ORTHO/MSK/TRAUMA
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
A patient with shoulder pain, with a positive Hawkins Test and Positive Neer Test likely has which pathology? What do these test?
Subacromial bursitis (pain of subacromial bursa). Hawkins test tests pain with abduction when shoulder is 90 degrees with internal rotation; Neer test is pain with shoulder forward flexion to 180 with shoulder internal rotation
What is the GCS Score?
Eyes
4 - Open
3 - Verbal
2 - Pain
1 - None
Verbal
5 - Oriented
4 - Confused
3 - Inappropriate words
2 - Incomprehensible sounds
1 - None
Motor
6 - Follows Commands
5 - Localizes Pain
4 - Withdraws to Pain
3 - Decorticate Posturing
2 - Decerebrate Posturing
1 - None
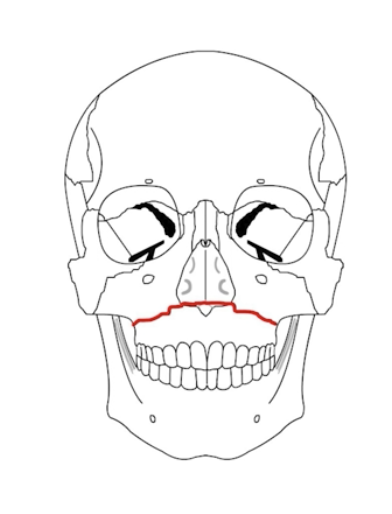
What is a LeFort 1 Fracture?
Transverse fracture separating the maxilla from the pterygoid plate and nasal septum.
(palate is mobile)
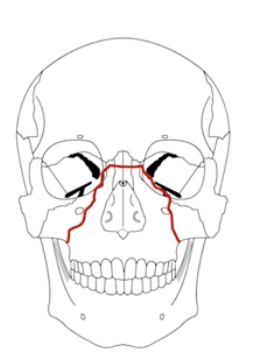
What is a LeFort 2 fracture?
Pyramidal fracture through the maxilla, orbital tib, nasal bridge, and hard palate
(nose and mouth mobile)
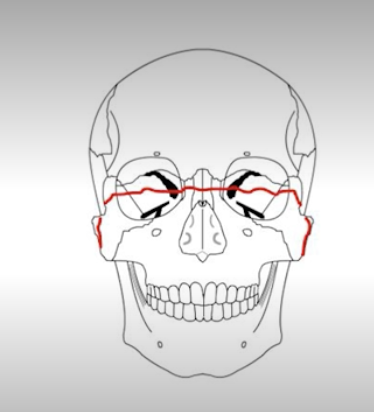
What is a lefort 3/4 fracture?
Lefort 3: Fracture through frontozygomatic sutures, orbits, nose, and ethmoids (face separated from skull)
Lefort 4: 3+frontal bone involvement
What is an Ellis Class 1 fracture, what color, and tx?
Ellis class 1: through enamel; WHITE COLOR tx is routine dental follow up
Whast is an ellis class 2 fracture, what color, and tx?
Ellis class 2: through enamel and dentin, YELLOW color, tx is calcium hydroxine and dental follow up
What is an ellis class 3 fracture, what color, and tx?
Ellis class 3: through enamel, dentil, and pulp, RED in color, Tx; calcium hydroxide and dental cement + ABX
When should an auricular hematoma be drained vs referred to ENT?
Needle aspiration if <2, otherwise I&D; if >7d refer to ENT with PRESSURE DRESSING
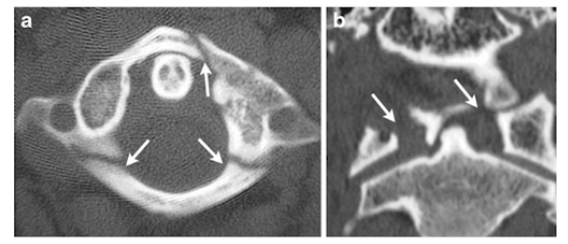
What is the fracture seen in the image below and how is it caused?
JEFFERSON (C1) FRACTURE caused by Axial Load
(Football player spearing another or diving into a shallow pool)

What is the fracture seen in the image below and how is it caused?
HANGMANS fracture (pedicles of C2) caused by a hyperextension injury
(classically due to hanging)

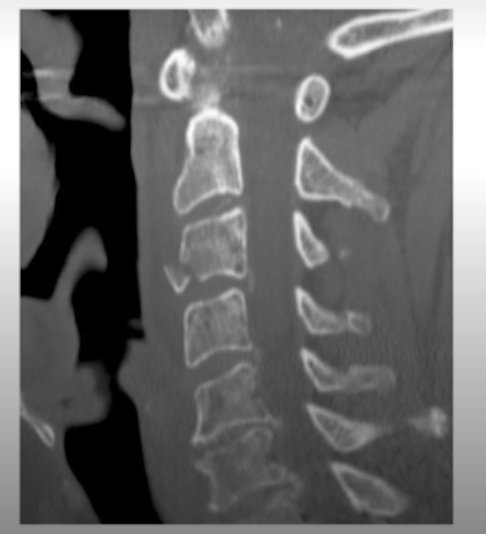
What is the fracture seen in the image below and how is it caused?
Flexion teardrop fracture of the vertebral body - results from extreme flexion. Often associated with ligamentous damage.
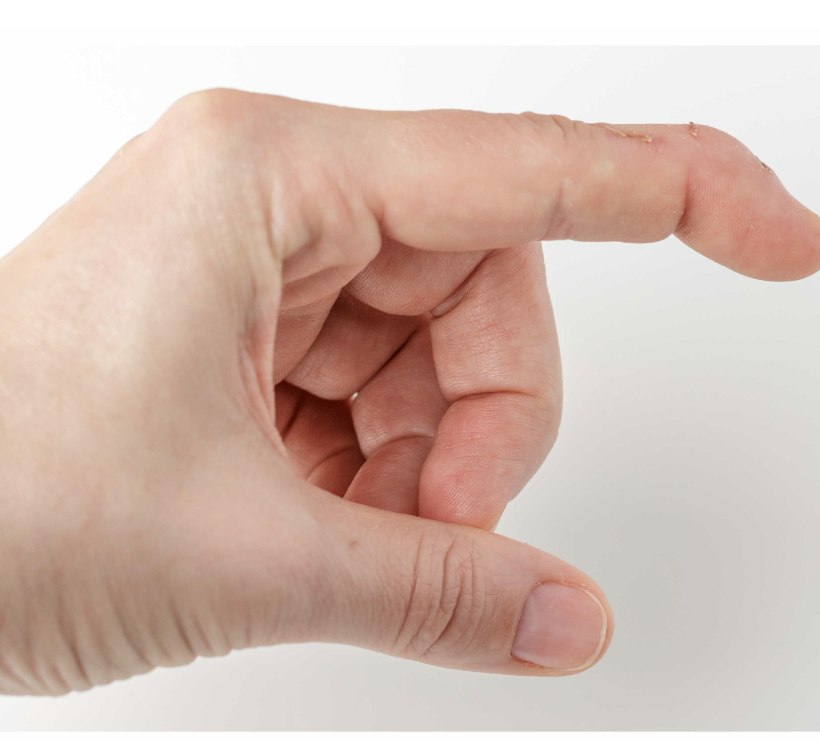


What is the deformity seen in the picture below?
Mallet finger - typically caused by hyperflexion of the DIP (from a ball most commonly)
This is due to disruption of the extensor tendon of the distal phalanx (thus held in flexion)

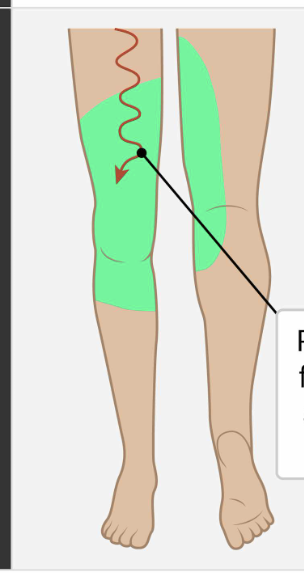
Which nerve root is responsible for the knee reflex, knee extension, hip adduction, and provides sensory innervation to the following area?
L3

Which nerve root is responsible for the knee reflex, knee extension, and provides sensory innervation to the following area?
L4
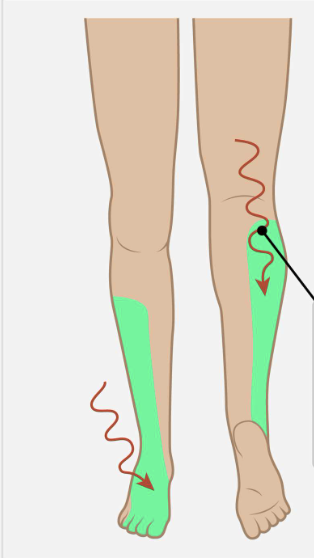
Which nerve root is responsible for foot and toe dorsiflexion, inversion/eversion and provides sensation to the following area?
L5
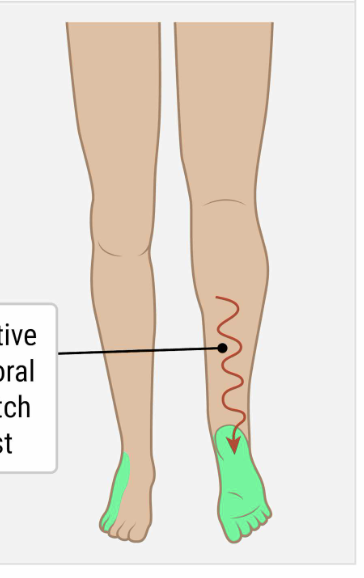
Which nerve root is responsible for the ankle reflex, knee flexion, plantarflexion, and provides sensory innervation to the following area?
S1

What type of fracture is shown in the image below?
GREENSTICK Fracture
Which nerve is commonly injured in a patient with a proximal fibular neck fracture? What deficits will the patient present with?
the common peroneal nerve (branch of sciatic nerve) which branches in to the superficial peroneal nerve and the deep peroneal nerve.
Foot eversion, foot dorsiflexion and toe extension.
Deficits = FOOT DROP
Which nerve injury would cause weakness in plantar flexion, inversion, and sensory loss over the sole of the foot?
Tibial nerve (POSTERIOR LEG)
What nerve is responsible for the sensation to the medial leg?
Saphenous nerve (branch of femoral nerve)
Asking the patient to make an “OK” sign is testing which nerve of the hand?
Median nerve
What motor and sensory function is the radial nerve responsible for? Damage to the radial nerve will cause what symptoms & what is this seen in?
MOTOR - WRIST EXTENSION
SENSATION - dorsum of hand (thumb/index, middle)
Saturday night palsy - compression of radial nerve in the axilla, which presents as WRIST DROP (inability to extend).
What is the ER treatment for a proximal humerus fracture?
Sling
Ortho referral
ORIF if multiple parts are displaced
What is the management of a humeral shaft fracture? What are the complications?
Closed & non-displaced: Coaptation splint or sling
Open, displaced: ortho consult
COMPLICATIONS: Injury to the Brachial artery, Injury to RADIAL nerve
What is a Monteggia Fracture? Mgmt? Which nerve is damaged?
Ulnar Fracture + Radial head dislocation (usually due to FOOSH)
Mgmt: Reduce, Long arm splint, ORIF
RADIAL NERVE
GRUesome MURder
What is a Galeazzi Fracture? Mgmt? Which nerve can be damaged?
Distal Radius shaft fracture + Ulnar dislocation
Mgmt: Reduction, sugar tong splint, ORIF
ULNAR NERVE DAMAGED
GRUesome MURder
What splint should be used for a elbow dislocation?
Long arm split with 90 degrees flexion
What is the treatment of a supracondylar fracture? What are the vessels that are damaged?
Displaced —> ORIF
Non-displaced —> long arm posterior splint
Damage to brachial artery, medial nerve
What is the management of a radial head/neck fracture if non-displaced vs displaced?
Non-displaced: Sling, ortho follow up
Displaced: Long arm posterior splint, ortho follow up
NOTE: XRAY MAY BE NORMAL!
What are the bones of the hand?
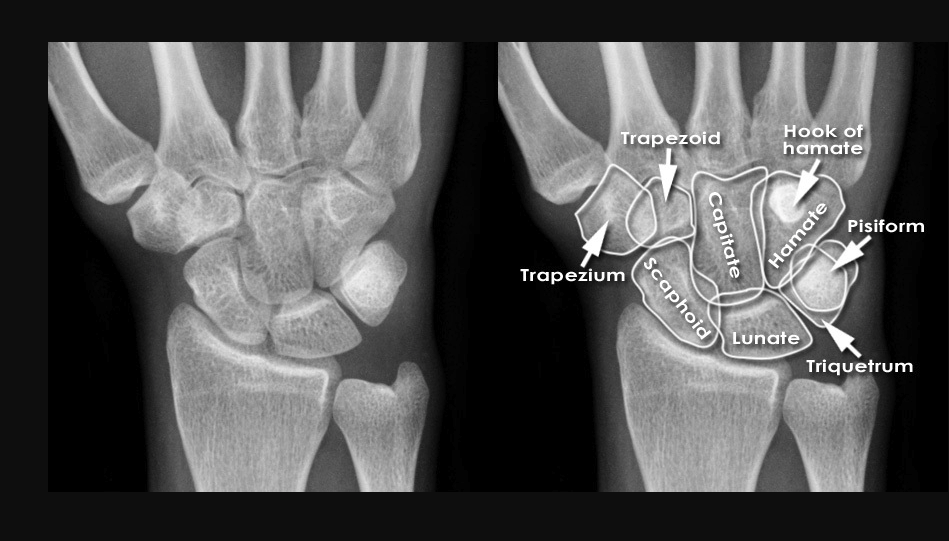
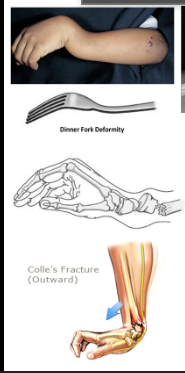
What is a Colles Fracture? Mgmt?
Distal Radius Fracture with dorsal displacement
Non-displaced: Sugar tong split
Displaced: Reduction, Splint
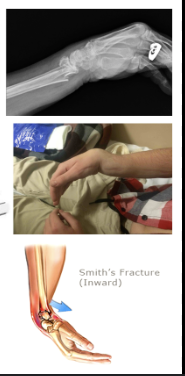
What is a SMITH fracture? Mgmt?
Distal Radius Fracture with volar displacement
Non-displaced: Sugar tong splint
Displaced: reduction, splint
What is the management of a scaphoid fracture?
THUMB SPICA SPLINT, ortho follow up
RISK OF AVASCULAR NECROSIS


What is the abnormality seen in the XR below? Management?
Scapholunate dissociation
THUMB SPICA SPLINT
Ortho follow up

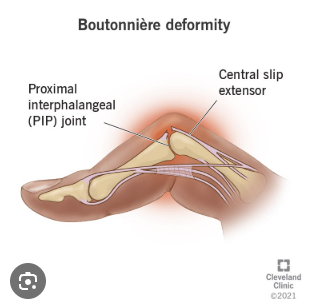
What is the abnormality seen in the image below?
Boutonniere deformity - damage to the proximal extensor tendon causes hyperflexion of finger
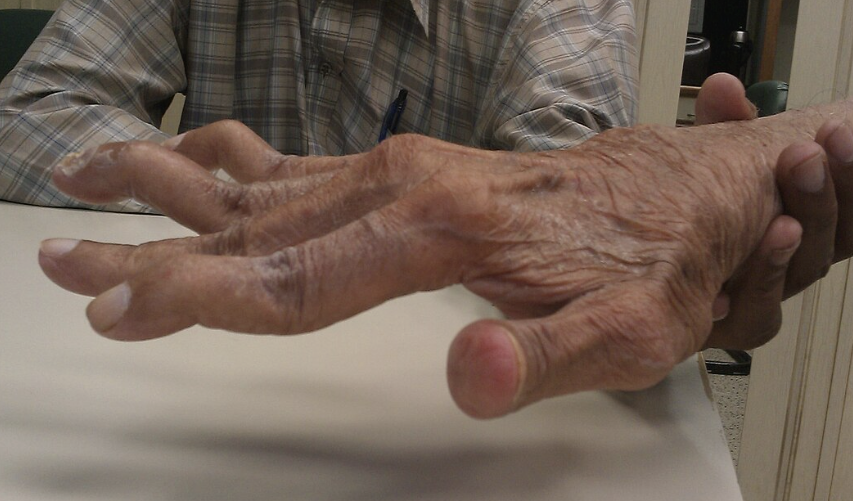
What is the deformity seen in the image below? What can it be caused by?
SWAN NECK - Usually caused by arthritis, but can be caused by untreated mallet finger

What is the treatment for a tibial plateau fracture?
knee immobilizer, NWB, ORTHO CONSULT
MAY BE MISSED ON XRAY
What is the the treatment for a Toddlers Fracture?
SPLINT or walking boot
Ortho follow up
What are the Ottowa Ankle and Foot Rules?
Imaging indications:
Tenderness on posterior 6cm of lateral OR medial mallelous
Inability to bear weight after injury and in the ED (4 steps)
Sensitivity 70-100%
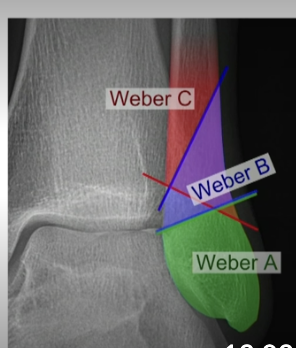
What are the Weber classification for a lateral malleolar fracture?
Weber A = stable, lower; WBAT
Weber B=higher up @ ankle joint, potentially unstable, immobilize, NWB, Urgent ortho follow up.
Weber C = higher up at ankle joint, needs surgery
What is a Maisonneuve Fracture and what is the treatment?
Proximal fibula fracture + tear of medial ligament and syndesmosis (medial malleolus)
Tx: Long leg splint, NWB, ortho for ORIF
A patient presents with ankle pain and felt a sudden pop. He has a positive Thompsons test. What is the likely dx and what is the tx?
Achilles tendon rupture (when calf is squeezed, there is NO plantar flexion)
SPLINT IN PLANTAR FLEXION (Equinus splint)
NWB —> ortho follow up urgently
A patient that has transient synovitis is usually holding the hip in which position?
Flexion, abduction, external rotation
(TYPICALLY HAVE PAIN WITH INTERNAL ROTATION)
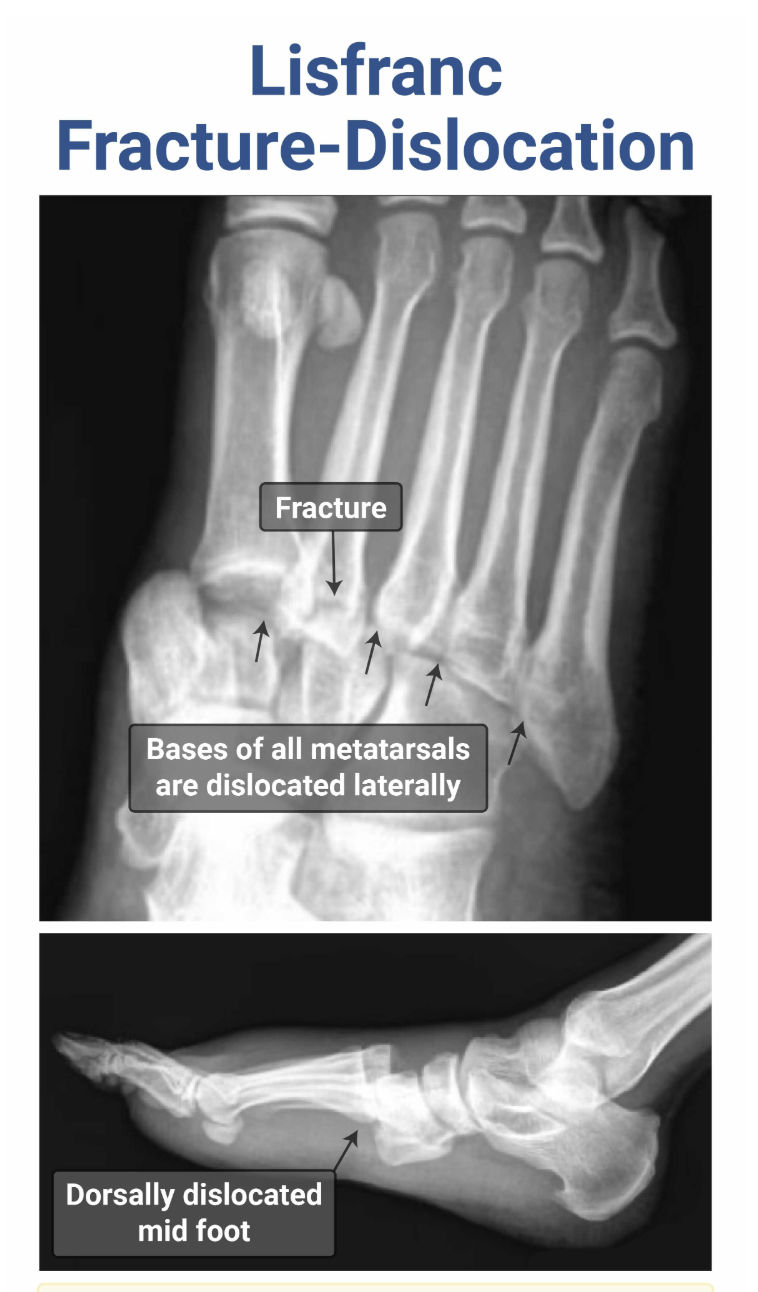
What is a Lisfranc Injury? Which joint is affected? Tx?
Lisfranc injury = fracture and dislocation of the tarsometatarsal joint, typically due to severe plantar flexion (sports, MVC, fall from heights), resulting in dorsal dislocation (pain is in dorsum of foot), may hear “clicking sound” on rotation of foot.
Tx: Immobilization, ortho ORIF