unit 2.10-2.18: fight for abolition & revolts
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
freedom’s journal
1st black-owned US newspaper in 1827 (same year as NY abolished slavery)
spoke out for black political rights, voting rights, abolition, & against lynching
initially against the American Colonization Society but changed —> lost majority of readers & ceased
inspired other black-owned newspapers to establish

the liberator
influential abolitionist newspaper published by William Lloyd Garrison & Isaac Knapp — major force in the abolitionist movement (+ women’s rights)
strived for immediate & complete emancipation of slaves
ceased when 13th amendment was ratified
featured abolitionist articles, speeches, and editorials (ex. Maria W. Stewart)

the colored american newspaper
black-owned newspaper founded by Charles Ray & Samuel Cornish
advocated for social & political progress of free black communities as platform for activism
wanted peaceful, gradual emancipation of slaves
counter-narrative to proslavery rhetoric in the South
most famous article “why we should have a paper”

American Colonization Society (what & why)
white led organization that supported the emigration of free black americans out of the US back to Africa, the Caribbean, or Latin America (since it had similar climate to Africa)
colony of Liberia founded in Africa
many opposed b/c many were 3rd, 4th gen w/ little to no connection to Africa and/or was a way to preserve slavery
Paul Cuffee: 1st to lead expedition of 39 to Freetown, Liberia 1815
Reverend Jesse Jackson
coined the term “African-American” to promote cultural identity; pivotal role in Civil Rights Movement w/ MLK
St. Augustine
oldest inhabited Spanish colony in Spanish Florida that became a refuge for escaped enslaved people from British colonies
requirement: converted to Catholicism
establishment of Ft. Mose led by Francisco Menendez
Who led Ft Mose?
Francisco Menendez
Stono Rebellion
largest slave revolt in SC led by Jemmy w/ 20—>60ppl who killed and set fire to various plantations along the Stono River
resulted in stricter slave codes & the destruction of Ft Mose (since they were headed towards there)
Salzburgers
only colonists in favor of abolition in Georgia Colony (lower class whites) b/c fear of riots —> more fearful after Stono Rebellion in SC
around 300 german-speaking protestants
Ft Mose
1st legally free black community established in Spanish FL near St. Augustine
led by Francisco Menedez
Spanish allowed as long as converted to Catholicism
constitution of haiti - article 14
erased racial categories & divisions that had existed under french colonial rule to create a unified national identity; declared all Haitians would be known simply as black
who led the Haitian Revolution in 1791-1804?
Toussaint L’Ouverture
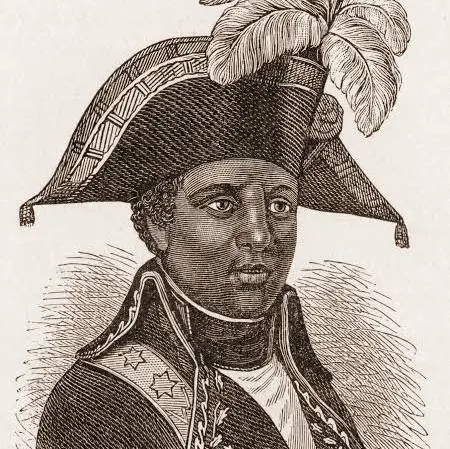

Haitian Revolution 1791-1804 (importance, who led, where, & what inspired it?)
only successful slave revolt that resulted in the establishment of Haiti as the 1st independent black republic + Haiti Constitution
Occurred in France’s most profitable colony Saint-Domingue in Haiti (around 773k ppl)
inspired by AM & French Rev
resulted in Haiti forever being in debt..
What two events inspired the Haitian people to revolt?
American Revolution (+ saw as unjust that FR aided them to gain freedom)
French Revolution (success for lower class)
Products of Saint Domingue in Haiti
Sugar, cotton, coffee, & indigo
why did the people of Haiti, including non-white, revolt (besides slavery)?
upset at high tariffs since they could only trade w/ FR
group included white plantation owners (didn’t have rep in FR gov), artisans, shopkeepers, and free/enslaved black population
German Coast Uprising AKA Louisiana Slave Revolt of 1811
largest organized slave rebellion in US history led by Charles Deslondes w/ 200+ armed & burned plantations
took place along the Mississippi River, moving towards New Orleans (port city) to leave AM through boat or settle free territory
significance: demonstrated courage and and impact on future resistances
__% were free African Americans in 1860
12
Mutual Aid societies
community-based organizations that provided social, economic, and emotional support to members (mostly freed)
response to discrimination & lack of support from mainstream
offered financial aid (through donations for funds), healthcare, burial services, & education
built community solidarity & advocated for civil rights
ex. African Union Society in Newport, RI
what 3 cities had the large populations of black people?
Philadelphia, NYC, & New Orleans
who wrote “why sit ye here and die?” & what was it about?
Maria W. Stewart — highlights mistreatment of free black people, especially women, from achieving education & economic opportunities to succeed b/c of racism (“little difference from slavery”)
has religious references
__ million enslaved ppl in brazil
10
“colored conventions”
black conventions that 1st occurred in Canada (no slavery) —> later US; purpose was to share identity, heritage, support mutual aid societies, & abolition
types of slave songs in brazilian music & culture
Capoeira
Congada
Capoeria
afro-brazilian marial art that combines dance, call&response, and music — practiced by slaves (mostly from Angola) in brazil as fighting resistance against oppression; influenced breakdancing

Congada
afro-brazilian cultural celebration of the King of Kongo & Our Lady of the Rosary through dance, music, & processions
combines African & Roman Catholic traditions
practiced by slaves under brazilian enslavement

Great Dismal Swamp
largest community settlement of Maroons located
Maroons
people who escaped slavery, born free, or self-emancipated
hid in private, unexplored, hard to find areas to evade slave patrol
created autonomous societies
ex. Great Dismal Swamp (b/w VA & NC), Seminoles in FL, Quilombos in Brazil, Pallenkays in Spanish AM
Seminoles
indigenous american tribe living in Spanish Florida 18th century who gave shelter to escaped enslaved Africans (Black Seminoles)
Black Seminoles aided against Spanish in 2nd Seminole war 1835
Quilombos
maroon communities of formerly enslaved people of african decent in brazil
palenques
maroon communities of formerly enslaved people of african decent in spanish america
why were military leaders in maroon communities needed? (+examples (what they do))
to direct defense & conduct treaties
ex. Bayano in Panama (led a major slave rebellion against spanish rule + alliance w/ pirates) & Queen Nanny in Jamaica
5 indigenous nations that eventually enslaved ppl
Creek, Cherokee, Choctaws, Chickasaw, Seminole
Paul Cuffee
led the 1st expedition of 39 ppl to Freetown, Liberia 1815
Martin Delany
believed “nation within a nation” (black & white), advocated for black self-determination & nationalism —> major supporter for emigration, & co-edited “The North Star” newspaper
served in union
frederick douglass
prominent abolitionist & feminist who published “the north star”
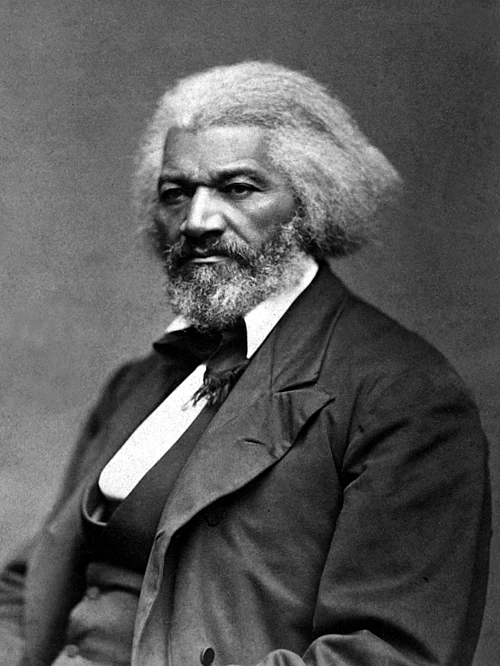
goal & belief of anti-emigration advocates
birthright citizenship (14th amdt)
abolition (freedom) + racial equality = political representation
so leaving the US wouldn’t make this possible
many believed it was a way to preserve slavery
“if there is no struggle, there is no progress” - Douglass
queen nanny
slave in jamaica, escaped & founded maroon community in blue mountains aka blue nanny, practiced folk magic w/ african religious roots, conducted raids on plantations —> freed around 1k

gabriel proser
planned 1st major slave rebellion, occurred in richmond, va —> found out & killed in 1800
Arkansas Petition for Freedmen’s Rights, 1869
a 1869 petition sent to the US Congress by members of the Arkansas General Assembly advocating for the rights of African Americans in the Choctaw and Chickasaw Nations
purpose: amend a 1866 treaty so freed people of African descent could remain in the Nations, be granted 40 acres of land, and receive the same rights and privileges as other citizens, including the right to vote.