AP Biology Chapter 5: Cell Communications - Majoros
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
signal transduction pathway
process where surface cellular responses cause responses within the cell
local regulator
a released, short-distance signaling molecule which travels between the secreting and target cell
hormone
a released, long-distance signaling molecule which travels between the secreting cell (endocrine) and the target cell
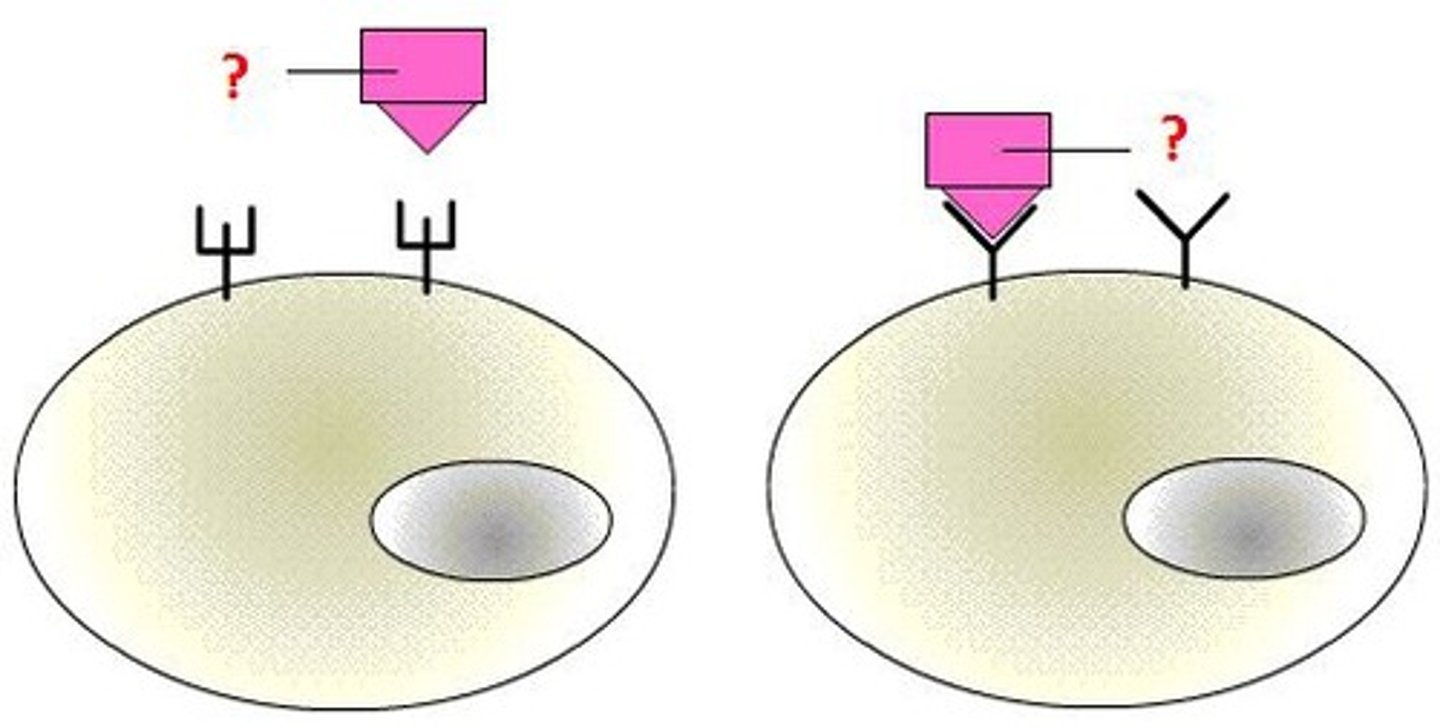
ligand
a signaling molecule
G protein-coupled receptors
uses a signaling molecule/ligand, a G protein/GTPase and GTP to activate an inactive enzyme; located in a membrane
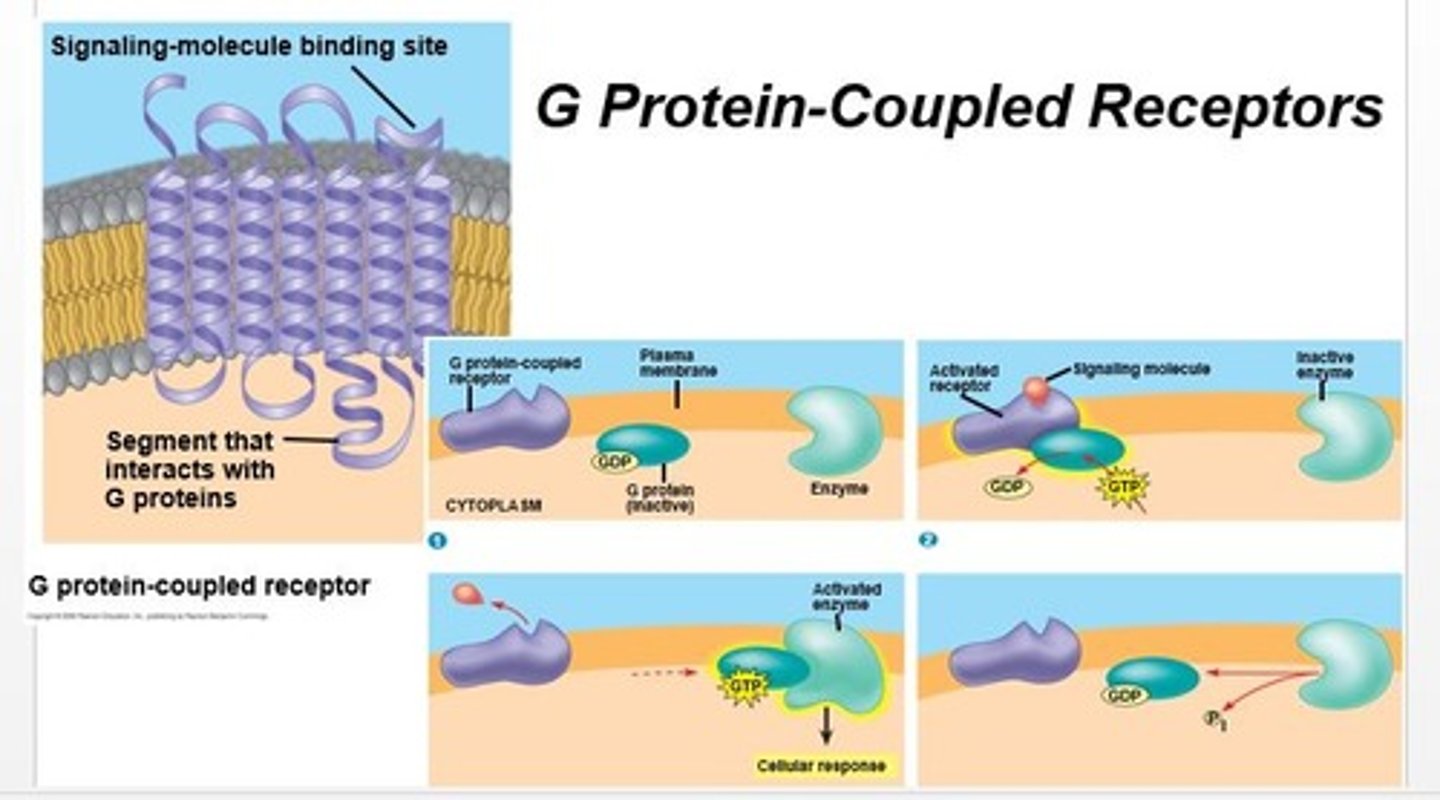
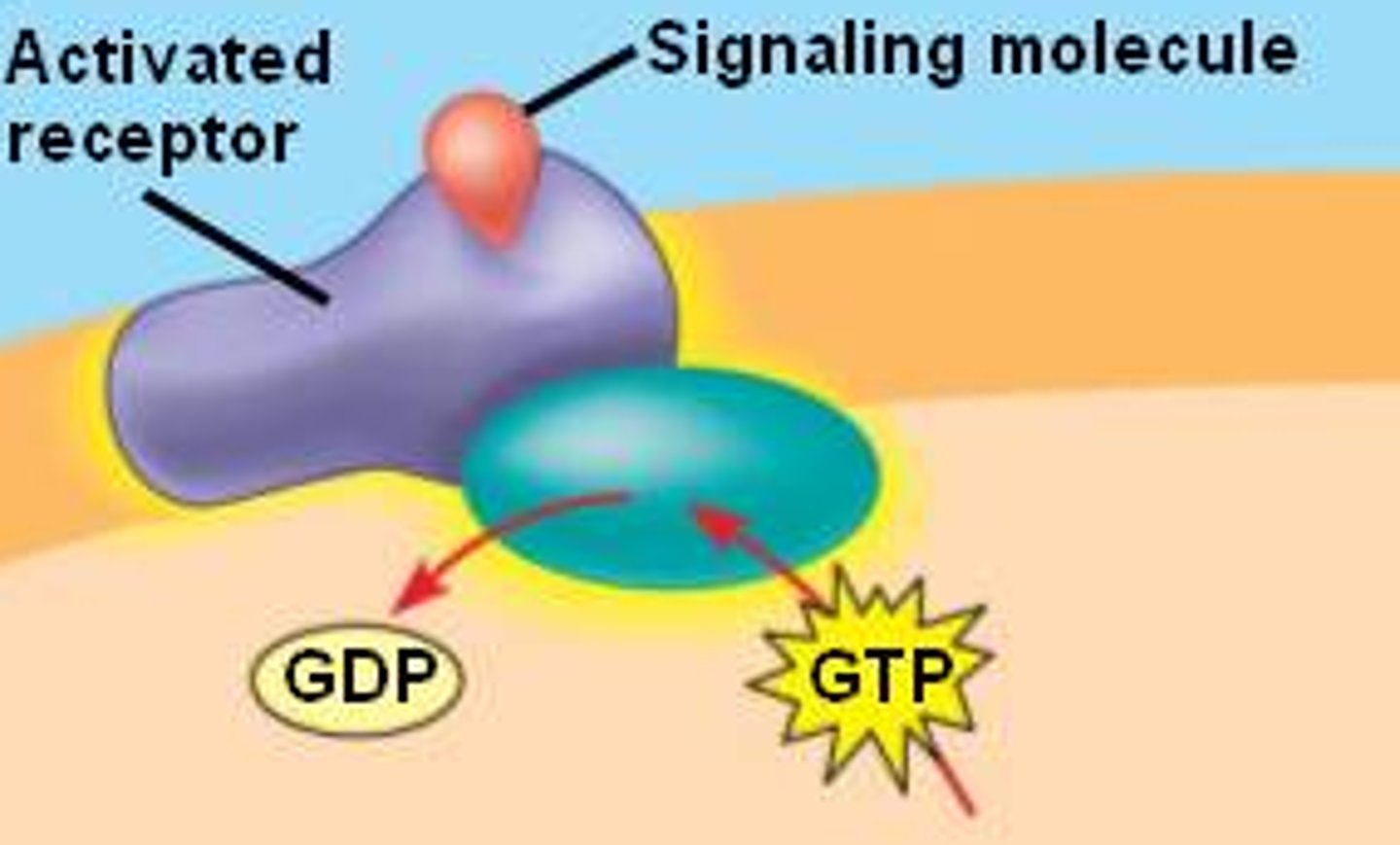
G proteins
relays signals from a plasma membrane signal receptor, known as a G protein-coupled receptor, to other signal transduction proteins in the cell
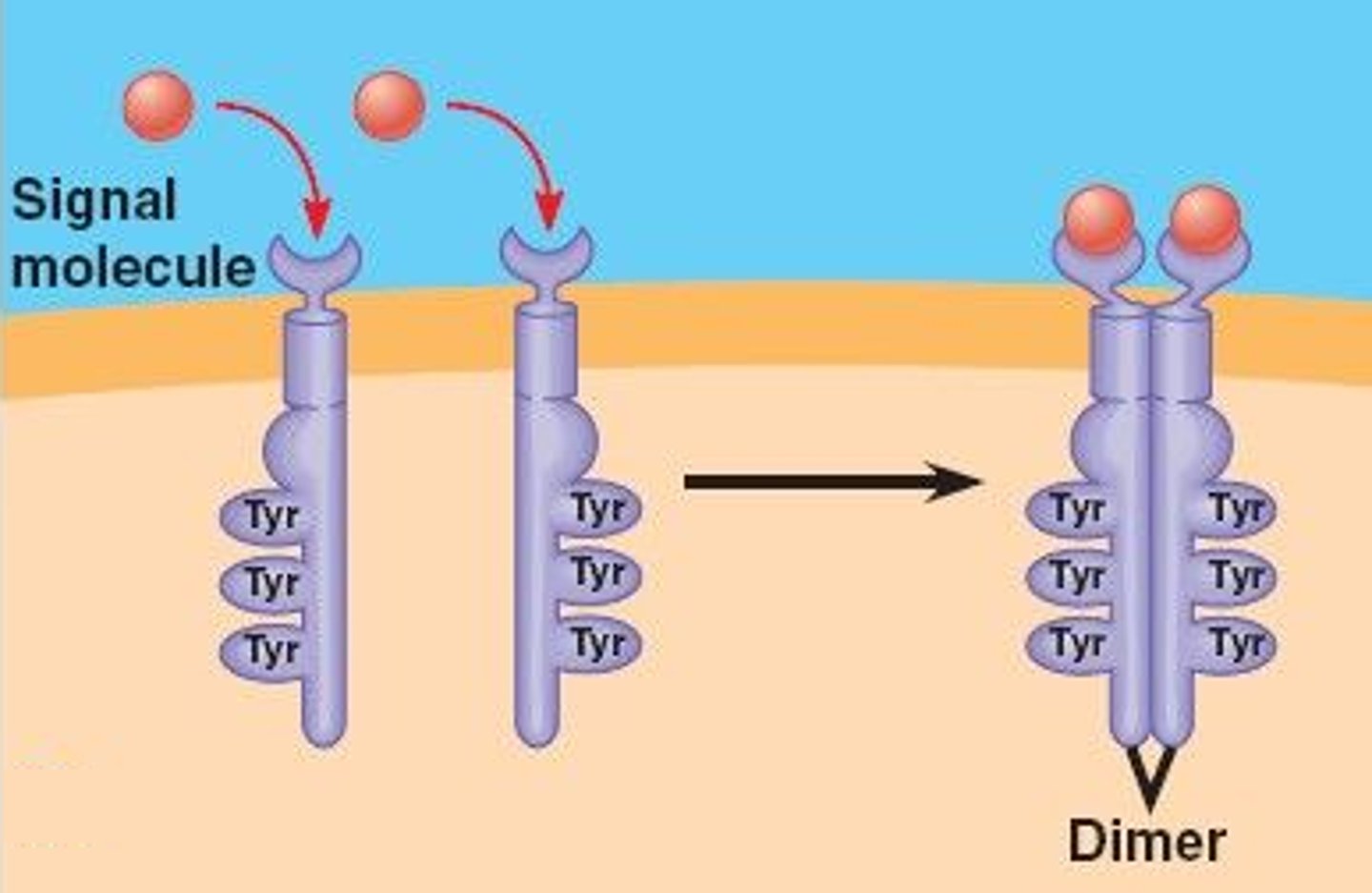
receptor tyrosine kinases
molecules activated by ligands and phosphates to activate a response
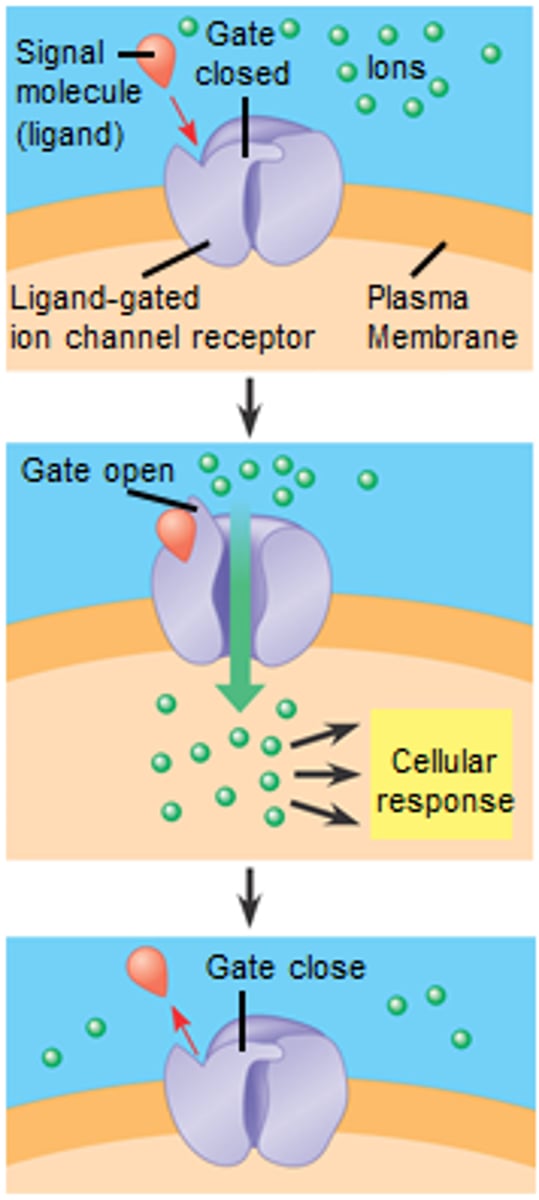
ligand gated ion channel receptors
block and allow ions in and out of the cell
protein kinase
general name for an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein
protein phosphatases
(PP) enzymes that rapidly remove phosphate groups from proteins during signal transduction
second messengers
small, non-protein, water-soluble molecules/ions that act as the signaling molecule/ligand
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
an important second messenger that helps make protein kinase A (PKA); made with help of the signaling molecule epinephrine
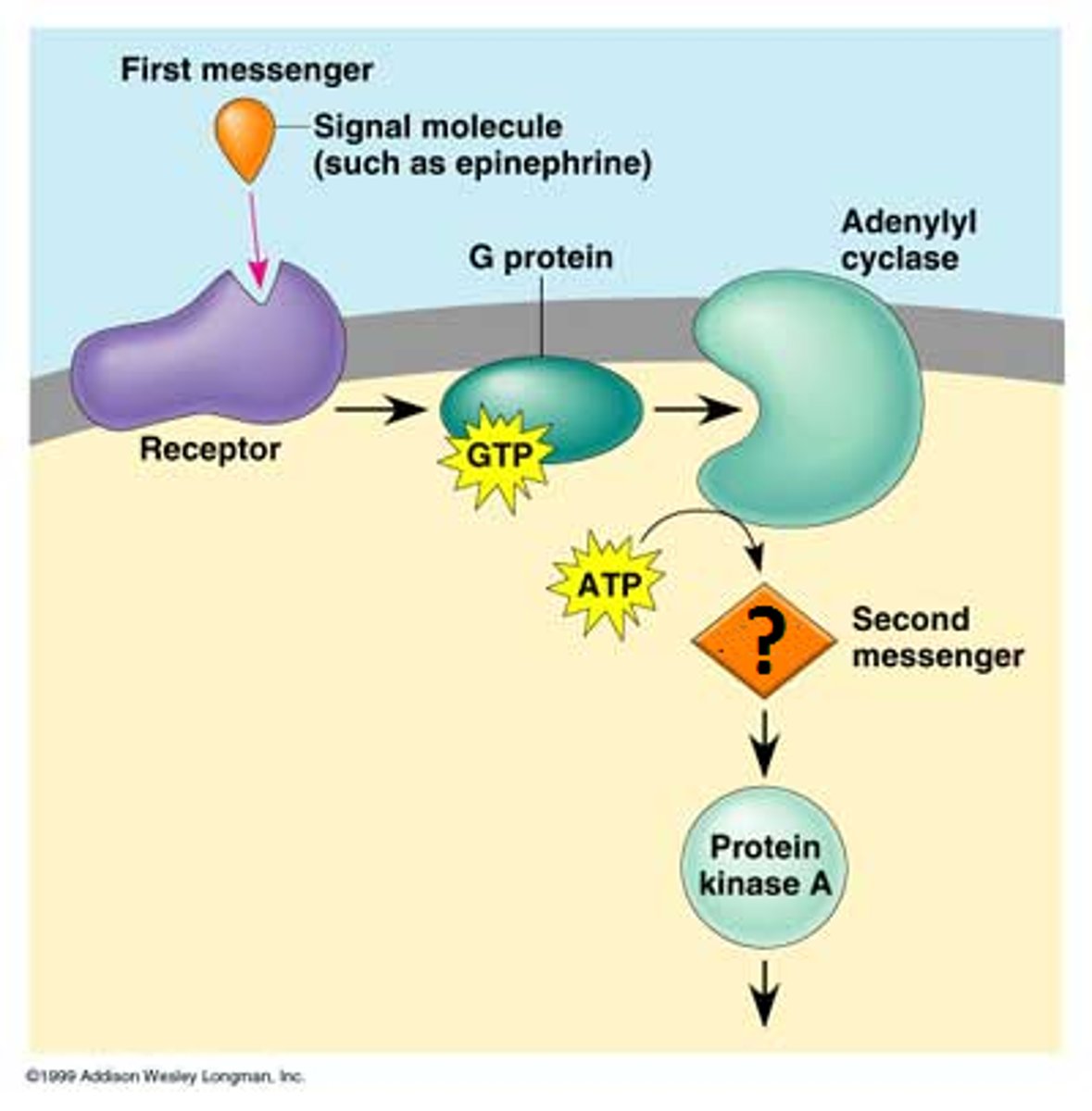
adenylyl cyclase
an enzyme that converts ATP to cAMP
apoptosis
cellular suicide
growth factors
compounds that stimulate nearby target cells to grow and divide
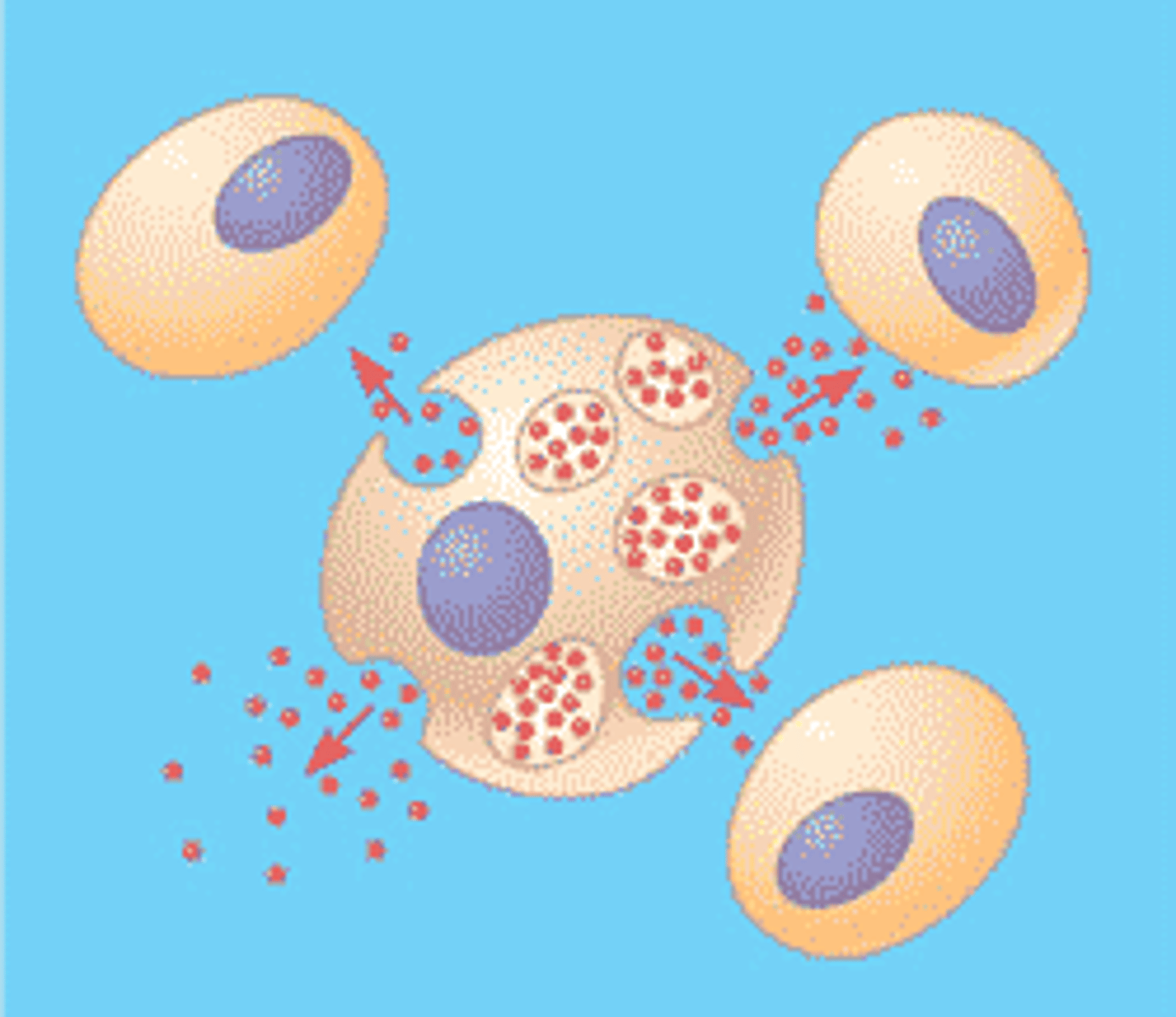
paracrine signaling
a type of local signaling where the target cell is close to the signal-releasing cell
synaptic signaling
a type of local signaling specific to neurotransmitters in nerve cells
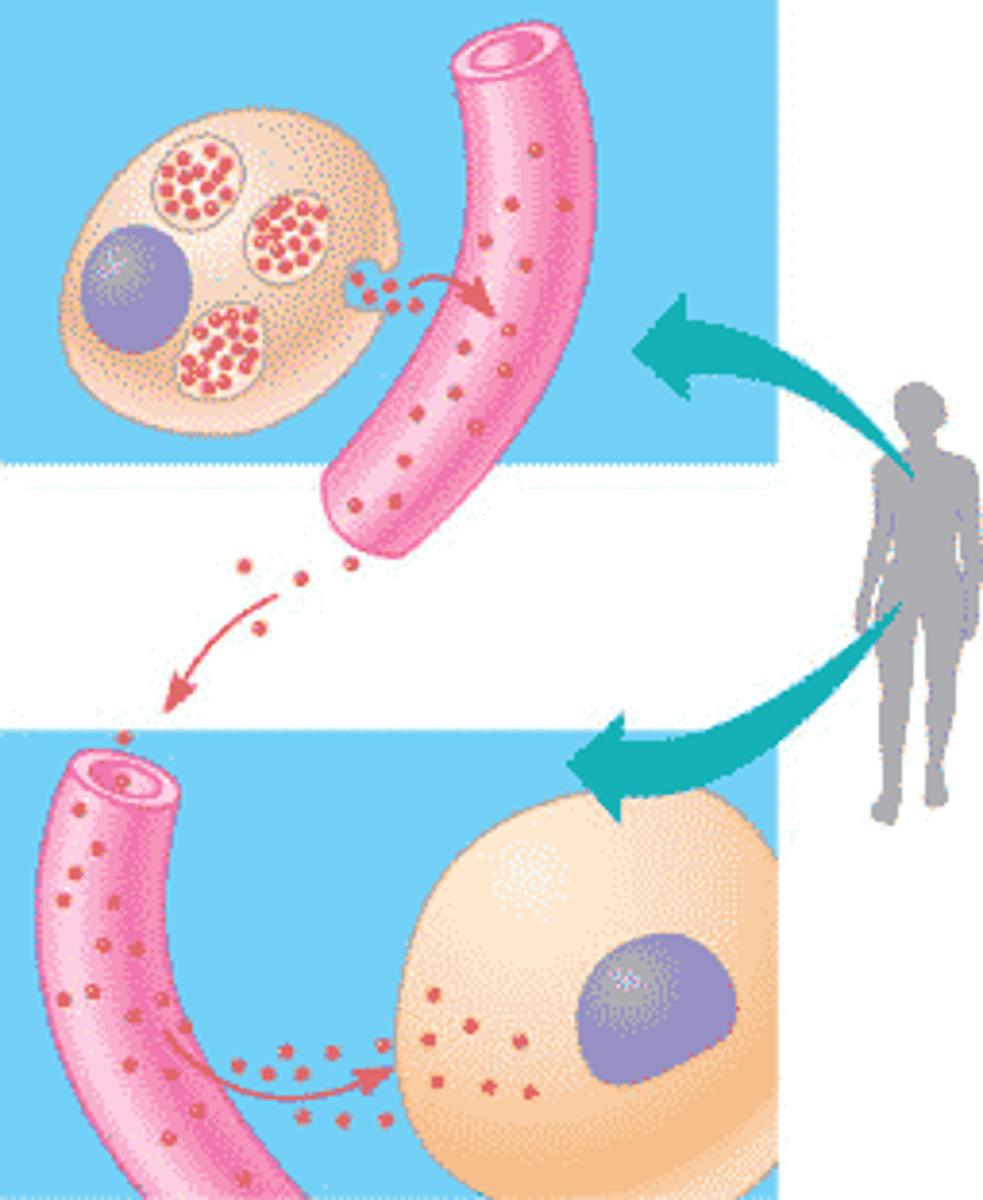
hormonal signaling
a type of long-distance signaling where an endocrine excretes hormones in a blood vessel to travel to a target cell
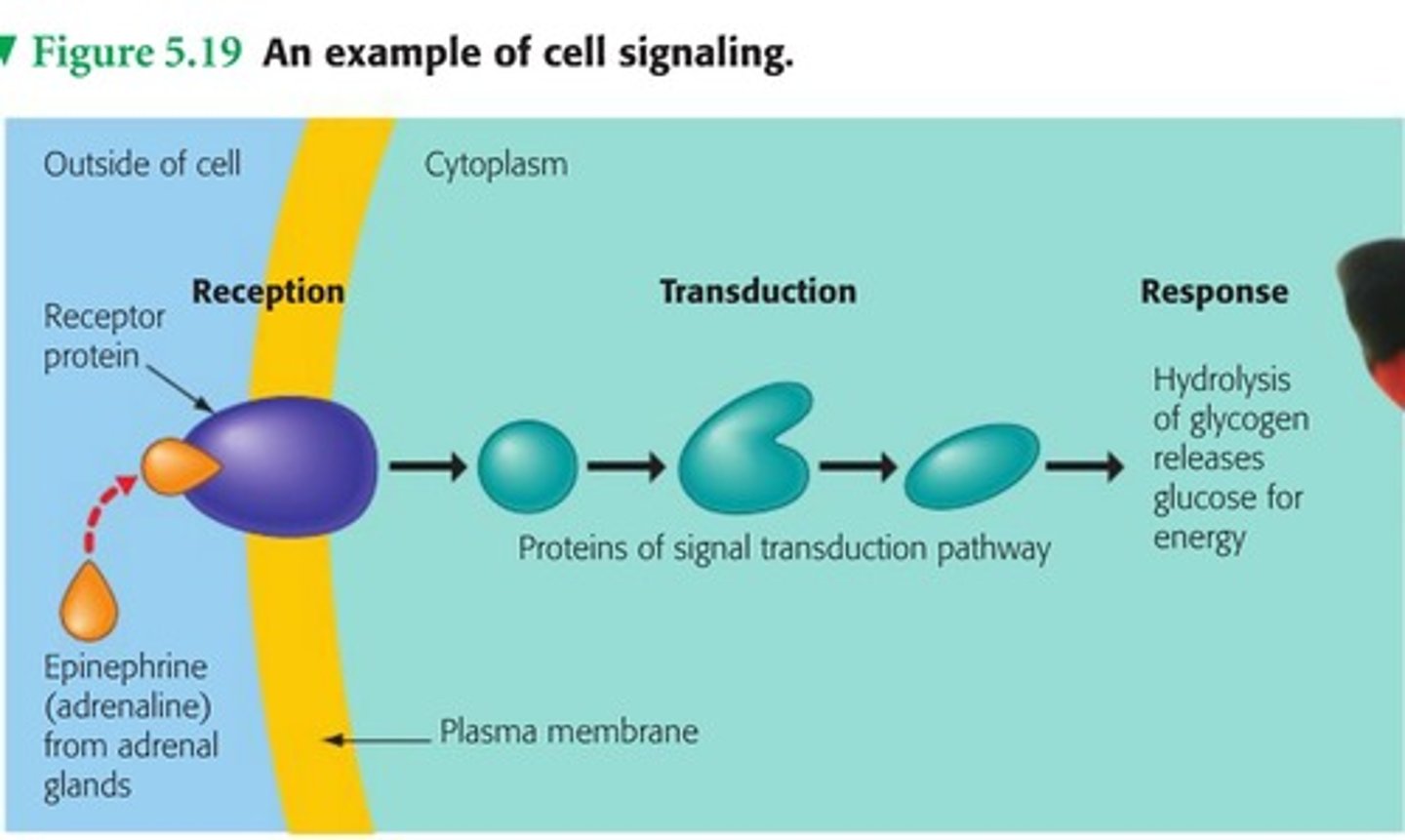
reception
when a signaling molecule binds to a receptor protein
Biomily
The people you can depend on and the people that depend on you.
response
when an enzyme is activated to do an activity in a cell
transcription factors
control which genes are written (transcribed) onto mRNA at a certain place and at a certain time
GTP
moves proteins around for cellular response, (like rage)
phosphorylation cascade
a chain reaction of chemical reactions where an enzyme adds a phosphate group to a series of proteins, activating each one in sequence.