optics types of light 10l
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
properties of light
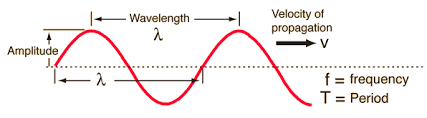
light energy travels very fast (c = 3.0 × 10^8 m/s)
light travels in a straight line but also as waves (electromagnetic waves)
radiates ( no medium needed)
electromagnetic spectrum
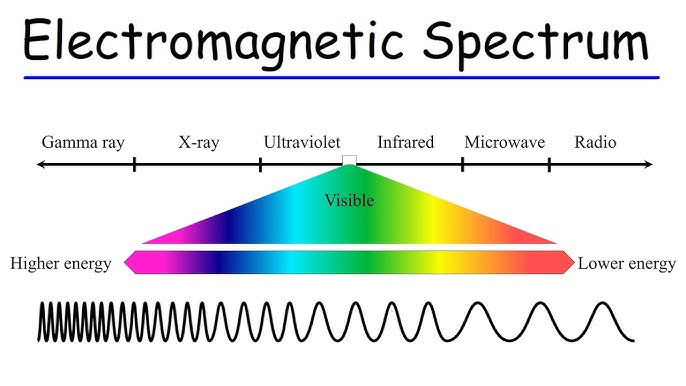
red has long waves but low energy
violet has high waves and high energy
radiation
form of electromagnetic energy ex. sunshine, x rays, radiant heating systems
light energy
form of electromagnetic radiation of a wavelength
photons - tiny packets of energy produced from the movement of atoms
incandescence
production of light as a result of high temp.
incandescnes light bulbs
electric discharge
process of producing light by passing an electric current through a gas
neon signs
lightening
fluorescence
(phosphors — hg → UV → phosphors) immediate
immediate emission of visible light, a result of the absorption of UV light
glow in the dark stickers
fluorscence lights
phosphorescence
producing light by absorption of UV light, resulting in the emission of visible light over an extended period of time
glow in the dark stickers
chemi and bioluminscence (chemical reaction)
direct production of light as the result of a chemical reaction w little or no heat produced
chemi - glow sticks
bio - fireflies
triboluminscennce
production of light from friction, result of scratching crushing or rubbing certain crystals
leds
light produced as a result of an electric current flowing in semiconductors
laser
has one continuous straight line, same wavelength so same colour
laws of reflection
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Oi and Or and normal lies in the same place
SALT
size - large small same
attitude - upright or inverted
location - object / image
type - virtual or real
virtual - light doesn’t meet and doesn’t interept usually the same orientation as an object can’t be projected, divergent
real - light converges and meets at a point
electromagnetic spectrum from highest to lowest
Gamma Rays
Used in cancer treatment (radiotherapy).
Emitted by radioactive substances and nuclear reactions.
Gamma-ray bursts in space.
2. X-Rays
Medical imaging (e.g., X-rays of bones).
Airport security scanners.
Used in astronomy to observe stars and black holes.
3. Ultraviolet (UV) Light
Causes sunburn (UV radiation from the Sun).
Sterilization of medical equipment.
Black lights and some insect traps.
4. Visible Light
Rainbow colors (ROYGBIV: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet).
Sunlight, light bulbs, and lasers.
5. Infrared (IR) Radiation
Heat emitted by objects (e.g., humans, stoves).
Used in remote controls and thermal imaging cameras.
Infrared astronomy to detect heat from celestial objects.
6. Microwaves
Microwave ovens.
Satellite communications (e.g., GPS, weather forecasting).
Radar systems.
7. Radio Waves
AM/FM radio broadcasting.
Television signals.
Cell phone and Wi-Fi communication.