CI 460 Machine Learning
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ERAU
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Irreducible Error
inherent noise or variability in the data that cannot be reduced.
Reducible Error
Error that can be reduced by improving the model
Prediction
estimation, we can make accurate predictions for the response
Inference
(inference) if we can understand how the output changes based on the input
Parametric Methods
Assume the functional form of F, fixed number of parameters. Simple with less flexibility. Examples: linear regression, logistic regression
Non-parametric methods
Learns directly from the data, adapts to complex patterns. Needs more training data and are more flexible. Examples: decision trees, random forests, KNN
MSE (Mean Squared Error)
Measure used to asses quality of fit/accuracy for regression model. Always want to minimize MSE.
MSE
Squared difference between actual and predicted values
n - number of observations
yi - observed values
^yi - predicted values
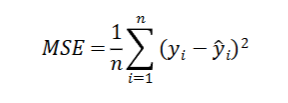
MSE example
True Y = [14, 7, 5, 9]
Predicted Y = [4, 8, 8, 10]
MSE = ( (14- 4)^2 + (7 - 8)^2 + (5 - 8)^2 + (9-10)^2 ) / 8
Error Rate
Measuring Quality of fit for classification. If the condition gives a 1 then the condition is incorrect, otherwise is a zero. Error rate represents a fraction of the incorrect classifications.
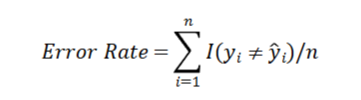
Loss Function
Measures how far the prediction is from the true outcome and assigns a numerical penalty to the incorrect predictions. Want to choose the weights that minimize the loss.
EX - MSE, Error Rate
Bias
(underfitting) error from modeling problems with too simple of the model. (Using a linear model to try and fit a complex pattern)
Variance
(Overfitting) How much the output (f) would change based on a different training data set. More flexible the model the more variance
Bias Variance Trade off
The more flexible the model the higher the variance and the less bias
Bayes Error Rate
Irreducible error in classification. It is the lowest error rate that any classifier can achieve.
KNN (K Nearest Neighbors)
Classification, Regression, uses the closest neighbors to decide classification, Non-parametric.
K = small value → High variance and low bias
In higher dimensions performs worse and fits to the noise
Is sensitive to scaling
Scaling
Scaling - making sure that no one feature will dominate the distance and outcome, pre processing technique
algorithms that have gradient decent need scaling
Normalization
when doesn’t linear conclusion
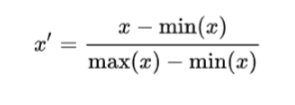
Standardization
when data follows a normal distribution
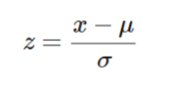
Peaking Phenomenon
As features go up so does performance until optimal and then goes down as more and more features are added.
Curse of Dimensionality
When the dimension is so high that all the points are basically the same distance apart and the center of the cube is empty. Need to reduce features
Binary Classifier Evaluation
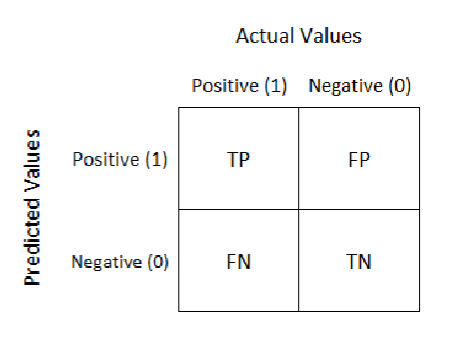
Accuracy
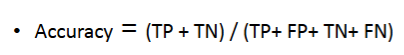
Sensitivity
True Positive Rate
TP/ ( TP +FN )
Specificity
Specificity is the proportion of actual negatives that got predicted
True Negative Rate
TN / ( TN + FP)
1 - Specificity
False Positive Rate
FP / ( FP + TN)
Logit Output
Probability Output
P( y=1 | x)
OLS (Ordinary Least Squared)
Minimizes the squared differences between actual and predicted values
Uses MSE and the Residuals
Normal Equations
Closed form solution
Minimize MSE
For simple linear regression, smaller datasets, and for model parameters
Gradient Decent
Efficient for large datasets and high dimensions
scales well in machine learning
iterative optimization algorithm to minimize the loss function
Normal Equations
Closed form solution
efficient for smaller datasets with few features
Precision
TP / ( TP + FP )
Information Theory
Study of qualification, storage, and digital information
Founded by Harry Nyquist, Ralph Hartley, Claude Shannon
Quantifying Information
Low probability event → high information (surprising)
High probability event → low information
Self Information
The measure of the information associated with the outcome of a random variable, (How much information is in a given variable)
1 unit of information = 1 bit
I(x) = -log(P(x))

Expected Value
The long term average

Entropy
The measure of the average uncertainty associated with a given random variable
Self Information vs Entropy
Self Information → measures the information/uncertainty in an event
Entropy → the amount of uncertainty/information in a set of events
Linear Regression
Models the relationship between the dependent and independent variable by using line of best fit
Gradient decent is efficient for
large datasets and high dimensions, scales well
least squares fit in terns of linear regression
is used to minimize the differences between the predicted and actual values.
normal equations are good for
small datasets and small features, involve inverting a matrix
Regression sum of squares
SST = SSR + SSE
SSTotal - total squared distance of observations of mean of y
SSRegression - distance from regression line to mean of y
SSRedidual (SSE) - variance around the regression line that is not explained by the regression line (this is what we are trying to minimize)
Coefficient of Determination (R²)
values range from 0 - 1
0 - model does not explain any variability in the data
1 - the model perfectly explains the variability in the data
R² = SSR/SST
The Higher the R² the better fit of the model to the data
Logistic Regression
for classification problems
instead of predicting y we predict P(Y=1) (aka yes or no)
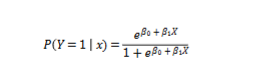
Logistic regression gives an
s shaped curve
odds ratio
measure that gives the change in the odds of an outcome if everything else is constant
values close to 0 indicate very low or very high probabilites
Logit

ROC vs AUC
ROC measures the classifier performance over all thresholds
AUC (area under the roc curve) - single numbered score that summarizes the performance
Regression Trees
Regression problems
divide predictor space into distinct regions
Split regression trees by using
the results with the lowest mse or entropy in the training data
Classification tree
predictions are categorical not continuous (regression)
split by minimizing the error rate
we know how far back to prune a tree by
using cross validation to see which tree has the lowest error rate
CP
Complexity parameter, use to control complexity and accuracy trade off
Pros vs Cons of decision trees
Pro - Trees are easy to explain, plotted graphically, used for both classification and regression
Cons - Don’t have prediction accuracy as more complicated models
Bagging
bootstrap aggregating
resampling of the observed dataset done by random sampling with replacement from the og dataset
averaging reduces variance
gives lots of training datasets
less interpretation
In random forests variable importance is computed
Through mean decrease gini
Mean Decrease Gini vs Entropy
Both used to evaluate quality of split
Gini - Based on probability of missclassification
Entropy - based on the amount of information needed to identify the class of an element
Random Forests
Same process as bagging but de-correlates the trees
Done by taking a random sample of predictors every time a split is considered
When random forests are built using m = p
This amounts to being a bagged tree
Validation Set Approach
Split data into training and testing (validation)
build multiple models and test on lowest error rate
can be highly variable
Leave - one - out cross validation
split data of size n into
training - n-1
test (validation) 1
validate and find mse
Has less bias, variability, computationally intensive
K - fold cross validation
divide dataset into parts
remove one part and test on last part
repeat with different part each time
average k different mse’s
more accurate, balances bias/variance trade off for error estimates