Microecon exam 22-25
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Market Structure
environment that influences output and pricing
perfect competition
A theory of market structure based on four assumptions: (1) There are many sellers and buyers
(2) the sellers sell a homogeneous good
(3) buyers and sellers have all relevant information
(4) entry into, and exit from, the market is easy.
(Demand curve is perfectly inelastic (horizontal))
public franchise
A firm’s government-granted right that permits the firm to provide a particular good or service and that excludes all others from doing so. (Think patents)
Natural monopoly
The condition in which economies of scale are so pronounced that only one firm can survive.
price searcher
A seller that has the ability to control, to some degree, the price of the product it sells.
Monopolists view
P > MR, P > MC, Price searcher
price taker
A seller that does not have the ability to control the price of the product it sells; the seller “takes” the price determined in the market.
Homogeneous product
essentially raw materials (cannot be more than one type)
Marginal revenue
change in TR resulting from sale of 1+ outputs (think change in revenue)
law of diminishing marginal returns
Marginal cost curve goes up and market supply goes up
profit maximization rule
Quantity of Output which MR = MC
Marginal Revenue =
Ch in TR / Ch in Q
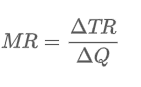
P = MC and Qd = MR
Only for a perfectly competitive firm
What are the steps to find price
Equate MR = MC
Compare Price to ATC
a. ATC < Price = profit
b. If ATC > price then go to 3
If loss then compare to AVC
a. Price > AVC = Good
b. Price < AVC = BAD
Resource allocative efficiency
output is at P = MC
Total revenue =
Price * Quantity
Total Cost =
Average Total Cost * Quantity
Total Variable Cost =
Average Variable Cost * Quantity
Profit =
Total Revenue - Total Costs
Total Revenue - (TVC + TFC)
Total Revenue - TFC
Should a perfectly competitive firm shutdown?
P > AVC → Firm produces
P < AVC → Firm shuts down
TR > TVC → Firm produces
TR < TVC → Firm shuts down
short-run (firm) supply curve
The portion of the firm’s marginal cost curve that lies above the average variable cost curve.
short-run market (industry) supply curve
The horizontal sum of all existing firms’ short-run supply curves.
Market supply curves are ____ sloping
upward
Long run competitive equilibrium
P = MC = SRATC = LRATC
Rise in Market demand = change in Equilibrium
Economic profit
should always be zero
when ATC and Price meet = zero
P = SRATC
productive efficiency
lowest ATC
Long Run Industry supply curves
A graphic representation of the quantities of output that an industry is prepared to supply at different prices after the entry and exit of firms are completed.
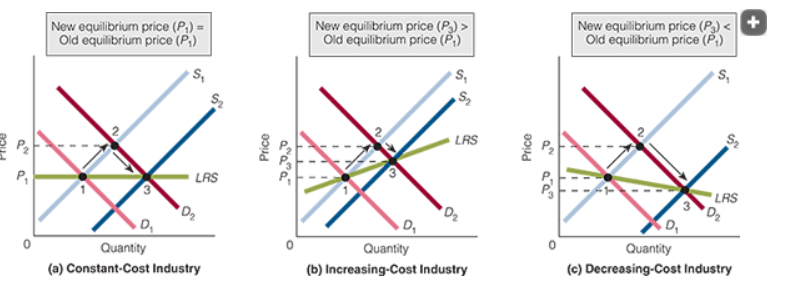
Increasing cost industry
An industry in which average total costs increase as output increases and decrease as output decreases when firms enter and exit the industry, respectively.
decreasing cost industry
An industry in which average total costs decrease as output increases and increase as output decreases when firms enter and exit the industry, respectively.
Monopoly
A theory of market structure based on three assumptions:
There is one seller,
it sells a product that has no close substitutes, and
the barriers to entry are extremely high.
Public Franchise
A firm’s government-granted right that permits the firm to provide a particular good or service and that excludes all others from doing so.
Natural monopoly
The condition in which economies of scale are so pronounced that only one firm can survive.
Perfect Competition vs. Monopoly
P ___ MR
P ___ MC
Price ______
Perfect Competition
P = MR
P = MC
Price Taker
Monopoly
P > MR
P > MC
Price searcher
deadweight loss of monopoly
The net value (the value to buyers over and above the costs to suppliers) of the difference between the competitive quantity of output (where ) and the monopoly quantity of output (where ); the loss due to not producing the competitive quantity of output.
X - Inefficiency
The increase in costs, due to the organizational slack in a monopoly, resulting from the absence of competitive pressure to push costs down to their lowest-possible level.
Price Discrimination
A price structure in which the seller charges different prices for the product it sells and the price differences do not reflect cost differences.
perfect Price Discrimination
A price structure in which the seller charges the highest price that each consumer is willing to pay for the product rather than go without it.
second degree Price Discrimination
A price structure in which the seller charges a uniform price per unit for one specific quantity, a lower price for an additional quantity, and so on.
third degree Price Discrimination
A price structure in which the seller charges different prices in different markets or charges different prices to various segments of the buying population.
Conditions of Price discrimination
The seller must exercise some control over price; that is, it must be a price searcher.
The seller must be able to distinguish among buyers who are willing to pay different prices.
Reselling the good to other buyers must be impossible or too costly.
Arbitrage
Buying a good at a low price and selling it for a higher price.
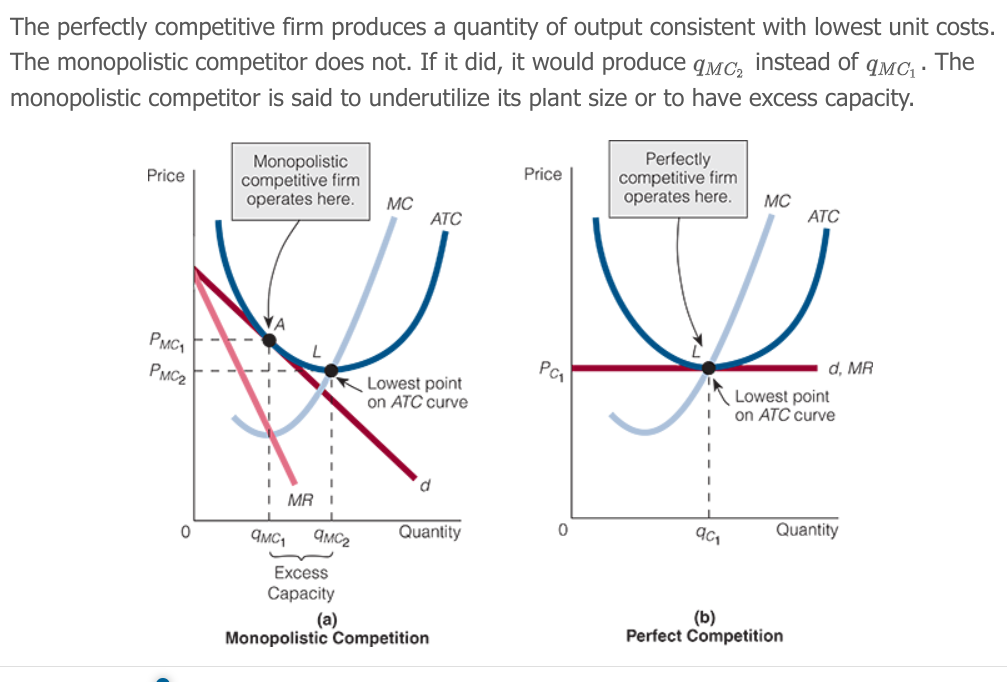
monopolistic competition
A theory of market structure based on three assumptions:
many sellers and buyers
firms producing and selling slightly differentiated products
easy entry and exit.
The perfectly competitive firm has ____ rivals all producing the same good with _______ substitutes
many, endless
in the perfectly competitive firm the elasticity of demand is so ____ that it is _____
high, horizontal
A monopoly firm has ______ ___ rivals and produces a good with _____ substitutes
practically no, no
In a monopoly firm the elasticity of demand is ___ so the demand curve is _____ ______
low, downward sloping
The monopolistically competitive firm has _____ rivals, producing a ______ ______ product
many, slightly differentiated
The monopolistically competitive firm has an elasticity of demand that is not as ____ as it faces a ______ sloping curve
high, downward
Excess Capacity Theorem
A monopolistic competitor in equilibrium produces an output smaller than the one that would minimize its costs of production.
oligopoly
A theory of market structure based on three assumptions:
few sellers and many buyers,
firms producing either homogeneous or
differentiated products, and significant barriers to entry.
Concentration ratio
The percentage of industry sales (or assets, output, labor force, or some other factor) accounted for by x number of firms in the industry.
(Cr4 = % industry sales accounted for by 4 largest firms)
(Cr8 = % industry sales accounted for by 8 largest firms)
A high concentration implies _____ make up the industry
few sellers
a low concentration implies _____ _____ __ ____ make up the industry
more than a few sellers
Cartel Theory
oligopoly firms act as one
(reduces output and increases price to increase joint profits)
Problems with a Cartel
Forming it
Forming Policy
entry into industry
cheating
Cartel Theory
A theory of oligopoly in which oligopolistic firms act as if there were only one firm in the industry.
Game Theory
A mathematical technique used to analyze the behavior of decision makers
What is the prisoners dilemma outcome?
individual rational behavior = inefficient joint outcome
When an oligopoly enters into a cartel it creates a _____ ______ so some ______ must enforce agreement
prisoner dilemma, entity
contestable market
A market in which
entry is easy and exit is costless,
new firms can produce the product at the same cost as current firms, and
exiting firms can easily dispose of their fixed assets by selling them.
Trust
A monopoly
A combination of firms that come together to act as a monopolist.
Antitrust law
Legislation passed for the stated purpose of controlling monopoly power and preserving and promoting competition.
Antitrust legislation =
helps create more competition, (more towards perfect competition
Sherman Act
Passed to deal with mergers of companies
Prohibits monopolies/combinations in restraint of trade.
(Basically = NO Monopolies)
Clayton Acts
Price discrimination (EX. different prices same product)
Exclusive dealing (EX. Selling to someone who cant use rival products)
tying contract (EX. arrangement where sale of one product is dependant on sale of another)
acquiring a competitor if that reduces competition
(basically made many business practices illegal)
Federal Trade Comission Act
Declares unfair methods of competition in commerce illegal
marked creation of FTC
(declares acts that are too aggressive in competition illegal)
Robinson-Patman Act
passed to increase small business success rate by protecting them from large chain stores
prohibits suppliers from offering special discounts to large chain stores only
wheeler-lea act
Empowers the FTC to deal with false and deceptive acts or practices (EX. False Advertising)
Celler-kefaver anti merger Act
closed merger loophole in Clayton act
market definition
defines whether or not a company is a monopoly
concentration ratios
gauges amount of competition in an industry
Herfindahl index
An index that measures the degree of concentration in an industry, equal to the sum of the squares of the market shares of each firm in the industry.
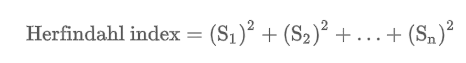
Horizontal merger
A merger between firms that are selling similar products in the same market.
vertical merger
A merger between companies in the same industry but at different stages of the production process.
conglomerate merger
A merger between companies in different industries.
network good
A good whose value increases as the expected number of units sold increases.
lock in effect
The situation in which a product or technology becomes the standard and is difficult or impossible to dislodge from that role.
How to regulate the natural monopoly
Price regulation
(MC Cost pricing)
profit regulation
(ATC = QD so only earns zero economic profit)
output regulation
(mandate quantity of output)
Regulatory lag
The period between the time a natural monopoly’s costs change and the time the regulatory agency adjusts prices to account for the change.
capture theory of regulation
A theory holding that, no matter what the motive is for the initial regulation and the establishment of the regulatory agency, the agency eventually will be captured (controlled) by the special interests of the industry being regulated.
(controlled by special interests of industries being regulated)
public interest theory of regulation
A theory holding that regulators are seeking to do—and will do through regulation—what is in the best interest of the public or society at large.
(controlled by interest of public or society)
public choice theory of regulation
A theory holding that regulators are seeking to do—and will do through regulation—what is in their best interest (specifically, to enhance their power and the size and budget of their regulatory agencies).
(controlled by wanting to enhance regulatory agency)
What theory/theories of regulation have lots of data?
Capture theory
public choice
What theory/theories of regulation have little data?
Public interest