Microeconomics Exam 3 Terms & Definitions - MSU Study Set
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
The marginal private benefit curve is also the:
supply curve
marginal external benefit curve minus the marginal social benefit curve
demand curve
marginal personal benefit curve
demand curve
When someone can enjoy the benefits of a good without bearing the cost, the good:
is subject to the free-rider problem
is excludable and rival
is a nonmarket good
is attractive to manufacturers
is subject to the free-rider problem
The marginal private benefit plus the marginal external benefit equals the _____ benefit.
total public
total externality
marginal social
marginal public
marginal social
Marginal social cost equals marginal ______ cost plus marginal ______ cost.
consumer; production
government; private
private; external
public; internal
private; external
When a good is nonrival and nonexcludable, the good is referred to as:
a free-ride benefit good
an external good
a private good
a public good
a public good
A tax designed to induce people to take account of the negative externalities that they cause is referred to as ______ tax.
an externality
an open offset
a corrective
a compensatory
a corrective
A corrective tax designed to resolve a negative externality problem is typically set at an amount equal to the ______ cost.
marginal social
marginal external
total externality
total social
marginal external
Which of the following is the amount of a corrective tax that would resolve a negative externality problem?
the marginal social cost
the total social cost
the total external cost
the marginal external cost
the marginal external cost
An externality is defined as:
the effect of an activity undertaken outside a building rather than inside a building.
an effect of market activity that impacts the opposite side of the market from the side whose decision caused the effect.
a side-effect of an activity that affects bystanders whose interests are not taken into account.
the impact of an activity on buyers and sellers in the market where the activity takes place.
a side-effect of an activity that affects bystanders whose interests are not taken into account
Use the data in Table: Wendy's Windows to answer the question.
If Wendy uses the Rational Rule for Employers, how many workers will she hire?
three
In a labor market, workers ____ labor, and employers _____ labor.
supply; demand
demand; supply
hire; use
use; hire
supply; demand
An employer's labor demand curve is equal to the
marginal revenue product curve
marginal product curve
marginal revenue curve
rational product curve
marginal revenue product curve
The ______________ measures how people respond to a change in relative prices when the wage rises.
substitution effect
income effect
opportunity cost
marginal benefit
substitution effect
An employer should hire one more worker if
the total benefit exceeds the total cost
the marginal cost is falling
the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost
demand is rising
the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost
When the income effect dominates, an individual's labor supply curve
slopes upward
slopes downward
is horizontal
is vertical
slopes downward
Which graph shows the scenario where the income effect dominates labor supply decisions only at high wages? 2
Graph A 2
When making labor supply decisions, your options are
working or doing homework
working, shopping, or relaxing
working or leisure
working, sleeping, or leisure
working or leisure
The labor demand is a/an ______ demand
modified
imputer
derived
inferred
derived
Workers on the night shift at a factory earn more per hour than workers on the day shift, although their human capital and productivity are the same. This is an example of:
discrimination based on time preferences
irrational decision making by an employer
a compensating differential
an efficiency wage
a compensating differential
The accumulated knowledge and skills that make a worker more productive are known as:
human capital
labor enhancement
labor factoring
efficiency investment
human capital
Which of the following is an example of a labor market characterized by compensating differentials?
a nursery school teacher earns less than a university professor
two real estate agents paid on commission earn different salaries due to different listings and sales volume
adjustments are made to the salaries of teachers in different states to equalize the purchasing power of income
outside window washers of skyscrapers earn higher salaries than outside window washers of single family homes
outside window washers of skyscrapers earn higher salaries than outside window washers of single family homes
An efficiency wage improves efficiency when:
the increase in worker effort and reduced turnover cover the cost of the higher wage
it is structured so that only the most productive workers receive a higher wage
capital costs are reduced enough to cover wage costs
improved technology accompanies the worker training
the increase in worker effort and reduced turnover cover the cost of the higher wage
The government increases the training requirements to obtain an electrician's license. What impact will this have in the labor market for electricians?
the demand for electricians will decrease, resulting in a lower wage and lower quantity of labor.
the demand for electricians will increase, resulting in a higher wage and higher quantity of labor.
the supply of electricians will decrease, resulting in a higher wage and lower quantity of labor.
the supply of electricians will increase, resulting in a lower wage and higher quantity of labor.
the supply of electricians will decrease, resulting in a higher wage and lower quantity of labor
There is evidence that, despite antidiscrimination laws, discrimination _____ in labor markets.
impacts wages
exists but has no impact
benefits groups that are discriminated against
accounts for all differences in wages across groups of workers
impacts wages
Which of the following is an example of statistical discrimination?
no companies will hire Marcella because they do not want to hire women
Arturo is unaware that he avoids hiring Asians
an employer relies on stereotypes in making hiring decisions
Ingrid refuses to hire people who do not have at least five years of experiences in their previous jobs
an employer relies on stereotypes in making hiring decisions
Explain Collusion
an agreement between sellers to limit competition (price fixing)
Which of the following is consistent with current US law on monopolies?
being a monopoly is illegal
gaining monopoly or market power through specified exclusionary business practices is illegal
monopolizing is legal
companies can act to reduce the number of competitors but cannot discourage new entrants
gaining monopoly or market power through specified exclusionary business practices is illegal
The market power of a firm is its:
ranking based on units sold compared to other firms selling the same product
ability to cause other firms in its market to drop out of the market
ability to raise its price without losing many of its customers to competing businesses
market shared based on the percentage of total market revenue
ability to raise its price without losing many of its customers to competing businesses
In which market structure do the actions of a rival have a significant impact on your operations?
monopoly
monopolistic competition
oligopoly
perfect competition
oligopoly
Imperfect competition stems from ____ and whether or not the product is _____.
the product price; produced by all firms in the market
the costs of production; identical across firms
market power; a good or a service
the number of sellers; differentiated
the number of sellers; differentiated
In a market, when a company's owner tries to make its product slightly different from the output of other companies so that it is more attractive to buyers, the company is engaged in
market fixation
product differentiation
dominant rivalry
rational competition
product differentiation
Walmart has a large aisle that displays many different types of shampoos. This observation indicated that the shampoo market is
a perfectly competitive market
a monopoly
an oligopoly
a monopolistically competitive market
a monopolistic competitive market
What type of relationship exists between the level of a company's market power and the price that its owner is able to charge for its product?
circular
positive
negative
opposing
positive
Companies with market power face a trade-off between
gaining market share and reducing costs
having a higher marginal cost and a reduction in output
reducing costs and increasing profit
having a higher profit margin and selling a larger quantity
having a higher profit margin and selling a larger quantity
With a _____ number of sellers in a market, _____ market power tends to exist in the market
smaller; more
small; less consistent
greater; more
greater; less consistent
smaller; more
When a seller is able to differentiate its product successfully, the seller
has a reduction in costs of production
takes its market closer to perfect competition
loses market share
gains market power
gains market power
A characteristic of oligopoly that is not present in any other market structure is that there
is only one seller and that seller has a high level of market power
are many sellers and each produces its own version of the product
are a small number of sellers with considerable market power
are many sellers that produce identical products
are a small number of sellers with considerable market power
The marginal private benefit is the:
extra benefit enjoyed by the buyer of one extra unit of a good or service
extra benefit that goes to bystanders for each additional unit of a good consumed by other
addition to the satisfaction a buyer receives from the total quantity of a product consumed
total extra benefit society gains from the consumption of an extra unit of a good
extra benefit enjoyed by the buyer of one extra unit of a good or service
A good is characterized as ____ when one person's use of the good does not reduce another person's ability to use the same unit of the good.
nonexcludable
nonrival
shareable
free
nonrival
The Nobel Prize‑winning economist Oliver Hart once said, "If we know the marginal social cost [of pollution] emissions, a tax is better, but if we know the optimal quantity, cap and trade is better." Given this statement and the knowledge of ways governments can intervene in markets, evaluate the following statement: Any outcome that can be achieved by taxing can also be accomplished by establishing a quota. This is because:
if we know the marginal social cost, we can set the tax so that price is equal to the optimal price. As a result, the optimal quantity will be achieved. If we know the optimal quantity, we can set a quota and the market will find the optimal price.
if we know the optimal quantity, cap and trade can be used to set the price. If we know the marginal social cost, a tax can be used to set the quantity.
if we know the marginal social cost, we can set the optimal quantity equal to the optimal price. If
if we know the marginal social cost, we can set the tax so that price is equal to the optimal price. As a result, the optimal quantity will be achieved. If we know the optimal quantity, we can set a quota and the market will find the optimal price.
A good has a free-rider problem when:
someone can enjoy the benefits of the good without bearing the costs
any seller provides it for free as a special promotion
it has no negative externalities but only positive externalities
it can be transported at no cost to the consumer, with sellers bearing all transportation costs
someone can enjoy the benefits of the good without bearing the costs
Which of the following illustrates a positive externality?
Artem loses sleep when an airport is built near his home, and planes fly overhead
the value of Maria's house rises when the city builds a park nearby, enhancing her view
Ella can buy a shirt at half price because someone else returned it
Martin's company experiences an increase in profits due to his cost-cutting initiatives
the value of Maria's house rises when the city builds a park nearby, enhancing her view
Which of the following would be both nonrival and nonexcludable?
an immunization
a road
a museum
a siren tornado warning
a siren tornado warning
The Rational Rule for Society is that society should produce another unit of a good if:
the marginal private benefit exceeds the marginal private cost
the marginal social benefit exceeds the marginal social cost
gains to the producer exceed losses to the producer
the total social benefit exceeds the total social cost
the marginal social benefit exceeds the marginal social cost
Which of the following statements describes the Coase Theorem?
even if bargaining is not costless, and property rights are unclear, externality problems can be solved through private bargaining
if the marginal benefit of a good exceeds the good's marginal cost, more of it should be produced
elimination of an externality is possible only when the marginal benefit of a good is no higher than its marginal cost
if bargaining is costless, and property rights are clearly established and enforced, then externality problems can be solved through private bargaining
if bargaining is costless, and property rights are clearly established and enforced, then externality problems can be solved through private bargaining
Externalities tend to occur because decision makers consider ____ and do NOT consider ____.
their own income as limitless; their income as limited
their own costs and benefits; the effects of their actions on others
the welfare of others; their own welfare
their own needs as most important; the fact that others also have needs
their own costs and benefits; the effects of their actions on others
Marjean walks to work every day along a busy road. As she does so, she breathes in the fumes of many cars, often arriving at work coughing. The economic term for the impact of the cars on Marjean is:
an externality
exploitative supply
a nonmarket repercussion
an alternative action
an externality
By contrast with a market that produces the socially optimal output, a market with negative externalities will:
overproduce
produce no output
underproduce
produce the correct output
overproduce
What conditions must be met for private bargaining to be effective in resolving an externality?
bargaining costs must be low, and property rights must be clear
property rights must be clear, and production must begin at a socially optimal level
taxes must be low, and regulations must be minimal
there must be trade in public goods
bargaining costs must be low, and property rights must be clear
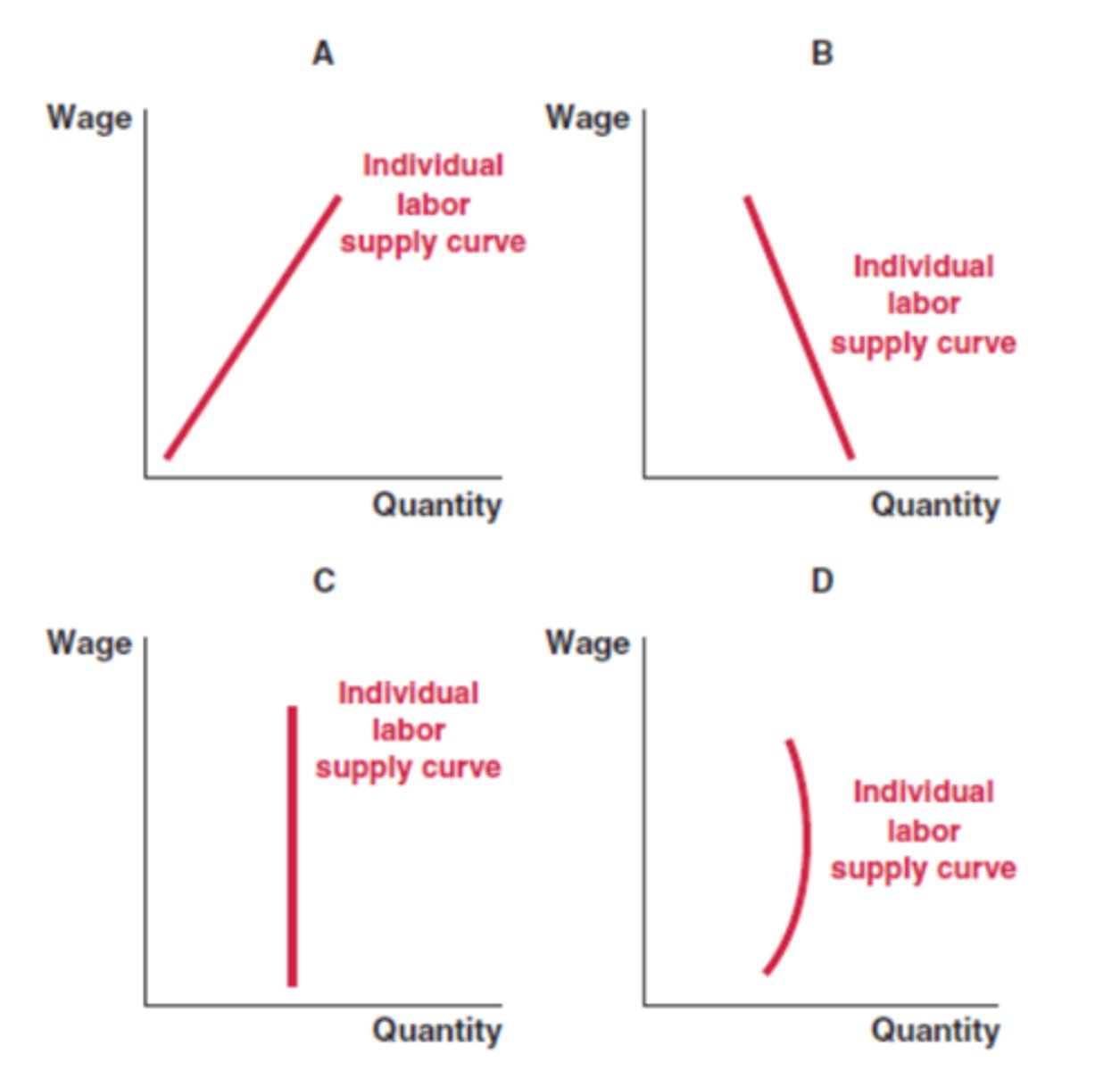
The graph shows the marginal social cost, supply, and demand curves in the hand sanitizer market. At what quantity could the government set a quota to control their externality?
8
The outcome that is most efficient for society as a whole -- including the interests of buyers, sellers, and bystanders -- is the _____ outcome.
public optimal
externally optimal
socially optimal
social benefit maximizing
socially optimal
In a perfectly competitive labor market, employers will not pay less than the market wage because at a wage below the equilibrium:
they would not be able to hire anyone
the equilibrium wage would rise
they would be inundated with excess workers
there would be a surplus of workers
they would not be able to hire anyone
Which of the following are true of statistical discrimination? There may be more than one correct answer.
"Ban the box" laws not allowing employers to ask potential employees whether or not they have been in jail is increasing discrimination against Black men, particularly those without a college degree.
Statistical discrimination occurs when firms base hiring decisions on which candidate will improve the firm's diversity statistics.
Some employers run complex statistical analysis of candidates' resumes before deciding who to interview for a position.
Statistical discrimination occurs when employers discriminate against job candidates based on an irrelevant but observable characteristic which correlates to an unmeasurable but relevant characteristic.
"Ban the box" laws not allowing employers to ask potential employees whether or not they have been in jail is increasing discrimination against Black men, particularly those without a college degree
Statistical discrimination occurs when employers discriminate against job candidates based on an irrelevant but observable characteristic which correlates to an unmeasurable but relevant characteristic
Which graph shows the scenario where the substitution effect dominates labor supply decisions?
Graph A
In a labor market graph, ____ is measured on the vertical axis, and ___ is measured on the horizontal axis.
product price; number of workers
hours of labor; wage
wage; hours of labor
number of workers; product price
wage; hours of labor
The graphs show individual labor supply curves for two different people. Use the graphs to answer the questions.
In Graph 1, ____ dominates ____.
In Graph 2, ____ dominates ____.
the substitution effect; the income effect
the income effect; the substitution effect
How many workers would the firm hire if it were required to pay a wage of $14/hour?
If the Federal minimum wage was suddenly increased to $20/hour, how many workers would the firm then employ?
4 workers
3 workers
Why does an employer's labor demand curve slope downward?
diminishing product demand
marginal cost adjustment
diminishing marginal product
substitution rule
diminishing marginal product
The Rational Rule for Employers implies that they keep hiring until
marginal product equals marginal revenue
the wage equals the marginal revenue product of the last worker hired
revenue equals cost
the wage equals marginal product
the wage equals the marginal revenue product of the last worker hired
Alena manages a small theme park. She hires one more custodian at $450 per week, and her park is cleaner and more attractive. As a result of this improvement, ticket sales rise by 40 tickets per week. Tickets sell for $12. Use the Rational Rule for Employers to determine if hiring the extra custodian was a good move.
No, it was a bad move because it added more to cost than revenue.
Yes, it was a good move because the ticket sales rose more than price.
Yes, it was a good move because it added more to revenue than to cost.
No, it was a bad move because price did not rise as much as ticket sales.
Yes, it was a good move because it added more to revenue than to cost
The marginal revenue from hiring an additional worker is known as:
marginal revenue product
labor marginal product
marginal worker revenue
labor marginal revenue
marginal revenue product
When a company has market power, it is ____ in its market
not able to impact the market equilibrium price
not a price-taker
a producer of nondifferentiated products
one of many small companies
not a price-taker
Based on the demand curves for four sellers, which of the following sellers has the most market power?
firm C (vertical line)
firm A (horizontal line)
firm B (downward sloping a lot)
firm D (downward sloping not that much)
firm C (vertical line)
Which of the following is a characteristic of monopoly that is not present in other market structures?
the product is identical across all sellers
sellers are price-takers
there is only one seller
there are many buyers
there is only one seller
In which market structure do the actions of a rival have a significant impact on your operations?
monopolistic competition
monopoly
perfect competition
oligopoly
oligopoly
What type of relationship exists between the level of a company's market power and the price that its owner is able to charge for its product?
circular
negative
postive
opposing
positive
Patents on drugs to treat AIDS were removed in South Africa. How would the market for these drugs have been different if there had never been patents on drugs?
the drug prices would have been lower from the start
the drug prices would have been even higher
the drugs would not have been developed
larger quantities of the drugs would have been produced
the drugs would not have been developed
To avoid harm to society, the government often becomes the supplier of a good or service when the respective market
would be a natural monopoly, and the good or service is considered essential
has high profit, and the government can use those to replace tax revenue
would be competitive enough to cause surpluses to develop
has been engaging in illegal activities that the government seeks to eliminate
would be a natural monopoly, and the good or service is considered essential
What is collusion?
a merger of two sellers
cooperation between sellers to increase the level of competition
regulatory restrictions on the entry of new sellers into an industry
agreements between sellers to increase their market power
agreements between sellers to increase their market power
Walmart has a large aisle that displays many different kinds of toothpastes. This observation indicates that the toothpaste market is:
an oligopoly
a monopoly
a monopolistic competitive market
a perfectly competitive market
a monopolistic competitive market