton gradient
across the ___________________
ATP synthesis
The electrochemical proton gradient drives ___________
electrochemical proton gradient
The crucial link between electron transport and ATP production
is an ________________________
coupled
ATP synthesis is _______ to electron transport
peter mitchell
In 1961 __________ proposed the chemiosmotic coupling model
electrochemical potential across a membrane
The essential feature of the chemiosmotic coupling model is that the link between electron transport and ATP formation is the _________________
respiratory complexes
The electrochemical potential is created by the pumping of
protons across a membrane as electrons are transferred
through the _______________
NADH, 10 protons
The transfer of two electrons from _______ is accompanied by the pumping of a total of _________
2.5 - 3 ATP
_______ per NADH oxidation
1.5 - 2 ATP
________ per FADH2 oxidation
glycolysis and TCA
Some of the energy of glucose is stored in reduced NADH
and FADH2
– Generated in both _____ and _____
F1Fo ATPase
_________ generates ATP by coupling H+ transport with ATP
synthesis
inner membrane
The F1 complex is attached to the Fo complex that is embedded in the ______________
proton translocator
Fo acts as a ____________, the channel through which protons flow across the membrane
Fo
provides a channel for exergonic flow of protons across
the membrane
F1
carries out the ATP synthesis, driven by the energy of the proton gradient
ATP synthase.
Together(F1 and Fo), they form a complete ___________
two, ten
Fo subunit has ___ b subunits, and __ c subunits
static, gear
The a and b subunits are _____. The c subunits form a ring that act as a ____ and can rotate
a subunit
The ________ is the proton channel
two b subunits
The _________ form the stator stalk, which connects the Fo and F1 complexes