quiz seven - membranes II (active transport)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
passive transport
no ATP cost, moves with concentration gradient
types of passive transport
diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
diffusion
small molecules can diffuse across phospholipid bilayer
facilitated diffusion
passive transport via transmembrane or carrier proteins
allows larger/charged molecules to diffuse
active transport
requires ATP and carrier proteins, moves against concentration gradient
types of active transport
primary active transport and secondary active transport
primary active transport
uses ATP
secondary active transport
uses energy set up by direct active transport
types of transmembrane proteins
channel protein
carrier protein
channel protein
opening in center, can be gated
carrier protein
changes shape, one end open at a time
types of carrier proteins
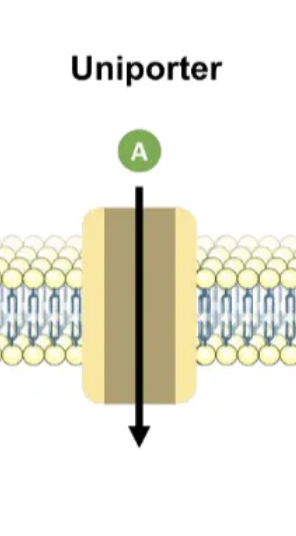
uniporter
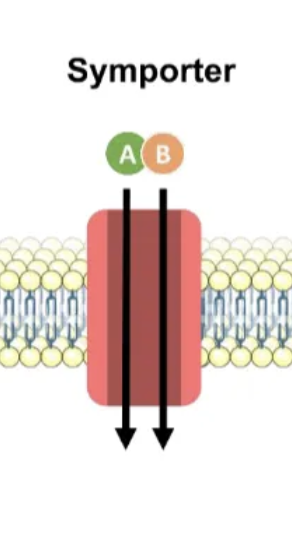
symporter
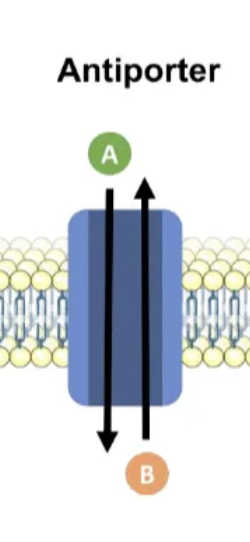
antiporter
uniporter
carrier protein, one molecule in one direction
symporter
carrier protein, 2 molecules in same direction
antiporter
carrier protein, 2 molecules in opposite directions
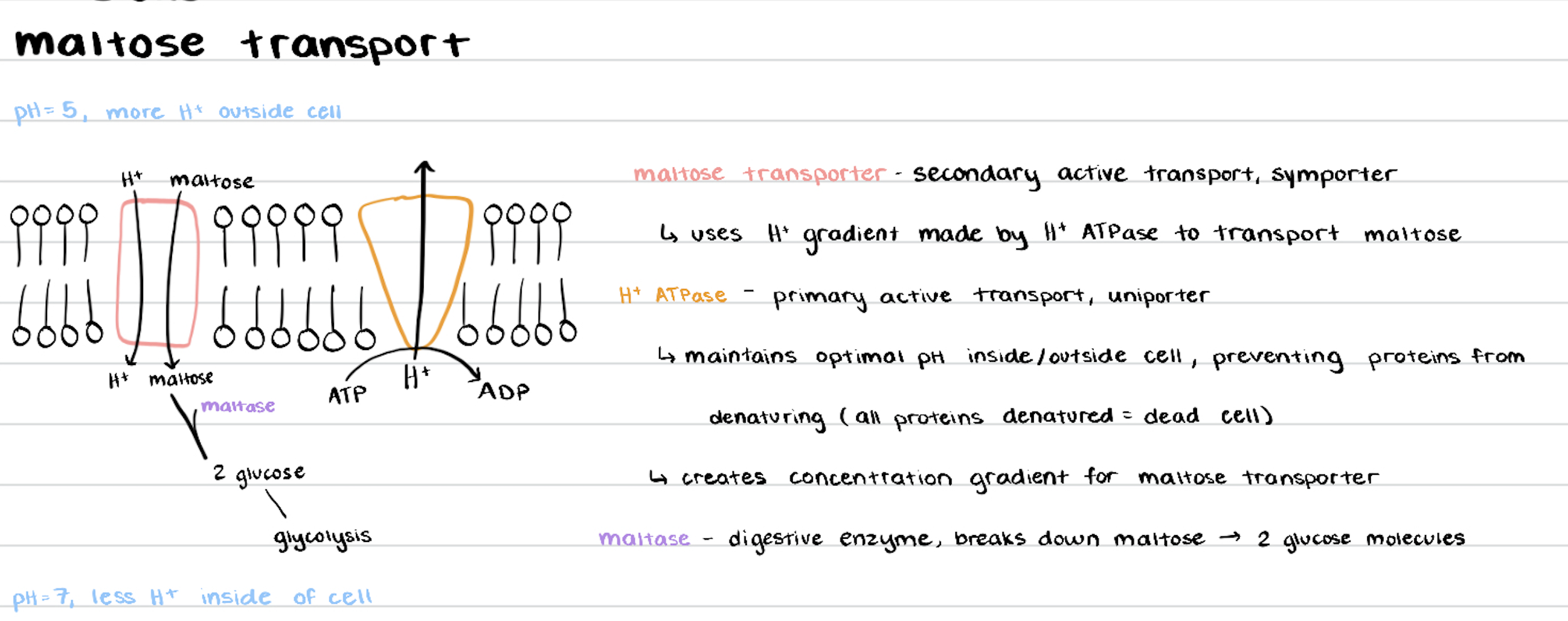
describe H+ ATPase function in maltose transport
primary active transport, uses ATP, uniporter
maintains optimal pH inside/outside cell, preventing proteins from denaturing (all proteins denatured = dead cell)
creates H+ concentration gradient for maltose transporter to use
describe maltose permease function in maltose transport
also known as maltose transporter
secondary active transport, symporter
powered by protein gradient made by H+ ATPase
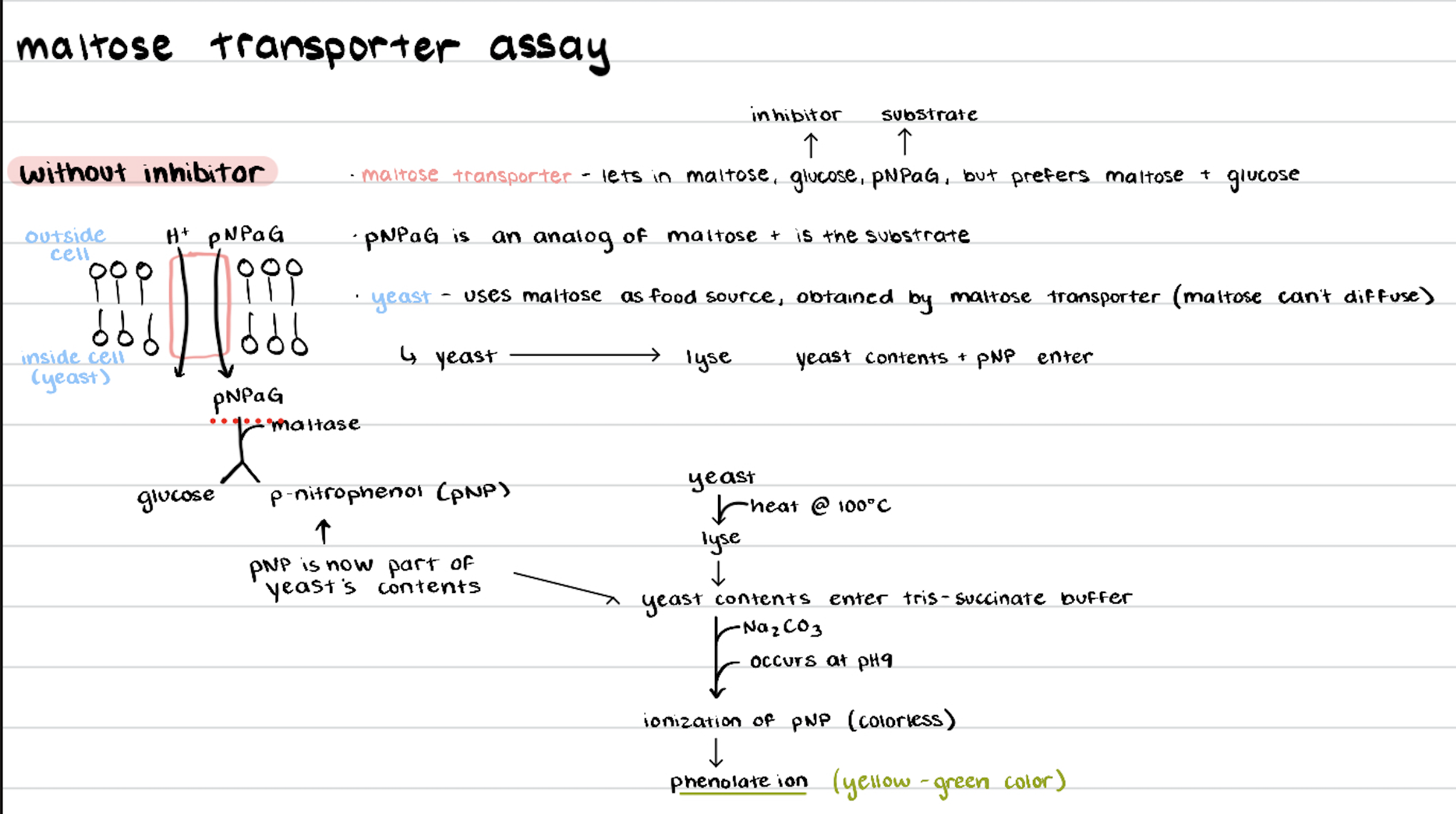
lets in maltose, glucose, pNPaG, but prefers maltose and glucose over pNPaG
maltase
enzyme that breaks down maltose → 2 glucose molecules
enters yeast cell through maltose permease/transporter
yeast
uses maltose as food source
maltose can’t diffuse through membrane, so maltose permease/transporter transports it into the cell
maltase breaks maltose → 2 glucose, which yeast cell uses
pNPaG breakdown
maltase breaks down pNPaG:
pNPaG + maltase → pNP (p-nitrophenol) + glucose
pNP at pH 9
pNP (colorless) → phenolate ion (yellow green color)
pNPaG and maltose relationship
pNPaG is an analog of maltose
analog
a molecule whose structure is similar to that of another molecule
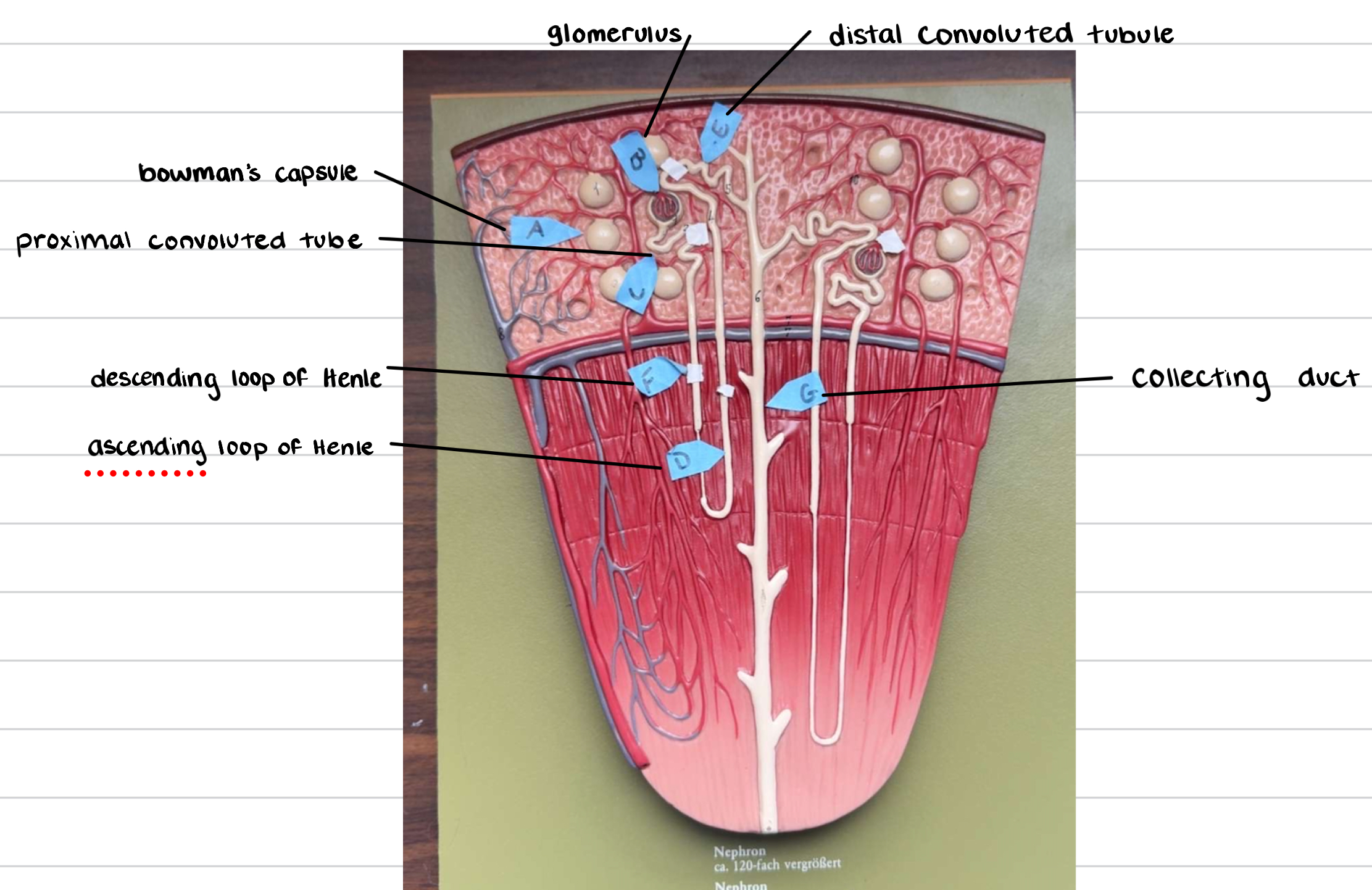
kidney functions - nephron
filtration, reabsorption, secretion
filtration of nephron
occurs in Bowman’s capsule
blood pressure forces fluid from glomerulus → capsule
filtrate contains water, urea, amino acids, and ions
reabsorption of nephron
occurs in proximal tubule, loop of Henle, distal tubule
reclaims essential molecules back into bloodstream (ions, nutrients, water)
maintains homeostasis
secretion of nephron
adds additional wastes from blood into nephron tubule
removes toxins, drugs, excess ions, and urea
calculating excretion of nephron
excretion = filtration - reabsorption + secretion
nephron
part of kidney, filters blood, reabsorbs what’s needed, secretes waste
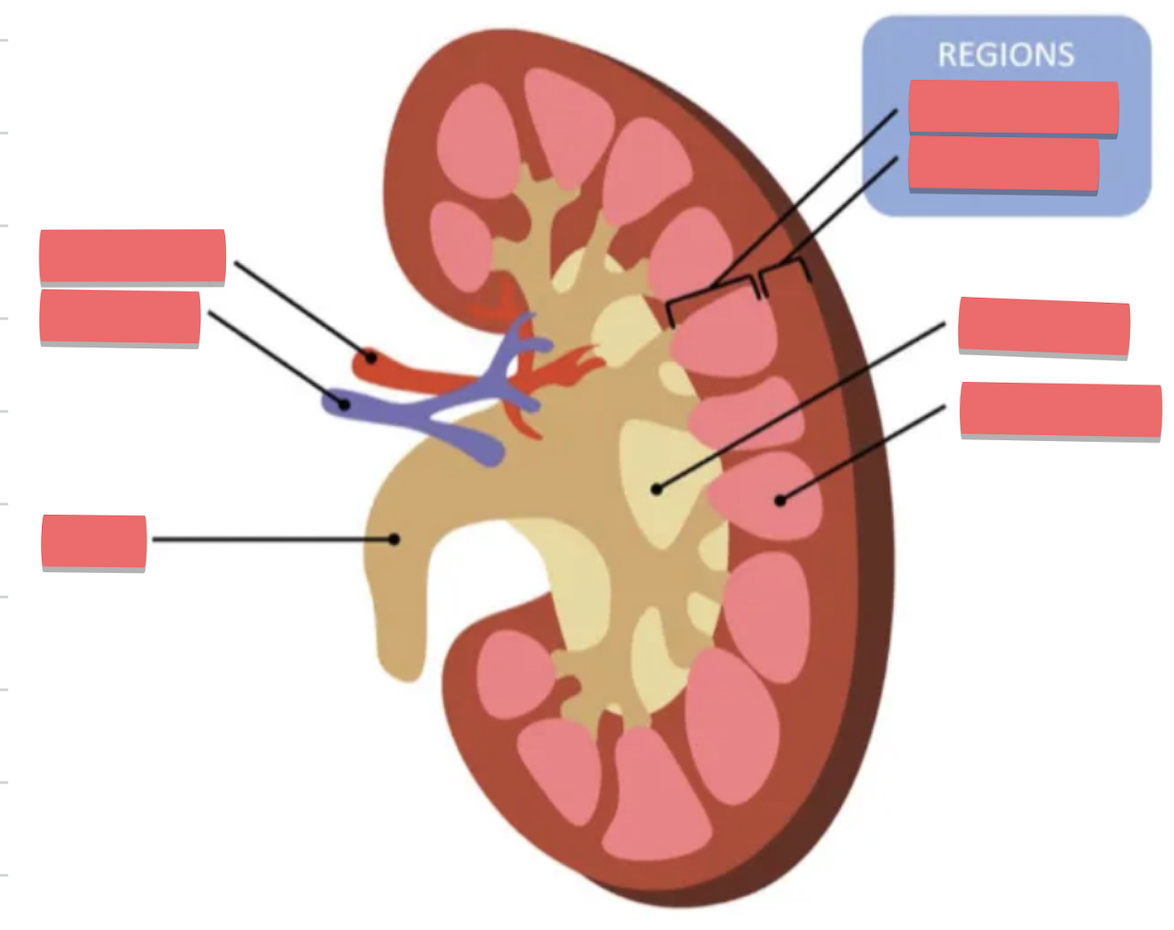
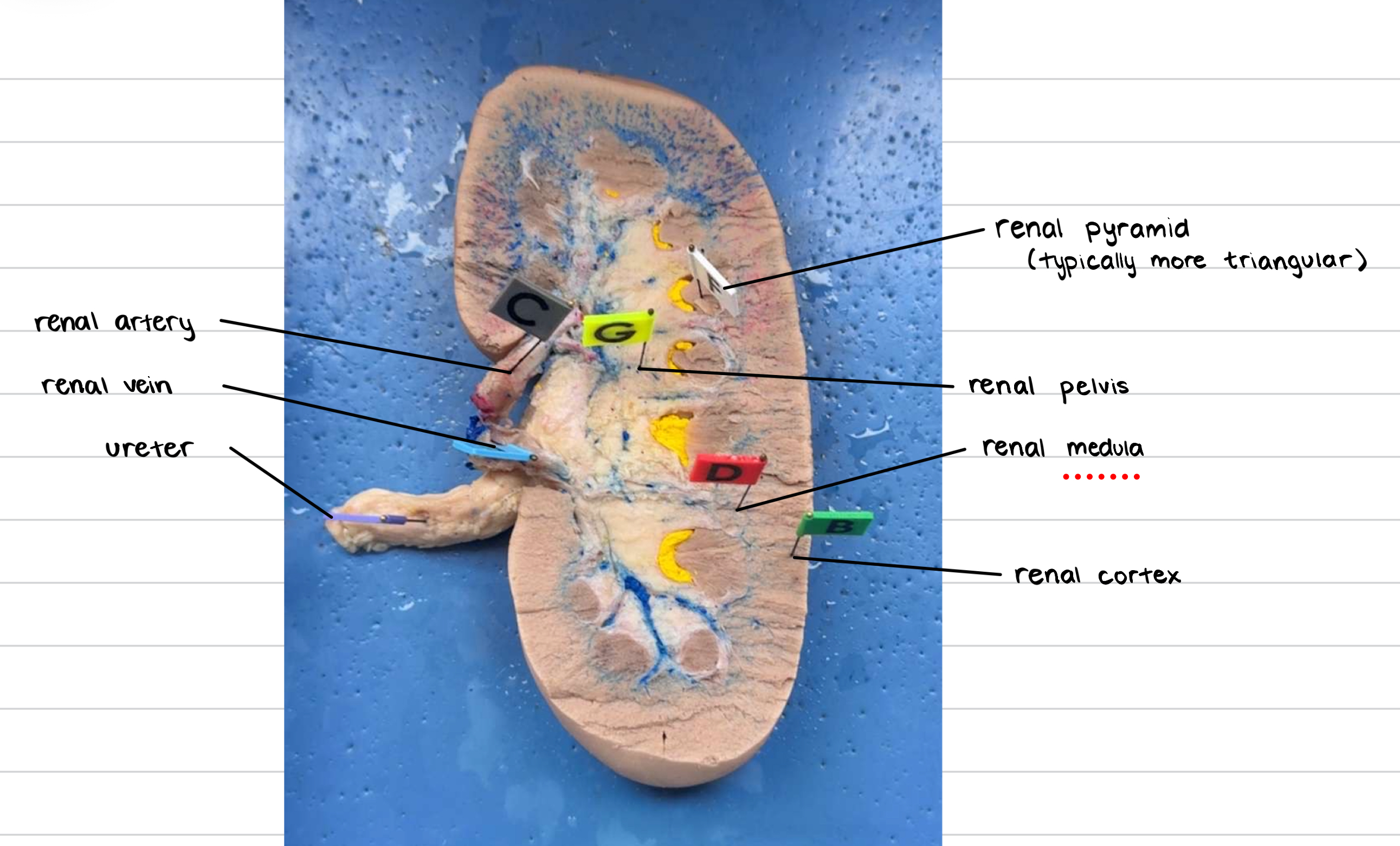
name the parts of the kidney
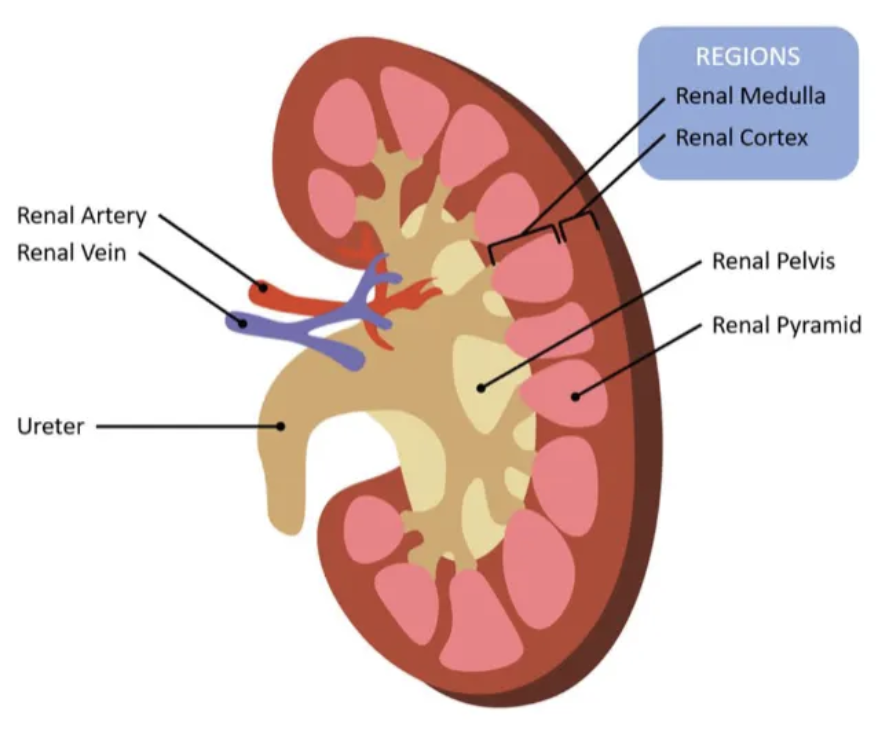
name the parts of the kidney
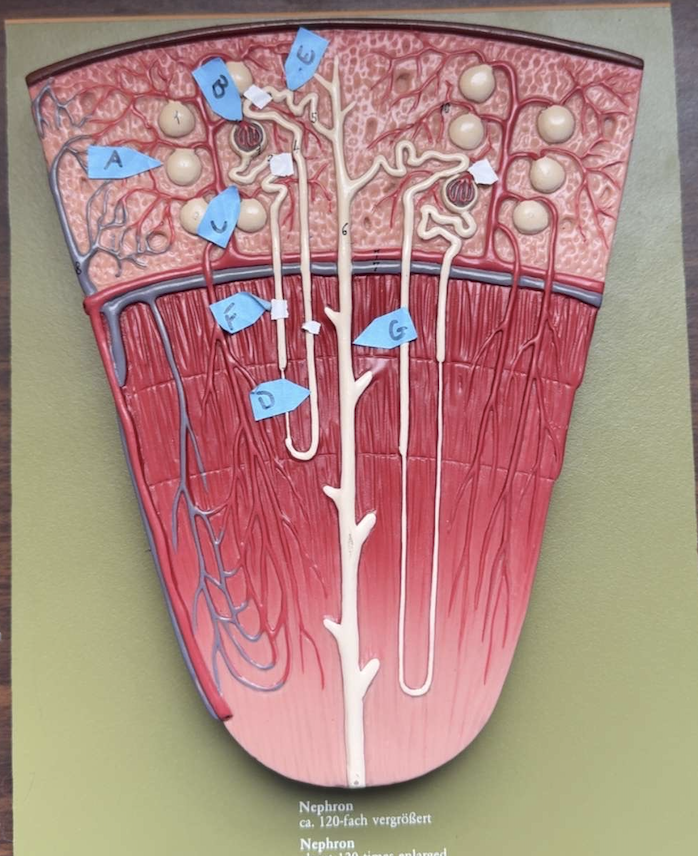
name the parts of the nephron
explain maltose transport
explain the maltose transporter assay WITHOUT inhibitor
explain the maltose transporter assay WITH inhibitor

what was the substrate in the maltose transporter assay?
pNPaG
what was the inhibitor in the maltose transporter assay?
glucose