Mitosis and Meiosis
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The notes from class on these topics in flashcard form.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
The Phases of the Cell Cycle:
Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, and Cytokinesis
Mitosis
One cell divides to form two or more cells, a division of only the nucleus, helps to replace any damaged or worn out cells.
Interphase (growing phase)
Doubling occurs
DNA doubles
Organelles double
Size doubles
Chromatin are long strands of DNA only in Interphase
Cell growth occurs
Prophase
Chromosomes condense
Chromosomes match and pair up
Nuclear membrane disappears
Centrioles move to the poles
Division of Sister Chromatids occur
Chromosomes are visible
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle
Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres (the chromosomes in the middle)
Anaphase
Spindle Fibers pull apart the centromeres, pulling them to one side (splitting them in half)
Half the centromeres are on one side, half on the other
Chromosomes are distributed equally to daughter cells
Telophase
Cytoplasm begins to tear
Cleavage furrow forms
New nuclear membranes form
Cytokinesis
One cell becomes two daughter cells
Two identical cells are formed
Cytoplasm divides
Sister Chromatids
Two identical chromosomes that pair up during mitosis, match up during Prophase and split during Anaphase
Pollination
Pollen comes into contact with the stigma, pollen grains form a pollen tube down the style to the ovary
Fertilization
Pollen fuses with a ovule, flowers and stamen wither, and the ovary develops into “fruit” to protect the next generation of seeds
Sepals
Green, leaf-like structures that protect the bud, then the base of the petals
Petals
The most visible part of the flower. It is like this so animals can be attracted by it, and pollinate it with another flower. Colors and smells attract animals.
Reproductive Parts
Flowers with both male and female parts are called “complete” or “perfect” flowers. Female inside, male on top. Reproductive parts are used to continue a species.
Germination
The process of a seed sprouting roots in the soil and anchoring the plant
Reproduction Process of Plants
Sends pollen to the stigma, the pollen makes a tube to the ovaries. After fertilizing, it loses it’s petals+stamen and starts to protect the seeds using fruit
Sepal

Ovary

Petals

Style
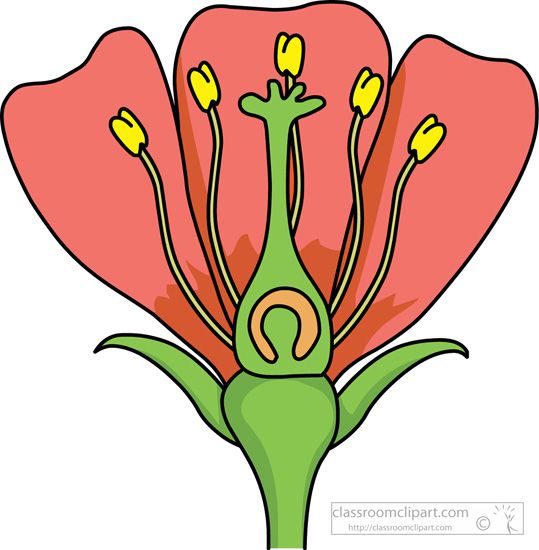

Stigma

Pistil
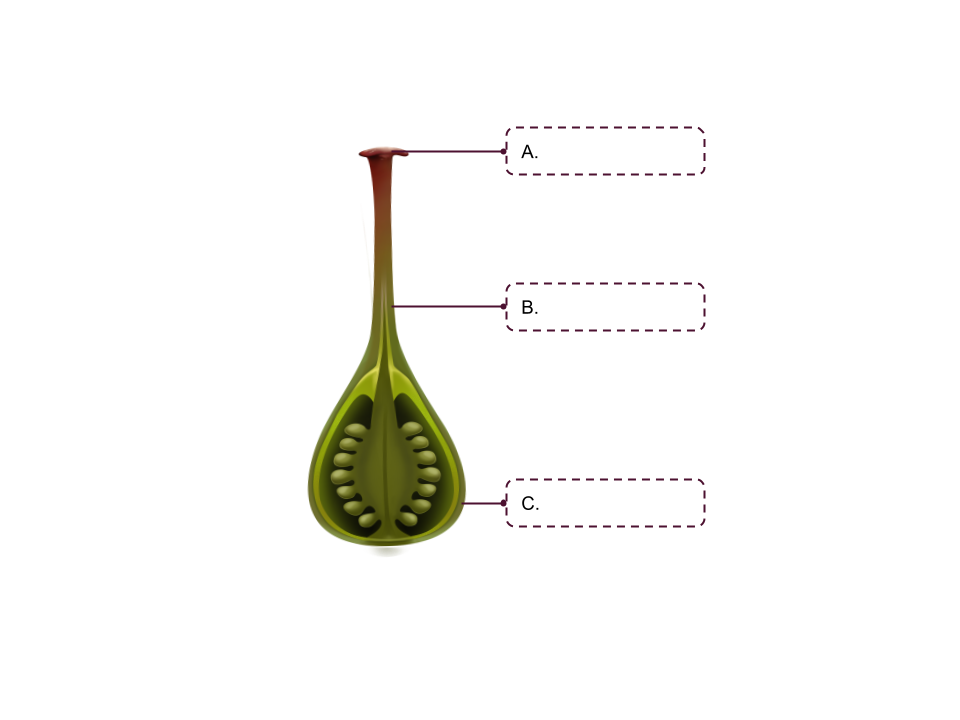
Stamen

Anther
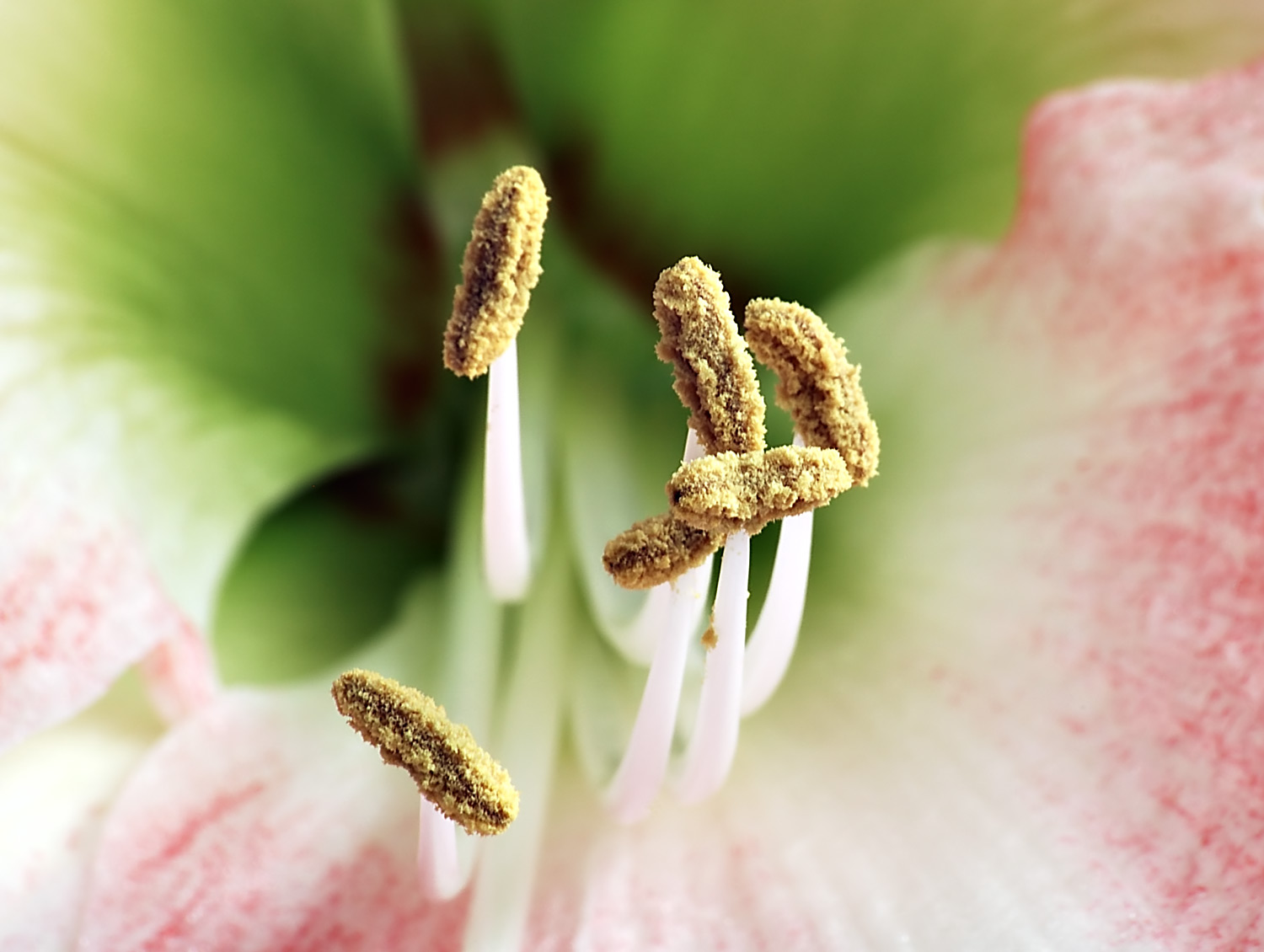

Filament
