Pancreatic Carcinoma (General Surgery EOR - Smarty PANCE)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Define pancreatic carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas arising from duct cells
What are the associated risk factors for pancreatic carcinoma?
Smoking 3 x risk, diabetes mellitus, heavy alcohol use, chronic pancreatitis, diet high in fried meats, previous gastrectomy
What is the male to female ratio for pancreatic carcinoma?
3:2
What is the African American to white ratio for pancreatic carcinoma?
2:1
What is the average age of dx for pancreatic carcinoma?
> 60
What are the different types of pancreatic carcinoma?
> 80% are duct cell adenocarcinomas; other types include cystadenocarcinoma and acinar cell carcinoma
What percentage of pancreatic carcinoma arise in the pancreatic head?
66% arise in the pancreatic head; 33% arise in the body and tail
Why are most pancreatic cancers in the tail nonresectable?
These tumors grow without symptoms until it is too late and they have already spread—head of the pancreas tumors draw attention earlier because of biliary obstruction
What are the signs/symptoms of pancreatic tumors based on location: Head of the pancreas?
Painless jaundice from obstruction of common bile duct; weight loss; abdominal pain; back pain; weakness; pruritus from bile salts in skin; anorexia; Courvoisier's sign; acholic stools; dark urine; diabetes
What are the signs/symptoms of pancreatic tumors based on location: Body or tail?
Weight loss and pain (90%); migratory thrombophlebitis (10%); jaundice ( 10%); nausea and vomiting; fatigue
What are the most common symptoms of pancreatic cancer of the pancreatic HEAD?
1. Weight loss (90%) 2. Pain (75%) 3. Jaundice (70%)
What is "Courvoisier's sign"?
Palpable, nontender, distended gallbladder
What percentage of patients with cancers of the pancreatic HEAD have Courvoisier's sign?
33%
What is the classic presentation of pancreatic cancer in the head of the pancreas?
Painless jaundice
What metastatic lymph nodes described classically for gastric cancer can be found with metastatic pancreatic cancer?
Virchow's node; Sister Mary Joseph's nodule
What are the associated lab findings in pancreatic carcinoma?
Increased direct bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase (as a result of biliary obstruction) Increased LFTs Elevated pancreatic tumor markers
Which tumor markers are associated with pancreatic cancer?
CA-19-9
What does CA-19-9 stand for?
Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9
What diagnostic studies are performed for pancreatic carcinoma?
Abdominal CT, U/S, cholangiography (ERCP to rule out choledocholithiasis and cell brushings), endoscopic U/S with biopsy
What are the pancreatic cancer STAGES: Stage I?
Tumor is limited to pancreas, with no nodes or metastases
What are the pancreatic cancer STAGES: Stage II?
Tumor extends into bile duct, peripancreatic tissues, or duodenum; there are no nodes or metastases
What are the pancreatic cancer STAGES: Stage III?
Same findings as stage II plus positive nodes or celiac or SMA involvement Stage
What are the pancreatic cancer STAGES: Stage IVA?
Tumor extends to stomach, colon, spleen, or major vessels, with any nodal status and no distant metastases
What are the pancreatic cancer STAGES: Stage IVB?
Distant metastases (any nodal status, any tumor size) are found
What is the treatment of pancreatic cancer based on location:
Head of the pancreas?
Body or tail?
Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy)
Body or tail: Distal resection
What factors signify inoperability in pancreatic cancer?
Vascular encasement (SMA, hepatic artery)
Liver metastasis
Peritoneal implants
Distant lymph node metastasis (periaortic/celiac nodes)
Distant metastasis
Malignant ascites
Is portal vein or SMV involvement an absolute contraindication for resection?
No—can be resected and reconstructed with vein interposition graft at some centers
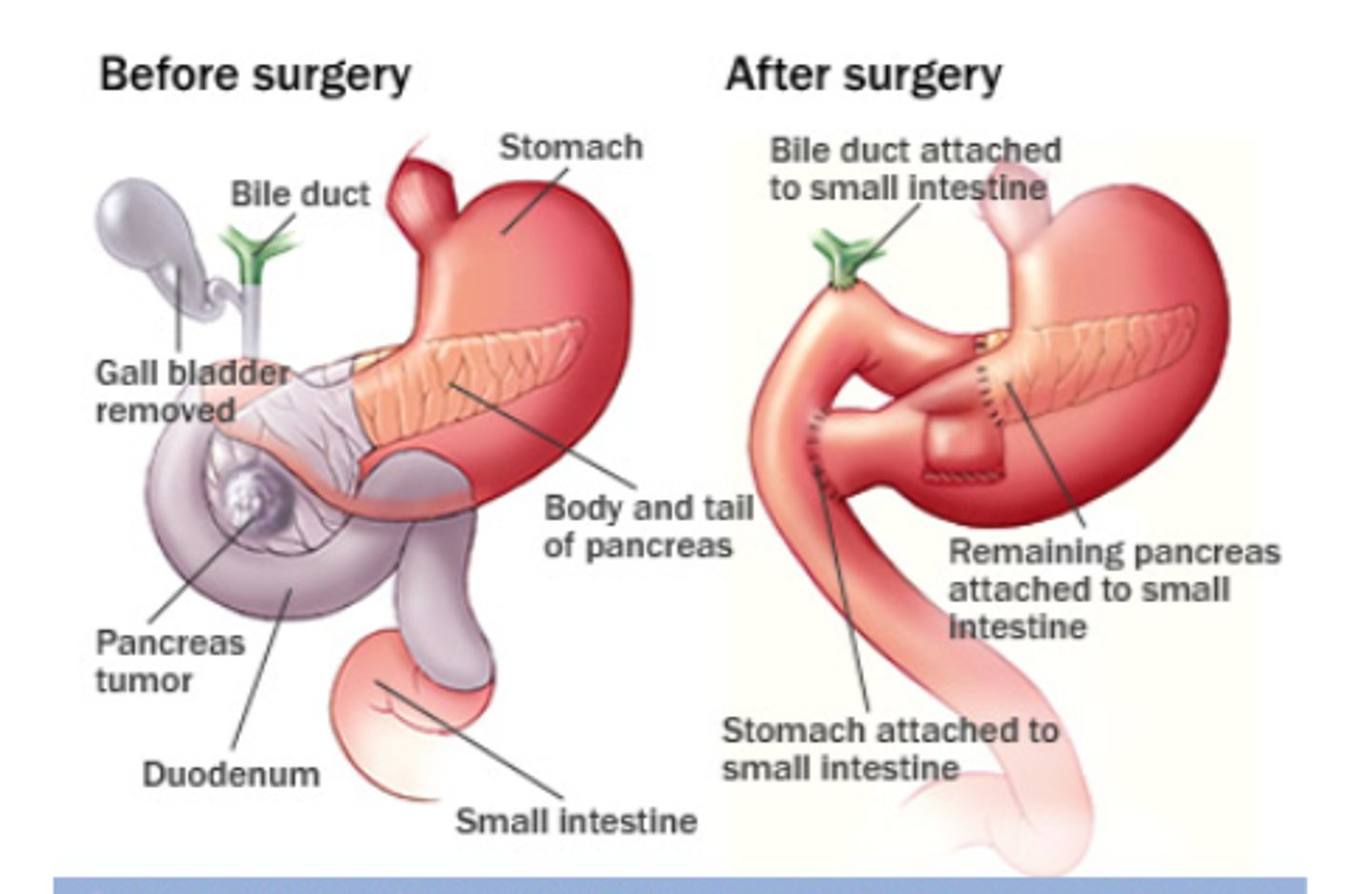
Define the Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy)
Cholecystectomy
Truncal vagotomy
Antrectomy
Pancreaticoduodenectomy—removal of head of pancreas and duodenum Choledochojejunostomy—anastomosis of common bile duct to jejunum
Pancreaticojejunostomy—anastomosis of distal pancreas remnant to jejunum
Gastrojejunostomy—anastomosis of stomach to jejunum
What is the complication rate after a Whipple procedure?
25%
What mortality rate is associated with a Whipple procedure?
5% at busy high volume centers
What are the possible post-Whipple complications?
Delayed gastric emptying (if antrectomy is performed); anastomotic leak (from the bile duct or pancreatic anastomosis), causing pancreatic/biliary fistula; wound infection; postgastrectomy syndromes; sepsis; pancreatitis
Why must the duodenum be removed if the head of the pancreas is resected?
They share the same blood supply
What is the postoperative adjuvant therapy?
Chemotherapy + XRT
What is the palliative treatment if the tumor is inoperable and biliary obstruction is present?
PTC or ERCP and placement of stent across obstruction
What is the prognosis at 1 year after diagnosis in pancreatic cancer?
Dismal; 90% of patients die within 1 year of diagnosis
What is the survival rate at 5 years after resection in pancreatic cancer?
20%