Small Animal Cardiology
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What valves can you typically see at the base of the heart?
Pulmonic and aortic
What valves can you typically hear at the apex of the heart?
Mitral and tricuspid
What is an extra heart sound usually called?
Gallop - heard in cats or dogs w/ DCM
Identify the heart sound:
Atrioventricular valve closing?
S1
Identify the heart sound:
Semilunar valve closing?
S2
Identify the heart sound:
Ventricular filling
S3
Identify the heart sound:
Atrial contraction
S4
When are we most likely to hear a gallop rhythm?
S3 - Ventricular filling
How do we grade a Heart murmur?
Loudest audible sound location will determine the murmur
Grade the murmur:
Faint murmur less intense than normal heart sounds?
Grade 1
Grade the murmur:
Slight murmur - heart sound is equal to murmur sound
Grade 2
Grade the murmur:
Moderate murmur - Murmur louder than heart and may radiate to both sides of chest?
Grade 3
Grade the murmur:
Loud - No normal heart sounds heard
Grade 4
Grade the murmur:
Very loud Palpable thrill
Grade 5
Grade the murmur:
Loudest possible - can hear w/out stethoscope
Grade 6
Atrioventrical (Tricuspid and mitral) murmurs are head in the ___ phase and will have the ___ intesity all the way through?
Systole (S1-S2)
Same intensity - plateau shaped
Semilunar (Pulmonary and aortic) murmurs are head in the ___ phase and are known as ___ murmurs?
Systole (S1- S2)
Ejection murmurs - turbulent blood flow
Ejection murmurs are more likely to be ___ in dogs?
Congenital
What is the most common type of ejection murmur in a cat?
HCM -acquired (can be congenital)
Where are most diastolic murmurs heard?
At all valves (S2-S1)
What does a weak femoral pulse suggest?
Less than 25% of systolic value and hypotension and aortic stenosis
What does a bounding femoral pulse suggest?
Low diastolic pressure in the case of PDA or aortic insufficiency
What position should an animal be in for an ECG?
R lateral
Identify where the following electrodes should go?
White
Black
Red
Green
White: FR
Black: FL
Red: HL
Green: RR
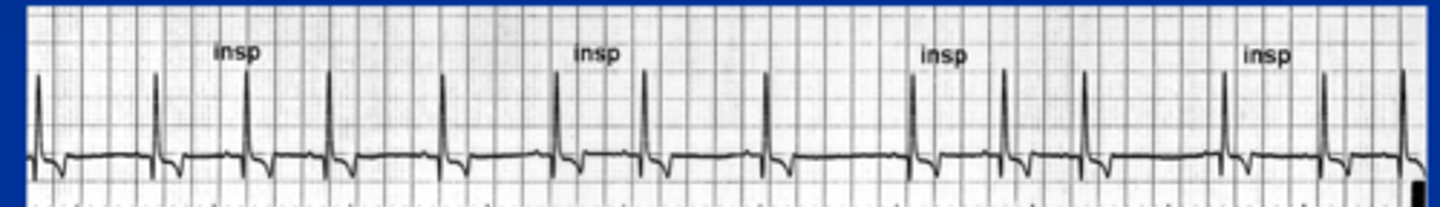
Identify the type of arrhythmia?
Sinus arrhythmia
What is the X axis of an ECG?
Speed/ time (Measured 50mm/s)
What is the Y axis of an ECG?
Sensitivity (10mm/mV) - full
How do you find HR on an ECG?
(# of boxes between 2 RR intervals @50mm/sec x 0.02s)/ 60s
A bic pen = how many ECG boxes?
30
How do you get an indirect Doppler bp?
Inflate cuff until there is no more signal and go 20mmHg beyond this point. Then deflate cuff until signal returns to find systolic BP.
What should be recorded in regards to indirect doppler BP?
5-7 consistent reading (discard 1st)
Cuff size
Measurement site
Pt recumbency
Pt demeanor
What is VHS?
vertebral heart score - diff between heart size and body length
The VHS should not be above what?
10.5
What is the VLAS?
Vertebral L atrial size
At what VLAS measurement would we consider the L atrial enlarged?
Greater than 2.3
At what VLAS measurement would we start vetmedin?
Greater than 3